Raleigh (; ) is the capital city of the state of
North Carolina and the
seat
A seat is a place to sit. The term may encompass additional features, such as back, armrest, head restraint but also headquarters in a wider sense.
Types of seat
The following are examples of different kinds of seat:
* Armchair (furniture), ...
of
Wake County in the United States. It is the
second-most populous city in North Carolina, after
Charlotte. Raleigh is the tenth-most populous city in the
Southeast,
the 41st-most populous city in the U.S., and the largest city of the
Research Triangle metro area. Raleigh is known as the "City of Oaks" for its many
oak trees, which line the streets in the heart of the city. The city covers a land area of . The
U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
counted the city's population as 474,069 in the
2020 census.
It is one of the fastest-growing cities in the United States.
The city of Raleigh is named after Sir
Walter Raleigh, who established the lost
Roanoke Colony
The establishment of the Roanoke Colony ( ) was an attempt by Sir Walter Raleigh to found the first permanent English settlement in North America. The English, led by Sir Humphrey Gilbert, had briefly claimed St. John's, Newfoundland, in 15 ...
in present-day
Dare County
Dare County is the easternmost county in the U.S. state of North Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 36,915. Its county seat is Manteo. Dare County is named after Virginia Dare, the first child born in the Americas to English p ...
.
Raleigh is home to
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The universit ...
(NC State) and is part of the
Research Triangle together with
Durham (home of
Duke University
Duke University is a private research university in Durham, North Carolina. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1892. In 1924, tobacco and electric power industrialist James ...
and
North Carolina Central University) and
Chapel Hill Chapel Hill or Chapelhill may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Chapel Hill (Antarctica) Australia
*Chapel Hill, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane
*Chapel Hill, South Australia, in the Mount Barker council area
Canada
* Chapel Hill, Ottawa, a neighbo ...
(home of the
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill). The name of the Research Triangle (often shortened to the "Triangle") originated after the 1959 creation of
Research Triangle Park
Research Triangle Park (RTP) is the largest research park in the United States, occupying in North Carolina and hosting more than 300 companies and 65,000 workers.
The facility is named for its location relative to the three surrounding cities ...
(RTP), located in Durham and Wake counties, among the three cities and universities. The Triangle encompasses the U.S. Census Bureau's Raleigh-Durham-Cary
Combined Statistical Area (CSA), which had an estimated population of 2,037,430 in 2013. The Raleigh
Metropolitan Statistical Area had an estimated population of 1,390,785 in 2019.
Most of Raleigh is located within
Wake County, with a small portion extending into
Durham County.
The towns of
Cary,
Morrisville,
Garner
Garner may refer to:
Places United States
* Garner, Arkansas
* Garner, Iowa
* Garner, Missouri
* Garner, North Carolina
Other uses
* Garner (surname), a surname
* Granary, a grain store
* ''Tennessee v. Garner'', a United States Supreme Court cas ...
,
Clayton,
Wake Forest,
Apex,
Holly Springs,
Fuquay-Varina,
Knightdale,
Wendell,
Zebulon
Zebulun (; also ''Zebulon'', ''Zabulon'', or ''Zaboules'') was, according to the Books of Genesis and Numbers,Genesis 46:14 the last of the six sons of Jacob and Leah (Jacob's tenth son), and the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Zebulun. Some ...
, and
Rolesville are some of Raleigh's primary nearby
suburbs
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separate ...
and
satellite towns.
Raleigh is an early example in the United States of a
planned city. Following the
American Revolutionary War when the U.S. gained independence, the area was chosen as the site of the state capital in 1788 and incorporated in 1792 as such. The city was originally laid out in a grid pattern with the
North Carolina State Capitol at the center, in Union Square. During the
American Civil War, the city was spared from any significant battle. It fell to the Union in the closing days of the war and struggled with the economic hardships in the postwar period, related to the reconstitution of labor markets, over-reliance on agriculture and the social unrest of the
Reconstruction Era
The Reconstruction era was a period in American history following the American Civil War (1861–1865) and lasting until approximately the Compromise of 1877. During Reconstruction, attempts were made to rebuild the country after the bloo ...
. The establishment of the
Research Triangle Park
Research Triangle Park (RTP) is the largest research park in the United States, occupying in North Carolina and hosting more than 300 companies and 65,000 workers.
The facility is named for its location relative to the three surrounding cities ...
(RTP) in 1959 helped create tens of thousands of jobs in the fields of science and technology. By the early 21st century, Raleigh had become one of the fastest-growing cities in the United States.
History
Earlier capitals
Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, the oldest town in North Carolina, was the first nominal capital of the colony from 1705 until 1722, when
Edenton
Edenton is a town in, and the county seat of, Chowan County, North Carolina, United States, on Albemarle Sound. The population was 4,397 at the 2020 census. Edenton is located in North Carolina's Inner Banks region. In recent years Edenton has b ...
took over the role. The colony had no permanent institutions of government until the new capital,
New Bern, was established in 1743.
18th century
In December 1770,
Joel Lane successfully petitioned the
North Carolina General Assembly
The North Carolina General Assembly is the Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of the Government of North Carolina, State government of North Carolina. The legislature consists of two chambers: the North Carolina Senate, Senate and the North Ca ...
to create a new county. On January 5, 1771, the bill creating Wake County was passed in the General Assembly. The county was formed from portions of
Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is a historic county in the far North West England. It covers part of the Lake District as well as the north Pennines and Solway Firth coast. Cumberland had an administrative function from the 12th century until 1974. From 19 ...
,
Orange, and
Johnston counties, and was named for
Margaret Wake Tryon
Margaret Wake Tryon (c.1732 – 1819) was an English heiress and the wife of William Tryon, who served as the Governor of North-Carolina (1712–1776), Colonial Governor of Province of North Carolina, North Carolina and the List of colonial govern ...
, the wife of Governor
William Tryon. The first county seat was Bloomsbury.
New Bern, a port town on the
Neuse River from the Atlantic Ocean, was the largest city and the capital of North Carolina during the
American Revolution. When the British Army laid siege to the city, that site could no longer be used as the capital. From 1789 to 1794, when Raleigh was being built, the state capital was
Fayetteville.
Raleigh was chosen as the site of the new capital in 1788, as its central location protected it from attacks from the coast. It was officially established in 1792 as both county seat and state capital. The city was incorporated on December 31, 1792, and a charter granted January 21, 1795. The city was named for
Sir Walter Raleigh
Sir Walter Raleigh (; – 29 October 1618) was an English statesman, soldier, writer and explorer. One of the most notable figures of the Elizabethan era, he played a leading part in English colonisation of North America, suppressed rebellion ...
, sponsor of
Roanoke, the "lost colony" on Roanoke Island.
No known city or town existed previously on the chosen city site. Raleigh is one of the few cities in the United States that was planned and built specifically to serve as a
state capital. Its original boundaries were formed by the downtown streets of North, East, West and South.
The plan, a grid with two main axes meeting at a central square and an additional square in each corner, was based on
Thomas Holme's 1682 plan for
Philadelphia.
The
North Carolina General Assembly
The North Carolina General Assembly is the Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of the Government of North Carolina, State government of North Carolina. The legislature consists of two chambers: the North Carolina Senate, Senate and the North Ca ...
first met in Raleigh in December 1794, and granted the city a
charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the rec ...
, with a board of seven appointed
commissioner
A commissioner (commonly abbreviated as Comm'r) is, in principle, a member of a commission or an individual who has been given a commission (official charge or authority to do something).
In practice, the title of commissioner has evolved to in ...
s and an "
Intendant
An intendant (; pt, intendente ; es, intendente ) was, and sometimes still is, a public official, especially in France, Spain, Portugal, and Latin America. The intendancy system was a centralizing administrative system developed in France. In ...
of Police" (which developed as the office of
Mayor) to govern it. After 1803, city commissioners were elected. In 1799, the ''N.C. Minerva and Raleigh Advertiser'' was the first newspaper published in Raleigh.
was the first Intendant of Police.
19th century
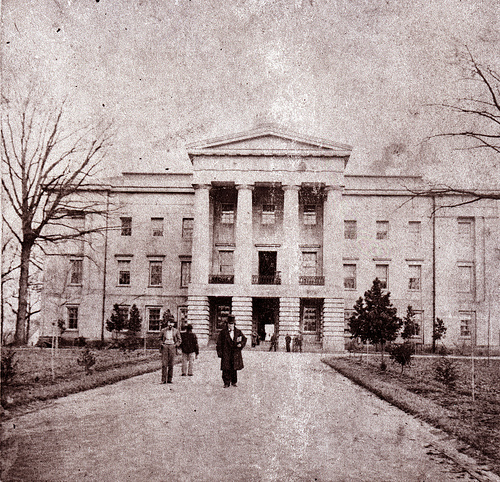



In 1808,
Andrew Johnson
Andrew Johnson (December 29, 1808July 31, 1875) was the 17th president of the United States, serving from 1865 to 1869. He assumed the presidency as he was vice president at the time of the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Johnson was a Dem ...
, the United States' future 17th President, was born at Casso's Inn in Raleigh. The city's first
water supply network was completed in 1818, although due to system failures, the project was abandoned. In 1819 Raleigh's first volunteer
fire company was founded, followed in 1821 by a full-time fire company.
In 1817, the
Episcopal Diocese of North Carolina was established and headquartered in Raleigh.
In 1831, a fire destroyed the
North Carolina State House. Two years later, reconstruction began with quarried
gneiss being delivered by the first railroad in the state. Raleigh celebrated the completion of the new
State Capitol
This is a list of state and territorial capitols in the United States, the building or complex of buildings from which the government of each U.S. state, the District of Columbia and the organized territories of the United States, exercise its ...
and new
Raleigh & Gaston Railroad Company in 1840.
In 1853, the first
State Fair was held near Raleigh. The first institution of higher learning in Raleigh,
Peace College, was established in 1857. Raleigh's
Historic Oakwood contains many houses from the 19th century that are still in good condition.
North Carolina seceded from the Union during the
American Civil War. After the war began, Governor
Zebulon Baird Vance ordered the construction of
breastworks around the city as protection from
Union troops. Near the end of the Civil War, Governor Vance arranged his evacuation to avoid capture as
Union General William Sherman's forces approached the city. Before leaving, Vance met with former governors
Graham
Graham and Graeme may refer to:
People
* Graham (given name), an English-language given name
* Graham (surname), an English-language surname
* Graeme (surname), an English-language surname
* Graham (musician) (born 1979), Burmese singer
* Clan G ...
and
Swain
Swain, Swains or Swain's may refer to:
Places
* Swain Islands, Antarctica
* Swain's Island (Newfoundland and Labrador), Canada
* Swains Island, an atoll in the Tokelau chain, American Samoa
* Swain County, North Carolina, United States
* Swains ...
to draft a letter of surrender for Raleigh. Their intention was to protect Raleigh from
the destruction inflicted on other cities by Union troops. Graham and Swain departed to meet the advancing Federal forces on the morning of April 12, 1865, and were to return by that evening. The evening struck, but Graham and Swain had not returned due to train delays and their temporary capture by Sherman. Governor Vance left the evening after Graham and Sherman failed to return, leaving behind a letter giving Mayor William H. Harrison the authority to surrender. On the morning of April 13, Mayor Harrison among others went to the southern Wake County area to meet General
Hugh Judson Kilpatrick and propose surrender. Kenneth Rayner, a long-time resident of Raleigh, delivered the proposal including a promise of no resistance. Kilpatrick agreed to accept the surrender and protect Raleigh from destruction. Kilpatrick's
cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
occupied Raleigh and removed the flagpole from the
state capitol
This is a list of state and territorial capitols in the United States, the building or complex of buildings from which the government of each U.S. state, the District of Columbia and the organized territories of the United States, exercise its ...
, replacing it with a
United States Flag
The national flag of the United States of America, often referred to as the ''American flag'' or the ''U.S. flag'', consists of thirteen equal horizontal stripes of red (top and bottom) alternating with white, with a blue rectangle in the ca ...
above the dome. Sherman arrived shortly after and established his headquarters in the governor's mansion. The city was spared significant destruction during the war. As
Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between ...
cavalry retreated west, Union soldiers followed, leading to the
Battle of Morrisville nearby.
Due to the economic and social problems of the post-war period and
Reconstruction, with a state economy still heavily dependent on agriculture, the city grew little over the next several decades.
Shaw University
Shaw University is a private Baptist historically black university in Raleigh, North Carolina. It is affiliated with the American Baptist Churches USA. Founded on December 1, 1865, Shaw University is the oldest HBCU to begin offering courses in ...
, the South's first African American college, began classes in 1865 and was chartered in 1875. Its
Estey Hall was the first building constructed for the higher education of Black women, and
Leonard Medical Center was the first four-year medical school in the country for African Americans.
In 1867,
Episcopal
Episcopal may refer to:
*Of or relating to a bishop, an overseer in the Christian church
*Episcopate, the see of a bishop – a diocese
*Episcopal Church (disambiguation), any church with "Episcopal" in its name
** Episcopal Church (United State ...
clergy founded
St. Augustine's College for the education of
freedmen. The biracial Reconstruction legislature created new welfare institutions: in 1869, it approved the United States' first school for blind and deaf Black people, to be located in Raleigh. In 1874, the federal government constructed the
Federal Building in Raleigh, the first
federal government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
project in the Southern U.S. following the Civil War.
In 1880, the newspapers ''News'' and ''Observer'' combined to form ''
The News & Observer''. It continues to be Raleigh's primary daily newspaper. The North Carolina College of Agriculture and Mechanic Arts, now known as
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The universit ...
, was founded as a
land-grant college in 1887. The city's
Rex Hospital
UNC Rex Hospital is a general hospital located in Raleigh, North Carolina. It is the capital city's oldest hospital, founded by a bequest from John T. Rex (1771-1839), a local tanner. Originally located on what is now Dorothea Dix campus, and ...
opened in 1889 and included the state's first nursing school. The Baptist Women's College, now known as
Meredith College
Meredith College is a private women's liberal arts college and coeducational graduate school in Raleigh, North Carolina. As of 2021 Meredith enrolls approximately 1,500 women in its undergraduate programs and 300 men and women in its graduate pr ...
, opened in 1891, and in 1898,
The Academy of Music
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the m ...
, a private music conservatory, was established.
In the late nineteenth century, two Black Congressmen were elected from
North Carolina's 2nd district, the last in 1898.
George Henry White
George Henry White (December 18, 1852 – December 28, 1918) was an American attorney and politician, elected as a Republican U.S. Congressman from North Carolina's 2nd congressional district between 1897 and 1901. He later became a banker ...
sought to promote civil rights for Black citizens and to challenge efforts by White Democrats to reduce Black voting by new discriminatory laws. He and his allies were unsuccessful. Based on a White supremacy campaign that returned Democrats to dominance, in 1900 the state legislature passed a new
constitution, with a suffrage amendment that raised barriers to voter registration, resulting in the
disenfranchisement of most Black citizens and many poor White citizens. Loss of the ability to vote also disqualified Black men (and later women) from sitting on juries and serving in any office—local, state or federal. The rising Black middle-class in Raleigh and other areas was politically silenced and shut out of local governance, and the
Republican Party
Republican Party is a name used by many political parties around the world, though the term most commonly refers to the United States' Republican Party.
Republican Party may also refer to:
Africa
*Republican Party (Liberia)
* Republican Part ...
was no longer competitive in the state.
It was not until after federal
civil rights legislation was passed in the mid-1960s that the majority of Black citizens in North Carolina would again be able to vote, sit on juries and serve in local offices. By that time many African Americans had left the state in the Great Migration to northern industrial cities for more opportunities. No African American was elected to Congress from North Carolina until 1992.
20th century

In 1912, Bloomsbury Park opened, featuring a popular carousel ride. Relocated to
Pullen Park, the
Pullen Park Carousel
The Pullen Park Carousel is a classic wood carousel at Pullen Park in Raleigh, North Carolina. Built in 1900, the carousel contains 52 hand-carved basswood animals, 2 chariots (or sleighs), 18 large gilded mirrors and canvas panels and a Wurlitze ...
is still operating.
From 1914 to 1917, an
influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms ...
epidemic killed 288 Raleighites.
In 1922, WLAC signed on as the city's first radio station, but lasted only two years. WFBQ signed on in 1924 and became WPTF in 1927. It is now Raleigh's oldest continuous radio broadcaster.
In 1923, the Raleigh Fall Festival was formed. The Festival was reorganized as the
North Carolina Debutante Ball
The North Carolina Debutante Ball, also known as the Terpsichorean Society Debutante Ball, is an annual debutante ball held in Raleigh, North Carolina. The ball, hosted by the Terpsichorean Club of Raleigh, is the oldest and most prestigious debu ...
in 1927.
Following immigration by Catholics, on December 12, 1924, the
Roman Catholic Diocese of Raleigh
The Diocese of Raleigh is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church that covers the eastern half of the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is a suffragan diocese in the ecclesiastical province of the metropolitan A ...
was officially established by
Pope Pius XI
Pope Pius XI ( it, Pio XI), born Ambrogio Damiano Achille Ratti (; 31 May 1857 – 10 February 1939), was head of the Catholic Church from 6 February 1922 to his death in February 1939. He was the first sovereign of Vatican City fro ...
. The
Sacred Heart Cathedral Sacred Heart Cathedral may refer to:
Africa
*Sacred Heart Cathedral, Moundou, Chad
*Sacred Heart Cathedral, Bamako, Mali
*Sacred Heart Cathedral, Brazzaville, Republic of Congo
*Sacred Heart Cathedral, Freetown, Sierra Leone
*Sacred Heart Cathedra ...
became the official seat of the diocese with
William Joseph Hafey
William Joseph Hafey (March 19, 1888 – May 12, 1954) was an American prelate of the Roman Catholic Church who served as bishop of the Diocese of Raleigh in North Carolina (1925–1937) and bishop of the Diocese of Scranton in Pennsylvania (1 ...
as its bishop.
The city's first airport, Curtiss-Wright Flying Field, opened in 1929. That same year, the
stock market crash resulted in six Raleigh banks closing.
During the difficult 1930s of the
Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, government at all levels was integral to creating jobs. The city provided recreational and educational programs, and hired people for public works projects. In 1932,
Raleigh Memorial Auditorium
Duke Energy Center for the Performing Arts is the main Theater (structure), venue for the performing arts in Raleigh, North Carolina.
The naming rights to the center currently are held by Duke Energy (formerly Progress Energy Inc, Progress Energy) ...
was dedicated. The
North Carolina Symphony, founded the same year, performed in its new home. From 1934 to 1937, the federal
Civilian Conservation Corps constructed the area now known as
William B. Umstead State Park. In 1939, the State General Assembly chartered the Raleigh-Durham Aeronautical Authority to build a larger airport between Raleigh and Durham, with the first flight occurring in 1943.
In 1947, Raleigh citizens adopted a
council–manager form of government, which is still the city's current form of government. Council members are elected from
single-member district
A single-member district is an electoral district represented by a single officeholder. It contrasts with a multi-member district, which is represented by multiple officeholders. Single-member districts are also sometimes called single-winner vo ...
s. They hire a city manager.
The
Dorton Arena, a 7,610-seat multi-purpose arena designed by
Matthew Nowicki
Matthew Nowicki (in Poland known as Maciej Nowicki) (26 June 1910 – 1 September 1950) was a Polish architect. He was chief architect of the new Indian city of Chandigarh.
Career
Nowicki was born in Chita in Siberia. After the Second Worl ...
, was opened in 1952 on the grounds of the North Carolina State Fair. It was listed in the
National Register of Historic Places in 1973.
Raleigh experienced significant damage from
Hurricane Hazel in 1954.
In 1953,
WNAO-TV, channel 28, became the city's first television station, though it folded in 1957.
With the opening of the
Research Triangle Park
Research Triangle Park (RTP) is the largest research park in the United States, occupying in North Carolina and hosting more than 300 companies and 65,000 workers.
The facility is named for its location relative to the three surrounding cities ...
in 1959, Raleigh began to experience a population increase, resulting in a total city population of 100,000 by 1960.
In 1960, the Census Bureau reported Raleigh's population as 76.4% White and 23.4% Black.
Following the passage of the federal
Voting Rights Act of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement ...
, one of the main achievements of the
Civil Rights Movement and the
Lyndon B. Johnson presidency, political participation and voting by African Americans in Raleigh increased rapidly.
From the early-to-mid 20th century
East Hargett Street was known as Raleigh's "Black Main Street" and hosted numerous Black-owned businesses. The area declined after the city desegregated its establishments.
By the early 1970s people in Raleigh were growing increasingly concerned about growth and
urban sprawl. Community organizations felt that municipal offices were being too heavily influenced by business interests when the city's population was rapidly growing and various development projects were being proposed. At their behest, the municipal elections were altered so that the mayor was to be directly elected, instead of being selected by the city council. Most city council seats were then made responsible to districts, instead of being held at-large. The 1973 elections were the first contests affected by the reforms. City Councilman
Clarence Lightner
Clarence Everett Lightner (August 15, 1921 – July 8, 2002) was an American politician and mortician. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as Mayor of Raleigh, North Carolina from 1973 to 1975. He was the first popularly elected Mayor o ...
defeated Raleigh Merchants bureau Executive Director G. Wesley Williams to become Raleigh's first Black mayor, and thus the first Black mayor in a major White-majority city in the South.
In 1976, the Raleigh City and Wake County schools merged to become the
Wake County Public School System, now the largest school system in the state and 19th largest in the country.
During the 1970s and 1980s, the
I-440 beltline was constructed, in an attempt to ease traffic congestion and providing access to most major city roads.
The first
Raleigh Convention Center
The Raleigh Convention Center is a convention and exhibition facility in downtown Raleigh, North Carolina that opened in September 2008. The architect was Tvsdesign with the participation of local firms O'Brien/Atkins Associates and Clearscapes. ...
(replaced in 2008) and Fayetteville Street Mall were both opened in 1977. Fayetteville Street was turned into a pedestrian-only street in an effort to help the then-ailing downtown area, but the plan was flawed and business declined for years to come. Fayetteville Street was reopened in 2007 as the main thoroughfare of Raleigh's downtown.
During the
1988 Raleigh tornado outbreak
The 1988 Raleigh tornado was the most destructive of the seven tornadoes reported in northeastern North Carolina and southeastern Virginia on November 28, 1988, between 1:00 AM and 5:45 AM. The Raleigh tornado produced over $77 million in damage, ...
of November 28, 1988, the city was affected by the most destructive of the seven tornadoes reported in
Northeastern North Carolina and southeastern
Virginia between 1:00 am and 5:45 am. The Raleigh tornado produced over $77 million in damage, along with four fatalities (two in the city of Raleigh, and two in
Nash County) and 154 injuries. The damage path from the storm was measured at long, and wide at times. The tornado was rated
F4.
In 1991, two large skyscrapers in Raleigh were completed,
First Union Capitol Center and
Two Hannover Square Two Hannover Square is a 29-story skyscraper at 434 Fayetteville Street in Raleigh, North Carolina with of office space. Its major tenant is Truist bank. From its opening in 1991 until the completion of RBC Plaza in 2008, it was Raleigh's talle ...
, along with the popular
Coastal Credit Union Music Park at Walnut Creek
Coastal Credit Union Music Park (originally named Walnut Creek Amphitheatre and formerly Alltel Pavilion) is an outdoor amphitheater located in Raleigh, North Carolina, United States, that specializes in hosting large concerts.
The amphitheater ...
in Southeast Raleigh.
In 1996, the
Olympic Flame passed through Raleigh while on its way to the
1996 Summer Olympics
The 1996 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXVI Olympiad, also known as Atlanta 1996 and commonly referred to as the Centennial Olympic Games) were an international multi-sport event held from July 19 to August 4, 1996, in Atlanta, ...
in
Atlanta. Also in 1996,
Hurricane Fran struck the area, causing massive flooding and extensive structural damage. In addition,
WRAL-TV became the first High-Definition broadcast station in the world.
In 1997, the
National Hockey League's
Hartford Whalers announced their intention to move to Raleigh as the
Carolina Hurricanes, becoming the city's first major league professional sports franchise.
In 1999, the Raleigh Entertainment and Sports Arena (later renamed the RBC Center and now called
PNC Arena), opened to provide a home for the Hurricanes and the
NC State Wolfpack men's basketball team, as well as an up-to-date major concert venue.
21st century


In the first decade of the 21st century, Raleigh was featured prominently in a number of "Top 10 Lists", including those by ''
Forbes'',
MSNBC and
''Money'' magazine, due to its quality of life and favorable business climate.
In 2001, the Raleigh Memorial Auditorium complex was expanded with the addition of the
Progress Energy Center for the Performing Arts, Meymandi Concert Hall, Fletcher Opera Theater, Kennedy Theatre,
Betty Ray McCain Gallery and Lichtin Plaza.
Fayetteville Street reopened to vehicular traffic in 2006. A variety of downtown building projects began around this time including the 34-story
RBC Bank Tower, multiple condominium projects and several new restaurants. Additional skyscrapers are in the proposal/planning phase.
In 2006, the city's NHL franchise, the
Carolina Hurricanes, won the
Stanley Cup
The Stanley Cup (french: La Coupe Stanley) is the championship trophy awarded annually to the National Hockey League (NHL) playoff champion. It is the oldest existing trophy to be awarded to a professional sports franchise in North America, an ...
, North Carolina's first and only professional sports championship.
With the opening of parts of
I-540 from 2005 to 2007, a new loop around Wake County, traffic congestion eased somewhat in the North Raleigh area. Completion of the entire loop is expected to take another 15 years.
In 2008, the city's
Fayetteville Street Historic District joined the
National Register of Historic Places.
In September 2010, Raleigh hosted the inaugural
Hopscotch Music Festival.
In January 2011, Raleigh hosted the
National Hockey League All-Star Game.
In April 2011, a devastating
EF-3 tornado hit Raleigh, and many other tornadoes touched down in the state (ultimately the largest, but not the
strongest outbreak to ever hit the state), killing 24 people. The tornado tracked northeast through parts of Downtown, East Central Raleigh and Northeast Raleigh and produced $115 million in damages in Wake County. There were 4 fatalities in the city.
In September 2015,
Holy Trinity Anglican Church was opened; the first church to be built in downtown Raleigh since 1958.
On July 26, 2017, the Catholic Diocese of Raleigh dedicated its new cathedral,
Holy Name of Jesus Cathedral, the fifth-largest in the United States.
On October 13, 2022,
a mass shooting occurred in Raleigh's Hedingham neighborhood. Five people were killed, and two others were injured.
The suspect, a 15-year-old boy, was detained after being cornered by police at a nearby residence and is in critical condition from injuries sustained during the incident.
Geography
According to the
United States Census Bureau, the city of Raleigh occupies a total area of ,
of which is land and , or 0.76%, is covered by water. The
Neuse River flows through the northeastern corner of the city.
Raleigh is located in the northeast central region of North Carolina, where the
Piedmont and
Atlantic coastal plain
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
regions meet. This area is known as the "
fall line" because it marks the elevation inland at which waterfalls begin to appear in creeks and rivers. As a result, most of Raleigh features gently rolling hills that slope eastward toward the state's flat coastal plain.
The city of Raleigh is located southeast of
Durham, northeast of
Fayetteville, northwest of
Wilmington, northeast of
Charlotte, and southwest of
Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
. A small portion of Raleigh is located in
Durham County, North Carolina.
Cityscape
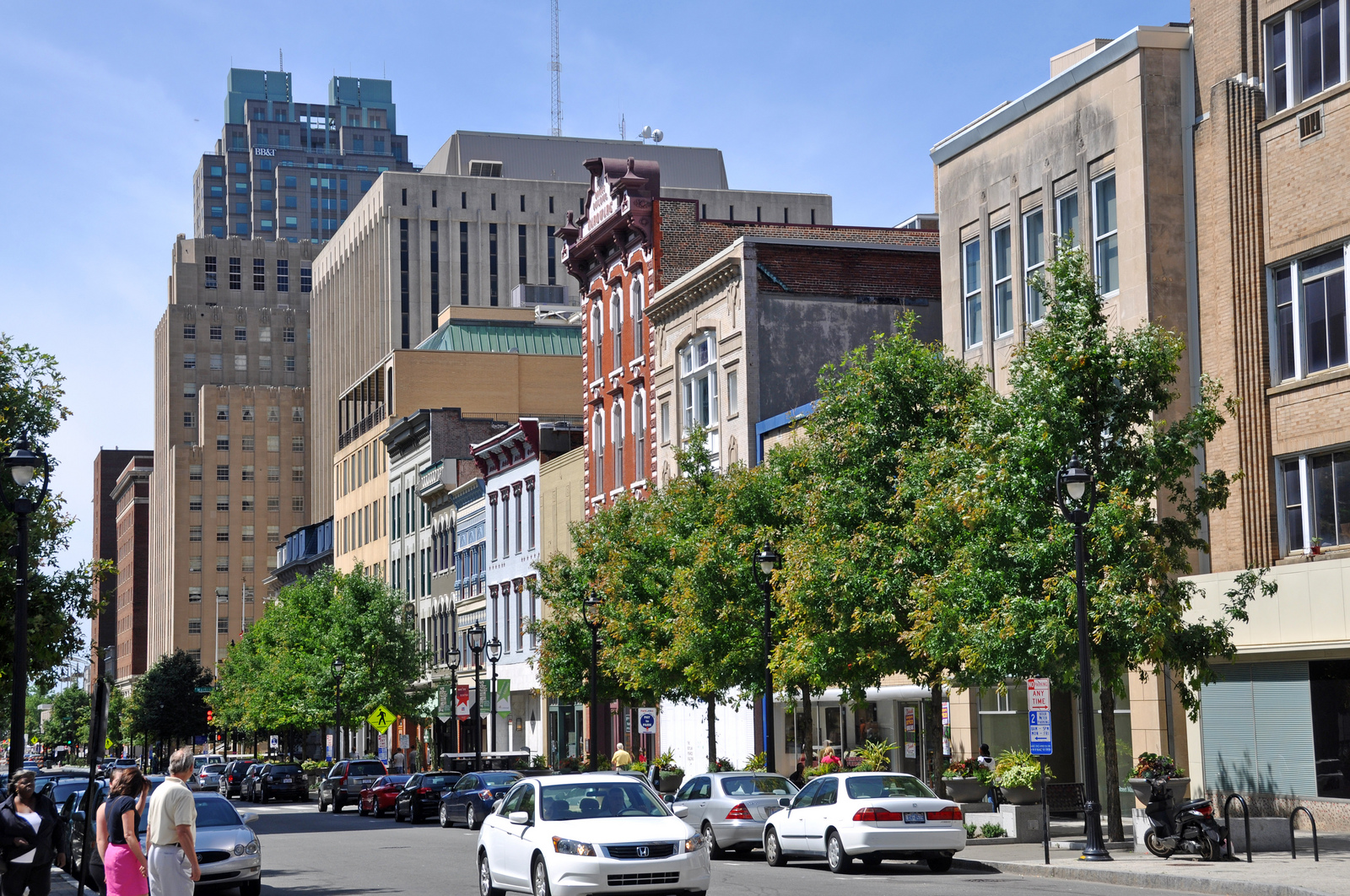

Raleigh is divided into several major geographic areas, each of which use a Raleigh address and a
ZIP code that begins with the digits 276.
PNC Plaza
PNC Plaza is a skyscraper in Downtown, Louisville, Kentucky and located at 500 West Jefferson Street. Owned by Pittsburgh-based PNC Bank, the 31-story, high structure was designed by architect Welton Becket and was completed in 1971. A notable ...
, formerly known as RBC Plaza, is the largest and tallest skyscraper in the city of Raleigh. The tower rises to a height of , with a floor count of 34.
Inside the Beltline
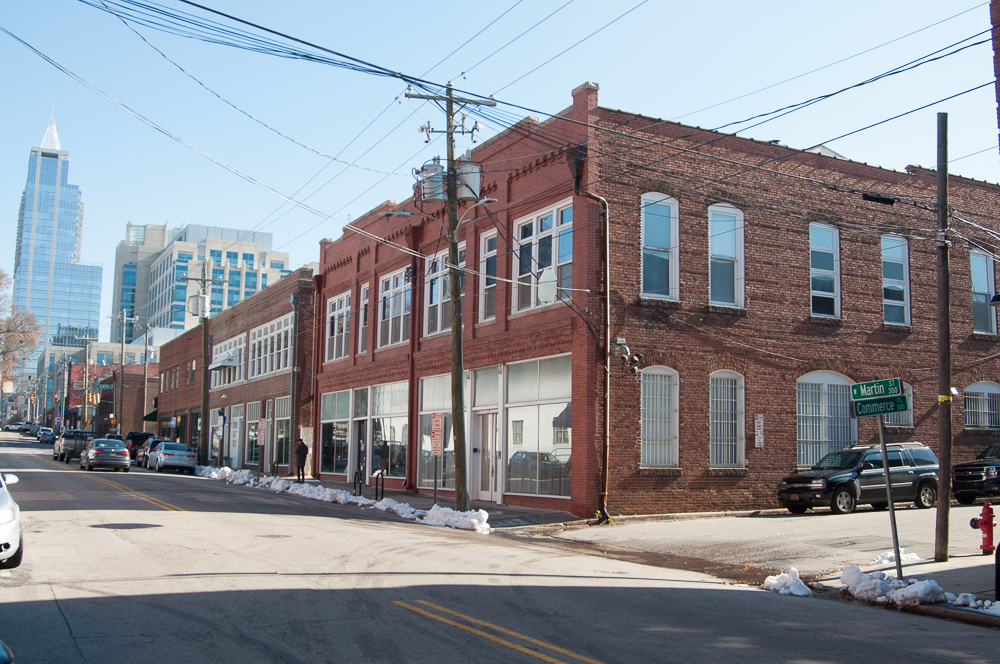

One common division of Raleigh is to differentiate the central part of the city, which lies inside of the
circumferential highway known as the Raleigh Beltline (
I-440 and
I-40) from areas outside of the Beltline. The area inside of the beltline includes the entirety of the central business district known as Downtown Raleigh, as well as several more residential areas surrounding it.
The downtown area is home to historic buildings such as the
Sir Walter Raleigh Hotel built in the early 20th century, the restored
City Market, the
Fayetteville Street downtown business district (which includes the
PNC Plaza
PNC Plaza is a skyscraper in Downtown, Louisville, Kentucky and located at 500 West Jefferson Street. Owned by Pittsburgh-based PNC Bank, the 31-story, high structure was designed by architect Welton Becket and was completed in 1971. A notable ...
and
Wells Fargo Capitol Center
Wells Fargo Capitol Center (formerly Wachovia Capitol Center and First Union Capitol Center) is a 30-story 121.92 m high-rise skyscraper at 150 Fayetteville Street in Raleigh, North Carolina with of space. Completed in 1990, it was one of the dow ...
buildings), as well as the
North Carolina Museum of History,
North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences,
North Carolina State Capitol,
William Peace University, the
City of Raleigh Museum
The City of Raleigh Museum is a local history museum associated with Raleigh, North Carolina. The museum is located in the historic Briggs Hardware Building on Fayetteville Street in downtown Raleigh and has a number of exhibits and programs that ...
,
Raleigh Convention Center
The Raleigh Convention Center is a convention and exhibition facility in downtown Raleigh, North Carolina that opened in September 2008. The architect was Tvsdesign with the participation of local firms O'Brien/Atkins Associates and Clearscapes. ...
,
Shaw University
Shaw University is a private Baptist historically black university in Raleigh, North Carolina. It is affiliated with the American Baptist Churches USA. Founded on December 1, 1865, Shaw University is the oldest HBCU to begin offering courses in ...
,
Campbell University School of Law, and
St. Augustine's College. In the 2000s, an effort by the Downtown Raleigh Alliance was made to separate this area of the city into five smaller districts:
Fayetteville Street,
Moore Square,
Glenwood South
Glenwood South is a major downtown district in Raleigh, North Carolina, Raleigh, North Carolina, U.S. Glenwood South is among the largest entertainment centers in Raleigh with a multitude of restaurants, clubs, and cafes. The district also has a r ...
,
Warehouse (Raleigh)
The Warehouse District is a major downtown district in Raleigh, North Carolina, The Warehouse District is a growing arts, restaurant, nightlife, and entrepreneurial district located three blocks west of the Raleigh Convention Center. The district c ...
, and
Capital District (Raleigh).
Some of the names have become commonplace among locals, such as the Warehouse District, Fayetteville Street, and
Glenwood South
Glenwood South is a major downtown district in Raleigh, North Carolina, Raleigh, North Carolina, U.S. Glenwood South is among the largest entertainment centers in Raleigh with a multitude of restaurants, clubs, and cafes. The district also has a r ...
. Other neighborhoods lying inside the Beltline include
Cameron Park,
Boylan Heights, Country Club Hills, Coley Forest, Five Points, Budleigh,
Glenwood-Brooklyn,
Hayes Barton Historic District
The Hayes Barton Historic District is a neighborhood located northwest of downtown Raleigh, North Carolina. Hayes Barton, an upper class neighborhood designed by landscape architect Earle Sumner Draper, contains 457 buildings on . The neighborhoo ...
,
Moore Square,
Mordecai
Mordecai (; also Mordechai; , IPA: ) is one of the main personalities in the Book of Esther in the Hebrew Bible. He is described as being the son of Jair, of the tribe of Benjamin. He was promoted to Vizier after Haman was killed.
Biblical acco ...
(home to the historic
Mordecai House
The Mordecai House (also called the Mordecai Plantation or Mordecai Mansion), built in 1785, is a registered historical landmark and museum in Raleigh, North Carolina that is the centerpiece of Mordecai Historic Park, adjacent to the Historic Oa ...
), Rochester Heights, South Park, Rosengarten Park, Belvidere Park, Woodcrest, Oberlin Village, and
Historic Oakwood. These neighborhoods were typically built before World War II, and roughly correspond to the extent of the city of Raleigh before the population boom of the latter half of the 20th century led to growth of the city limits beyond the historic urban core.
Midtown Raleigh

Midtown Raleigh is a
relatively new term used to describe the residential and commercial area lying on the northside of the I-440 Beltline and is part of North Raleigh. It is roughly framed by Glenwood/Six Forks Road to the West, Wake Forest Road to the East, and Millbrook Road to the North. It includes shopping centers such as
North Hills and
Crabtree Valley Mall. It also includes North Hills Park and part of the Raleigh Greenway System. The term was coined by the Greater Raleigh Chamber of Commerce, developer John Kane and planning director Mitchell Silver. ''The'' ''News & Observer'' newspaper started using the term for marketing purposes only. The Midtown Raleigh Alliance was founded on July 25, 2011, as a way for community leaders to promote the area. The center of the area, especially around the North Hills development at the junction of Six Forks Road and the Beltline, is experiencing rapid urbanization as several high-rise buildings have been built since 2010.
East Raleigh
East Raleigh is situated roughly from
Capital Boulevard
Capital Boulevard is a major thoroughfare in Wake County, North Carolina. At various points along the route, it carries NC 50, U.S. Route 70 in North Carolina, U.S. Highway 70 (US 70), US 401, and U.S. Route 1 in North Carolina, US ...
near the
I-440 beltline to New Hope Road. Most of East Raleigh's development is along primary corridors such as
U.S. 1
U.S. Route 1 or U.S. Highway 1 (US 1) is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway System, United States Numbered Highway that serves the East Coast of the United States. It runs from Key West, Florida, north to Fort Kent, ...
(Capital Boulevard), New Bern Avenue, Poole Road, Buffaloe Road, and New Hope Road. Neighborhoods in East Raleigh include Hedingham, Longview, Lockwood,
Madonna Acres, New Hope, Thompson-Hunter and Wilder's Grove. The area is bordered to the east by the town of
Knightdale.
West Raleigh

West Raleigh lies along
Hillsborough Street
Hillsborough Street is a business and cultural thoroughfare through Raleigh, North Carolina, Raleigh, North Carolina, United States. The street serves as a center for social life among North Carolina State University and Meredith College students.
...
and Western Boulevard. The area is bordered to the west and south by
Cary. It is home to
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The universit ...
,
Meredith College
Meredith College is a private women's liberal arts college and coeducational graduate school in Raleigh, North Carolina. As of 2021 Meredith enrolls approximately 1,500 women in its undergraduate programs and 300 men and women in its graduate pr ...
,
Pullen Park,
Pullen Memorial Baptist Church, the Islamic Association of Raleigh,
Village District
Village District (formerly Cameron Village), was the first planned community to be developed in Raleigh, North Carolina. Development was started in 1947 when J.W. York and R.A Bryan bought of undeveloped land two miles west of downtown Raleigh, ...
, Lake Johnson, the
North Carolina Museum of Art
The North Carolina Museum of Art (NCMA) is an art museum in Raleigh, North Carolina. It opened in 1956 as the first major museum collection in the country to be formed by state legislation and funding. Since the initial 1947 appropriation that e ...
and historic
Saint Mary's School. Primary thoroughfares serving West Raleigh, in addition to Hillsborough Street, are Avent Ferry Road, Blue Ridge Road, and Western Boulevard. The
PNC Arena is also located here adjacent to the
North Carolina State Fairgrounds. These are located approximately 2 miles from
Rex Hospital
UNC Rex Hospital is a general hospital located in Raleigh, North Carolina. It is the capital city's oldest hospital, founded by a bequest from John T. Rex (1771-1839), a local tanner. Originally located on what is now Dorothea Dix campus, and ...
.
North Raleigh
North Raleigh is an expansive, diverse, and fast-growing suburban area of the city that is home to established neighborhoods to the south along with many newly built
subdivisions and along its northern fringes. The area generally falls North of Millbrook Road. It is primarily suburban with large shopping areas. Primary neighborhoods and subdivisions in North Raleigh include Bartons Creek Bluffs, Bedford, Bent Tree, Black Horse Run, Brier Creek, Brookhaven, Coachman's Trail, Crossgate, Crosswinds, Dominion Park, Durant Trails, Ethan's Glenn, Falls River, Greystone Village, Harrington Grove, Hidden Valley, Lake Park, Long Lake, North Haven,
North Ridge, Oakcroft, Shannon Woods, Six Forks Station, Springdale Estates, Stonebridge, Stone Creek, Stonehenge, Summerfield, The Sanctuary, Valley Estates, Wakefield, Weathersfield, Windsor Forest, and Wood Valley. The area is served by a number of primary transportation corridors including Glenwood Avenue
U.S. Route 70
U.S. Route 70 or U.S. Highway 70 (US 70) is an east–west United States highway that runs for from eastern North Carolina to east-central Arizona. It is a major east–west highway of the Southeastern United States, Southeastern, Southern Unite ...
,
Interstate 540, Wake Forest Road, Millbrook Road, Lynn Road, Six Forks Road, Spring Forest Road,
Creedmoor Road
North Carolina Highway 50 (NC 50) is a primary state highway in the U.S. state of North Carolina. It goes from Topsail Beach in the south to Creedmoor in the north, connecting the cities of Warsaw, Newton Grove, Benson, and Raleigh.
R ...
, Leesville Road, Norwood Road, Strickland Road, and North Hills Drive.
South Raleigh
South Raleigh is located along
U.S. 401 south toward
Fuquay-Varina and along
US 70 into suburban
Garner
Garner may refer to:
Places United States
* Garner, Arkansas
* Garner, Iowa
* Garner, Missouri
* Garner, North Carolina
Other uses
* Garner (surname), a surname
* Granary, a grain store
* ''Tennessee v. Garner'', a United States Supreme Court cas ...
. This area is the least developed and least dense area of Raleigh (much of the area lies within the
Swift Creek watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
district, where development regulations limit housing densities and construction). The area is bordered to the west by
Cary, to the east by
Garner
Garner may refer to:
Places United States
* Garner, Arkansas
* Garner, Iowa
* Garner, Missouri
* Garner, North Carolina
Other uses
* Garner (surname), a surname
* Granary, a grain store
* ''Tennessee v. Garner'', a United States Supreme Court cas ...
, to the southwest by
Holly Springs and the southeast by Fuquay-Varina. Neighborhoods in South Raleigh include Eagle Creek, Renaissance Park, Lake Wheeler, Swift Creek, Carolina Pines, Rhamkatte, Riverbrooke, and Enchanted Oaks.
Southeast Raleigh
Southeast Raleigh is bounded by downtown on the west,
Garner
Garner may refer to:
Places United States
* Garner, Arkansas
* Garner, Iowa
* Garner, Missouri
* Garner, North Carolina
Other uses
* Garner (surname), a surname
* Granary, a grain store
* ''Tennessee v. Garner'', a United States Supreme Court cas ...
on the southwest, and rural
Wake County to the southeast. The area includes areas along Rock Quarry Road, Poole Road, and New Bern Avenue. Primary neighborhoods include Abbington Ridge, Pearl Ridge, Chastain, Chavis Heights, Raleigh Country Club, Southgate, Kingwood Forest, Rochester Heights, Emerald Village and Biltmore Hills.
Coastal Credit Union Music Park
Coastal Credit Union Music Park (originally named Walnut Creek Amphitheatre and formerly Alltel Pavilion) is an outdoor amphitheater located in Raleigh, North Carolina, United States, that specializes in hosting large concerts.
The amphitheater ...
(formerly Time Warner Cable Music Pavilion, Alltel Pavilion and Walnut Creek Amphitheatre) is one of the region's major outdoor concert venues and is located on Rock Quarry Road.
Shaw University
Shaw University is a private Baptist historically black university in Raleigh, North Carolina. It is affiliated with the American Baptist Churches USA. Founded on December 1, 1865, Shaw University is the oldest HBCU to begin offering courses in ...
is located in this part of the city. Starting in 2020, large tracts of formerly unoccupied land along Rock Quarry Road between New Hope Road and Barwell Road, and between Barwell Road and Battle Bridge Road, have been cleared for new developments.
Climate

Like much of the Southeastern United States, Raleigh has a
humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(
Köppen ''Cfa''). Winters are generally cool, with a normal January daily mean temperature of .
On average, there are 69 nights per year that drop to or below freezing, and only 2.7 days that fail to rise above freezing.
Raleigh receives an average annual rainfall of . Annual and monthly temperature and precipitation data are in chart below, based on 1991–2020 climate data. February is the driest month, with an average of of precipitation. Precipitation is well distributed around the year, with a slight maximum between July and September, owing to generally frequent, sometimes heavy, showers and thunderstorms, and the threat of tropical weather systems (primarily in from August to early October) bringing heavy rainfall. Summers are hot and humid, with a normal July daily mean temperature of .
There are 48 days per year with highs at or above .
Autumn is similar to spring overall but has fewer days of rainfall, but greater potential for extremely heavy rainfall in a one/two-day period, owing to occasional threat from tropical weather systems (hurricanes and tropical storms) packing torrential rainfall. In September 1999, Raleigh recorded its wettest month ever, with over 21 inches of rain, due to torrential rainfall from tropical weather systems, most notably Hurricane Floyd on September 15–16. Extremes in temperature have ranged from on
January 21, 1985 up to , most recently on
June 29–30 and July 8, 2012.
Raleigh falls in
USDA hardiness zones 7b (5 °F to 10 °F) and 8a (10 °F to 15 °F).

Raleigh receives an average of of snow in winter.
Freezing rain and
sleet also occur most winters, and occasionally the area experiences a major damaging
ice storm. On January 24–25, 2000, Raleigh received its greatest snowfall from a single stormthe
Winter Storm of January 2000. Storms of this magnitude are generally the result of
cold air damming that affects the city due to its proximity to the
Appalachian Mountains. Winter storms have caused traffic problems in the past as well.
The region also experiences occasional periods of drought, during which the city sometimes has restricted water use by residents. During the late summer and early fall, Raleigh can experience
hurricanes. In 1996,
Hurricane Fran caused severe damage in the Raleigh area, mostly from falling trees. Hurricanes Dennis and Floyd in September 1999 were primary contributors to that month's extreme rainfall of over 21 inches. The most recent hurricane to have a considerable effect on the area was
Hurricane Florence in 2018. Tornadoes also have on occasion affected the city of Raleigh, most notably the November 28, 1988, tornado which occurred in the early morning hours and rated F4 on the
Fujita scale and affected northwestern portions of the city. There also was the April 16, 2011, EF3 tornado, which affected portions of downtown and northeast Raleigh and the suburb of Holly Springs.
Demographics
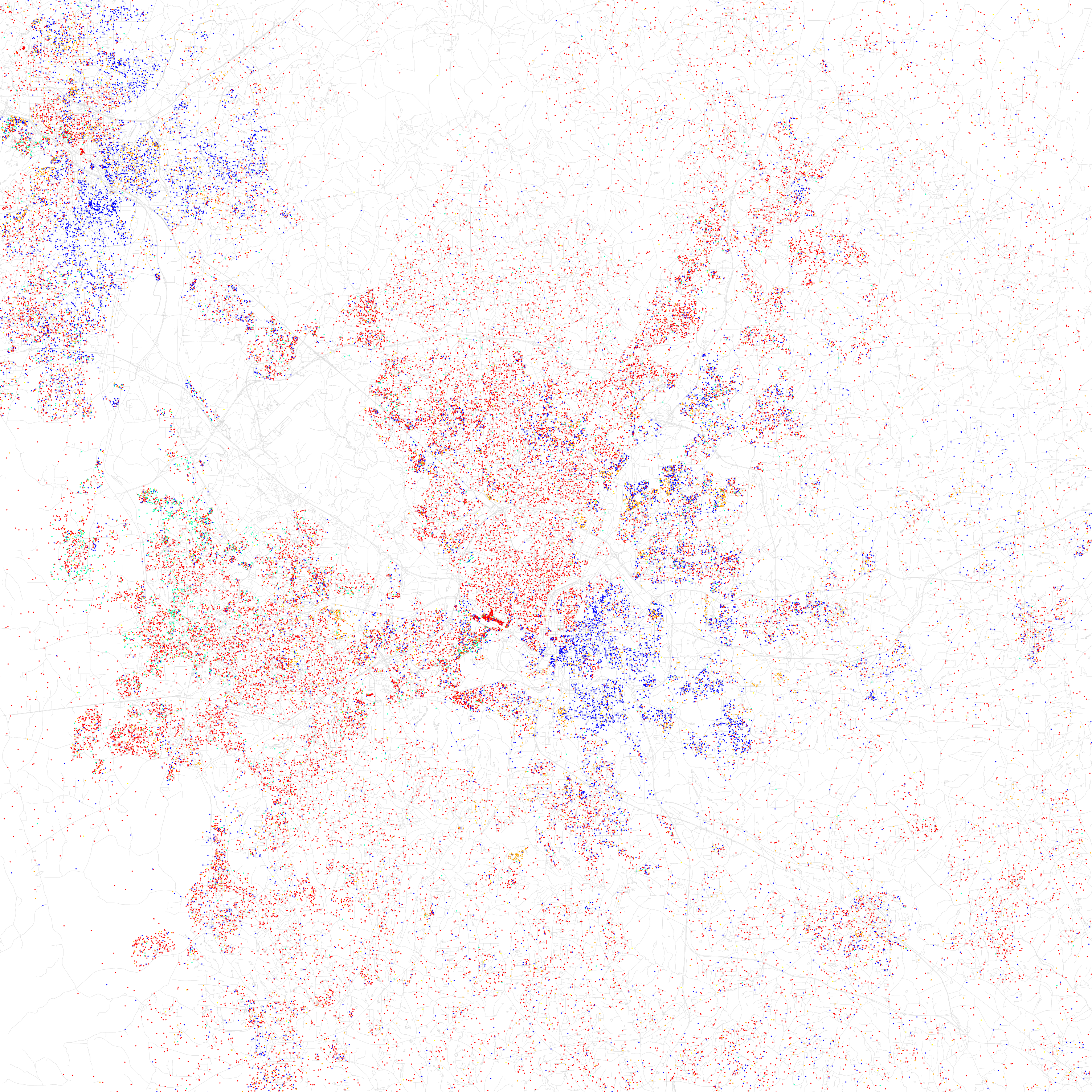
2020 census
''Note: the US Census treats Hispanic/Latino as an ethnic category. This table excludes Latinos from the racial categories and assigns them to a separate category. Hispanics/Latinos can be of any race.''
As of the
2020 United States census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to of ...
, there were 467,665 people, 188,412 households, and 104,848 families residing in the city. In the
American Community Survey
The American Community Survey (ACS) is a demographics survey program conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. It regularly gathers information previously contained only in the long form of the decennial census, such as ancestry, citizenship, educati ...
of 2019, the city of Raleigh's population was estimated at 474,708; an earlier estimate determined the population at 474,069.
At the 2000 United States census,
there were 276,093 persons (July 2008 estimate was 380,173) and 61,371 families residing in Raleigh. The population density was 2,409.2 people per square mile (930.2/km
2). There were 120,699 housing units at an average density of 1,053.2 per square mile (406.7/km
2). There were 112,608 households in the city in 2000, of which 26.5% included children below the age of 18, 39.5% were composed of married couples living together, 11.4% reported a female householder with no husband present, and 45.5% classified themselves as nonfamily. Unmarried partners were present in 2.2% of households. In addition, 33.1% of all households were composed of individuals living alone, of which 6.2% was someone 65 years of age or older. The average household size in Raleigh was 2.30 persons, and the average family size was 2.97 persons.
Raleigh's population in 2000 was evenly distributed with 20.9% below the age of 18, 15.9% aged 18 to 24, 36.6% from 25 to 44, and 18.4% from 45 to 64. An estimated 8.3% of the population was 65 years of age or older, and the median age was 31 years. For every 100 females, there were 98.0 males; for every 100 females aged 18 or older, there were 96.6 males aged 18 or older.
The racial makeup of Raleigh in 2019 was 52.5% non-Hispanic White, 28.3% Black or African American, 0.4% American Indian or Alaska Native, 4.0% Asian American, 0.1% from some other race, 2.1% two or more races, 12.5% Hispanic or Latin American of any race. According to the 2010 United States census, the racial composition of the city was: 57.5%
White (53.3%
non-Hispanic White
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Amer ...
), 29.3%
Black or African American, 4.3% Asian American (1.2%
Indian, 0.8%
Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
, 0.7%
Vietnamese, 0.5%
Korean, 0.4%
Filipino, 0.1%
Japanese), 2.6%
two or more races
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many culture ...
, 1.4%
some other race, 0.5% Native American, and <0.1%
Native Hawaiian or
other Pacific Islander In addition, 11.4% of city residents were
Hispanic or
Latino Americans, of any race (5.9%
Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
, 1.1%
Puerto Rican, 0.9%
Salvadoran
Salvadorans (Spanish: ''Salvadoreños''), also known as Salvadorians (alternate spelling: Salvadoreans), are citizens of El Salvador, a country in Central America. Most Salvadorans live in El Salvador, although there is also a significant Salvado ...
, 0.6%
Dominican, 0.6%
Honduran, 0.3%
Colombian, 0.3%
Cuban
Cuban may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Cuba, a country in the Caribbean
* Cubans, people from Cuba, or of Cuban descent
** Cuban exile, a person who left Cuba for political reasons, or a descendant thereof
* Cuban citizen, a perso ...
, 0.2%
Guatemalan, 0.2%
Spanish, 0.2%
Peruvian, 0.1%
Venezuelan
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, 0.1% Ecuadorian Americans, Ecuadorian, 0.1% Argentine Americans, Argentine, and 0.1% Panamanian Americans, Panamanian). In 2000, the racial composition of the city was: 63.31% White, 27.80% Black or African American, 7.01% Hispanic or Latino American, 3.38% Asian American, 0.36% Native American, 0.04% Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, 3.24% some other race, and 1.88% two or more races.
The median household income in the United States, household income in the city was $46,612 in 2000, and the median family income was $60,003. Males earned a median income of $39,248, versus $30,656 for females. The median per capita income for the city was $25,113, and an estimated 11.5% of the population and 7.1% of families were living below the poverty threshold, poverty line. Of the total population, 18.8% of those below the age of 18, and 9.3% of those 65 and older, were living below the poverty line. In 2019, an estimated 10.9% of the local population were at or below the poverty line. The median household income from 2014 to 2018 was $63,891 and the per capita income was $36,875.
There were 180,046 households with an average of 2.43 persons per household. The median value of an owner-occupied housing unit was $236,700 in 2018 and the monthly cost with a mortgage was $1,480. The cost without a mortgage was $526. Raleigh had a median gross rent of $1,074.
Religion
Raleigh is home to a wide variety of religious practitioners. The predominant religion in Raleigh is Christianity, with the largest numbers of adherents being Baptist (14.1%), Methodist (5.6%), and Roman Catholic (4.2%). Others include Presbyterianism (2.8%), Pentecostalism (1.7%), Anglicanism/Episcopalianism (1.2%), Lutheranism (0.6%), the Latter Day Saint movement, Latter-Day Saints (0.7%), and other Christian denominations (10.2%) including the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodox, Jehovah's Witness, Christian Science, Christian Unitarianism, other Mainline Protestant groups, and Nondenominational Christianity, non-denominational Christians.
The
Roman Catholic Diocese of Raleigh
The Diocese of Raleigh is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church that covers the eastern half of the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is a suffragan diocese in the ecclesiastical province of the metropolitan A ...
, the
Episcopal Diocese of North Carolina, the North Carolina Annual Conference, North Carolina Annual Conference of the United Methodist Church, and the New Hope Presbytery of the PC(USA), Presbyterian Church (USA) are all headquartered in Raleigh.
Other religions, including Hinduism, Buddhism, Baháʼí Faith, Baháʼí, Druze, Taoism, and Shintoism make up 1.31% of religious practitioners. Judaism (0.9%) and Islam (0.8%) are also practiced.
In Wake County, 29% of the population are affiliated with the Southern Baptist Convention, 22% are affiliated with the Catholic Church, 17% are affiliated with the United Methodist Church, 6% are affiliated with the Presbyterian Church (USA), and 27% are religiously affiliated with other denominations, religions, or are not religiously affiliated.
Crime
According to the Federal Bureau of Investigation's Uniform Crime Reports, in 2019 the Raleigh Police Department (North Carolina), Raleigh Police Department and other agencies in the city reported 1,222 incidents of violent crime and 8,520 incidents of property crime – far below both the national average and the North Carolina average. Of the violent crimes reported, 5 were murders, 164 were rape/sexual assaults and 322 were robbery, robberies. Aggravated assault accounted for 731 of the total violent crimes. Property crimes included burglary, burglaries which accounted for 1,200, larceny, larcenies for 6,572 and Motor vehicle theft accounted for 748 incidents out of the total.
Economy
Raleigh's industrial base includes financial services, electrical, medical, electronic and telecommunications equipment, clothing and apparel, food processing, paper products, and pharmaceuticals. Raleigh is part of North Carolina's Research Triangle, one of the country's largest and most successful research parks, and a major center in the United States for high tech, high-tech and biotechnology, biotech research, as well as advanced textile development. The city is a major retail shipping point for eastern North Carolina and a wholesale distributing point for the grocery industry.
The healthcare and pharmaceutical industry has experienced major growth in recent years with many companies based in Raleigh including PRA Health Sciences, Chiesi USA (subsidiary of Chiesi Farmaceutici), formerly Mallinckrodt prior to tax evasion with Ireland, MAKO Surgical Corp., Metabolon, Inc., TearScience, and American Board of Anesthesiology.
Raleigh was number one on the 2015
Forbes list of the best place for businesses and careers. Companies based in Raleigh include Advance Auto Parts, Bandwidth (company), Bandwidth, Truist Financial, Building Materials Holding Corporation, Capitol Broadcasting Company, Carquest, First Citizens BancShares, Golden Corral, Martin Marietta Materials, PRA Health Sciences, Red Hat, Vontier, Waste Industries, and Lulu (company), Lulu.
Social Blade, a website that tracks social media statistics and analytics, and Temple Run developer Imangi Studios are based in Raleigh.
The North Carolina Air National Guard, a unit of the Air National Guard, is also headquartered in Raleigh.
In April 2014 Steven P. Rosenthal of Northland Investment Corp. referred to Raleigh as "a real concentration of brain power. You have a lot of smart people living in the same place. That will drive the economy."
Top employers
According to Raleigh's 2017–18 Comprehensive Annual Financial Report, the top employers in the city are:
Arts and culture
Museums


*African American Cultural Complex
*Contemporary Art Museum of Raleigh
*Gregg Museum of Art & Design at
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The universit ...
*Haywood Hall House & Gardens
*Marbles Kids Museum
*
North Carolina Museum of Art
The North Carolina Museum of Art (NCMA) is an art museum in Raleigh, North Carolina. It opened in 1956 as the first major museum collection in the country to be formed by state legislation and funding. Since the initial 1947 appropriation that e ...
*
North Carolina Museum of History
*
North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences
*North Carolina Sports Hall of Fame
*
City of Raleigh Museum
The City of Raleigh Museum is a local history museum associated with Raleigh, North Carolina. The museum is located in the historic Briggs Hardware Building on Fayetteville Street in downtown Raleigh and has a number of exhibits and programs that ...
*J. C. Raulston Arboretum
*Joel Lane House
*Mordecai House, Mordecai Plantation
*Pope House Museum

Performing arts
The
Coastal Credit Union Music Park at Walnut Creek
Coastal Credit Union Music Park (originally named Walnut Creek Amphitheatre and formerly Alltel Pavilion) is an outdoor amphitheater located in Raleigh, North Carolina, United States, that specializes in hosting large concerts.
The amphitheater ...
hosts major international touring acts. In 2011, the Downtown Raleigh Amphitheater opened (now sponsored as the Red Hat Amphitheater), which hosts numerous concerts primarily in the summer months. An additional amphitheater sits on the grounds of the North Carolina Museum of Art, which hosts a summer concert series and outdoor movies. Nearby Cary is home to the Koka Booth Amphitheatre which hosts additional summer concerts and outdoor movies, and serves as the venue for regularly scheduled outdoor concerts by the North Carolina Symphony based in Raleigh. During the North Carolina State Fair,
Dorton Arena hosts headline acts. The private Lincoln Theatre is one of several clubs in downtown Raleigh that schedules many concerts throughout the year in multiple formats (rock, pop, country).
The Duke Energy Center for the Performing Arts complex houses the Raleigh Memorial Auditorium, the Fletcher Opera Theater, the Kennedy Theatre, and the Meymandi Concert Hall. In 2008, a new theatre space, the Meymandi Theatre at the Murphey School, was opened in the restored auditorium of the historic Murphey School. Theater performances are also offered at the Raleigh Little Theatre, Long View Center, Theatre In The Park, Ira David Wood III Pullen Park Theatre, and Stewart and Thompson Theaters at North Carolina State University.
Raleigh is home to several professional arts organizations, including the
North Carolina Symphony, the Opera Company of North Carolina, Theatre in the Park, Burning Coal Theatre Company, the North Carolina Theatre, Broadway Series South and the Carolina Ballet. The numerous local colleges and universities significantly add to the options available for viewing live performances.
Visual arts
North Carolina Museum of Art
The North Carolina Museum of Art (NCMA) is an art museum in Raleigh, North Carolina. It opened in 1956 as the first major museum collection in the country to be formed by state legislation and funding. Since the initial 1947 appropriation that e ...
, occupying a large suburban campus on Blue Ridge Road near the North Carolina State Fairgrounds, maintains one of the premier public art collections located between Washington, D.C., and Atlanta. In addition to its extensive collections of Visual arts of the United States, American Art, Western art history, European Art and ancient art, the museum recently has hosted major exhibitions featuring Auguste Rodin (in 2000) and Claude Monet (in 2006–07), each attracting more than 200,000 visitors. Unlike most prominent public museums, the North Carolina Museum of Art acquired a large number of the works in its permanent collection through purchases with public funds. The museum's outdoor park is one of the largest such sculpture park, art parks in the country. The museum facility underwent a major expansion which greatly expanded the exhibit space that was completed in 2010. The 127,000 sf new expansion is designed by NYC architect Thomas Phifer, Thomas Phifer and Partners.
Raleigh's downtown is also home to many local art galleries such as Art Space in
City Market, Visual Art Exchange, and 311 Gallery, on Martin Street, and Bee Hive Studios on Hargett Street. Contemporary Art Museum of Raleigh, CAM Raleigh is a downtown contemporary art museum, also on Martin Street, that serves to promote new artists and does not house a permanent collection. CAM Raleigh was designed by the award-winning architectural firm Brooks+Scarpa of Los Angeles.
Sports
Professional
The
National Hockey League's
Carolina Hurricanes franchise moved to Raleigh in 1997 from Hartford, Connecticut (where it was known as the
Hartford Whalers). The team played its first two seasons more than 60 miles away at Greensboro Coliseum while its home arena, Raleigh Entertainment and Sports Arena (later RBC Center and now
PNC Arena), was under construction. The Hurricanes are the only major league (National Football League, NFL, National Hockey League, NHL, National Basketball Association, NBA, Major League Baseball, MLB) professional sports team in North Carolina to have won a championship, winning the
Stanley Cup
The Stanley Cup (french: La Coupe Stanley) is the championship trophy awarded annually to the National Hockey League (NHL) playoff champion. It is the oldest existing trophy to be awarded to a professional sports franchise in North America, an ...
in 2006, over the Edmonton Oilers. The city played host to the 2011 National Hockey League All-Star Game, 2011 NHL All-Star Game.

In addition to the Hurricanes, the North Carolina FC of the United Soccer League and North Carolina Courage women's professional soccer team play in suburban Cary to the west; the Carolina Mudcats, a Single-A (baseball), Single-A minor-league baseball team, play in the city's eastern suburbs; the newly formed Single-A (baseball), Single-A minor-league baseball Fayetteville Woodpeckers, who formerly played in Buies Creek, North Carolina, Buies Creek, began play in the nearby out-of-county southern suburb of
Fayetteville when their Fayetteville Ballpark, new ballpark opened in 2019; the Carolina Flyers of the American Ultimate Disc League play primarily at Cardinal Gibbons High School near the PNC Arena; and the Durham Bulls, the Triple-A (baseball), AAA minor-league baseball team made internationally famous by the movie ''Bull Durham'', play in the neighboring city of Durham.
Several other professional sports leagues have had former franchises (now defunct) in Raleigh, including the Raleigh IceCaps of the ECHL (1991–1998); Carolina Cobras of the Arena Football League (2000–2004); the Raleigh–Durham Skyhawks of the World League of American Football (1991); the Raleigh Bullfrogs of the Global Basketball Association (1991–1992); the Raleigh Cougars of the United States Basketball League (1997–1999); and most recently, the Carolina Courage of the Women's United Soccer Association (2000–2001 in Chapel Hill, 2001–2003 in suburban Cary), which won that league's championship Founders Cup in 2002.
The Raleigh area has hosted the Professional Golfers' Association of America, Professional Golfers' Association (PGA) Nationwide Tour Rex Hospital Open since 1994, with the current location of play at Raleigh's Wakefield Plantation. Nearby Prestonwood Country Club hosts the PGA SAS Championship every fall.
Collegiate
North Carolina State University is located in southwest Raleigh where the North Carolina State Wolfpack, Wolfpack competes nationally in 24 intercollegiate varsity sports as a member of the Atlantic Coast Conference. The university's football team plays in Carter–Finley Stadium, the second largest football stadium in North Carolina, while the men's basketball team shares the PNC Arena with the Carolina Hurricanes hockey club. The Wolfpack women's basketball, volleyball, and gymnastics as well as men's wrestling events are held on campus at Reynolds Coliseum. The men's baseball team plays at Doak Field.
Amateur
The North Carolina Tigers compete as an Australian rules football club in the United States Australian Football League, in the Eastern Australian Football League.
Raleigh is also home to one of the Cheer Extreme All Stars gyms. In 2009 and again in 2010, Cheer Extreme Raleigh's Small Senior Level 5 Team were silver medalists at the Cheerleading Worlds Competition in Orlando, Florida, and in 2012 they received the bronze medal. Raleigh is also home to one of the Southeast's premier Hardcourt Bike Polo clubs.
Because of the area's many billiards rooms, Raleigh is home to one of the largest amateur league franchises for playing pool (cue sports), pool, the Raleigh, Durham, Chapel Hill American Poolplayers Association. There are leagues available in formats for players of any skill level.
Parks and recreation

Raleigh is the home of Raleigh Kubb, both a competitive and non-competitive kubb club. Raleigh Kubb hosts kubb tournaments benefitting various charities in the Raleigh area.
The Raleigh Parks and Recreation Department offers a wide variety of leisure opportunities at more than 200 sites throughout the city, which include: of park land, of greenway (landscape), greenway, 22 community centre, community centers, a Bicycle Motocross, BMX championship-caliber race track, 112 tennis courts among 25 locations, 5 public lakes, and 8 public aquatic facilities. The park system includes the historic
Pullen Park, the oldest public park in North Carolina. The J. C. Raulston Arboretum, an 8-acre (32,000 m
2) arboretum and botanical garden in west Raleigh administered by
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The universit ...
, maintains a year-round collection that is open daily to the public without charge.
Government
Historically, Raleigh voters have tended to elect conservative Democrats in local, state, and national elections, a holdover from their one-party system of the late 19th century.
City Council
Raleigh operates under a council-manager government. Raleigh City Council consists of eight members; all seats, including the Mayor of Raleigh, North Carolina, Mayor's, are open for election every two years. Five of the council seats are district representatives and two seats are citywide representatives elected at-large.
*Mary-Ann Baldwin, mayor
*Jonathan Melton, Council Member, At-Large
*Nicole Stewart, Council Member, At-Large
*Patrick Buffkin, Council Member (District A, north-central Raleigh)
*David Cox, Council Member (District B, northeast Raleigh)
*Corey Branch, Council Member (District C, southeast Raleigh)
*Stormie Forte, Council Member (District D, southwest Raleigh)
*David Knight, Council Member (District E, west and northwest Raleigh)
Education




As of 2011, ''Time (magazine), Time'' ranked Raleigh as the third most educated city in the US based on the percentage of residents who held college degrees. This statistic can most likely be credited to the presence of universities in and around Raleigh, as well as the presence of
Research Triangle Park
Research Triangle Park (RTP) is the largest research park in the United States, occupying in North Carolina and hosting more than 300 companies and 65,000 workers.
The facility is named for its location relative to the three surrounding cities ...
(RTP) to the Northwest.
Higher education
Public
*
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The universit ...
*Wake Technical Community College
Private
*Campbell University Norman Adrian Wiggins School of Law (Baptist)
*
Meredith College
Meredith College is a private women's liberal arts college and coeducational graduate school in Raleigh, North Carolina. As of 2021 Meredith enrolls approximately 1,500 women in its undergraduate programs and 300 men and women in its graduate pr ...
(Baptist)
*Montreat College's ''School of Professional and Adult Studies'' (Presbyterian)
*
William Peace University (Presbyterian)
*
Shaw University
Shaw University is a private Baptist historically black university in Raleigh, North Carolina. It is affiliated with the American Baptist Churches USA. Founded on December 1, 1865, Shaw University is the oldest HBCU to begin offering courses in ...
(Baptist)
*Skema Business School, the first French Business School to open a campus in the USA
*St. Augustine's University (Episcopal)
Private, for profit
*ECPI College of Technology
*The Medical Arts School
*Strayer University
Primary and secondary education
Public schools
Public schools in Raleigh are operated by the
Wake County Public School System, the largest public school system of the Carolinas. Observers have praised the Wake County Public School System for its innovative efforts to maintain a socially, economically and racial balanced system by using income as a prime factor in assigning students to schools. Raleigh is home to several magnet school, magnet high schools and several schools offering the International Baccalaureate program. There are four early college high schools in Raleigh. Raleigh also has two Alternative school, alternative high schools.
Wake County Public high schools in Raleigh include:
=Traditional schools
=
*Needham B. Broughton High School (International Baccalaureate)
*Leesville Road High School
*Jesse O. Sanderson High School
*Wakefield High School (Raleigh, North Carolina), Wakefield High School
=Magnet schools
=
*Athens Drive High School
*William G. Enloe High School, William G. Enloe GT/IB Center for the Humanities, Sciences, and the Arts (International Baccalaureate)
*Millbrook High School (North Carolina), Millbrook High School (International Baccalaureate)
*Southeast Raleigh Magnet High School
=Alternative schools
=
*Longview School
*Phillips High School (North Carolina), Mary E. Phillips High School
=Early college schools
=
*Wake Young Men's Leadership Academy
*Wake Young Women's Leadership Academy
*Wake STEM Early College High School
*Wake Early College of Health and Sciences
Charter schools
The State of North Carolina provides for a legislated number of charter schools. These schools are administered independently of the Wake County Public School System. Raleigh is currently home to 11 such charter schools:
*Casa Esperanza Montessori method, Montessori School (K-8)
*Endeavor Charter School (K-8)
*Exploris Middle School (1–8)
*Hope Elementary School (K-5)
*Longleaf School of the Arts (9–12)
*Magellan Charter School (3–8)
*PreEminent Charter School (K-8)
*Quest Academy (K-8)
*Raleigh Charter High School (9–12)
*Torchlight Academy (K-6)
*Woods Charter School (K-12)
State-operated schools
*Governor Morehead School, school for the blind
Private and religion-based schools
*Al-Iman Islamic School (K-8)
*An Noor Quran Academy (3–8)
*Bonner Academy (5–8)
*Follow the Child Montessori School (K-6)
*Friendship Christian School (North Carolina), Friendship Christian School of Raleigh (Baptist, 1–12)
*Gethsemane Seventh-day Adventist Church School (K-8)
*Grace Christian School (North Carolina), Grace Christian School (K-12)
*Jewish Academy of Wake County (K-3)
*Montessori School of Raleigh (K-9)
*Neuse Baptist Christian School (K-12)
*North Raleigh Christian Academy (Protestant Christian, K-12)
*Raleigh Christian Academy (Baptist, K-12)
*Raleigh School, The Raleigh School (K-5)
*Ravenscroft School (K-12)
*The Trilogy School (2–12)
*Trinity Academy of Raleigh (Protestant Christian, K-12)
*Upper Room Christian Academy (closed) (PreK-12)
*Wake Christian Academy (K-12)
*Word of God Christian Academy (Protestant Christian, K-12)
*Thales Academy (PreK-12)
;Episcopal schools
*St. David's School (Raleigh, North Carolina), St. David's School (Episcopal, K-12)
*St. Timothy's School
*Saint Mary's School (Raleigh, North Carolina), St. Mary's School (Episcopal, 9–12)
;Catholic secondary schools
*Cardinal Gibbons High School (Raleigh, North Carolina), Cardinal Gibbons High School (Catholic, 9–12)
*Saint Thomas More Academy, St. Thomas More Academy (Catholic, 9–12)
;Catholic primary schools
*The Franciscan School (Catholic, K-8)
*Sacred Heart Cathedral (Raleigh, North Carolina), Cathedral School (Catholic, PreK-8)
*Our Lady of Lourdes Catholic School (K-8)
*St. Raphael the Archangel Catholic Church, St. Raphael the Archangel Catholic School (PreK-8)
Media
Print publications
There are several newspapers and periodicals serving Raleigh:
* ''
The News & Observer'', a large daily newspaper owned by The McClatchy Company
* ''The Triangle Downtowner Magazine'', a locally owned free monthly print magazine centered around high-density areas of the Triangle with features on dining, entertainment, wine, community, history and more
*''Technician (newspaper), Technician'', student publication of North Carolina State University
* ''The Carolinian'', North Carolina's oldest and largest African-American newspaper published twice weekly
* ''Midtown Magazine'' an upscale Raleigh lifestyle magazine
* ''Raleigh Magazine'' a glossy print magazine covering exclusively Raleigh
* ''Walter Magazine'' a magazine covering Covering the art, culture and people of Raleigh
* ''The Slammer'', a paid bi-weekly newspaper featuring Raleigh crime news
* ''Carolina Journal'', a free monthly newspaper
* ''Independent Weekly'', a free weekly tabloid covering Raleigh, Durham, and the surrounding area
Television
Broadcast
Raleigh is part of the Raleigh-Durham-
Fayetteville Designated Market Area, the 24th largest broadcast television market in the United States. The following stations are licensed to Raleigh and/or have significant operations and viewers in the city:
* UNC-TV, WUNC-TV (4, PBS): City of license, licensed to Chapel Hill, owned by the University of North Carolina
*
WRAL-TV (5, NBC): licensed to Raleigh, owned by Capitol Broadcasting Company
* WTVD (11, American Broadcasting Company, ABC): licensed to Durham; news bureau located in Raleigh. ABC Owned-and-operated station, O&O owned by ABC Owned Television Stations
* WNCN, WNCN-TV (17, CBS): studios located in Raleigh, licensed to the city of Goldsboro, North Carolina, Goldsboro southeast of Raleigh; owned by Nexstar Media Group
* WLFL, WLFL-TV (22, The CW, CW): licensed to Raleigh, owned by Sinclair Broadcast Group
* WRDC (28, MyNetworkTV, MyNet) licensed to Durham, owned by Sinclair Broadcast Group
* WRAY-TV (30, TCT) licensed to Wilson. TCT O&O owned by Tri-State Christian Television
* WUVC-DT (40, Univision) licensed to Fayetteville. Univision Owned-and-operated station, O&O owned by TelevisaUnivision
* WRPX-TV (47, Ion Television, Ion) licensed to Rocky Mount, with studios in Raleigh. Ion O&O owned by Ion Media
* WRAZ (TV), WRAZ-TV (50, Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox): licensed to Raleigh, owned by Capitol Broadcasting Company
* WAUG-LD (8, Independent station) licensed to Raleigh, owned and operated by Saint Augustine's College
* WRTD-CD (54, Telemundo): licensed to Raleigh. Telemundo Owned-and-operated station, O&O owned by NBCUniversal
Broadcast radio
Public and listener-supported
* WKNC-FM – 88.1 FM (College rock), operated by students of
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The universit ...
* WRKV – 88.9 FM (Contemporary Christian), operated by Educational Media Foundation
* WCPE, WCPE-FM – 89.7 FM (Classical)
* WUNC (FM), WUNC-FM – 91.5 FM (National Public Radio, North Carolina Public Radio) operated by the
University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
* WRLY-LP – 93.5 FM (Adult hits), operated by Triangle Access Broadcasting, Inc.
* WKRP-LP – 101.9 FM (Variety (radio), Variety), operated by Oak City Media, Inc.
Commercial
* WDCG-FM (G105, Contemporary hit radio)
* WDCG-HD2 (ALT 95.3, Alternative rock, analogue broadcast on 95.3 FM W237BZ)
* WQDR-FM (94.7QDR, Country music, Country)
* WBBB-FM 96.1 (Radio 96.1, Adult hits)
* WRAL (FM), WRAL-FM (Mix 101.5, Adult contemporary music, Adult contemporary)
* WKIX-FM (KIX 102.9, Classic hits)
* WPTF-AM (NewsRadio 680, Talk radio, News/Talk)
* WQOK-FM (K97.5, Hip hop)
* WFXC-FM/WFXK-FM (Foxy 107/104, Urban adult contemporary)
* WRDU-FM (100.7, Classic rock)
* WNCB-FM (93.9 B939 FM, Country music, Country)
* WTKK-FM (106.1 FM, Talk radio, News/Talk)
* WNNL-FM (103.9 The Light, Urban contemporary gospel)
* WWPL-FM (96.9 Pulse FM, Contemporary hits)
* WKIX (AM), WKIX (Just Right Radio 850 and 104.7 FM, Popular standards)
* WQDR(AM), WQDR-AM (570, classic rock)
* WCLY-AM (That Station, Adult album alternative)
* WAUG (AM), 750 WAUG
Infrastructure
Transportation
Air

=Raleigh-Durham International Airport
=
Raleigh-Durham International Airport, the region's primary airport and the second-largest in North Carolina, located northwest of downtown Raleigh via Interstate-40 between Raleigh and
Durham, serves the city and greater Research Triangle metropolitan region, as well as much of eastern North Carolina. The airport offers service to more than 50 domestic and international destinations and serves approximately 10 million passengers a year. International destinations include London, Montreal, Toronto, Cancún, Mexico, Cancún, Paris, and seasonal service to Keflavík. American Airlines operates the daily service to London Heathrow. Delta Air Lines announced in November 2008 that service from RDU to Paris, France would begin in June 2009, but the route would not take flight until 2016. The airport also offers facilities for cargo airline, cargo and general aviation. The airport authority tripled the size of its Terminal 2 (formerly Terminal C) in January 2011.
Private general aviation airports in Raleigh include Triple W Airport .
Freeways and primary designated routes
=Interstate Highways
=
* traverses the southern part of the city, connecting Raleigh to Durham and Chapel Hill toward the west, and coastal Wilmington, North Carolina to the southeast.
* also known locally as the Raleigh Beltline, it forms part of the inner beltway around central Raleigh, forming the eastern, northern, and western portions, with I-40 forming the southern portion.
* when complete, will be a full outer beltway around Raleigh. The northern and western quadrants are complete and open to traffic, while the remaining two quadrants are currently under construction.
* designated September 5, 2017, follows the former route of Interstate 495. It begins at the I-40/I-440 interchange southeast of Raleigh and runs east, meeting I-540 and currently terminating at Rolesville Road. It is entirely concurrent with US 64. When the route is completed it will link Raleigh to the Norfolk, Virginia area.
=United States Highways
=
* enters the city from the southwest as the US 1/US 64 expressway from Cary, joining I-440 at the I-40 interchange, and leaves I-440 along with US 401 on
Capital Boulevard
Capital Boulevard is a major thoroughfare in Wake County, North Carolina. At various points along the route, it carries NC 50, U.S. Route 70 in North Carolina, U.S. Highway 70 (US 70), US 401, and U.S. Route 1 in North Carolina, US ...
, before leaving the city to the north.
* is the main east–west route through Raleigh; all segments share routes with another highway. It enters the city from the southwest as the US 1/US 64 expressway from Cary, follows I-40 at the western I-440 interchange, briefly joins I-440 in Southeast Raleigh, and then joins I-87 and US 264 along the Knightdale Bypass east of the city. A former alignment, designated as Business US-64, follows New Bern Avenue from the I-440 Beltline to the eastern boundary of the city, where it continues into Knightdale.
* enters the city from the south cosigned with US 401 and NC 50 along Wilmington Street, following South Saunders Street into Downtown Raleigh, through which it follows the paired one-way streets of McDowell and Dawson. North of Downtown it follows Capital Boulevard, Wade Avenue, and Glenwood Avenue before leaving the city to the Northwest heading towards Durham.
* cosigned with US 64 through East Raleigh.
* enters the city from the south cosigned with US 70 and NC 50 along Wilmington Street, following South Saunders Street into Downtown Raleigh, through which it follows the paired one-way streets of McDowell and Dawson. North of Downtown it follows Capital Boulevard and Louisburg Road, before leaving the city to the northeast towards Rolesville.
=North Carolina Highways
=
* follows Chapel Hill Road and
Hillsborough Street
Hillsborough Street is a business and cultural thoroughfare through Raleigh, North Carolina, Raleigh, North Carolina, United States. The street serves as a center for social life among North Carolina State University and Meredith College students.
...
in West Raleigh. The route ends at its interchange with
I-440.
* enters the city from the south cosigned with US 70 and US 401 along Wilmington Street, following South Saunders Street into Downtown Raleigh, through which it follows the paired one-way streets of McDowell and Dawson. North of Downtown it follows Capital Boulevard, Wade Avenue, Glenwood Avenue, and Creedmoor Road, before heading north towards Creedmoor.
* known as Durham Road in North Raleigh, traverses the extreme northeastern part of the city, where it borders Wake Forest.
Intercity rail



Raleigh (Amtrak station), Raleigh's train station is one of Amtrak's busiest stops in the Southern United States, Southern U.S.
The station is served by five passenger trains daily: the ''Silver Star (Amtrak train), Silver Star'', thrice-daily ''Piedmont (train), Piedmont'' service, and the ''Carolinian (train), Carolinian.''
Daily service is offered between Raleigh and:
*
Charlotte, with intermediate stops including Cary, Durham, Burlington, North Carolina, Burlington and Greensboro, North Carolina, Greensboro, North Carolina.
*New York City, with intermediate stops including
Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
; Washington, D.C.; Baltimore; and
Philadelphia.
*Miami, with intermediate stops including Columbia, South Carolina, and Savannah, Georgia; as well as Jacksonville, Florida, Jacksonville, Orlando, Florida, Orlando and Tampa, Florida.
Public transit
Public transportation in and around Raleigh is provided by GoRaleigh (formerly Capital Area Transit), which operates 33 fixed bus routes, including the R-Line (Capital Area Transit), R-Line and the Wake-Forest Loop. Although there are 33 routes, some routes are designed to cover multiple other routes at times when they are not served. Depending on the time of the day, and the day of the week, the number of routes operating is between 5 and 29.
Raleigh is also served by GoTriangle (formerly Triangle Transit Authority). GoTriangle offers scheduled, fixed-route regional and commuter bus service between Raleigh and the region's other principal cities of Durham, Cary and Chapel Hill, as well as to and from the Raleigh-Durham International Airport,
Research Triangle Park
Research Triangle Park (RTP) is the largest research park in the United States, occupying in North Carolina and hosting more than 300 companies and 65,000 workers.
The facility is named for its location relative to the three surrounding cities ...
and several of the region's larger suburban communities. Triangle Transit also coordinates an extensive vanpool and carpool, rideshare program that serves the region's larger employers and commute destinations.
North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State) is a public land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina. Founded in 1887 and part of the University of North Carolina system, it is the largest university in the Carolinas. The universit ...
also maintains its own transit system, the Wolfline, that provides zero-fare bus service to the general public along multiple routes serving the university's campuses in southwest Raleigh.
Government agencies throughout the Raleigh-Durham metropolitan area have struggled with determining the best means of providing fixed-rail transit service for the region.
From 1995 the cornerstone of Triangle Transit's long-term plan was a 28-mile rail corridor from northeast Raleigh, through downtown Raleigh,
Cary, and
Research Triangle Park
Research Triangle Park (RTP) is the largest research park in the United States, occupying in North Carolina and hosting more than 300 companies and 65,000 workers.
The facility is named for its location relative to the three surrounding cities ...
, to
Durham using Diesel multiple unit, DMU technology. There were proposals to extend this corridor 7 miles to
Chapel Hill Chapel Hill or Chapelhill may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Chapel Hill (Antarctica) Australia
*Chapel Hill, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane
*Chapel Hill, South Australia, in the Mount Barker council area
Canada
* Chapel Hill, Ottawa, a neighbo ...
with light rail technology. However, in 2006 Triangle Transit deferred implementation indefinitely when the Federal Transit Administration declined to fund the program due to low ridership projections.
The region's two metropolitan planning organizations appointed a group of local citizens in 2007 to reexamine options for future transit development in light of Triangle Transit's problems. The Special Transit Advisory Commission (STAC) retained many of the provisions of Triangle Transit's original plan, but recommended adding new bus services and raising additional revenues by adding a new local half-cent sales tax to fund the project.
Greyhound Lines provides an inter-city bus service to Durham, Charlotte, Richmond, Washington, D.C., Atlanta, and other cities.
Bicycle and pedestrian
*The Maine-to-Florida U.S. Bicycle Route#1 routes through suburban Raleigh, along with North Carolina Bicycle Route 2, N.C. Bicycle Route #2, the "Mountains To Sea" route. As of September 2010, maps and signage for both US Bike Route No. 1 and NC Bike Route No. 2 are out-of-date for the Raleigh area. North Carolina Bicycle Route 5, N.C. Bicycle Route #5 is routed nearby, connecting Apex to
Wilmington and closely paralleling the NCBC Randonneurs 600-kilometer brevet route.
*Most public buses are equipped with bicycle racks, and some roads have dedicated bicycle-only lanes. Bicyclists and pedestrians also may use Raleigh's extensive Capital Area Greenway, greenway system, with paths and trails located throughout the city.
*In May 2011, Raleigh was designated a Bicycle Friendly Community by the League of American Bicyclists at the Bronze level.
*A 2011 study by Walk Score ranked Raleigh 36th most walkable of fifty largest U.S. cities.
*In 2002, the "Walk [Your City]" initiative was started in the city which provides a tool kit for neighborhood organizations to post signs giving a distance by bike or foot, with directions in scannable QR code. The movement has spread to more than 400 communities in 55 countries.
Public safety
The Raleigh Fire Department provides fire protection throughout the city. The North Carolina Correctional Institution for Women, the state's primary correctional facility housing female inmates, is based in Raleigh.
Notable people
Sister cities
Raleigh has several sister cities:
* Compiègne, Oise, Hauts-de-France, France
* Kingston upon Hull, England, United Kingdom
* Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany
* Nairobi, Kenya
* Gibraltar, Gibraltar, United Kingdom
See also
*List of capitals in the United States
*List of municipalities in North Carolina
*National Register of Historic Places listings in Wake County, North Carolina
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*Benjamin, Karen (March 2012)
"Suburbanizing Jim Crow: The Impact of School Policy on Residential Segregation in Raleigh" ''Journal of Urban History'', ''38''(2), pp. 225–46. .
*
*
External links
*
*
*Raleigh Directory
18751883189619031927Guide to the Ray Winstead Collection of Aerial Photographs of Raleigh, North Carolina Circa 1970
{{Authority control
Raleigh, North Carolina,
1792 establishments in North Carolina
Cities in Durham County, North Carolina
Cities in Wake County, North Carolina
County seats in North Carolina
Planned cities in the United States
Populated places established in 1792
Populated places on the Neuse River
Research Triangle
Walter Raleigh
Capitals of North Carolina


 In 1808,
In 1808,  In 1912, Bloomsbury Park opened, featuring a popular carousel ride. Relocated to Pullen Park, the
In 1912, Bloomsbury Park opened, featuring a popular carousel ride. Relocated to Pullen Park, the 
 In the first decade of the 21st century, Raleigh was featured prominently in a number of "Top 10 Lists", including those by '' Forbes'', MSNBC and ''Money'' magazine, due to its quality of life and favorable business climate.
In 2001, the Raleigh Memorial Auditorium complex was expanded with the addition of the Progress Energy Center for the Performing Arts, Meymandi Concert Hall, Fletcher Opera Theater, Kennedy Theatre, Betty Ray McCain Gallery and Lichtin Plaza.
Fayetteville Street reopened to vehicular traffic in 2006. A variety of downtown building projects began around this time including the 34-story RBC Bank Tower, multiple condominium projects and several new restaurants. Additional skyscrapers are in the proposal/planning phase.
In 2006, the city's NHL franchise, the Carolina Hurricanes, won the
In the first decade of the 21st century, Raleigh was featured prominently in a number of "Top 10 Lists", including those by '' Forbes'', MSNBC and ''Money'' magazine, due to its quality of life and favorable business climate.
In 2001, the Raleigh Memorial Auditorium complex was expanded with the addition of the Progress Energy Center for the Performing Arts, Meymandi Concert Hall, Fletcher Opera Theater, Kennedy Theatre, Betty Ray McCain Gallery and Lichtin Plaza.
Fayetteville Street reopened to vehicular traffic in 2006. A variety of downtown building projects began around this time including the 34-story RBC Bank Tower, multiple condominium projects and several new restaurants. Additional skyscrapers are in the proposal/planning phase.
In 2006, the city's NHL franchise, the Carolina Hurricanes, won the  Raleigh is divided into several major geographic areas, each of which use a Raleigh address and a ZIP code that begins with the digits 276.
Raleigh is divided into several major geographic areas, each of which use a Raleigh address and a ZIP code that begins with the digits 276.  One common division of Raleigh is to differentiate the central part of the city, which lies inside of the circumferential highway known as the Raleigh Beltline ( I-440 and I-40) from areas outside of the Beltline. The area inside of the beltline includes the entirety of the central business district known as Downtown Raleigh, as well as several more residential areas surrounding it.
The downtown area is home to historic buildings such as the Sir Walter Raleigh Hotel built in the early 20th century, the restored City Market, the Fayetteville Street downtown business district (which includes the
One common division of Raleigh is to differentiate the central part of the city, which lies inside of the circumferential highway known as the Raleigh Beltline ( I-440 and I-40) from areas outside of the Beltline. The area inside of the beltline includes the entirety of the central business district known as Downtown Raleigh, as well as several more residential areas surrounding it.
The downtown area is home to historic buildings such as the Sir Walter Raleigh Hotel built in the early 20th century, the restored City Market, the Fayetteville Street downtown business district (which includes the  Midtown Raleigh is a relatively new term used to describe the residential and commercial area lying on the northside of the I-440 Beltline and is part of North Raleigh. It is roughly framed by Glenwood/Six Forks Road to the West, Wake Forest Road to the East, and Millbrook Road to the North. It includes shopping centers such as North Hills and Crabtree Valley Mall. It also includes North Hills Park and part of the Raleigh Greenway System. The term was coined by the Greater Raleigh Chamber of Commerce, developer John Kane and planning director Mitchell Silver. ''The'' ''News & Observer'' newspaper started using the term for marketing purposes only. The Midtown Raleigh Alliance was founded on July 25, 2011, as a way for community leaders to promote the area. The center of the area, especially around the North Hills development at the junction of Six Forks Road and the Beltline, is experiencing rapid urbanization as several high-rise buildings have been built since 2010.
Midtown Raleigh is a relatively new term used to describe the residential and commercial area lying on the northside of the I-440 Beltline and is part of North Raleigh. It is roughly framed by Glenwood/Six Forks Road to the West, Wake Forest Road to the East, and Millbrook Road to the North. It includes shopping centers such as North Hills and Crabtree Valley Mall. It also includes North Hills Park and part of the Raleigh Greenway System. The term was coined by the Greater Raleigh Chamber of Commerce, developer John Kane and planning director Mitchell Silver. ''The'' ''News & Observer'' newspaper started using the term for marketing purposes only. The Midtown Raleigh Alliance was founded on July 25, 2011, as a way for community leaders to promote the area. The center of the area, especially around the North Hills development at the junction of Six Forks Road and the Beltline, is experiencing rapid urbanization as several high-rise buildings have been built since 2010.
 West Raleigh lies along
West Raleigh lies along  Like much of the Southeastern United States, Raleigh has a
Like much of the Southeastern United States, Raleigh has a  Raleigh receives an average of of snow in winter. Freezing rain and sleet also occur most winters, and occasionally the area experiences a major damaging ice storm. On January 24–25, 2000, Raleigh received its greatest snowfall from a single stormthe Winter Storm of January 2000. Storms of this magnitude are generally the result of cold air damming that affects the city due to its proximity to the Appalachian Mountains. Winter storms have caused traffic problems in the past as well.
The region also experiences occasional periods of drought, during which the city sometimes has restricted water use by residents. During the late summer and early fall, Raleigh can experience hurricanes. In 1996, Hurricane Fran caused severe damage in the Raleigh area, mostly from falling trees. Hurricanes Dennis and Floyd in September 1999 were primary contributors to that month's extreme rainfall of over 21 inches. The most recent hurricane to have a considerable effect on the area was Hurricane Florence in 2018. Tornadoes also have on occasion affected the city of Raleigh, most notably the November 28, 1988, tornado which occurred in the early morning hours and rated F4 on the Fujita scale and affected northwestern portions of the city. There also was the April 16, 2011, EF3 tornado, which affected portions of downtown and northeast Raleigh and the suburb of Holly Springs.
Raleigh receives an average of of snow in winter. Freezing rain and sleet also occur most winters, and occasionally the area experiences a major damaging ice storm. On January 24–25, 2000, Raleigh received its greatest snowfall from a single stormthe Winter Storm of January 2000. Storms of this magnitude are generally the result of cold air damming that affects the city due to its proximity to the Appalachian Mountains. Winter storms have caused traffic problems in the past as well.
The region also experiences occasional periods of drought, during which the city sometimes has restricted water use by residents. During the late summer and early fall, Raleigh can experience hurricanes. In 1996, Hurricane Fran caused severe damage in the Raleigh area, mostly from falling trees. Hurricanes Dennis and Floyd in September 1999 were primary contributors to that month's extreme rainfall of over 21 inches. The most recent hurricane to have a considerable effect on the area was Hurricane Florence in 2018. Tornadoes also have on occasion affected the city of Raleigh, most notably the November 28, 1988, tornado which occurred in the early morning hours and rated F4 on the Fujita scale and affected northwestern portions of the city. There also was the April 16, 2011, EF3 tornado, which affected portions of downtown and northeast Raleigh and the suburb of Holly Springs.


 *African American Cultural Complex
*Contemporary Art Museum of Raleigh
*Gregg Museum of Art & Design at
*African American Cultural Complex
*Contemporary Art Museum of Raleigh
*Gregg Museum of Art & Design at 
 In addition to the Hurricanes, the North Carolina FC of the United Soccer League and North Carolina Courage women's professional soccer team play in suburban Cary to the west; the Carolina Mudcats, a Single-A (baseball), Single-A minor-league baseball team, play in the city's eastern suburbs; the newly formed Single-A (baseball), Single-A minor-league baseball Fayetteville Woodpeckers, who formerly played in Buies Creek, North Carolina, Buies Creek, began play in the nearby out-of-county southern suburb of Fayetteville when their Fayetteville Ballpark, new ballpark opened in 2019; the Carolina Flyers of the American Ultimate Disc League play primarily at Cardinal Gibbons High School near the PNC Arena; and the Durham Bulls, the Triple-A (baseball), AAA minor-league baseball team made internationally famous by the movie ''Bull Durham'', play in the neighboring city of Durham.
Several other professional sports leagues have had former franchises (now defunct) in Raleigh, including the Raleigh IceCaps of the ECHL (1991–1998); Carolina Cobras of the Arena Football League (2000–2004); the Raleigh–Durham Skyhawks of the World League of American Football (1991); the Raleigh Bullfrogs of the Global Basketball Association (1991–1992); the Raleigh Cougars of the United States Basketball League (1997–1999); and most recently, the Carolina Courage of the Women's United Soccer Association (2000–2001 in Chapel Hill, 2001–2003 in suburban Cary), which won that league's championship Founders Cup in 2002.
The Raleigh area has hosted the Professional Golfers' Association of America, Professional Golfers' Association (PGA) Nationwide Tour Rex Hospital Open since 1994, with the current location of play at Raleigh's Wakefield Plantation. Nearby Prestonwood Country Club hosts the PGA SAS Championship every fall.
In addition to the Hurricanes, the North Carolina FC of the United Soccer League and North Carolina Courage women's professional soccer team play in suburban Cary to the west; the Carolina Mudcats, a Single-A (baseball), Single-A minor-league baseball team, play in the city's eastern suburbs; the newly formed Single-A (baseball), Single-A minor-league baseball Fayetteville Woodpeckers, who formerly played in Buies Creek, North Carolina, Buies Creek, began play in the nearby out-of-county southern suburb of Fayetteville when their Fayetteville Ballpark, new ballpark opened in 2019; the Carolina Flyers of the American Ultimate Disc League play primarily at Cardinal Gibbons High School near the PNC Arena; and the Durham Bulls, the Triple-A (baseball), AAA minor-league baseball team made internationally famous by the movie ''Bull Durham'', play in the neighboring city of Durham.
Several other professional sports leagues have had former franchises (now defunct) in Raleigh, including the Raleigh IceCaps of the ECHL (1991–1998); Carolina Cobras of the Arena Football League (2000–2004); the Raleigh–Durham Skyhawks of the World League of American Football (1991); the Raleigh Bullfrogs of the Global Basketball Association (1991–1992); the Raleigh Cougars of the United States Basketball League (1997–1999); and most recently, the Carolina Courage of the Women's United Soccer Association (2000–2001 in Chapel Hill, 2001–2003 in suburban Cary), which won that league's championship Founders Cup in 2002.
The Raleigh area has hosted the Professional Golfers' Association of America, Professional Golfers' Association (PGA) Nationwide Tour Rex Hospital Open since 1994, with the current location of play at Raleigh's Wakefield Plantation. Nearby Prestonwood Country Club hosts the PGA SAS Championship every fall.
 Raleigh is the home of Raleigh Kubb, both a competitive and non-competitive kubb club. Raleigh Kubb hosts kubb tournaments benefitting various charities in the Raleigh area.
The Raleigh Parks and Recreation Department offers a wide variety of leisure opportunities at more than 200 sites throughout the city, which include: of park land, of greenway (landscape), greenway, 22 community centre, community centers, a Bicycle Motocross, BMX championship-caliber race track, 112 tennis courts among 25 locations, 5 public lakes, and 8 public aquatic facilities. The park system includes the historic Pullen Park, the oldest public park in North Carolina. The J. C. Raulston Arboretum, an 8-acre (32,000 m2) arboretum and botanical garden in west Raleigh administered by
Raleigh is the home of Raleigh Kubb, both a competitive and non-competitive kubb club. Raleigh Kubb hosts kubb tournaments benefitting various charities in the Raleigh area.
The Raleigh Parks and Recreation Department offers a wide variety of leisure opportunities at more than 200 sites throughout the city, which include: of park land, of greenway (landscape), greenway, 22 community centre, community centers, a Bicycle Motocross, BMX championship-caliber race track, 112 tennis courts among 25 locations, 5 public lakes, and 8 public aquatic facilities. The park system includes the historic Pullen Park, the oldest public park in North Carolina. The J. C. Raulston Arboretum, an 8-acre (32,000 m2) arboretum and botanical garden in west Raleigh administered by 


 As of 2011, ''Time (magazine), Time'' ranked Raleigh as the third most educated city in the US based on the percentage of residents who held college degrees. This statistic can most likely be credited to the presence of universities in and around Raleigh, as well as the presence of
As of 2011, ''Time (magazine), Time'' ranked Raleigh as the third most educated city in the US based on the percentage of residents who held college degrees. This statistic can most likely be credited to the presence of universities in and around Raleigh, as well as the presence of 


 Raleigh (Amtrak station), Raleigh's train station is one of Amtrak's busiest stops in the Southern United States, Southern U.S. The station is served by five passenger trains daily: the ''Silver Star (Amtrak train), Silver Star'', thrice-daily ''Piedmont (train), Piedmont'' service, and the ''Carolinian (train), Carolinian.'' Daily service is offered between Raleigh and:
* Charlotte, with intermediate stops including Cary, Durham, Burlington, North Carolina, Burlington and Greensboro, North Carolina, Greensboro, North Carolina.
*New York City, with intermediate stops including
Raleigh (Amtrak station), Raleigh's train station is one of Amtrak's busiest stops in the Southern United States, Southern U.S. The station is served by five passenger trains daily: the ''Silver Star (Amtrak train), Silver Star'', thrice-daily ''Piedmont (train), Piedmont'' service, and the ''Carolinian (train), Carolinian.'' Daily service is offered between Raleigh and:
* Charlotte, with intermediate stops including Cary, Durham, Burlington, North Carolina, Burlington and Greensboro, North Carolina, Greensboro, North Carolina.
*New York City, with intermediate stops including