RZ Piscium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
RZ Piscium (or RZ Psc) is a UX Orionis type
 In 2017, RZ Piscium was studied using the XMM-Newton satellite, the Shane 3-meter telescope at
In 2017, RZ Piscium was studied using the XMM-Newton satellite, the Shane 3-meter telescope at
variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as ...
away, in the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
Pisces
Pisces may refer to:
* Pisces, an obsolete (because of land vertebrates) taxonomic superclass including all fish
* Pisces (astrology), an astrological sign
* Pisces (constellation), a constellation
**Pisces Overdensity, an overdensity of stars in ...
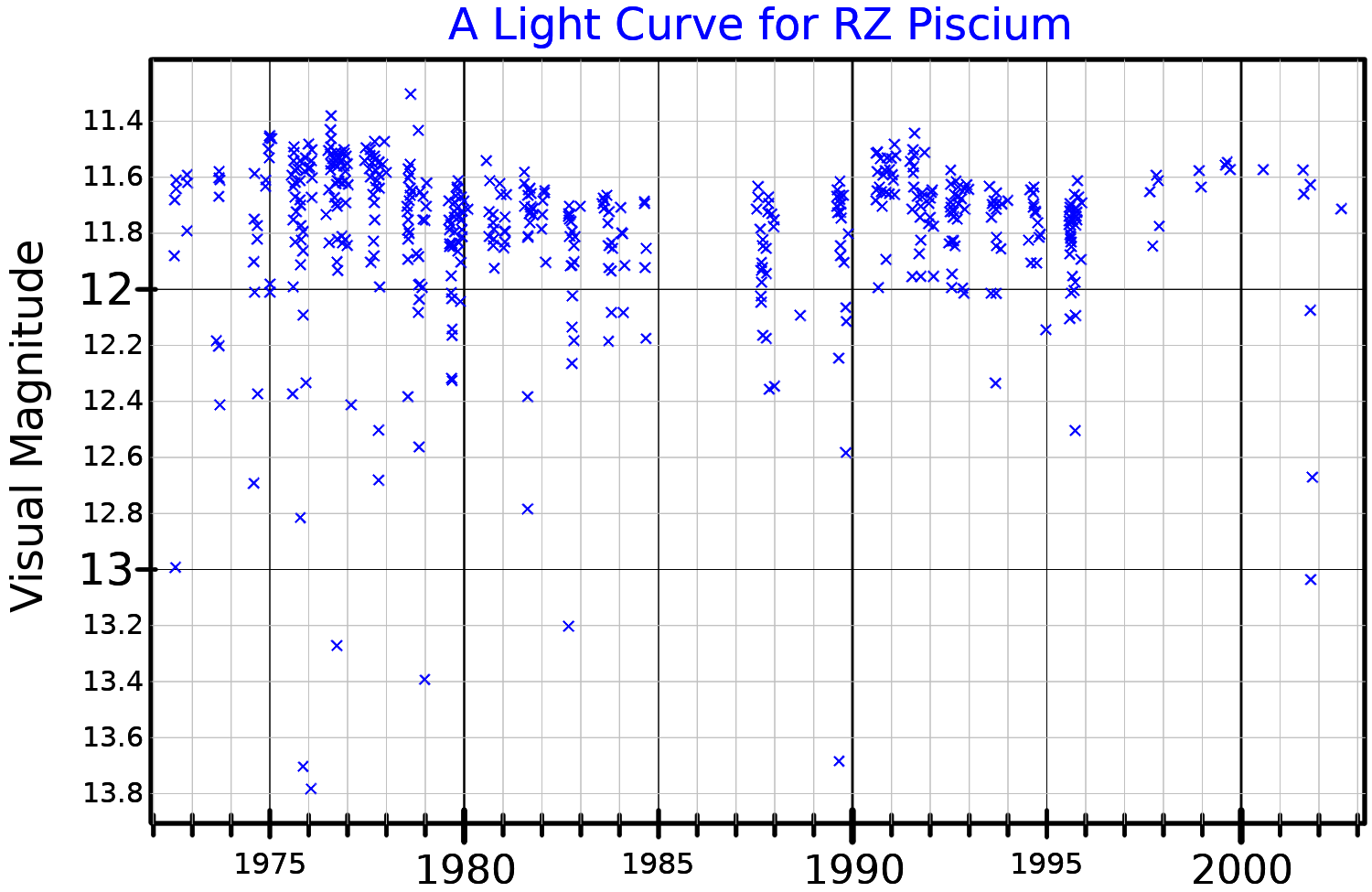
. Over the years, the star has been found to brighten and dim erratically, dimming by as much as a tenth of its usual luminosity. RZ Piscium has been found to emit large amounts of infrared radiation
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
, suggesting the presence of a substantial mass of gas and dust orbiting the star, possibly from a "disrupted planet
In astronomy, a disrupted planet is a planet or exoplanet or, perhaps on a somewhat smaller scale, a planetary-mass object, planetesimal, moon, exomoon or asteroid that has been disrupted or destroyed by a nearby or passing astronomical body or ...
".
Disrupted planet
Because of theinfrared excess
An infrared excess is a measurement of an astronomical source, typically a star, that in their spectral energy distribution has a greater measured infrared flux than expected by assuming the star is a blackbody radiator. Infrared excesses are o ...
and rapid light variations, astronomers conclude that:
According to astronomer Ben Zuckerman:
Observations
 In 2017, RZ Piscium was studied using the XMM-Newton satellite, the Shane 3-meter telescope at
In 2017, RZ Piscium was studied using the XMM-Newton satellite, the Shane 3-meter telescope at Lick Observatory
The Lick Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the University of California. It is on the summit of Mount Hamilton, in the Diablo Range just east of San Jose, California, United States. The observatory is managed by th ...
in California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
and the 10-meter Keck I telescope at W. M. Keck Observatory
The W. M. Keck Observatory is an astronomical observatory with two telescopes at an elevation of 4,145 meters (13,600 ft) near the summit of Mauna Kea in the U.S. state of Hawaii. Both telescopes have aperture primary mirrors, and when comp ...
in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
. The temperature of the star was found to be about the same as the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
(). Further, the star was found to produce about a thousand times more x-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s than the Sun, suggesting that the star is relatively young. On the other hand, RZ Piscium was found to contain a relatively small amount of surface lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid el ...
, which suggests the star is between 30 − 50 million years old; this is somewhat "old" for a star with so much circumstellar dust. Most young stars that are as dusty as RZ Piscium may be producing planets, but given its relatively advanced age, RZ Piscium may be destroying and consuming its planets instead.
In 2020, the red dwarf companion with the mass of 0.12 Solar mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass ...
was detected on the projected separation of the 23 AU from the primary star. The incandescence of the companion star thus make up about one third of excess infrared emission previously attributed to the dust.
See also
*List of stars that have unusual dimming periods
This list of stars that have unusual dimming periods is a table of stars that have been observed to darken and brighten and don't appear to be eclipsing binaries or intrinsic variables. It's based on studies searching for analogs of Tabby's S ...
References
External links
* , star with unusual light fluctuations (21 December 2017). * , a presentation byTabetha S. Boyajian
Tabetha "Tabby" Suzanne Boyajian is an American astronomer of Armenian descent and astrophysics, astrophysicist on faculty (academic staff), faculty at Louisiana State University. She was a post-doctoral fellow 2012–16 at Yale University, workin ...
* , a presentation by Issac Arthur
{{Sky, 01, 09, 42.0523, +, 27, 57, 01.9121, 550
Pisces (constellation)
Planetary rings
2017 in science
Piscium, RZ
J01094205+2757020
K-type subgiants
Herbig Ae/Be stars