RR Pictoris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 RR Pictoris, also known as Nova Pictoris 1925, is a
RR Pictoris, also known as Nova Pictoris 1925, is a
"New Star May Hold Clue to Solar Puzzle," ''Milwaukee Sentinel'', February 1, 1944, Final Edition, page 1
{{DEFAULTSORT:RR Pictoris Novae Pictor (constellation) 1925 in science Pictoris, RR 031481

 RR Pictoris, also known as Nova Pictoris 1925, is a
RR Pictoris, also known as Nova Pictoris 1925, is a cataclysmic variable
In astronomy, cataclysmic variable stars (CVs) are stars which irregularly increase in brightness by a large factor, then drop back down to a quiescent state. They were initially called novae (), since ones with an outburst brightness visible to ...
star system that flared up as a nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
that lit up in the constellation Pictor
Pictor is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, located between the star Canopus and the Large Magellanic Cloud. Its name is Latin for Painting, painter, and is an abbreviation of the older name Equuleus Pictoris (the "painter's ...
in 1925. It was discovered by South African amateur astronomer R. Watson who lived in Beaufort West
Beaufort West (Afrikaans: ''Beaufort-Wes''; Xhosa: ''eBhofolo'') is a town in the Western Cape province in South Africa. It is the largest town in the arid Great Karoo region, and is known as the "Capital of the Karoo". It forms part of the Beauf ...
. At 05:50 AM on 25 May 1925, Mr. Watson was walking to work and noticed a star that he did not recognize in line with the stars α Crucis
Acrux is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Crux. It has the Bayer designation α Crucis, which is Latinised to Alpha Crucis and abbreviated Alpha Cru or α Cru. With a combined visual magnitude of +0.76, it is the 13 ...
and β Carinae. He consulted his copy of Norton's Star Atlas
{{refimprove, date=August 2015
''Norton's Star Atlas'' is a set of 16 celestial charts, first published in 1910 and currently in its 20th edition under the editorship of Ian Ridpath. The ''Star Atlas'' covers the entire northern and southern sky, ...
, and realized that the unfamiliar star was a nova. Fortuitously, Mr. Watson was employed as a telegraph operator, and he promptly sent a telegram describing his discovery to the Royal Observatory at Cape Town. This quick reporting of the event allowed southern observatories to obtain spectra of the nova before it had reached maximum brightness.
At the time of its discovery, RR Pictoris had an apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
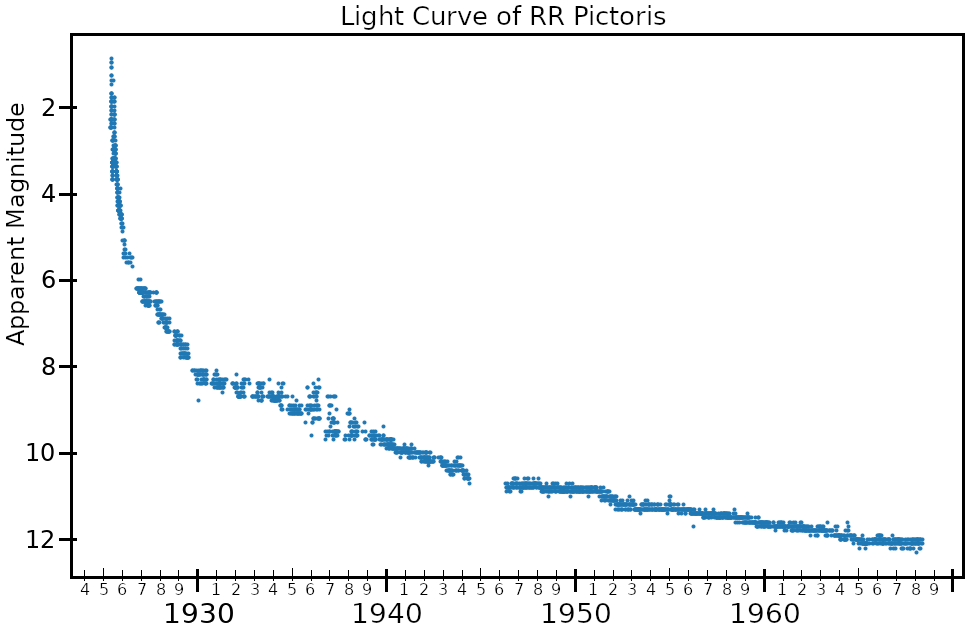
of 2.3. It continued to brighten to magnitude 1.2, which it reached on 9 June 1925. It dimmed to magnitude 4 by 4 July, but brightened again to 1.9 on 9 August. Six months after its peak brightness, RR Pictoris faded to be invisible to the unaided eye, and was magnitude 12.5 by 1975. RR Pictoris is classified as a slow nova and its light curve exhibits positive superhump
In astronomy, a superhump is a periodic brightness variation in a cataclysmic variable star system, with a period within a few percent of the orbital period of the system.
History
Superhumps were first seen in SU Ursae Majoris (SU UMa) stars, a ...
s, meaning superhumps with a period a few percent (8.6% in this case) longer than the star system's orbital period.
Measurements by the Gaia spacecraft
''Gaia'' is a space observatory of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 2013 and expected to operate until 2025. The spacecraft is designed for astrometry: measuring the positions, distances and motions of stars with unprecedented preci ...
show that the RR Pictoris system is around 510 parsecs (1670 light-years) from the Earth.
Novae are close binary systems composed of a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes fro ...
and secondary star that is so close it is filling up its Roche lobe
In astronomy, the Roche lobe is the region around a star in a binary system within which orbiting material is gravitationally bound to that star. It is an approximately teardrop-shaped region bounded by a critical gravitational equipotential, wit ...
with stellar material, which is then transferred onto the first star's accretion disc
An accretion disk is a structure (often a circumstellar disk) formed by diffuse material in orbital motion around a massive central body. The central body is typically a star. Friction, uneven irradiance, magnetohydrodynamic effects, and other f ...
. Once this material reaches a critical mass, it ignites and the system brightens tremendously. The two stars of RR Pictoris orbit each other every 3.48 hours. Calculations of the speed suggest the secondary star is not dense enough for its size to still be on the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Her ...
, so it itself must have begun expanding and cooling already as its core has run out of hydrogen fuel.
Small variations in the observed orbital period suggest that RR Pictoris system may include a low mass (0.25 M⊙) third star orbiting the close binary pair with a period of about 70 years.
A small (< 30 arc second) filamentary nebula surrounds the nova, and comparisons of images taken several years apart have allowed its rate of expansion to be measured.
References
External links
"New Star May Hold Clue to Solar Puzzle," ''Milwaukee Sentinel'', February 1, 1944, Final Edition, page 1
{{DEFAULTSORT:RR Pictoris Novae Pictor (constellation) 1925 in science Pictoris, RR 031481