Quality function deployment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Quality function deployment (QFD) a method developed in Japan beginning in 1966 to help transform the
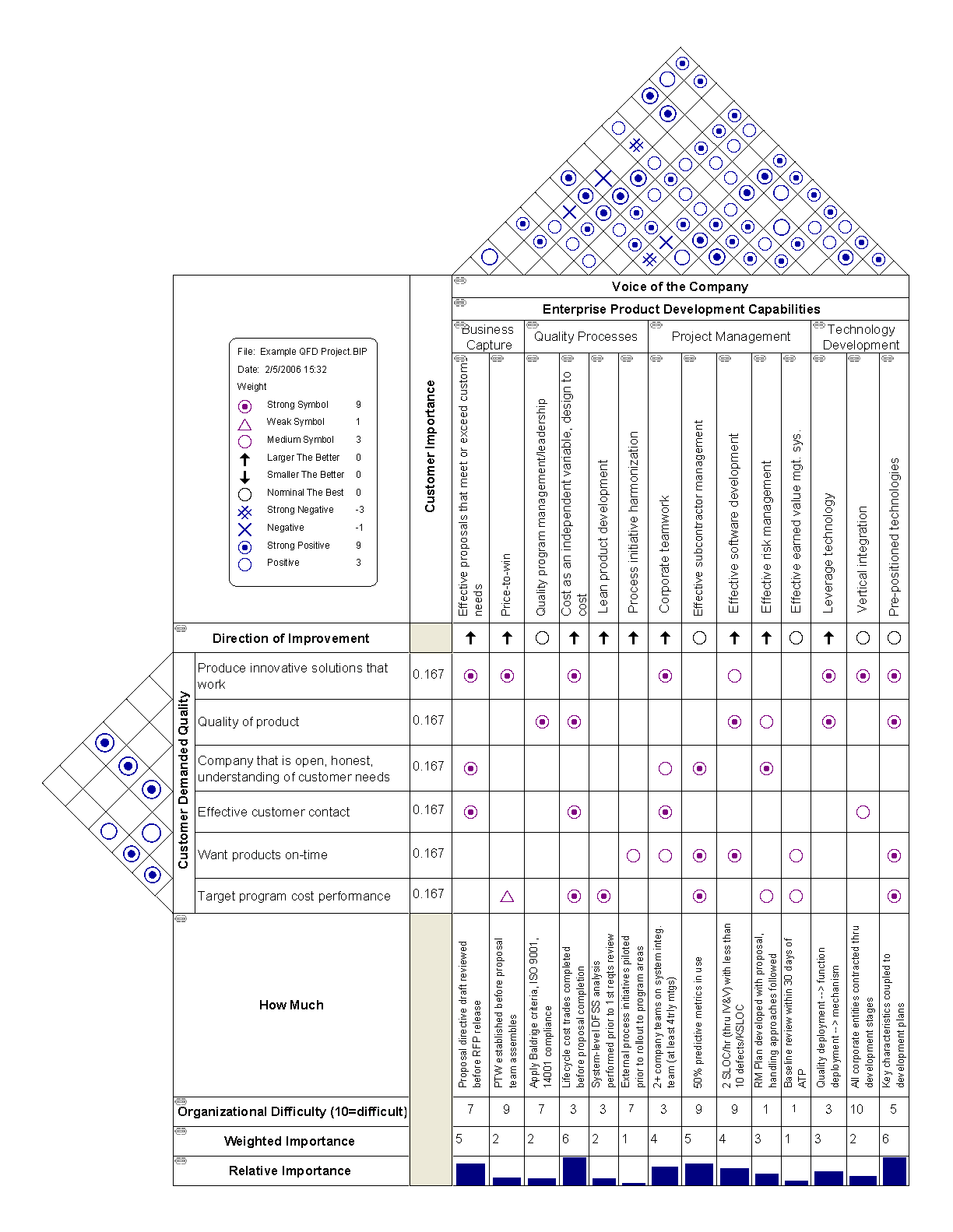 The house of quality, a part of QFD, is the basic design tool of quality function deployment. It identifies and classifies customer desires (What's), identifies the importance of those desires, identifies engineering characteristics which may be relevant to those desires (How's), correlates the two, allows for verification of those correlations, and then assigns objectives and priorities for the system requirements. This process can be applied at any system composition level (e.g. system, subsystem, or component) in the design of a product, and can allow for assessment of different abstractions of a system. It is intensely progressed through a number of hierarchical levels of What’s and How’s and analyse each stage of product growth (service enhancement), and production (service delivery).
The house of quality appeared in 1972 in the design of an oil tanker by
The house of quality, a part of QFD, is the basic design tool of quality function deployment. It identifies and classifies customer desires (What's), identifies the importance of those desires, identifies engineering characteristics which may be relevant to those desires (How's), correlates the two, allows for verification of those correlations, and then assigns objectives and priorities for the system requirements. This process can be applied at any system composition level (e.g. system, subsystem, or component) in the design of a product, and can allow for assessment of different abstractions of a system. It is intensely progressed through a number of hierarchical levels of What’s and How’s and analyse each stage of product growth (service enhancement), and production (service delivery).
The house of quality appeared in 1972 in the design of an oil tanker by
voice of the customer
In marketing, the voice of the customer (VOC) summarizes customers' expectations, preferences and aversions.
A widely used form of VOC market research produces a detailed set of customer wants and needs, organized into a hierarchical structure, ...
into engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
characteristics for a product.Larson et al. (2009). p. 117. Yoji Akao was a Japanese planning specialist recognized as the developer of Hoshin Kanri (a strategic planning methodology). With the late Shigeru Mizuno, he developed Quality Function Deployment (a group decision making technique). Akao and Mizuno also co ...
, the original developer, described QFD as a "method to transform qualitative user demands into quantitative parameters, to deploy the functions forming quality, and to deploy methods for achieving the design quality into subsystems and component parts, and ultimately to specific elements of the manufacturing process." The author combined his work in quality assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is the term used in both manufacturing and service industries to describe the systematic efforts taken to ensure that the product(s) delivered to customer(s) meet with the contractual and other agreed upon performance, design ...
and quality control
Quality control (QC) is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. ISO 9000 defines quality control as "a part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements".
This approach place ...
points with function deployment used in value engineering.
House of quality
 The house of quality, a part of QFD, is the basic design tool of quality function deployment. It identifies and classifies customer desires (What's), identifies the importance of those desires, identifies engineering characteristics which may be relevant to those desires (How's), correlates the two, allows for verification of those correlations, and then assigns objectives and priorities for the system requirements. This process can be applied at any system composition level (e.g. system, subsystem, or component) in the design of a product, and can allow for assessment of different abstractions of a system. It is intensely progressed through a number of hierarchical levels of What’s and How’s and analyse each stage of product growth (service enhancement), and production (service delivery).
The house of quality appeared in 1972 in the design of an oil tanker by
The house of quality, a part of QFD, is the basic design tool of quality function deployment. It identifies and classifies customer desires (What's), identifies the importance of those desires, identifies engineering characteristics which may be relevant to those desires (How's), correlates the two, allows for verification of those correlations, and then assigns objectives and priorities for the system requirements. This process can be applied at any system composition level (e.g. system, subsystem, or component) in the design of a product, and can allow for assessment of different abstractions of a system. It is intensely progressed through a number of hierarchical levels of What’s and How’s and analyse each stage of product growth (service enhancement), and production (service delivery).
The house of quality appeared in 1972 in the design of an oil tanker by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
is a Japanese multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. MHI is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group and its automobile division is the predecessor of Mitsubishi ...
.
The output of the house of quality is generally a matrix with customer desires on one dimension and correlated nonfunctional requirement
In systems engineering and requirements engineering, a non-functional requirement (NFR) is a requirement that specifies criteria that can be used to judge the operation of a system, rather than specific behaviours. They are contrasted with func ...
s on the other dimension.Larson et al. (2009). p. 119. The cells of matrix table are filled with the weights assigned to the stakeholder characteristics where those characteristics are affected by the system parameters across the top of the matrix. At the bottom of the matrix, the column is summed, which allows for the system characteristics to be weighted according to the stakeholder characteristics. System parameters not correlated to stakeholder characteristics may be unnecessary to the system design and are identified by empty matrix columns, while stakeholder characteristics (identified by empty rows) not correlated to system parameters indicate "characteristics not addressed by the design parameters". System parameters and stakeholder characteristics with weak correlations potentially indicate missing information, while matrices with "too many correlations" indicate that the stakeholder needs may need to be refined.
Areas of application
QFD is applied in a wide variety of applications viz product design, manufacturing, production, engineering, research and development (R&D), information technology (IT), support, testing, regulatory, and other phases in hardware, software, service, and system organizations. organization functions necessary to assure customer satisfaction, including business planning, packaging and logistics, procurement, marketing, sales & service. QFD is also deployed in quality improvement, quality management, military needs and consumer products. Customer services Applications for Education improvement and services in hotels etc.Fuzziness
The concepts offuzzy logic
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic in which the truth value of variables may be any real number between 0 and 1. It is employed to handle the concept of partial truth, where the truth value may range between completely true and completel ...
have been applied to QFD ("Fuzzy QFD" or "FQFD"). A review of 59 papers in 2013 by Abdolshah and Moradi found a number of conclusions: most FQFD "studies were focused on quantitative methods" to construct a house of quality matrix based on customer requirements, where the most-employed techniques were based on multiple-criteria decision analysis
Multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) or multiple-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) is a sub-discipline of operations research that explicitly evaluates multiple conflicting criteria in decision making (both in daily life and in settings ...
methods. They noted that there are factors other than the house of quality relevant to product development, and called metaheuristic
In computer science and mathematical optimization, a metaheuristic is a higher-level procedure or heuristic designed to find, generate, or select a heuristic (partial search algorithm) that may provide a sufficiently good solution to an optimizati ...
methods "a promising approach for solving complicated problems of FQFD."
Derived techniques and tools
The process of quality function deployment (QFD) is described in ISO 16355-1:2015.Pugh concept selection
The decision-matrix method, also Pugh method or Pugh concept selection, invented by Stuart Pugh,S. Pugh (1981) Concept selection: a method that works. In: Hubka, V. (ed.), Review of design methodology. Proceedings international conference on engin ...
can be used in coordination with QFD to select a promising product or service configuration from among listed alternatives.
Modular function deployment Modular Function Deployment (MFD) is a method for creating modular product architectures, based on research performed at KTH Royal Institute of Technology in the 1990s. As a result of said research, the companModular Managementwas registered in 199 ...
uses QFD to establish customer requirements and to identify important design requirements with a special emphasis on modularity. There are three main differences to QFD as applied in modular function deployment compared to house of quality: The benchmarking data is mostly gone; the checkboxes and crosses have been replaced with circles, and the triangular "roof" is missing.
Notes
References
*Further reading
* * * {{ISO standards Business terms Product management Quality Systems thinking