Qin Empire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in
 According to the
According to the

 Lord
Lord
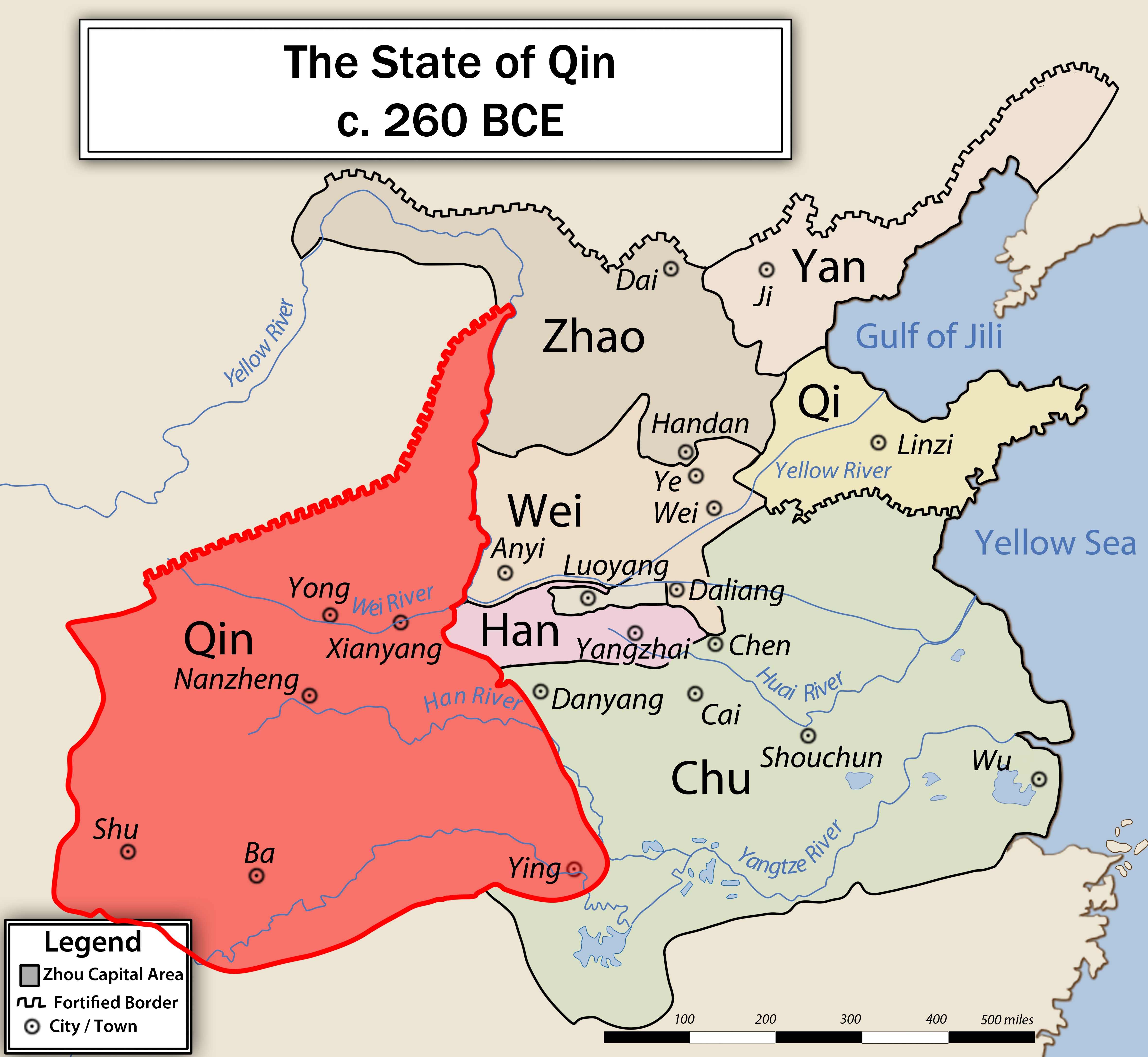
 During the Warring States period preceding the Qin dynasty, the major states vying for dominance were Yan,
During the Warring States period preceding the Qin dynasty, the major states vying for dominance were Yan,
 In 214 BC, Qin Shi Huang secured his boundaries to the north with a fraction (100,000 men) of his large army, and sent the majority (500,000 men) of his army south to conquer the territory of the southern tribes. Prior to the events leading to Qin dominance over China, they had gained possession of much of
In 214 BC, Qin Shi Huang secured his boundaries to the north with a fraction (100,000 men) of his large army, and sent the majority (500,000 men) of his army south to conquer the territory of the southern tribes. Prior to the events leading to Qin dominance over China, they had gained possession of much of
 Three assassination attempts were made on Qin Shi Huang, leading him to become paranoid and obsessed with immortality. He died in 210 BC, while on a trip to the far eastern reaches of his empire in an attempt to procure an elixir of immortality from
Three assassination attempts were made on Qin Shi Huang, leading him to become paranoid and obsessed with immortality. He died in 210 BC, while on a trip to the far eastern reaches of his empire in an attempt to procure an elixir of immortality from
 Warring States-era architecture had several definitive aspects. City walls, used for defense, were made longer, and indeed several secondary walls were also sometimes built to separate the different districts. Versatility in federal structures was emphasized, to create a sense of authority and absolute power. Architectural elements such as high towers, pillar gates, terraces, and high buildings amply conveyed this.
Warring States-era architecture had several definitive aspects. City walls, used for defense, were made longer, and indeed several secondary walls were also sometimes built to separate the different districts. Versatility in federal structures was emphasized, to create a sense of authority and absolute power. Architectural elements such as high towers, pillar gates, terraces, and high buildings amply conveyed this.
 The written language of the Qin was
The written language of the Qin was
 The Qin government was highly bureaucratic, and was administered by a hierarchy of officials, all serving the First Emperor. The Qin put into practice the teachings of
The Qin government was highly bureaucratic, and was administered by a hierarchy of officials, all serving the First Emperor. The Qin put into practice the teachings of
Wade–Giles
Wade–Giles () is a romanization system for Mandarin Chinese. It developed from a system produced by Thomas Francis Wade, during the mid-19th century, and was given completed form with Herbert A. Giles's '' Chinese–English Dictionary'' o ...
romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A ...
of Imperial China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapt ...
. Named for its heartland in Qin state (modern Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
and Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
), the Qin dynasty arose as a fief of the Western Zhou
The Western Zhou ( zh, c=, p=Xīzhōu; c. 1045 BC – 771 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the first half of the Zhou dynasty. It began when King Wu of Zhou overthrew the Shang dynasty at the Battle of Muye and ended when the Quanrong n ...
and endured for over five centuries until 221 BCE when it founded its brief empire, which lasted only until 206 BCE. It often causes confusion that the ruling family of the Qin kingdom (what is conventionally called a "dynasty") ruled for over five centuries, while the "Qin Dynasty," the conventional name for the first Chinese empire, comprises the last fourteen years of Qin's existence. The divide between these two periods occurred in 221 BCE when King Zheng of Qin declared himself the First Emperor of Qin, though he had already been king of Qin since 246 BCE.
Qin was a minor power for the early centuries of its existence. The strength of the Qin state was greatly increased by the Legalist
Legalist, Inc. is an investment firm that specializes in alternative assets in the private credit industry. Today the firm manages approximately $750 million across three separate strategies: litigation finance, bankruptcy ( debtor-in-possession ...
reforms of Shang Yang
Shang Yang (; c. 390 – 338 BC), also known as Wei Yang () and originally surnamed Gongsun, was a Chinese jurist, philosopher, and politician.Antonio S. Cua (ed.), 2003, p. 362, ''Encyclopedia of Chinese Philosophy'"The fifth important legali ...
in the fourth century BC, during the Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded ...
. In the mid and late third century BC, the Qin state carried out a series of swift conquests, destroying the powerless Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by th ...
and eventually conquering the other six of the Seven Warring States. Its 15 years was the shortest major dynasty in Chinese history, consisting of only two emperors. Despite its short reign, however, the lessons and strategies of the Qin shaped the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
and became the starting point of the Chinese imperial system that lasted from 221 BC, with interruption, development, and adaptation, until 1912 AD.
The Qin sought to create a state unified by structured centralized political power and a large military supported by a stable economy.Tanner 2010, pp. 85–89 The central government moved to undercut aristocrats and landowners to gain direct administrative control over the peasantry, who comprised the overwhelming majority of the population and labour force. This allowed ambitious projects involving three hundred thousand peasants and convicts: projects such as connecting walls along the northern border, eventually developing into the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic grou ...
, and a massive new national road system, as well as the city-sized Mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor
The Mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor () is the mausoleum of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of the Qin dynasty. It is located in Lintong District, Xi'an, Shaanxi province of China. It was constructed over 38 years, from 246 to 208 BCE, and ...
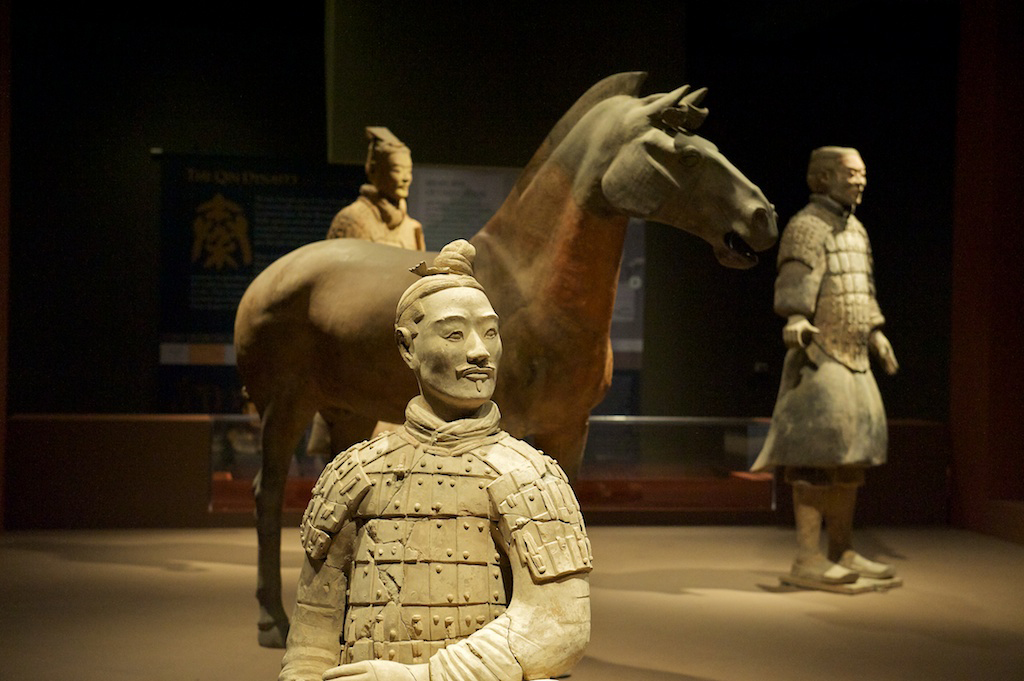
guarded by the life-sized Terracotta Army
The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BCE with the purpose of protecting the emperor ...
.
The Qin introduced a range of reforms such as standardized currency, weights, measures and a uniform system of writing, which aimed to unify the state and promote commerce. Additionally, its military used the most recent weaponry, transportation and tactics, though the government was heavy-handedly bureaucratic. Han Confucians portrayed the legalistic Qin dynasty as a monolithic tyranny, notably citing a purge known as the burning of books and burying of scholars
The burning of books and burying of scholars (), also known as burning the books and executing the ru scholars, refers to the purported burning of texts in 213 BCE and live burial of 460 Confucian scholars in 212 BCE by the Chinese emperor ...
although some modern scholars dispute the veracity of these accounts. Qin created a system of administrating people and land that greatly increased the power of the government to transform environment, and it has been argued that the subsequent impact of this system on East Asia's environments makes Qin's rise an important event in China's environmental history.
When the first emperor died in 210 BC, two of his advisors placed an heir on the throne in an attempt to influence and control the administration of the dynasty. These advisors squabbled among themselves, resulting in both of their deaths and that of the second Qin Emperor. Popular revolt broke out and the weakened empire soon fell to a Chu general, Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (, –202 BC), born Xiang Ji (), was the Hegemon-King (Chinese: 霸王, ''Bà Wáng'') of Western Chu during the Chu–Han Contention period (206–202 BC) of China. A noble of the Chu state, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dyna ...
, who was proclaimed Hegemon-King of Western Chu and Liu Bang, who founded the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
.
History
Origins and early development
 According to the
According to the Records of the Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese his ...
, in the 9th century BC, Feizi
Feizi (; died 858 BC), also known by the title Qin Ying, was the founder of the ancient Chinese state of Qin, predecessor of the Qin Dynasty that would conquer all other Chinese states and unite China in 221 BC.
Mythical origin of Qin
Accordi ...
, a supposed descendant of the ancient political advisor Gao Yao, was granted rule over the settlement of Qin (秦邑) in present-day Qingshui County
Qingshui County () is a county in Gansu province of the People's Republic of China, bordering Shaanxi province to the east. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Tianshui. In 2014 its population was 324,300 people, of whi ...
of Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see § Name) is a landlocked province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), N ...
. During the rule of King Xiao of Zhou, the eighth king of the Zhou dynasty, this area became known as the state of Qin. In 897 BC, under the Gonghe Regency
The Gonghe Regency () was an interregnum period in Chinese history from 841 BC to 828 BC, after King Li of Zhou was exiled by his nobles during the Compatriots Rebellion, when the Chinese people rioted against their old corrupt king. It lasted u ...
, the area became a dependency allotted for the purpose of raising and breeding horses.Lewis 2007, p. 17 One of Feizi's descendants, Duke Zhuang, became favoured by King Ping of Zhou, the 13th king in that line. As a reward, Zhuang's son, Duke Xiang, was sent eastward as the leader of a war expedition, during which he formally established the Qin.
The state of Qin first began a military expedition into central China in 672 BC, though it did not engage in any serious incursions due to the threat from neighbouring tribesmen. By the dawn of the fourth century BC, however, the neighbouring tribes had all been either subdued or conquered, and the stage was set for the rise of Qin expansionism.Lewis 2007, pp. 17–18
Growth of power

 Lord
Lord Shang Yang
Shang Yang (; c. 390 – 338 BC), also known as Wei Yang () and originally surnamed Gongsun, was a Chinese jurist, philosopher, and politician.Antonio S. Cua (ed.), 2003, p. 362, ''Encyclopedia of Chinese Philosophy'"The fifth important legali ...
, a Qin statesman of the Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded ...
, advocated a philosophy of Legalism, introducing a number of militarily advantageous reforms from 361 BC until his death in 338 BC.
Yang also helped construct the Qin capital, commencing in the mid-fourth century BC Xianyang
Xianyang () is a prefecture-level city in central Shaanxi province, situated on the Wei River a few kilometers upstream (west) from the provincial capital of Xi'an. Once the capital of the Qin dynasty, it is now integrated into the Xi'an m ...
. The resulting city greatly resembled the capitals of other Warring States.
Notably, Qin Legalism encouraged practical and ruthless warfare.Morton 1995, p. 45 During the Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
,Origins of Statecraft in China the prevalent philosophy had dictated war as a gentleman's activity; military commanders were instructed to respect what they perceived to be Heaven's laws in battle.Morton 1995, p. 26 For example, when Duke Xing of the rival state of Song was at war with the state of Chu during the Warring States period, he declined an opportunity to attack the enemy force, commanded by Zhu, while they were crossing a river. After allowing them to cross and marshal their forces, he was decisively defeated in the ensuing battle. When his advisors later admonished him for such excessive courtesy to the enemy, he retorted, "The sage does not crush the feeble, nor give the order for attack until the enemy have formed their ranks."Morton 1995, pg. 26
The Qin disregarded this military tradition, taking advantage of their enemy's weaknesses. A nobleman in the state of Wei accused the Qin state of being "avaricious, perverse, eager for profit, and without sincerity. It knows nothing about etiquette, proper relationships, and virtuous conduct, and if there be an opportunity for material gain, it will disregard its relatives as if they were animals." It was this Legalist thought combined with strong leadership from long-lived rulers, openness to employ talented men from other states, and little internal opposition that gave the Qin such a strong political base.Kinney and Clark 2005, p. 10
Another advantage of the Qin was that they had a large, efficient army and capable generals. They utilised the newest developments in weaponry and transportation as well, which many of their enemies lacked. These latter developments allowed greater mobility over several different terrain types which were most common in many regions of China. Thus, in both ideology and practice, the Qin were militarily superior.
Finally, the Qin Empire had a geographical advantage due to its fertility and strategic position, protected by mountains that made the state a natural stronghold. This was the heart of the Guanzhong
Guanzhong (, formerly romanised as Kwanchung) region, also known as the Guanzhong Basin, Wei River Basin, or uncommonly as the Shaanzhong region, is a historical region of China corresponding to the crescentic graben basin within present-day ce ...
region, as opposed to the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ; ) is the longest river in Asia, the third-longest in the world, and the longest in the world to flow entirely within one country. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains (Tibetan Plateau) and flows ...
drainage basin, known as Guandong. The warlike nature of the Qin in Guanzhong inspired a Han dynasty adage: "Guanzhong produces generals, while Guandong produces ministers." Its expanded agricultural output helped sustain Qin's large army with food and natural resources; the Wei River canal built in 246 BC was particularly significant in this respect.Lewis 2007, pp. 18–19
Conquest of the Warring States
 During the Warring States period preceding the Qin dynasty, the major states vying for dominance were Yan,
During the Warring States period preceding the Qin dynasty, the major states vying for dominance were Yan, Zhao Zhao may refer to:
* Zhao (surname) (赵), a Chinese surname
** commonly spelled Chao in Taiwan or up until the early 20th century in other regions
** Chiu, from the Cantonese pronunciation
** Cho (Korean surname), represent the Hanja 趙 (Chine ...
, Qi, Chu, Han, Wei
Wei or WEI may refer to:
States
* Wey (state) (衛, 1040–209 BC), Wei in pinyin, but spelled Wey to distinguish from the bigger Wei of the Warring States
* Wei (state) (魏, 403–225 BC), one of the seven major states of the Warring States per ...
and Qin. The rulers of these states styled themselves as kings, rather than using the titles of lower nobility they had previously held. However, none elevated himself to believe that he had the "Mandate of Heaven", as the Zhou kings had claimed, nor that he had the right to offer sacrifices—they left this to the Zhou rulers.Morton 1995, p. 25
Before their conquest in the fourth and third centuries BC, the Qin suffered several setbacks. Shang Yang was executed in 338 BC by King Huiwen due to a personal grudge harboured from his youth. There was also internal strife over the Qin succession in 307 BC, which decentralised Qin authority somewhat. Qin was defeated by an alliance of the other states in 295 BC, and shortly after suffered another defeat by the state of Zhao, because the majority of their army was then defending against the Qi. The aggressive statesman Fan Sui ( 范雎), however, soon came to power as prime minister even as the problem of the succession was resolved, and he began an expansionist policy that had originated in Jin and Qi, which prompted the Qin to attempt to conquer the other states.Lewis 2007, pp. 38–39
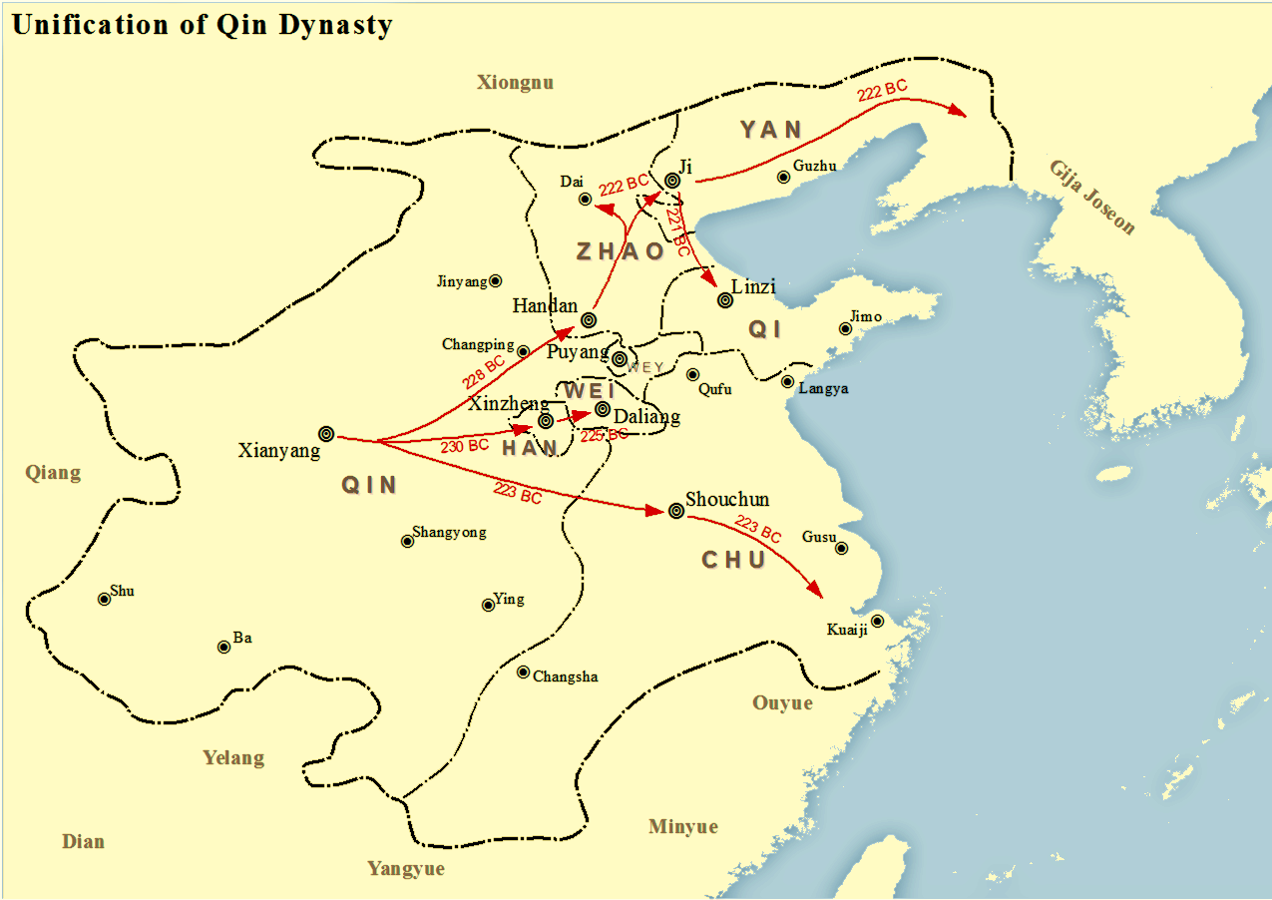
The Qin were swift in their assault on the other states. They first attacked the Han, directly east, and took their capital city of Xinzheng in 230 BC. They then struck northward; the state of Zhao surrendered in 228 BC, and the northernmost state of Yan followed, falling in 226 BC. Next, Qin armies launched assaults to the east, and later the south as well; they took the Wei city of Daliang (now called Kaifeng) in 225 BC and forced the Chu to surrender by 223 BC. Lastly, they deposed the Zhou dynasty's remnants in Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
and conquered the Qi, taking the city of Linzi in 221 BC.Lewis 2007, p. 10
When the conquests were complete in 221 BC, King Zhengwho had first assumed the throne of the Qin state at age 9became the effective ruler of China. The subjugation of the six states was done by King Zheng who had used efficient persuasion and exemplary strategy. He solidified his position as sole ruler with the abdication of his prime minister, Lü Buwei
Lü Buwei (291–235 BCE) was a Chinese merchant and politician of the Qin state during the Warring States period. Originally an influential merchant from the Wei () state, Lü Buwei met and befriended King Zhuangxiang of Qin, who was then a ...
. The states made by the emperor were assigned to officials dedicated to the task rather than place the burden on people from the royal family. He then combined the titles of the earlier Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors
The Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors were two groups of mythological rulers in ancient north China. The Three Sovereigns supposedly lived long before The Five Emperors, who have been assigned dates in a period from 3162 BC to 2070 BC. Today t ...
into his new name: Shi Huangdi () or "First Emperor".World and Its Peoples: Eastern and Southern Asia, p. 36 The newly declared emperor ordered all weapons not in the possession of the Qin to be confiscated and melted down. The resulting metal was sufficient to build twelve large ornamental statues at the Qin's newly declared capital, Xianyang
Xianyang () is a prefecture-level city in central Shaanxi province, situated on the Wei River a few kilometers upstream (west) from the provincial capital of Xi'an. Once the capital of the Qin dynasty, it is now integrated into the Xi'an m ...
.Morton 1995, p. 47
Southward expansion
 In 214 BC, Qin Shi Huang secured his boundaries to the north with a fraction (100,000 men) of his large army, and sent the majority (500,000 men) of his army south to conquer the territory of the southern tribes. Prior to the events leading to Qin dominance over China, they had gained possession of much of
In 214 BC, Qin Shi Huang secured his boundaries to the north with a fraction (100,000 men) of his large army, and sent the majority (500,000 men) of his army south to conquer the territory of the southern tribes. Prior to the events leading to Qin dominance over China, they had gained possession of much of Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of t ...
to the southwest. The Qin army was unfamiliar with the jungle terrain, and it was defeated by the southern tribes' guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run ta ...
tactics with over 100,000 men lost. However, in the defeat Qin was successful in building a canal to the south, which they used heavily for supplying and reinforcing their troops during their second attack to the south. Building on these gains, the Qin armies conquered the coastal lands surrounding Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Guangdong Provinces of China, province in South China, sou ...
, and took the provinces of Fuzhou
Fuzhou (; , Fuzhounese: Hokchew, ''Hók-ciŭ''), alternately romanized as Foochow, is the capital and one of the largest cities in Fujian province, China. Along with the many counties of Ningde, those of Fuzhou are considered to constitute ...
and Guilin
Guilin (Standard Zhuang: ''Gveilinz''; alternatively romanized as Kweilin) is a prefecture-level city in the northeast of China's Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. It is situated on the west bank of the Li River and borders Hunan to the nort ...
. They struck as far south as Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi i ...
. After these victories in the south, Qin Shi Huang moved over 100,000 prisoners and exiles to colonize the newly conquered area. In terms of extending the boundaries of his empire, the First Emperor was extremely successful in the south.
Campaigns against the Xiongnu
However, while the empire at times was extended to the north, the Qin could rarely hold on to the land for long. The tribes of these locations, collectively called the Hu by the Qin, were free from Chinese rule during the majority of the dynasty.Lewis 2007, p. 129 Prohibited from trading with Qin dynasty peasants, theXiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
tribe living in the Ordos region in northwest China often raided them instead, prompting the Qin to retaliate. After a military campaign led by General Meng Tian, the region was conquered in 215 BC and agriculture was established; the peasants, however, were discontented and later revolted. The succeeding Han dynasty also expanded into the Ordos due to overpopulation, but depleted their resources in the process. Indeed, this was true of the dynasty's borders in multiple directions; modern Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwes ...
, Tibet, Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
, Inner Mongolia, and regions to the southeast were foreign to the Qin, and even areas over which they had military control were culturally distinct.
Fall from power
 Three assassination attempts were made on Qin Shi Huang, leading him to become paranoid and obsessed with immortality. He died in 210 BC, while on a trip to the far eastern reaches of his empire in an attempt to procure an elixir of immortality from
Three assassination attempts were made on Qin Shi Huang, leading him to become paranoid and obsessed with immortality. He died in 210 BC, while on a trip to the far eastern reaches of his empire in an attempt to procure an elixir of immortality from Taoist
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Tao ...
magicians, who claimed the elixir was stuck on an island guarded by a sea monster. The chief eunuch
A eunuch ( ) is a male who has been castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function.
The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millenni ...
, Zhao Gao, and the prime minister, Li Si
Li Si (Mandarin: ; BCSeptember or October 208 BC) was a Chinese philosopher, politician, and calligrapher of the Qin dynasty. He served as Chancellor (or Prime Minister) from 246 to 208 BC under two rulers: Qin Shi Huang, the king of the Qin ...
, hid the news of his death upon their return until they were able to alter his will to place on the throne the dead emperor's most pliable son, Huhai, who took the name of Qin Er Shi. They believed that they would be able to manipulate him to their own ends, and thus effectively control the empire. Qin Er Shi was, indeed, inept and pliable. He executed many ministers and imperial princes, continued massive building projects (one of his most extravagant projects was lacquering the city walls), enlarged the army, increased taxes, and arrested messengers who brought him bad news. As a result, men from all over China revolted, attacking officials, raising armies, and declaring themselves kings of seized territories.Kinney and Hardy 2005, pp. 13–15
During this time, Li Si and Zhao Gao fell out, and Li Si was executed. Zhao Gao decided to force Qin Er Shi to commit suicide due to Qin Er Shi's incompetence. Upon this, Ziying, a nephew of Qin Er Shi, ascended the throne, and immediately executed Zhao Gao. Ziying, seeing that increasing unrest was growing among the peopleThis was largely caused by regional differences which survived despite the Qin's attempt to impose uniformity. and that many local officials had declared themselves kings, attempted to cling to his throne by declaring himself one king among all the others. He was undermined by his ineptitude, however, and popular revolt broke out in 209 BC. When Chu rebels under the lieutenant Liu Bang attacked, a state in such turmoil could not hold for long. Ziying was defeated near the Wei River in 207 BC and surrendered shortly after; he was executed by the Chu leader Xiang Yu
Xiang Yu (, –202 BC), born Xiang Ji (), was the Hegemon-King (Chinese: 霸王, ''Bà Wáng'') of Western Chu during the Chu–Han Contention period (206–202 BC) of China. A noble of the Chu state, Xiang Yu rebelled against the Qin dyna ...
. The Qin capital was destroyed the next year, and this is considered by historians to be the end of the Qin Empire.The first emperor of the Qin had boasted that the dynasty would last 10,000 generations; it lasted only about 15 years. (Morton 1995, p. 49) Liu Bang then betrayed and defeated Xiang Yu, declaring himself Emperor GaozuMeaning "High Progenitor". of the new Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
on 28 February 202 BC.Morton 1995, pp. 49–50 Despite the short duration of the Qin dynasty, it was very influential on the structure of future dynasties.
Culture and society
Domestic life
The aristocracy of the Qin were largely similar in their culture and daily life. Regional variations in culture were considered a symbol of the lower classes. This stemmed from the Zhou and was seized upon by the Qin, as such variations were seen as contrary to the unification that the government strove to achieve.Lewis 2007, p. 11 Commoners and rural villagers, who made up over 90% of the population,Lewis 2007, p. 102 very rarely left the villages or farmsteads where they were born. Forms of employment differed by region, though farming was almost universally common. Professions were hereditary; a father's employment was passed to his eldest son after he died.Lewis 2007, p. 15 The '' Lüshi Chunqiu''A text named for its sponsorLü Buwei
Lü Buwei (291–235 BCE) was a Chinese merchant and politician of the Qin state during the Warring States period. Originally an influential merchant from the Wei () state, Lü Buwei met and befriended King Zhuangxiang of Qin, who was then a ...
; the prime minister of the Qin directly preceding the conquest of the other states. gave examples of how, when commoners are obsessed with material wealth, instead of the idealism of a man who "makes things serve him", they were "reduced to the service of things".Lewis 2007, p. 16
Peasants were rarely figured in literature during the Qin dynasty and afterwards; scholars and others of more elite status preferred the excitement of cities and the lure of politics. One notable exception to this was Shen Nong, the so-called "Divine Father", who taught that households should grow their own food. "If in one's prime he does not plow, someone in the world will grow hungry. If in one's prime she does not weave, someone in the world will be cold." The Qin encouraged this; a ritual was performed once every few years that consisted of important government officials taking turns with the plow on a special field, to create a simulation of government interest and activity within agriculture.
Architecture
 Warring States-era architecture had several definitive aspects. City walls, used for defense, were made longer, and indeed several secondary walls were also sometimes built to separate the different districts. Versatility in federal structures was emphasized, to create a sense of authority and absolute power. Architectural elements such as high towers, pillar gates, terraces, and high buildings amply conveyed this.
Warring States-era architecture had several definitive aspects. City walls, used for defense, were made longer, and indeed several secondary walls were also sometimes built to separate the different districts. Versatility in federal structures was emphasized, to create a sense of authority and absolute power. Architectural elements such as high towers, pillar gates, terraces, and high buildings amply conveyed this.
Philosophy and literature
 The written language of the Qin was
The written language of the Qin was logographic
In a written language, a logogram, logograph, or lexigraph is a written character that represents a word or morpheme. Chinese characters (pronounced '' hanzi'' in Mandarin, '' kanji'' in Japanese, '' hanja'' in Korean) are generally logograms ...
, as that of the Zhou had been. As one of his most influential achievements in life, prime minister Li Si
Li Si (Mandarin: ; BCSeptember or October 208 BC) was a Chinese philosopher, politician, and calligrapher of the Qin dynasty. He served as Chancellor (or Prime Minister) from 246 to 208 BC under two rulers: Qin Shi Huang, the king of the Qin ...
standardized the writing system to be of uniform size and shape across the whole country. This would have a unifying effect on the Chinese culture for thousands of years. He is also credited with creating the "small seal script
The small seal script (), or Qin script (, ''Qínzhuàn''), is an archaic form of Chinese calligraphy. It was standardized and promulgated as a national standard by the government of Qin Shi Huang, the founder of the Chinese Qin dynasty.
Name ...
" () style of calligraphy, which serves as a basis for modern Chinese and is still used in cards, posters, and advertising.
During the Warring States period, the Hundred Schools of Thought
The Hundred Schools of Thought () were philosophies and schools that flourished from the 6th century BC to 221 BC during the Spring and Autumn period and the Warring States period of ancient China.
An era of substantial discrimination in China ...
comprised many different philosophies proposed by Chinese scholars. In 221 BC, however, the First Emperor conquered all of the states and governed with a single philosophy, Legalism. At least one school of thought, Mohism
Mohism or Moism (, ) was an ancient Chinese philosophy of ethics and logic, rational thought, and science developed by the academic scholars who studied under the ancient Chinese philosopher Mozi (c. 470 BC – c. 391 BC), embodied in an ep ...
, was eradicated, though the reason is not known. Despite the Qin's state ideology and Mohism being similar in certain regards, it is possible that Mohists were sought and killed by the state's armies due to paramilitary activities.
Confucius
Confucius ( ; zh, s=, p=Kǒng Fūzǐ, "Master Kǒng"; or commonly zh, s=, p=Kǒngzǐ, labels=no; – ) was a Chinese philosopher and politician of the Spring and Autumn period who is traditionally considered the paragon of Chinese sages. C ...
's school of thought, called Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a Religious Confucianism, religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, ...
, was also influential during the Warring States period, as well as throughout much of the later Zhou dynasty and early imperial periods.The term "Confucian" is rather ill-defined in this context—many self-dubbed Confucians in fact rejected tenets of what was known as "the Way of Confucius", and were disorganized, unlike the later Confucians of the Song
A song is a musical composition intended to be performed by the human voice. This is often done at distinct and fixed pitches (melodies) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs contain various forms, such as those including the repetiti ...
and Yuan dynasties. This school of thought had a so-called Confucian canon of literature, known as the "six classics": the Odes, Documents, Ritual, Music, Spring and Autumn Annals
The ''Spring and Autumn Annals'' () is an ancient Chinese chronicle that has been one of the core Chinese classics since ancient times. The '' Annals'' is the official chronicle of the State of Lu, and covers a 241-year period from 722 to 481 ...
, and Changes, which embodied Chinese literature at the time.Lewis 2007, p. 206
During the Qin dynasty, Confucianism—along with all other non-Legalist philosophies, such as Daoism—were suppressed by the First Emperor; early Han dynasty emperors did the same. Legalism denounced the feudal system and encouraged severe punishments, particularly when the emperor was disobeyed. Individuals' rights were devalued when they conflicted with the government's or the ruler's wishes, and merchants and scholars were considered unproductive, fit for elimination.Borthwick, p. 17
One of the more drastic allegations, however the infamous burning of books and burying of scholars
The burning of books and burying of scholars (), also known as burning the books and executing the ru scholars, refers to the purported burning of texts in 213 BCE and live burial of 460 Confucian scholars in 212 BCE by the Chinese emperor ...
incident, does not appear to be true, as it was not mentioned until many years later. The Han dynasty historian, Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years be ...
wrote that First Emperor, in an attempt to consolidate power, in 213 BC ordered the burning of all books advocating viewpoints that challenged Legalism or the state, and also stipulated that all scholars who refused to submit their books to be burned would be executed by premature burial. Only texts considered productive were to be preserved, mostly those that discussed pragmatic subjects, such as agriculture, divination, and medicine.Borthwick, p. 11 However, Sinologists now argue that the "burying of scholars" is not literally true, as the term probably meant simply "put to death".
Government and military

 The Qin government was highly bureaucratic, and was administered by a hierarchy of officials, all serving the First Emperor. The Qin put into practice the teachings of
The Qin government was highly bureaucratic, and was administered by a hierarchy of officials, all serving the First Emperor. The Qin put into practice the teachings of Han Feizi
The ''Han Feizi'' or ''Hanfeizi'' (" ritings ofMaster Han Fei") is an ancient Chinese text named for its attribution to the political philosopher Han Fei. It comprises a selection of essays in the Legalist tradition on theories of state power, ...
, allowing the First Emperor to control all of his territories, including those recently conquered. All aspects of life were standardized, from measurements and language to more practical details, such as the length of chariot axles.
The states made by the emperor were assigned to officials dedicated to the task rather than placing the burden on people from the royal family. Zheng and his advisors also introduced new laws and practices that ended feudalism in China, replacing it with a centralized, bureaucratic government. The form of government created by the first emperor and his advisors was used by later dynasties to structure their own government. Under this system, both the military and government thrived, as talented individuals could be more easily identified in the transformed society. Later Chinese dynasties emulated the Qin government for its efficiency, despite its being condemned by Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
philosophy. There were incidences of abuse, however, with one example having been recorded in the "Records of Officialdom". A commander named Hu ordered his men to attack peasants in an attempt to increase the number of "bandits" he had killed; his superiors, likely eager to inflate their records as well, allowed this.
Qin Shi Huang also improved the strong military, despite the fact that it had already undergone extensive reforms.Borthwick 2006, p. 10 The military used the most advanced weaponry of the time. It was first used mostly in bronze form, but by the third century BC, kingdoms such as Chu and Qin were using iron and/or steel swords. The demand for this metal resulted in improved bellows
A bellows or pair of bellows is a device constructed to furnish a strong blast of air. The simplest type consists of a flexible bag comprising a pair of rigid boards with handles joined by flexible leather sides enclosing an approximately airtig ...
. The crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an Elasticity (physics), elastic launching device consisting of a Bow and arrow, bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar ...
had been introduced in the fifth century BC and was more powerful and accurate than the composite bows used earlier. It could also be rendered ineffective by removing two pins, which prevented enemies from capturing a working crossbow.
The Qin also used improved methods of transportation and tactics. The state of Zhao had first replaced chariot
A chariot is a type of cart driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, dated to c. 2000&n ...
s with cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in ...
in 307 BC, but the change was swiftly adopted by the other states because cavalry had greater mobility over the terrain of China.Morton 1995, p. 27
The First Emperor developed plans to fortify his northern border, to protect against nomadic invasions. The result was the initial construction of what later became the Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China (, literally "ten thousand ''li'' wall") is a series of fortifications that were built across the historical northern borders of ancient Chinese states and Imperial China as protection against various nomadic grou ...
, which was built by joining and strengthening the walls made by the feudal lords, which would be expanded and rebuilt multiple times by later dynasties, also in response to threats from the north. Another project built during Qin Shi Huang's rule was the Terracotta army
The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BCE with the purpose of protecting the emperor ...
, intended to protect the emperor after his death. The Terracotta Army was inconspicuous due to its underground location, and was not discovered until 1974.
Religion
The dominant religious belief in China during the reign of the Qin, and, in fact, during much of early imperial China, was focused on the '' shen'' (roughly translating to "spirits" or "gods"), ''yin'' ("shadows"), and the realm they were said to live in. The Chinese offered animal sacrifices in an attempt to contact this other world, which they believed to be parallel to the earthly one. The dead were said to have simply moved from one world to the other. The rituals mentioned, as well as others, served two purposes: to ensure that the dead journeyed and stayed in the other realm, and to receive blessings from the spirit realm.Mystics from the state of Qi, however, saw sacrifices differently—as a way to become immortal.Lewis 2007, p. 178Lewis 2007, p. 186 Religious practices were usually held in local shrines and sacred areas, which contained sacrificial altars. During a sacrifice or other ritual, the senses of all participants and witnesses would be dulled and blurred with smoke, incense, and music. The lead sacrificer wouldfast
Fast or FAST may refer to:
* Fast (noun), high speed or velocity
* Fast (noun, verb), to practice fasting, abstaining from food and/or water for a certain period of time
Acronyms and coded Computing and software
* ''Faceted Application of Subje ...
and meditate
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally calm ...
before a sacrifice to further blur his senses and increase the likelihood of perceiving otherworldly phenomena. Other participants were similarly prepared, though not as rigorously.
Such blurring of the senses was also a factor in the practice of spirit intermediaries, or mediumship
Mediumship is the practice of purportedly mediating communication between familiar spirits or spirits of the dead and living human beings. Practitioners are known as "mediums" or "spirit mediums". There are different types of mediumship or spir ...
. Practitioners of the art would fall into trances or dance to perform supernatural tasks. These people would often rise to power as a result of their art—Luan Da
Luan Da (, died 112 BC;Sima Qian 1994, p. 239) was a Chinese occultist, politician, and religious leader during the early Han Dynasty from the state of Yue. He professed to know the secret to immortality and be able to communicate with spiritu ...
, a Han dynasty medium, was granted rule over 2,000 households. Noted Han historian Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years be ...
was scornful of such practices, dismissing them as foolish trickery.Lewis 2007, p. 180
Divination
Divination (from Latin ''divinare'', 'to foresee, to foretell, to predict, to prophesy') is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic, standardized process or ritual. Used in various forms throughout history ...
—to predict and/or influence the future—was yet another form of religious practice. An ancient practice that was common during the Qin dynasty was cracking bones or turtle shells to gain knowledge of the future. The forms of divination which sprang up during early imperial China were diverse, though observing natural phenomena was a common method. Comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s, eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three c ...
s, and droughts were considered omens of things to come.Lewis 2007, p. 181
Etymology of China
The name 'Qin' is believed to be the etymological ancestor of the modern-day European name of the country, China. The word probably made its way into theIndo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, P ...
first as 'Cina' or 'Sina' and then into Greek and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
as 'Sinai' or 'Thinai'. It was then transliterated into English and French as 'China' and 'Chine'. This etymology is dismissed by some scholars, who suggest that 'Sina' in Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion ...
evolved much earlier before the Qin dynasty. ' Jin', a state controlled by the Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by th ...
in seventh century BC, is another possible origin.Keay 2009, p. 98. Others argued for the state of Jing (荆, another name for Chu), as well as other polities in the early period as the source of the name.
Sovereigns
Qin Shi Huang was the first Chinese sovereign to proclaim himself "Emperor", after unifying China in 221 BC. That year is therefore generally taken by historians to be the start of the "Qin dynasty" which lasted for fifteen years until 207 when it was cut short by civil wars.Bodde 1986, p. 20Imperial family tree
See also
* Chinese sovereign *Emperor of China
''Huangdi'' (), translated into English as Emperor, was the superlative title held by monarchs of China who ruled various imperial regimes in Chinese history. In traditional Chinese political theory, the emperor was considered the Son of Heav ...
* Yíng
Yíng () is an ancient Chinese surname. It was the noble house name of the Qin state during the Eastern Zhou dynasty, and the royal name of the subsequent Qin dynasty. Yíng Zheng was the first emperor of the unified Chinese empire.
Ying was ...
* Zhao (surname)
* Hata clan
* Later Qin
* '' The Legend of Qin''
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * *External links
* {{Authority control Dynasties in Chinese history Iron Age Asia Former countries in East Asia States and territories established in the 3rd century BC 221 BC 220s BC establishments States and territories disestablished in the 3rd century BC 1st-millennium BC disestablishments in China Qin Shi Huang Former monarchies of East Asia Former empires