Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) provides a novel contrast mechanism in
Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) provides a novel contrast mechanism in
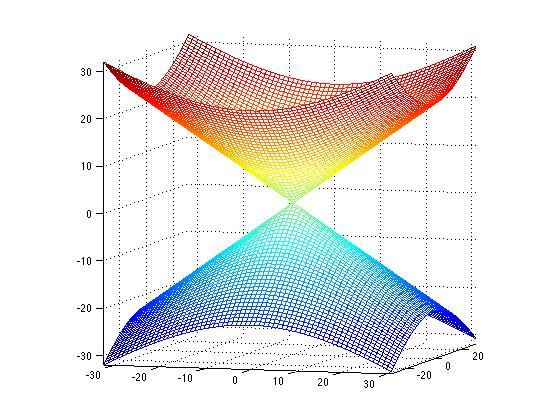 In
In
 In human
In human
 COSMOS solves the inverse problem by
COSMOS solves the inverse problem by
 It has been confirmed in ''
It has been confirmed in ''
 Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) provides a novel contrast mechanism in
Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) provides a novel contrast mechanism in Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) different from traditional Susceptibility Weighted Imaging
Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI), originally called BOLD venographic imaging, is an MRI sequence that is exquisitely sensitive to venous blood, hemorrhage and iron storage. SWI uses a fully flow compensated, long echo, gradient recalled echo ( ...
. The voxel intensity in QSM is linearly proportional to the underlying tissue apparent magnetic susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility (Latin: , "receptive"; denoted ) is a measure of how much a material will become magnetized in an applied magnetic field. It is the ratio of magnetization (magnetic moment per unit volume) to the ap ...
, which is useful for chemical identification and quantification of specific biomarkers
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, p ...
including iron, calcium, gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
, and super paramagnetic
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, d ...
iron oxide (SPIO) nano-particles. QSM utilizes phase images, solves the magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
to susceptibility source inverse problem, and generates a three-dimensional susceptibility distribution. Due to its quantitative nature and sensitivity to certain kinds of material, potential QSM applications include standardized quantitative stratification of cerebral microbleeds and neurodegenerative disease
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic ...
, accurate gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
quantification in contrast enhanced MRI, and direct monitoring of targeted theranostic drug biodistribution in nanomedicine
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology. Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials and BioBrick, biological devices, to Nanoelectronics, nanoelectronic biosensors, and even possible future applicatio ...
.
Background
 In
In MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
, the local field induced by non-ferromagnetic biomaterial susceptibility along the main polarization B0 field is the convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is ...
of the volume susceptibility distribution with the dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways:
*An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system i ...
kernel : . This spatial convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is ...
can be expressed as a point-wise multiplication in Fourier domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a signa ...
: . This Fourier expression provides an efficient way to predict the field perturbation when the susceptibility distribution is known. However, the field to source inverse problem involves division by zero at a pair of cone surfaces at the magic angle
The magic angle is a precisely defined angle, the value of which is approximately 54.7356°. The magic angle is a root of a second-order Legendre polynomial, , and so any interaction which depends on this second-order Legendre polynomial vanishes a ...
with respect to B0 in the Fourier domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a signa ...
. Consequently, susceptibility is underdetermined at the spatial frequencies on the cone surface, which often leads to severe streaking artifacts in the reconstructed QSM.
Techniques
Data acquisition
In principle, any 3D gradient echo sequence can be used for data acquisition. In practice, high resolution imaging with a moderately long echo time is preferred to obtain sufficient susceptibility effects, although the optimal imaging parameters depend on the specific applications and the field strength. A multi-echo acquisition is beneficial for accurate B0 field measurement without the contribution from B1 inhomogeneity. Flow compensation may further improve the accuracy of susceptibility measurement in venous blood, but there are certain technical difficulties to devise a fully flow compensated multi-echo sequence.Background field removal
 In human
In human brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
quantitative susceptibility mapping, only the local susceptibility sources inside the brain are of interest. However, the magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
induced by the local sources is inevitably contaminated by the field induced by other sources such as main field inhomogeneity (imperfect shimming) and the air-tissue interface, whose susceptibility difference is orders of magnitudes stronger than that of the local sources. Therefore, the non-biological background field needs to be removed for clear visualization on phase images and precise quantification on QSM.
Ideally, the background field can be directly measured with a separate reference scan, where the sample of interest is replaced by a uniform phantom with the same shape while keeping the scanner shimming identical. However, for clinical application, such an approach is impossible and post-processing based methods are preferred. Traditional heuristic methods, including high-pass filter
A high-pass filter (HPF) is an electronic filter that passes signals with a frequency higher than a certain cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies lower than the cutoff frequency. The amount of attenuation for each frequency d ...
ing, are useful for the background field removal, although they also tamper with the local field and degrade the quantitative accuracy.
More recent background field removal methods directly or indirectly exploit the fact that the background field is a harmonic function
In mathematics, mathematical physics and the theory of stochastic processes, a harmonic function is a twice continuously differentiable function f: U \to \mathbb R, where is an open subset of that satisfies Laplace's equation, that is,
: \f ...
. Two recent methods which are based on physical principles, Projection onto Dipole Fields (PDF) and Sophisticated Harmonic Artifact Reduction on Phase data (SHARP), demonstrated improved contrast and higher precision on the estimated local field. Both methods model the background field as a magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
generated by an unknown background susceptibility distribution, and differentiate it from the local field using either the approximate orthogonality or the harmonic property. The background field can also be directly computed by solving the Laplace's equation with simplified boundary values, as demonstrated in the Laplacian boundary value (LBV) method.
Field-to-source inversion
The field-to-source inverse problem can be solved by several methods with various associated advantages and limitations.Calculation Of Susceptibility through Multiple Orientation Sampling (COSMOS)
 COSMOS solves the inverse problem by
COSMOS solves the inverse problem by oversampling
In signal processing, oversampling is the process of sampling a signal at a sampling frequency significantly higher than the Nyquist rate. Theoretically, a bandwidth-limited signal can be perfectly reconstructed if sampled at the Nyquist rate o ...
from multiple orientations. COSMOS utilizes the fact that the zero cone surface in the Fourier domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a signa ...
is fixed at the magic angle
The magic angle is a precisely defined angle, the value of which is approximately 54.7356°. The magic angle is a root of a second-order Legendre polynomial, , and so any interaction which depends on this second-order Legendre polynomial vanishes a ...
with respect to the B0 field. Therefore, if an object is rotated with respect to the B0 field, then in the object's frame, the B0 field is rotated and thus the cone. Consequently, data that cannot be calculated due to the cone becomes available at the new orientations.
COSMOS assumes a model-free susceptibility distribution and keeps full fidelity to the measured data. This method has been validated extensively in ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology an ...
'', ''ex vivo
''Ex vivo'' (Latin: "out of the living") literally means that which takes place outside an organism. In science, ''ex vivo'' refers to experimentation or measurements done in or on tissue from an organism in an external environment with minimal ...
'' and phantom experiments. Quantitative susceptibility maps obtained from ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
'' human brain imaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the neuroanatomy, structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive ...
also showed high degree of agreement with previous knowledge about brain anatomy. Three orientations are generally required for COSMOS, limiting the practicality for clinical applications. However, it may serve as a reference standard when available for calibrating other techniques.
Morphology Enabled Dipole Inversion (MEDI)
A unique advantage ofMRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
is that it provides not only the phase image but also the magnitude image. In principle, the contrast change, or equivalently the edge, on a magnitude image arises from the underlying change of tissue type, which is the same cause for the change of susceptibility. This observation is translated into mathematics in MEDI, where edges in a QSM which do not exist in the corresponding magnitude image are sparsified by solving a weighted norm minimization problem.
MEDI has also been validated extensively in phantom, ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology an ...
'' and ''ex vivo
''Ex vivo'' (Latin: "out of the living") literally means that which takes place outside an organism. In science, ''ex vivo'' refers to experimentation or measurements done in or on tissue from an organism in an external environment with minimal ...
'' experiments. In ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
'' human brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
, MEDI calculated QSM showed similar results compared to COSMOS without statistically significant difference. MEDI only requires a single angle acquisition, so it is a more practical solution to QSM.
Thresholded K-space Division (TKD)
The underdetermined data inFourier domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a signa ...
is only at the location of the cone and its immediate vicinity. For this region in k-space, spatial-frequencies of the dipole kernel are set to a predetermined non-zero value for the division. Investigation of more advanced strategies for recovering data in this k-space region is also a topic of ongoing research.
Thresholded k-space division only requires a single angle acquisition, and benefits from the ease of implementation as well as the fast calculation speed. However, streaking artifacts are frequently present in the QSM and the susceptibility value is underestimated compared to COSMOS calculated QSM.
Potential clinical applications
Differentiating calcification from iron
 It has been confirmed in ''
It has been confirmed in ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
'' and phantom experiments that cortical bones, whose major composition is calcification, are diamagnetic
Diamagnetic materials are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted ...
compared to water. Therefore, it is possible to use this diamagnetism
Diamagnetic materials are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted ...
to differentiate calcifications from iron deposits that usually demonstrate strong paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
. This may allow QSM to serve as a problem solving tool for the diagnosis of confounding hypointense findings on T2* weighted images.
Quantification of contrast agent
For exogenous susceptibility sources, the susceptibility value is theoretically linearly proportional to the concentration of the contrast agent. This provides a new way for ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
'' quantification of gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. Gadolinium is a silvery-white metal when oxidation is removed. It is only slightly malleable and is a ductile rare-earth element. Gadolinium reacts with atmospheric oxygen ...
or SPIO
In Greek mythology, Spio (Ancient Greek: Σπειώ means 'the dweller in the caves') was one of the 50 Nereids, marine-nymph daughters of the 'Old Man of the Sea' Nereus and the Oceanid Doris. Variations of her name were Speio and Speo.
Mythol ...
concentrations.
References
{{reflist Magnetic resonance imaging