QZ Puppis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
QZ Puppis (QZ Pup, b Pup) is a class B2.5V (blue main-sequence) 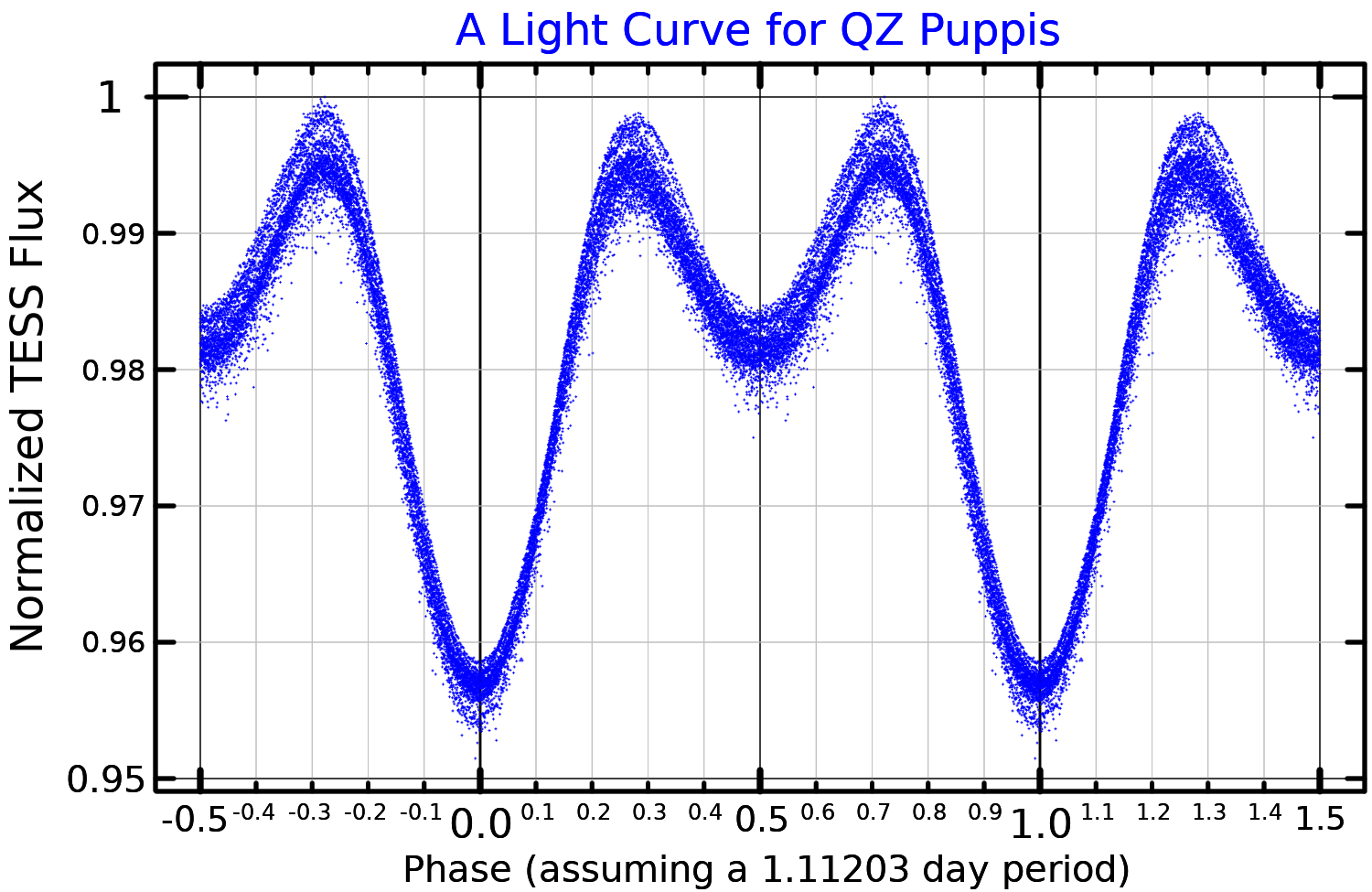 QZ Puppis was identified as a small-amplitude
QZ Puppis was identified as a small-amplitude
star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
in the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
Puppis
Puppis is a constellation in the southern sky. Puppis, the Latin translation of "poop deck", was originally part of an over-large constellation Argo Navis (the ship of Jason and the Argonauts), which centuries after its initial description, was ...
. Its apparent magnitude is 4.5 and it is approximately 650 light years away based on parallax.
 QZ Puppis was identified as a small-amplitude
QZ Puppis was identified as a small-amplitude variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as ...
in 1974, but the nature of the variability was unclear. It was thought to be a spectroscopic binary
A binary star is a system of two star, stars that are gravity, gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separa ...
on the basis of variability in the radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the temporal rate of change, rate of change of the distance or Slant range, range between the two points. It is e ...
of its spectral lines. As a hot B-class main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Her ...
star with variable spectral lines, it was suspected of being a β Cephei variable Beta Cephei variables, also known as Beta Canis Majoris stars, are variable stars that exhibit small rapid variations in their brightness due to pulsations of the stars' surfaces, thought due to the unusual properties of iron at temperatures of 200, ...
but this classification was repeatedly rejected. The short-period sinusoidal variations in brightness with an amplitude of 0.03 magnitudes were interpreted as ellipsoidal variations as the star, distorted by a close companion, rotates with a period of 1.1 days. Later analysis of Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial obj ...
photometry Photometry can refer to:
* Photometry (optics), the science of measurement of visible light in terms of its perceived brightness to human vision
* Photometry (astronomy), the measurement of the flux or intensity of an astronomical object's electrom ...
detected shallow eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ce ...
s.
The companion to QZ Puppis is only known from its effect on the visible star as they orbit. The primary shows radial velocity variations of as it orbits every 1.112 days.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:QZ Puppis Puppis B-type main-sequence stars Rotating ellipsoidal variables Puppis, b Puppis, QZ CD-38 3769 038455 3084 064503 Spectroscopic binaries