Q-Chem on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Q-Chem is a general-purpose electronic structure package featuring a variety of established and new methods implemented using innovative algorithms that enable fast calculations of large systems on various computer architectures, from laptops and regular lab workstations to midsize clusters and HPCC, using
 In preparation for the first commercial release, the company hired Eugene Fleischmann as marketing director and acquired its URL www.q-chem.com in January 1997. The first commercial product, Q-Chem 1.0, was released in March 1997. Advertising postcards celebrated the release with the proud headline, "Problems which were once impossible are now routine"; however, version 1.0 had many shortcomings, and a wit once remarked that the words "impossible" and "routine" should probably be interchanged! However, vigorous code development continued, and by the following year Q-Chem 1.1 was able to offer most of the basic quantum chemical functionality as well as a growing list of features (the continuous fast multipole method, J-matrix engine, COLD PRISM for integrals, and G96
In preparation for the first commercial release, the company hired Eugene Fleischmann as marketing director and acquired its URL www.q-chem.com in January 1997. The first commercial product, Q-Chem 1.0, was released in March 1997. Advertising postcards celebrated the release with the proud headline, "Problems which were once impossible are now routine"; however, version 1.0 had many shortcomings, and a wit once remarked that the words "impossible" and "routine" should probably be interchanged! However, vigorous code development continued, and by the following year Q-Chem 1.1 was able to offer most of the basic quantum chemical functionality as well as a growing list of features (the continuous fast multipole method, J-matrix engine, COLD PRISM for integrals, and G96 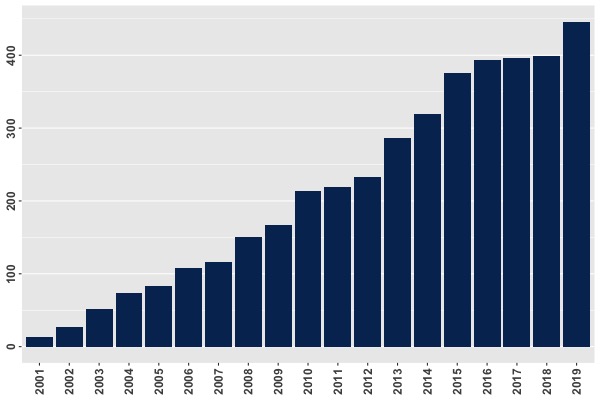 Q-Chem has been used as an engine in high-throughput studies, such as the Harvard
Q-Chem has been used as an engine in high-throughput studies, such as the Harvard  Innovative algorithms and new approaches to electronic structure have been enabling cutting-edge scientific discoveries. This transition, from in-house code to major electronic structure engine, has become possible due to contributions from numerous scientific collaborators; the Q-Chem business model encourages broad developer participation. Q-Chem defines its genre as open-teamware: its source code is open to a large group of developers. In addition, some Q-Chem modules are distributed as open source. Since 1992, over 400 man- (and woman-) years have been devoted to code development. Q-Chem 5.2.2, released in December 2019, consists of 7.5 million lines of code, which includes contributions by more than 300 active developers (current estimate is 312). See Figure 3.
Innovative algorithms and new approaches to electronic structure have been enabling cutting-edge scientific discoveries. This transition, from in-house code to major electronic structure engine, has become possible due to contributions from numerous scientific collaborators; the Q-Chem business model encourages broad developer participation. Q-Chem defines its genre as open-teamware: its source code is open to a large group of developers. In addition, some Q-Chem modules are distributed as open source. Since 1992, over 400 man- (and woman-) years have been devoted to code development. Q-Chem 5.2.2, released in December 2019, consists of 7.5 million lines of code, which includes contributions by more than 300 active developers (current estimate is 312). See Figure 3.
Wavefunction, Inc., Spartan Graphical Interface accesses and includes Q-Chem computational EnginesWebMOBrianQC
{{Chemistry software Computational chemistry software Chemistry software for Linux Science software that uses Qt Proprietary commercial software for Linux Proprietary software that uses Qt
density functional
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-bod ...
and wave-function based approaches. It offers an integrated graphical interface and input generator; a large selection of functionals and correlation methods, including methods for electronically excited states and open-shell systems; solvation models; and wave-function analysis tools. In addition to serving the computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of mo ...
community, Q-Chem also provides a versatile code development platform.
History
Q-Chem software is maintained and distributed by Q-Chem, Inc., located in Pleasanton, California, USA. It was founded in 1993 as a result of disagreements within theGaussian
Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) is the eponym of all of the topics listed below.
There are over 100 topics all named after this German mathematician and scientist, all in the fields of mathematics, physics, and astronomy. The English eponymo ...
company that led to the departure (and subsequent "banning") of John Pople
Sir John Anthony Pople (31 October 1925 – 15 March 2004) was a British theoretical chemist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Walter Kohn in 1998 for his development of computational methods in quantum chemistry.
Early ...
and a number of his students and postdocs (see Gaussian License Controversy
The first lines of the Q-Chem code were written by Peter Gill, at that time a postdoc of Pople Pople is an Anglo-French (Old French) surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*John Pople (1925–2004), British theoretical chemist and 1998 Nobel laureate in chemistry
*Luke Pople (born 1991), Australian wheelchair basketball player.
* ...
, during a winter vacation (December 1992) in Australia. Gill was soon joined by Benny Johnson (a Pople Pople is an Anglo-French (Old French) surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*John Pople (1925–2004), British theoretical chemist and 1998 Nobel laureate in chemistry
*Luke Pople (born 1991), Australian wheelchair basketball player.
* ...
graduate student) and Carlos Gonzalez (another Pople Pople is an Anglo-French (Old French) surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*John Pople (1925–2004), British theoretical chemist and 1998 Nobel laureate in chemistry
*Luke Pople (born 1991), Australian wheelchair basketball player.
* ...
postdoc), but the latter left the company shortly thereafter. In mid-1993, Martin Head-Gordon
Martin Philip Head-Gordon (''né'' Martin Philip Head) is a professor of chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory working in the area of computational quantum chemistry. He is a member of th ...
, formerly a Pople Pople is an Anglo-French (Old French) surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*John Pople (1925–2004), British theoretical chemist and 1998 Nobel laureate in chemistry
*Luke Pople (born 1991), Australian wheelchair basketball player.
* ...
student, but at that time on the Berkeley tenure track, joined the growing team of academic developers.
 In preparation for the first commercial release, the company hired Eugene Fleischmann as marketing director and acquired its URL www.q-chem.com in January 1997. The first commercial product, Q-Chem 1.0, was released in March 1997. Advertising postcards celebrated the release with the proud headline, "Problems which were once impossible are now routine"; however, version 1.0 had many shortcomings, and a wit once remarked that the words "impossible" and "routine" should probably be interchanged! However, vigorous code development continued, and by the following year Q-Chem 1.1 was able to offer most of the basic quantum chemical functionality as well as a growing list of features (the continuous fast multipole method, J-matrix engine, COLD PRISM for integrals, and G96
In preparation for the first commercial release, the company hired Eugene Fleischmann as marketing director and acquired its URL www.q-chem.com in January 1997. The first commercial product, Q-Chem 1.0, was released in March 1997. Advertising postcards celebrated the release with the proud headline, "Problems which were once impossible are now routine"; however, version 1.0 had many shortcomings, and a wit once remarked that the words "impossible" and "routine" should probably be interchanged! However, vigorous code development continued, and by the following year Q-Chem 1.1 was able to offer most of the basic quantum chemical functionality as well as a growing list of features (the continuous fast multipole method, J-matrix engine, COLD PRISM for integrals, and G96 density functional
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-bod ...
, for example) that were not available in any other package.
Following a setback when Johnson left, the company became more decentralized, establishing and cultivating relationships with an ever-increasing circle of research groups in universities around the world. In 1998, Fritz Schaefer accepted an invitation to join the Board of Directors and, early in 1999, as soon as his non-compete agreement with Gaussian
Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) is the eponym of all of the topics listed below.
There are over 100 topics all named after this German mathematician and scientist, all in the fields of mathematics, physics, and astronomy. The English eponymo ...
had expired, John Pople
Sir John Anthony Pople (31 October 1925 – 15 March 2004) was a British theoretical chemist who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Walter Kohn in 1998 for his development of computational methods in quantum chemistry.
Early ...
joined as both a Director and code developer.
In 2000, Q-Chem established a collaboration with Wavefunction Inc., which led to the incorporation of Q-Chem as the ab initio
''Ab initio'' ( ) is a Latin term meaning "from the beginning" and is derived from the Latin ''ab'' ("from") + ''initio'', ablative singular of ''initium'' ("beginning").
Etymology
Circa 1600, from Latin, literally "from the beginning", from a ...
engine in all subsequent versions of the Spartan package. The Q-Chem Board was expanded in March 2003 with the addition of Anna Krylov
Anna I. Krylov (Russian: Анна Игоревна Крылова) is a Professor of Chemistry at the University of Southern California (USC), working in the field of theoretical and computational quantum chemistry. She is the inventor of the sp ...
and Jing Kong. In 2012, John Herbert joined the Board and Fritz Schaefer became a Member Emeritus. In 2018, Evgeny Epifanovsky was named Chief Operations Officer. The following year, Shirin Faraji joined the Board; Peter Gill, who had been President of Q-Chem since 1988, stepped down; and Anna Krylov
Anna I. Krylov (Russian: Анна Игоревна Крылова) is a Professor of Chemistry at the University of Southern California (USC), working in the field of theoretical and computational quantum chemistry. She is the inventor of the sp ...
became the new president. The active Board of Directors currently consists of Faraji, Gill (past-President), Herbert, Krylov
Krylov (masculine; russian: Крылов) and Krylova (feminine; russian: Крылова) is a Russian surname, derived from the word "''крыло́"'' (wing). Alternative spellings are Krilov, Kryloff, Kriloff (masculine) and Krilova (feminine). ...
(President), and Hilary Pople ( John's daughter). Martin Head-Gordon
Martin Philip Head-Gordon (''né'' Martin Philip Head) is a professor of chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley, and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory working in the area of computational quantum chemistry. He is a member of th ...
remains a Scientific Advisor to the Board.
Currently, there are thousands of Q-Chem licenses in use, and Q-Chem's user base is expanding, as illustrated by citation records for releases 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0, which reached 400 per year in 2016 (see Figure 2).  Q-Chem has been used as an engine in high-throughput studies, such as the Harvard
Q-Chem has been used as an engine in high-throughput studies, such as the Harvard Clean Energy Project
The Clean Energy Project (CEP) was a virtual high-throughput discovery and design effort for the next generation of plastic solar cell materials that has finished. It studies millions of candidate structures to identify suitable compounds for the ...
, in which about 350,000 calculations were performed daily on the IBM World Community Grid
World Community Grid (WCG) is an effort to create the world's largest volunteer computing platform to tackle scientific research that benefits humanity. Launched on November 16, 2004, with proprietary Grid MP client from United Devices and addin ...
.
 Innovative algorithms and new approaches to electronic structure have been enabling cutting-edge scientific discoveries. This transition, from in-house code to major electronic structure engine, has become possible due to contributions from numerous scientific collaborators; the Q-Chem business model encourages broad developer participation. Q-Chem defines its genre as open-teamware: its source code is open to a large group of developers. In addition, some Q-Chem modules are distributed as open source. Since 1992, over 400 man- (and woman-) years have been devoted to code development. Q-Chem 5.2.2, released in December 2019, consists of 7.5 million lines of code, which includes contributions by more than 300 active developers (current estimate is 312). See Figure 3.
Innovative algorithms and new approaches to electronic structure have been enabling cutting-edge scientific discoveries. This transition, from in-house code to major electronic structure engine, has become possible due to contributions from numerous scientific collaborators; the Q-Chem business model encourages broad developer participation. Q-Chem defines its genre as open-teamware: its source code is open to a large group of developers. In addition, some Q-Chem modules are distributed as open source. Since 1992, over 400 man- (and woman-) years have been devoted to code development. Q-Chem 5.2.2, released in December 2019, consists of 7.5 million lines of code, which includes contributions by more than 300 active developers (current estimate is 312). See Figure 3.
Features
Q-Chem can perform a number of general quantum chemistry calculations, such as Hartree–Fock,density functional theory
Density-functional theory (DFT) is a computational quantum mechanical modelling method used in physics, chemistry and materials science to investigate the electronic structure (or nuclear structure) (principally the ground state) of many-bo ...
(DFT) including time-dependent DFT ( TDDFT), Møller–Plesset perturbation theory
Møller–Plesset perturbation theory (MP) is one of several quantum chemistry post–Hartree–Fock ab initio methods in the field of computational chemistry. It improves on the Hartree–Fock method by adding electron correlation effects by m ...
(MP2), coupled cluster
Coupled cluster (CC) is a numerical technique used for describing many-body systems. Its most common use is as one of several post-Hartree–Fock ab initio quantum chemistry methods in the field of computational chemistry, but it is also used ...
(CC), equation-of-motion coupled-cluster (EOM-CC), configuration interaction
Configuration interaction (CI) is a post-Hartree–Fock linear variational method for solving the nonrelativistic Schrödinger equation within the Born–Oppenheimer approximation for a quantum chemical multi-electron system. Mathemati ...
(CI), algebraic diagrammatic construction (ADC), and other advanced electronic structure methods. Q-Chem also includes QM/MM
The hybrid QM/MM (quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics) approach is a molecular simulation method that combines the strengths of ''ab initio'' QM calculations (accuracy) and MM (speed) approaches, thus allowing for the study of chemical processes ...
functionality. Q-Chem 4.0 and higher releases come with the graphical user interface, IQMol, which includes a hierarchical input generator, a molecular builder, and general visualization capabilities (MOs, densities, molecular vibrations, reaction pathways, etc.). IQMol is developed by Andrew Gilbert (in coordination with Q-Chem) and is distributed as free open-source software. IQmol is written using the Qt libraries, enabling it to run on a range of platforms, including OS X, Widows, and Linux. It provides an intuitive environment to set up, run, and analyze Q-Chem calculations. It can also read and display a variety of file formats, including the widely available formatted checkpoint format. A complete, up-to-date list of features is published on the Q-Chem website and in the user manual.
In addition, Q-Chem is interfaced with WebMO and is used as the computing engine in Spartan
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred ...
, or as a back-end to CHARMM
Chemistry at Harvard Macromolecular Mechanics (CHARMM) is the name of a widely used set of force fields for molecular dynamics, and the name for the molecular dynamics simulation and analysis computer software package associated with them. The CHA ...
, GROMACS, NAMD
Nanoscale Molecular Dynamics (NAMD, formerly Not Another Molecular Dynamics Program) is computer software for molecular dynamics simulation, written using the Charm++ parallel programming model. It is noted for its parallel efficiency and is often ...
, and ChemShell. Other popular visualization programs such as Jmol
Jmol is computer software for molecular modelling chemical structures in 3-dimensions. Jmol returns a 3D representation of a molecule that may be used as a teaching tool, or for research e.g., in chemistry and biochemistry.
It is written in th ...
and Molden
Molden is a general molecular and electronic structure processing program. Major features
* Reads output from the ab initio packages GAMESS (US), Gaussian, MOLPRO, PySCF and from semi-empirical packages such as MOPAC, and supports a number ...
can also be used.
In 2018, Q-Chem established a partnership with BrianQC, produced by StreamNovation, Ltd., a new integral engine exploiting the computational power of GPUs. The BrianQC plug-in speeds up Q-Chem calculations by taking advantage of GPUs on mixed architectures, which is highly efficient for simulating large molecules and extended systems. BrianQC is the first GPU Quantum Chemistry software capable of calculating high angular momentum orbitals.
Ground State Self-Consistent Field Methods
*Restricted, unrestricted, and restricted open-shell formulations *Analytical first and second derivatives for geometry optimizations, harmonic frequency analysis, and ab initio molecular dynamics *Efficient algorithms for fast convergence *Variety of guess options (including MOM)Density functional theory
*Variety of local, GGA, mGGA, hybrid, double-hybrid, dispersion-corrected, range separated functionals (energies and analytic first and second derivatives) *TDDFT and spin-flip-TDDFT formulations (energies, gradients, and frequencies) *Constrained DFTInnovative algorithms for faster performance and reduced scaling of integral calculations, HF/DFT and many-body methods
*Dual basis
In linear algebra, given a vector space ''V'' with a basis ''B'' of vectors indexed by an index set ''I'' (the cardinality of ''I'' is the dimension of ''V''), the dual set of ''B'' is a set ''B''∗ of vectors in the dual space ''V''∗ with ...
*Resolution of identity
*Cholesky decomposition of electron-repulsion integrals
* Continuous Fast Multipole Method (CFMM)
*Fast numerical integration of exchange-correlation with mrXC (multiresolution exchange-correlation)
*Linear-scaling HF-exchange method (LinK)
*Fourier transform Coulomb method (FTC)
*COLD PRISM and J-matrix engine
*Mixed-precision arithmetic for correlated methods
Post Hartree–Fock methods
*MP2 (including RI-MP2, energies and analytic gradients) *SCS, SOS-MP2, and OO-MP2 *CCD, QCISD, CCSD, OOCCD, VOOCCD *(T), (2), (dT), and (fT) corrections *EOM-XX-CCSD methods for open-shell and electronically excited species (XX=EE, SF, IP, EA, DIP, DEA, 2SF; energies, properties, and gradients for most methods), including complex-valued variants for treating resonances (states metastable with respect to electron detachment) *Extensions of DFT and many-body methods to treat core-level states and related spectroscopies *ADC methods *CIS, TDDFT, CIS(D), and SOS-CIS(D) methods for excited states *Variety of implicit solvent models *Wave-function analysis tools enabled by libwfa developed by Felix Plasser and co-workersQM/MM and QM/EFP methods for extended systems
*JanusQM/MM
The hybrid QM/MM (quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics) approach is a molecular simulation method that combines the strengths of ''ab initio'' QM calculations (accuracy) and MM (speed) approaches, thus allowing for the study of chemical processes ...
interface
*YinYang Atom model without linked atoms
*ONIOM model
* EFP method (including library of effective fragments, EFP interface with CC/EOM, DFT/TDDFT, and other methods)
Version history
Beginning with Q-Chem 2.0 only major releases versions are shown. *Q-Chem 1.0: March 1997 *Q-Chem 1.1: 1997 *Q-Chem 1.2 1998 *Q-Chem 2.0: 2000 *Q-Chem 3.0: 2006 *Q-Chem 4.0: February 2012 *Q-Chem 5.0: June 2017 *Q-Chem 5.2.2: December 2019 *Q-Chem 5.3.2: December 2020 *Q-Chem 5.4: June 2021 *Q-Chem 5.4.1: August 2021 *Q-Chem 5.4.2: December 2021See also
References
External links
*Wavefunction, Inc., Spartan Graphical Interface accesses and includes Q-Chem computational Engines
{{Chemistry software Computational chemistry software Chemistry software for Linux Science software that uses Qt Proprietary commercial software for Linux Proprietary software that uses Qt