Pythagorean interval on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
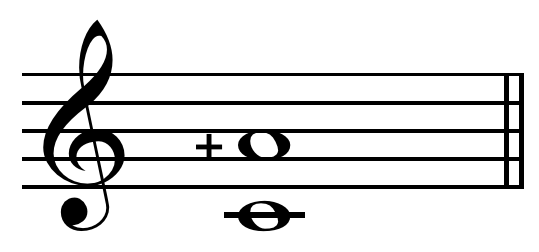

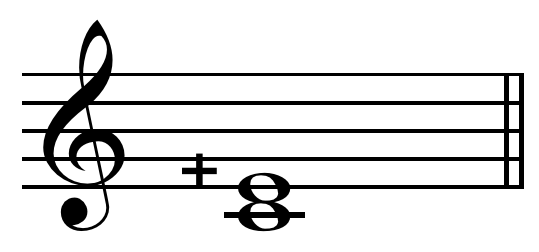





Neo-Gothic usage by Margo Schulter
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pythagorean Interval 3-limit tuning and intervals cs:Ditón de:Ditonus es:Ditono eo:Ditono nl:Ditonus ru:Дитон
 In
In musical tuning
In music, there are two common meanings for tuning:
* #Tuning practice, Tuning practice, the act of tuning an instrument or voice.
* #Tuning systems, Tuning systems, the various systems of Pitch (music), pitches used to tune an instrument, and ...
theory, a Pythagorean interval is a musical interval
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch (music), pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and v ...
with a frequency ratio equal to a power of two divided by a power of three, or vice versa.Benson, Donald C. (2003). ''A Smoother Pebble: Mathematical Explorations'', p.56. . "The frequency ratio of every Pythagorean interval is a ratio between a power of two and a power of three...confirming the Pythagorean requirements that all intervals be associated with ratios of whole numbers." For instance, the perfect fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the Interval (music), musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitch (music), pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so.
In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval f ...
with ratio 3/2 (equivalent to 31/ 21) and the perfect fourth
A fourth is a interval (music), musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending int ...
with ratio 4/3 (equivalent to 22/ 31) are Pythagorean intervals.
All the intervals between the notes of a scale are Pythagorean if they are tuned using the Pythagorean tuning
Pythagorean tuning is a system of musical tuning in which the frequency ratios of all intervals are determined by choosing a sequence of fifthsBruce Benward and Marilyn Nadine Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice'', seventh editi ...
system. However, some Pythagorean intervals are also used in other tuning systems. For instance, the above-mentioned Pythagorean perfect fifth and fourth are also used in just intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a musical tuning, tuning system in which the space between notes' frequency, frequencies (called interval (music), intervals) is a natural number, whole number ratio, ratio. Intervals spaced in thi ...
.
Interval table
Notice that the terms ''ditone'' and ''semiditone'' are specific for Pythagorean tuning, while ''tone'' and ''tritone'' are used generically for all tuning systems. Despite its name, a semiditone (3 semitones, or about 300 cents) can hardly be viewed as half of a ditone (4 semitones, or about 400 cents).12-tone Pythagorean scale
The table shows from which notes some of the above listed intervals can be played on an instrument using a repeated-octave 12-tone scale (such as a piano) tuned with D-based symmetric Pythagorean tuning. Further details about this table can be found in Size of Pythagorean intervals.






Fundamental intervals
The fundamental intervals are the superparticular ratios 2/1, 3/2, and 4/3. 2/1 is theoctave
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referr ...
or ''diapason'' (Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
for "across all"). 3/2 is the perfect fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the Interval (music), musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitch (music), pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so.
In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval f ...
, ''diapente'' ("across five"), or ''sesquialterum''. 4/3 is the perfect fourth
A fourth is a interval (music), musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending int ...
, ''diatessaron'' ("across four"), or ''sesquitertium''. These three intervals and their octave equivalents, such as the perfect eleventh and twelfth, are the only absolute consonances of the Pythagorean system. All other intervals have varying degrees of dissonance, ranging from smooth to rough.
The difference between the perfect fourth and the perfect fifth is the ''tone'' or major second
In Western music theory, a major second (sometimes also called whole tone or a whole step) is a second spanning two semitones (). A second is a musical interval encompassing two adjacent staff positions (see Interval number for more de ...
. This has the ratio 9/8, also known as epogdoon
In Western culture, Western music theory, a major second (sometimes also called whole tone or a whole step) is a second spanning two semitones (). A second is a interval (music), musical interval encompassing two adjacent staff positions ( ...
and it is the only other superparticular ratio of Pythagorean tuning, as shown by Størmer's theorem.
Two tones make a ''ditone'', a dissonantly wide major third
In music theory, a third is a Interval (music), musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval (music)#Number, Interval number for more details), and the major third () is a third spanning four Semitone, half steps or two ...
, ratio 81/64. The ditone differs from the just major third (5/4) by the syntonic comma
In music theory
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first i ...
(81/80). Likewise, the difference between the tone and the perfect fourth is the ''semiditone'', a narrow minor third
In music theory, a minor third is a interval (music), musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval (music)#Number, interval numb ...
, 32/27, which differs from 6/5 by the syntonic comma. These differences are "tempered out" or eliminated by using compromises in meantone temperament
Meantone temperaments are musical temperaments; that is, a variety of Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning systems constructed, similarly to Pythagorean tuning, as a sequence of equal fifths, both rising and descending, scaled to remain within th ...
.
The difference between the minor third and the tone is the ''minor semitone'' or ''limma'' of 256/243. The difference between the tone and the limma is the ''major semitone'' or ''apotome'' ("part cut off") of 2187/2048. Although the limma and the apotome are both represented by one step of 12-pitch equal temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning system that approximates Just intonation, just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequency, frequencie ...
, they are not equal in Pythagorean tuning, and their difference, 531441/524288, is known as the Pythagorean comma.
Contrast with modern nomenclature
There is a one-to-one correspondence between interval names (number of scale steps + quality) and frequency ratios. This contrasts with equal temperament, in which intervals with the same frequency ratio can have different names (e.g., the diminished fifth and the augmented fourth); and with other forms of just intonation, in which intervals with the same name can have different frequency ratios (e.g., 9/8 for the major second from C to D, but 10/9 for the major second from D to E).
See also
* Generated collection *Just intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a musical tuning, tuning system in which the space between notes' frequency, frequencies (called interval (music), intervals) is a natural number, whole number ratio, ratio. Intervals spaced in thi ...
* List of meantone intervals
* List of intervals in 5-limit just intonation
* Shí-èr-lǜ
* Whole-tone scale
References
External links
Neo-Gothic usage by Margo Schulter
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pythagorean Interval 3-limit tuning and intervals cs:Ditón de:Ditonus es:Ditono eo:Ditono nl:Ditonus ru:Дитон