Provinces of the Ottoman Empire on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

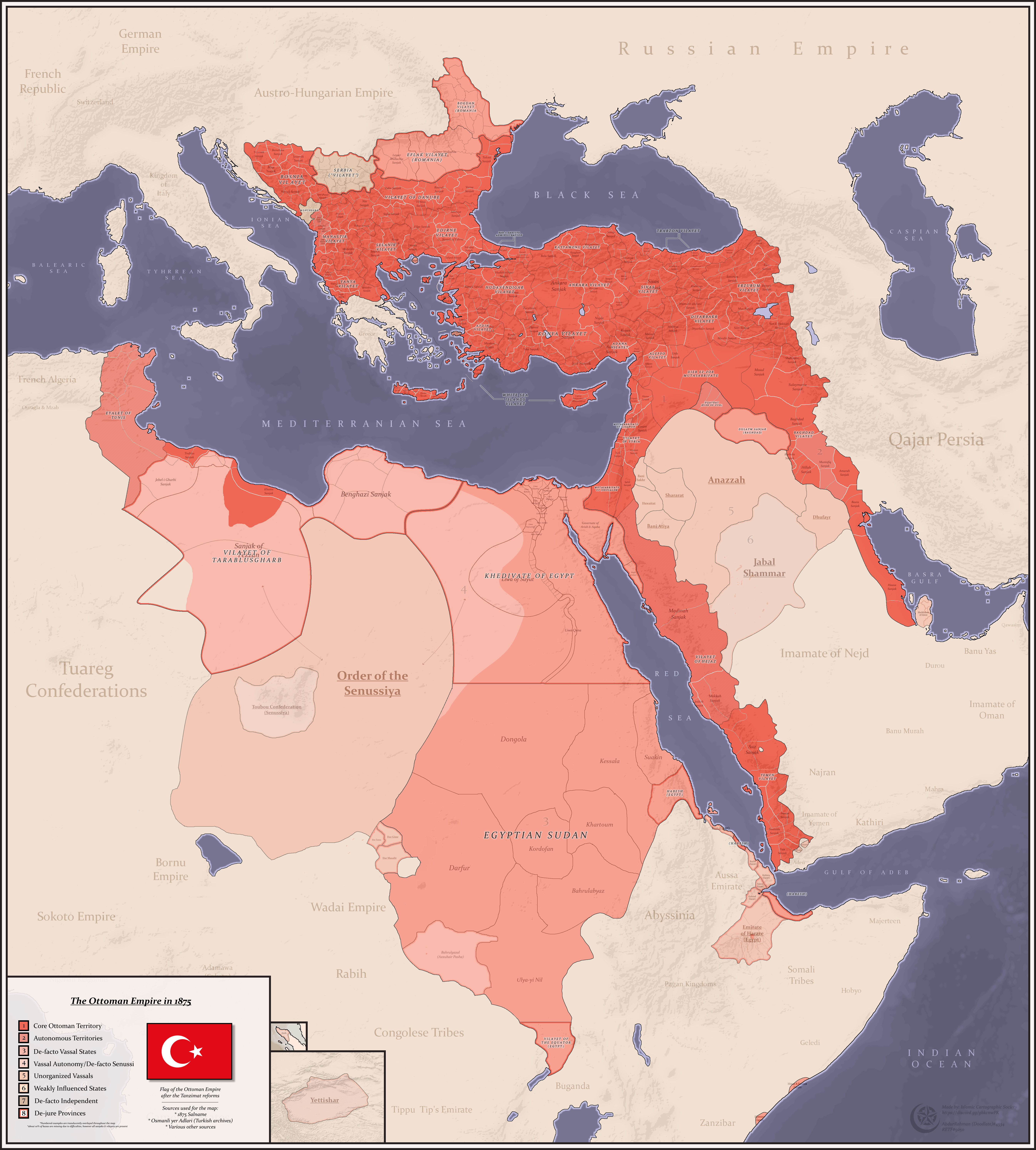

 The administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire were
The administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire were
(p. 12) It is considered extremely difficult to define the number and exact borders of Ottoman provinces and domains, as their borders were changed constantly. Until the Tanzimat period, the borders of administrative units fluctuated, reflecting the changing strategies of the Ottomans, the emergence of new threats in the region, and the rise of powerful Ayans. All the subdivisions were very unequal in regard of area and population, and the presence of numerous nomadic tribes contributed to the extreme variability of the population figures.System of universal geography founded on the works of Malte-Brun and Balbi
/ref>

 An ''eyalet'' (also ''
An ''eyalet'' (also ''

 The Vilayets were introduced with the promulgation of the "Vilayet Law" ( tr, Teskil-i Vilayet Nizamnamesi) in 1864, as part of the administrative reforms of the Tanzimat period that were being enacted throughout the empire.''The Arabs of the Ottoman Empire, 1516-1918: A Social and Cultural History''
The Vilayets were introduced with the promulgation of the "Vilayet Law" ( tr, Teskil-i Vilayet Nizamnamesi) in 1864, as part of the administrative reforms of the Tanzimat period that were being enacted throughout the empire.''The Arabs of the Ottoman Empire, 1516-1918: A Social and Cultural History''
p. 177. Bruce Masters, Cambridge University Press, 2013. Unlike the previous eyalet system, the 1864 law established a hierarchy of administrative units: the vilayet, liva/
Map of Europe in year 1500 with the subdivisions of the Ottoman Empire



 The administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire were
The administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire were administrative division
Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ...
s of the state organisation of the Ottoman Empire. Outside this system were various types of vassal and tributary states.
The Ottoman Empire was first subdivided into provinces, in the sense of fixed territorial units with governors appointed by the sultan, in the late 14th century. The beylerbey, or governor, of each province was appointed by the central government. ''Sanjaks'' (banners) were governed by sanjak-beys, selected from the high military ranks by the central government. Beylerbeyis had authority over all the sancakbeyis in a region. Kaza
A kaza (, , , plural: , , ; ota, قضا, script=Arab, (; meaning 'borough')
* bg, околия (; meaning 'district'); also Кааза
* el, υποδιοίκησις () or (, which means 'borough' or 'municipality'); also ()
* lad, kaza
, ...
was a subdivision of sancak and referred to the basic administrative district, governed by a kadi.Sacred Obligations, Precious Interests: Ottoman Grain Administration in Comparative Perspective(p. 12) It is considered extremely difficult to define the number and exact borders of Ottoman provinces and domains, as their borders were changed constantly. Until the Tanzimat period, the borders of administrative units fluctuated, reflecting the changing strategies of the Ottomans, the emergence of new threats in the region, and the rise of powerful Ayans. All the subdivisions were very unequal in regard of area and population, and the presence of numerous nomadic tribes contributed to the extreme variability of the population figures.System of universal geography founded on the works of Malte-Brun and Balbi
/ref>
List of types
In English, Ottoman subdivisions are seldom known by myriad Turkish terms (vilayet, eyalet, beylerbeylik, sancak, nahiye, kaza, etc.) which are often eschewed in favour of the English-language denomination (e.g. "province", "county", or "district") that is perceived to be the closest to the Turkish original. These translations are rarely consistent between the works of different scholars, however. Sanjaks were further divided into ''timar
A timar was a land grant by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries, with an annual tax revenue of less than 20,000 akçes. The revenues produced from the land acted as compensation for military service ...
s'' (fiefs held by ''timariots
Timariot (or ''tımar'' holder; ''tımarlı'' in Turkish) was the name given to a Sipahi cavalryman in the Ottoman army. In return for service, each timariot received a parcel of revenue called a timar, a fief, which were usually recently conqu ...
''), kadiluks (the area of responsibility of a judge, or Kadi) and (also ; larger ).
Initial organization (pre-1362)
The initial organization dates back to the Ottoman beginnings as a Seljuk vassal state (''Uç Beyligi'') in centralAnatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
. The Ottoman Empire over the years became an amalgamation of pre-existing polities, the Anatolian beyliks, brought under the sway of the ruling House of Osman.
This extension was based on an already established administrative structure of the Seljuk system in which the hereditary rulers of these territories were known as ''bey
Bey ( ota, بك, beğ, script=Arab, tr, bey, az, bəy, tk, beg, uz, бек, kz, би/бек, tt-Cyrl, бәк, translit=bäk, cjs, пий/пек, sq, beu/bej, sh, beg, fa, بیگ, beyg/, tg, бек, ar, بك, bak, gr, μπέης) is ...
s''. These beys (local leadership), which were not eliminated, continued to rule under the suzerainty of the Ottoman sultans. The term bey came to be applied not only to these former rulers but also to new governors appointed where the local leadership had been eliminated.
The Ottoman Empire was, at first, subdivided into the sovereign's ''sanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province" ...
'' and other sanjaks entrusted to the Ottoman sultan’s sons. Sanjaks were governed by ''sanjakbey
''Sanjak-bey'', ''sanjaq-bey'' or ''-beg'' ( ota, سنجاق بك) () was the title given in the Ottoman Empire to a bey (a high-ranking officer, but usually not a pasha) appointed to the military and administrative command of a district (''sanjak' ...
s'', military governors who received a flag or standard – a "''sanjak''" (the literal meaning) – from the sultan.
As the Empire expanded into Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, the need for an intermediate level of administration arose and, under the rule of Murad I
Murad I ( ota, مراد اول; tr, I. Murad, Murad-ı Hüdavendigâr (nicknamed ''Hüdavendigâr'', from fa, خداوندگار, translit=Khodāvandgār, lit=the devotee of God – meaning "sovereign" in this context); 29 June 1326 – 15 Jun ...
(r. 1359-1389), a '' beylerbey'' ("bey of beys") or governor-general was appointed to oversee Rumelia, the European part of the empire. At the end of the 14th century, a '' beylerbeylik'' was also established for Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, with his capital at Kütahya. He was always considered inferior in rank to the ''beylerbey'' of Rumelia, since large areas nominally under his control were given to the ruler's sons.
Following the establishment of ''beylerbeyliks'', ''sanjaks'' became second-order administrative divisions, although they continued to be of the first order in certain circumstances such as newly conquered areas that had yet to be assigned a ''beylerbey''. In addition to their duties as governors-general, ''beylerbeys'' were the commanders of all troops in their province.
Following the conquests between 1362 and 1400 of Murad I
Murad I ( ota, مراد اول; tr, I. Murad, Murad-ı Hüdavendigâr (nicknamed ''Hüdavendigâr'', from fa, خداوندگار, translit=Khodāvandgār, lit=the devotee of God – meaning "sovereign" in this context); 29 June 1326 – 15 Jun ...
and his son Bayezid I
Bayezid I ( ota, بايزيد اول, tr, I. Bayezid), also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt ( ota, link=no, یلدیرم بايزيد, tr, Yıldırım Bayezid, link=no; – 8 March 1403) was the Ottoman Sultan from 1389 to 1402. He adopted ...
, a need arose for the formal organisation of Ottoman territory.
First-level divisions
There were two main eras of administrative organisation. The first was the initial organisation that evolved with the rise of the Empire and the second was the organisation after extensive administrative reforms of 1864.Eyalets (1362–1864)

 An ''eyalet'' (also ''
An ''eyalet'' (also ''pasha
Pasha, Pacha or Paşa ( ota, پاشا; tr, paşa; sq, Pashë; ar, باشا), in older works sometimes anglicized as bashaw, was a higher rank in the Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitar ...
lik'' or ''beylerbeylik'') was the territory of office of a '' beylerbey'', and was further subdivided in ''sanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province" ...
s''. Toward the end of the 16th century, the ''beylerbeyliks'' began to be known as ''eyalets''. The ''beylerbeyliks'' where the ''timar
A timar was a land grant by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries, with an annual tax revenue of less than 20,000 akçes. The revenues produced from the land acted as compensation for military service ...
'' system was not applied, such as Habesh, Algers, Egypt, Baghdad, Basra and Lahsa, were more autonomous than the others. Instead of collecting provincial revenues through the timariot ''sipahi
''Sipahi'' ( ota, سپاهی, translit=sipâhi, label=Persian, ) were professional cavalrymen deployed by the Seljuks, and later the Ottoman Empire, including the land grant-holding (''timar'') provincial '' timarli sipahi'', which constituted ...
s'', the ''beylerbey'' transferred fixed annuals sums to Istanbul, known as the '' salyane''.
Vilayets (1864–1922)

 The Vilayets were introduced with the promulgation of the "Vilayet Law" ( tr, Teskil-i Vilayet Nizamnamesi) in 1864, as part of the administrative reforms of the Tanzimat period that were being enacted throughout the empire.''The Arabs of the Ottoman Empire, 1516-1918: A Social and Cultural History''
The Vilayets were introduced with the promulgation of the "Vilayet Law" ( tr, Teskil-i Vilayet Nizamnamesi) in 1864, as part of the administrative reforms of the Tanzimat period that were being enacted throughout the empire.''The Arabs of the Ottoman Empire, 1516-1918: A Social and Cultural History''p. 177. Bruce Masters, Cambridge University Press, 2013. Unlike the previous eyalet system, the 1864 law established a hierarchy of administrative units: the vilayet, liva/
sanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province" ...
(cf. Liwa (Arabic)), kaza
A kaza (, , , plural: , , ; ota, قضا, script=Arab, (; meaning 'borough')
* bg, околия (; meaning 'district'); also Кааза
* el, υποδιοίκησις () or (, which means 'borough' or 'municipality'); also ()
* lad, kaza
, ...
and village council, to which the 1871 Vilayet Law added the nabiye. The 1864 law also specified the responsibilities of the governor (wali
A wali (''wali'' ar, وَلِيّ, '; plural , '), the Arabic word which has been variously translated "master", "authority", "custodian", "protector", is most commonly used by Muslims to indicate an Islamic saint, otherwise referred to by the ...
) of the vilayet and their councils. At the same time, the law left to the governors vast scope for independent action as well as responsibility, as part of a system intended to achieve a large degree of efficiency in ruling the provinces.
The new provincial system could not be introduced in provinces at the same time, due to both insufficient funds and a lack of experience in administering the new law. Therefore, the new Danube Vilayet, composed of the former eyalets of Silistria, Vidin
Vidin ( bg, Видин, ; Old Romanian: Diiu) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as ...
, and Nis, was selected to be the pilot project. Midhat Pasha
Ahmed Şefik Midhat Pasha ( ota , احمد شفيق مدحت پاشا, 18 October 1822 – 26 April 1883) was an Ottoman democrat, kingmaker and one of the leading statesmen during the late Tanzimat period. He is most famous for leading the O ...
and Cevdet Pasha Cevdet is a Turkish form of the Arabic name Jawdat and may refer to:
Given name
* Cevdet Bey (1878–1955), (also D'jedvet Bey) governor of the Van vilayet of the Ottoman Empire, convicted war criminal, responsible for massacre of over 55 000 Assyr ...
were particularly successful in applying the new law in the Vilayets of Danube and Aleppo, respectively.
By 1865 the four vilayets of Danube, Aleppo, Erzurum
Erzurum (; ) is a city in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. It is the largest city and capital of Erzurum Province and is 1,900 meters (6,233 feet) above sea level. Erzurum had a population of 367,250 in 2010.
The city uses the double-headed eagle as ...
and Bosnia were fully organized and in operation. Damascus, Tripolitania
Tripolitania ( ar, طرابلس '; ber, Ṭrables, script=Latn; from Vulgar Latin: , from la, Regio Tripolitana, from grc-gre, Τριπολιτάνια), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province o ...
, and Edirne
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis ( Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders ...
followed the next year. In 1867, 13 new vilayets were organized, including Bursa, Izmir, Trabzon
Trabzon (; Ancient Greek: Tραπεζοῦς (''Trapezous''), Ophitic Pontic Greek: Τραπεζούντα (''Trapezounta''); Georgian: ტრაპიზონი (''Trapizoni'')), historically known as Trebizond in English, is a city on the B ...
, Salonica
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
, Prizren, and Iskodra, with an autonomous Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
being organized as a vilayet by Ali Pasha in 1871. By the end of 1876 the new provincial system was in operation all over the empire, with the sole exception of the Arabian Peninsula and autonomous provinces like Egypt.
Mahmud Nedim Pasha
Mahmud Nedim Pasha ( 1818 – 14 May 1883) was an Ottoman conservative statesman of ethnic Georgian background,Buṭrus Abū Mannah (2001), ''Studies on Islam and the Ottoman Empire in the 19th century, 1826-1876'', p. 163. Isis Press, wh ...
reduced the size of some of the larger provinces, thus taking Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
from the Danube Vilayet, Sebinkarahisar from Trabzon, and Maras from Adana and making them into separate provinces, and also taking Herzegovina from Bosnia and joining it with Novipazar in a new province.
Second-level divisions (sanjaks)
The provinces (eyalets, later vilayets) were divided intosanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province" ...
s (also called ''livas'') governed by sanjakbey
''Sanjak-bey'', ''sanjaq-bey'' or ''-beg'' ( ota, سنجاق بك) () was the title given in the Ottoman Empire to a bey (a high-ranking officer, but usually not a pasha) appointed to the military and administrative command of a district (''sanjak' ...
s (also called ''Mutesarrifs'') and were further subdivided into ''timar
A timar was a land grant by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries, with an annual tax revenue of less than 20,000 akçes. The revenues produced from the land acted as compensation for military service ...
s'' (fiefs held by ''timariots
Timariot (or ''tımar'' holder; ''tımarlı'' in Turkish) was the name given to a Sipahi cavalryman in the Ottoman army. In return for service, each timariot received a parcel of revenue called a timar, a fief, which were usually recently conqu ...
''), kadiluks (the area of responsibility of a judge, or Kadi) and (also ; larger timars).
Governors
Beylerbey
The Turkish word for governor-general is Beylerbey, meaning ‘lord of lords’. In times of war, they would assemble under his standard and fight as a unit in the sultan's army. However, as a territorial governor, the Beylerbey now had wider responsibilities. He played the major role in allocating fiefs in his eyalet, and had a responsibility for maintaining order and dispensing justice. His household, like the sultan's in the capital, was the political centre of the eyalet. By the mid-16th century, apart from the principalities north of the Danube, all eyalets came under the direct rule of the sultan. The Beylerbeys were all his appointees, and he could remove or transfer them at will. Their term of office was limited: governorships were not hereditary, and no one could serve for life. The office of Beylerbey was the most prestigious and the most profitable in the provincial government, and it was from among the Beylerbeys that the sultan almost always chose his viziers. There was also, it appears, a hierarchy among the governors themselves. The senior was the Beylerbey of Rumelia who, from 1536, had the right to sit on the Imperial Council. Precedence among the remainder, according to Ayn Ali in 1609, followed the order in which the eyalets were conquered, although he does not make it clear whether this ranking had anything other than a ceremonial significance. However, before 1650, there was another development. During this period, the practice began of appointing some Beylerbeys with the rank of vizier. A vizieral governor, according to the chancellor Abdurrahman Pasha in 1676, had command over the governors of adjoining eyalets who ‘should have recourse to him and obey his command’. Furthermore, ‘when Beylerbeys with Vizierates are dismissed from their eyalet, they listen to lawsuits and continue to exercise Vizieral command until they reach Istanbul’.Sanjak-bey
The office of Sanjak-bey resembled that of Beylerbey on a more modest scale. Like the Beylerbey, the Sanjak-bey drew his income from a prebend, which consisted usually of revenues from the towns, quays and ports within the boundary of his sanjak. Like the Beylerbey, the Sanjak-bey was also a military commander. The term sanjak means ‘flag’ or ‘standard’ and, in times of war, the cavalrymen holding fiefs in his sanjak, gathered under his banner. The troops of each sanjak, under the command of their governor, would then assemble as an army and fight under the banner of the Beylerbey of the eyalet. In this way, the structure of command on the battlefield resembled the hierarchy of provincial government. Within his own sanjak, a governor was responsible above all for maintaining order and, with the cooperation of the fief holders, arresting and punishing wrongdoers. For this, he usually received half of the fines imposed on miscreants, with the fief holder on whose lands the misdeed took place, receiving the other half. Sanjak governors also had other duties, for example, the pursuit of bandits, the investigation of heretics, the provision of supplies for the army, or the despatch of materials for shipbuilding, as the sultan commanded. Sanjak governors also served as military commanders of all of the timariot and -holding cavalrymen in their sanjak. Some provinces such asEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
, Abyssinia, and Al-Hasa (the salyane provinces) were not subdivided into sanjaks and timars. The area governed by an Aga was often known as an Agaluk
An Agaluk ( tr, Ağalık) was a feudal unit of the Ottoman Empire governed by an ''agha'' (tax collector landlord).
In Bosnian history, an agaluk may often refer to land ''owned'' by an ''aga''.
See also
*Subdivisions of the Ottoman Empire
*Ka ...
. The term Arpalik ( tr, Arpalik), or Arpaluk, refers to large estate (i.e. sanjak
Sanjaks (liwāʾ) (plural form: alwiyāʾ)
* Armenian: նահանգ (''nahang''; meaning "province")
* Bulgarian: окръг (''okrǔg''; meaning "county", "province", or "region")
* el, Διοίκησις (''dioikēsis'', meaning "province" ...
) entrusted to some holder of senior position, or to some margrave, as temporary arrangement before they were appointed to some appropriate position. The barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
corn was known as ''arpa'' in Turkish, and the feudal system in Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
employed the term Arpalik, or "barley-money", to refer to a second allowance made to officials to offset the costs of fodder for their horses (for covering the expenses of keeping a small unit of cavalry).
See also
*Subdivisions of the Ottoman Empire
The administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire were administrative divisions of the state organisation of the Ottoman Empire. Outside this system were various types of vassal and tributary states.
The Ottoman Empire was first subdivided ...
* Vassal and tributary states of the Ottoman Empire
References
External links
Map of Europe in year 1500 with the subdivisions of the Ottoman Empire
Further reading
* Colin Imber. ''The Ottoman Empire, 1300-1650: The Structure of Power''. (Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire, UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2002.) * Halil Inalcik. ''The Ottoman Empire: The Classical Age 1300-1600''. Trans. Norman Itzkowitz and Colin Imber. (London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 1973.) * Paul Robert Magocsi. ''Historical Atlas of Central Europe''. (2nd ed.) Seattle, WA, USA: Univ. of Washington Press, 2002) * ''Nouveau Larousse illustré'', undated (early 20th century), passim (in French) * Donald Edgar Pitcher. ''An Historical Geography of the Ottoman Empire''. (Leiden, Netherlands: E.J.Brill,1972.) (Includes 36 color maps) * Westermann, ''Großer Atlas zur Weltgeschichte'' (in German) (includes maps) {{DEFAULTSORT:Administrative divisions of the Ottoman Empire Geography of the Ottoman Empire Government of the Ottoman Empire Ottoman Ottoman Ottoman