protein dynamics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Many residues are in close spatial proximity in protein structures. This is true for most residues that are contiguous in the primary sequence, but also for many that are distal in sequence yet are brought into contact in the final folded structure. Because of this proximity, these residue's energy landscapes become coupled based on various biophysical phenomena such as hydrogen bonds,
Many residues are in close spatial proximity in protein structures. This is true for most residues that are contiguous in the primary sequence, but also for many that are distal in sequence yet are brought into contact in the final folded structure. Because of this proximity, these residue's energy landscapes become coupled based on various biophysical phenomena such as hydrogen bonds,  When these coupled residues form pathways linking functionally important parts of a protein,
they may participate in allosteric signaling.
For example, when a molecule of oxygen binds to one subunit of the
When these coupled residues form pathways linking functionally important parts of a protein,
they may participate in allosteric signaling.
For example, when a molecule of oxygen binds to one subunit of the
 A study by Hayward found that the termini of α-helices and β-sheets form hinges in a large number of cases. Many hinges were found to involve two secondary structure elements acting like hinges of a door, allowing an opening and closing motion to occur. This can arise when two neighbouring strands within a β-sheet situated in one domain, diverge apart as they join the other domain. The two resulting termini then form the bending regions between the two domains. α-helices that preserve their hydrogen bonding network when bent are found to behave as mechanical hinges, storing `elastic energy' that drives the closure of domains for rapid capture of a substrate. Khade et. al. worked on prediction of the hinges in any conformation and further built an Elastic Network Model called hdANM that can model those motions.
A study by Hayward found that the termini of α-helices and β-sheets form hinges in a large number of cases. Many hinges were found to involve two secondary structure elements acting like hinges of a door, allowing an opening and closing motion to occur. This can arise when two neighbouring strands within a β-sheet situated in one domain, diverge apart as they join the other domain. The two resulting termini then form the bending regions between the two domains. α-helices that preserve their hydrogen bonding network when bent are found to behave as mechanical hinges, storing `elastic energy' that drives the closure of domains for rapid capture of a substrate. Khade et. al. worked on prediction of the hinges in any conformation and further built an Elastic Network Model called hdANM that can model those motions.
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
s are generally thought to adopt unique structures determined by their amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
sequences. However, proteins are not strictly static objects, but rather populate ensembles of (sometimes similar) conformations. Transitions between these states occur on a variety of length scales (tenths of Å to nm) and time scales (ns to s),
and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis.
The study of protein dynamics is most directly concerned with the transitions between these states,
but can also involve the nature and equilibrium populations of the states themselves.
These two perspectives— kinetics and thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of th ...
, respectively—can be conceptually synthesized in an "energy landscape" paradigm:
highly populated states and the kinetics of transitions between them can be described by the depths of energy wells and the heights of energy barriers, respectively.
Local flexibility: atoms and residues
Portions of protein structures often deviate from the equilibrium state. Some such excursions are harmonic, such as stochastic fluctuations ofchemical bond
A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of ...
s and bond angles.
Others are anharmonic, such as sidechains that jump between separate discrete energy minima, or rotamer
In chemistry, conformational isomerism is a form of stereoisomerism in which the isomers can be interconverted just by rotations about formally single bonds (refer to figure on single bond rotation). While any two arrangements of atoms in a mole ...
s.
Evidence for local flexibility is often obtained from NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. The sample is placed in a magnetic fie ...
. Flexible and potentially disordered regions of a protein can be detected using the random coil index. Flexibility in folded proteins can be identified by analyzing the spin relaxation
Spin or spinning most often refers to:
* Spinning (textiles), the creation of yarn or thread by twisting fibers together, traditionally by hand spinning
* Spin, the rotation of an object around a central axis
* Spin (propaganda), an intentionally b ...
of individual atoms in the protein. Flexibility can also be observed in very high-resolution electron density maps produced by X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles ...
,
particularly when diffraction data is collected at room temperature instead of the traditional cryogenic temperature (typically near 100 K). Information on the frequency distribution and dynamics of local protein flexibility can be obtained using Raman and optical Kerr-effect spectroscopy as well as anisotropic microspectroscopy in the terahertz frequency domain.
Regional flexibility: intra-domain multi-residue coupling
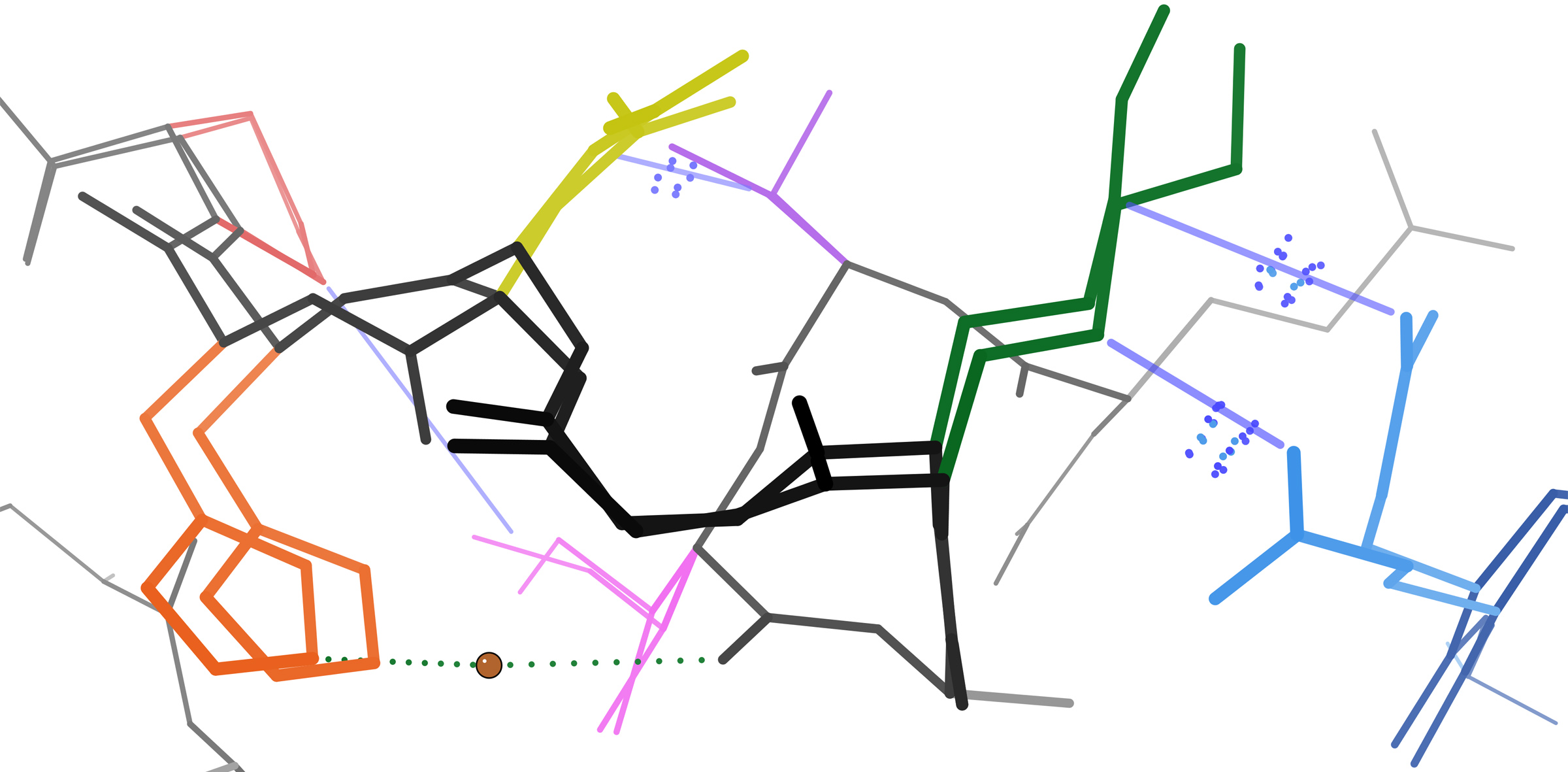
 Many residues are in close spatial proximity in protein structures. This is true for most residues that are contiguous in the primary sequence, but also for many that are distal in sequence yet are brought into contact in the final folded structure. Because of this proximity, these residue's energy landscapes become coupled based on various biophysical phenomena such as hydrogen bonds,
Many residues are in close spatial proximity in protein structures. This is true for most residues that are contiguous in the primary sequence, but also for many that are distal in sequence yet are brought into contact in the final folded structure. Because of this proximity, these residue's energy landscapes become coupled based on various biophysical phenomena such as hydrogen bonds, ionic bond
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds ...
s, and van der Waals interactions (see figure).
Transitions between states for such sets of residues therefore become correlated.
This is perhaps most obvious for surface-exposed loops, which often shift collectively to adopt different conformations in different crystal structures (see figure). However, coupled conformational heterogeneity is also sometimes evident in secondary structure. For example, consecutive residues and residues offset by 4 in the primary sequence often interact in α helices
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues ear ...
. Also, residues offset by 2 in the primary sequence point their sidechains toward the same face of β sheets and are close enough to interact sterically, as are residues on adjacent strands of the same β sheet. Some of these conformational changes are induced by post-translational modifications in protein structure, such as phosphorylation and methylation.
 When these coupled residues form pathways linking functionally important parts of a protein,
they may participate in allosteric signaling.
For example, when a molecule of oxygen binds to one subunit of the
When these coupled residues form pathways linking functionally important parts of a protein,
they may participate in allosteric signaling.
For example, when a molecule of oxygen binds to one subunit of the hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyt ...
tetramer,
that information is allosterically propagated to the other three subunits, thereby enhancing their affinity for oxygen.
In this case, the coupled flexibility in hemoglobin allows for cooperative oxygen binding,
which is physiologically useful because it allows rapid oxygen loading in lung tissue and rapid oxygen unloading in oxygen-deprived tissues (e.g. muscle).
Global flexibility: multiple domains
The presence of multiple domains in proteins gives rise to a great deal of flexibility and mobility, leading to protein domain dynamics. Domain motions can be inferred by comparing different structures of a protein (as inDatabase of Molecular Motions
The Database of Macromolecular Motions is a bioinformatics database and software-as-a-service tool that attempts to
categorize macromolecular motions, sometimes also known as conformational change. It was originally developed by Mark B. Gerstein, ...
), or they can be directly observed using spectra
measured by neutron spin echo
Neutron spin echo spectroscopy is an inelastic neutron scattering technique invented by Ferenc Mezei in the 1970s, and developed in collaboration with John Hayter. In recognition of his work and in other areas, Mezei was awarded the first Walte ...
spectroscopy.
They can also be suggested by sampling in extensive molecular dynamics trajectories and principal component analysis. Domain motions are important for:
* ABC transporter
The ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC transporters) are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC transpo ...
s
* catalysis
* cellular locomotion and motor proteins
Motor proteins are a class of molecular motors that can move along the cytoplasm of cells. They convert chemical energy into mechanical work by the hydrolysis of ATP. Flagellar rotation, however, is powered by a proton pump.
Cellular function ...
* formation of protein complexes
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multienzyme complexes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain.
Protein ...
* ion channels
* mechanoreceptors and mechanotransduction
In cellular biology, mechanotransduction ('' mechano'' + '' transduction'') is any of various mechanisms by which cells convert mechanical stimulus into electrochemical activity. This form of sensory transduction is responsible for a number of ...
* regulatory activity
* transport of metabolites across cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment ( ...
s
One of the largest observed domain motions is the 'swivelling' mechanism in pyruvate phosphate dikinase. The phosphoinositide domain swivels between two states in order to bring a phosphate group from the active site of the nucleotide binding domain to that of the phosphoenolpyruvate/pyruvate domain. The phosphate group is moved over a distance of 45 Å involving a domain motion of about 100 degrees around a single residue. In enzymes, the closure of one domain onto another captures a substrate by an induced fit, allowing the reaction to take place in a controlled way. A detailed analysis by Gerstein led to the classification of two basic types of domain motion; hinge and shear. Only a relatively small portion of the chain, namely the inter-domain linker and side chains undergo significant conformational changes upon domain rearrangement.
Hinge motions
 A study by Hayward found that the termini of α-helices and β-sheets form hinges in a large number of cases. Many hinges were found to involve two secondary structure elements acting like hinges of a door, allowing an opening and closing motion to occur. This can arise when two neighbouring strands within a β-sheet situated in one domain, diverge apart as they join the other domain. The two resulting termini then form the bending regions between the two domains. α-helices that preserve their hydrogen bonding network when bent are found to behave as mechanical hinges, storing `elastic energy' that drives the closure of domains for rapid capture of a substrate. Khade et. al. worked on prediction of the hinges in any conformation and further built an Elastic Network Model called hdANM that can model those motions.
A study by Hayward found that the termini of α-helices and β-sheets form hinges in a large number of cases. Many hinges were found to involve two secondary structure elements acting like hinges of a door, allowing an opening and closing motion to occur. This can arise when two neighbouring strands within a β-sheet situated in one domain, diverge apart as they join the other domain. The two resulting termini then form the bending regions between the two domains. α-helices that preserve their hydrogen bonding network when bent are found to behave as mechanical hinges, storing `elastic energy' that drives the closure of domains for rapid capture of a substrate. Khade et. al. worked on prediction of the hinges in any conformation and further built an Elastic Network Model called hdANM that can model those motions.
Helical to extended conformation
The interconversion of helical and extended conformations at the site of a domain boundary is not uncommon. In calmodulin, torsion angles change for five residues in the middle of a domain linking α-helix. The helix is split into two, almost perpendicular, smaller helices separated by four residues of an extended strand.Shear motions
Shear motions involve a small sliding movement of domain interfaces, controlled by the amino acid side chains within the interface. Proteins displaying shear motions often have a layered architecture: stacking of secondary structures. The interdomain linker has merely the role of keeping the domains in close proximity.Domain motion and functional dynamics in enzymes
The analysis of the internal dynamics of structurally different, but functionally similar enzymes has highlighted a common relationship between the positioning of the active site and the two principal protein sub-domains. In fact, for several members of the hydrolase superfamily, the catalytic site is located close to the interface separating the two principal quasi-rigid domains. Such positioning appears instrumental for maintaining the precise geometry of the active site, while allowing for an appreciable functionally oriented modulation of the flanking regions resulting from the relative motion of the two sub-domains.Implications for macromolecular evolution
Evidence suggests that protein dynamics are important for function, e.g. enzyme catalysis in DHFR, yet they are also posited to facilitate the acquisition of new functions bymolecular evolution
Molecular evolution is the process of change in the sequence composition of cellular molecules such as DNA, RNA, and proteins across generations. The field of molecular evolution uses principles of evolutionary biology and population genetics ...
.
This argument suggests that proteins have evolved to have stable, mostly unique folded structures,
but the unavoidable residual flexibility leads to some degree of functional promiscuity,
which can be amplified/harnessed/diverted by subsequent mutations.
However, there is growing awareness that intrinsically unstructured proteins are quite prevalent in eukaryotic genomes,
casting further doubt on the simplest interpretation of Anfinsen's dogma: "sequence determines structure (singular)".
In effect, the new paradigm is characterized by the addition of two caveats: "sequence and cellular environment determine structural ensemble".
References
{{Protein topics Protein folding Protein biosynthesis