Propylon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
Https://Www.worldhistory.org#Organization , 24 July 2022, https://www.worldhistory.org/Propylaea/ .
Propylaea.org
– leads to a variety of material, some scholarly, but many photographs as well Acropolis of Athens Ancient Greek buildings and structures in Athens Ancient Greek culture Types of gates

 In
In ancient Greek architecture
Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greek-speaking people (''Hellenic'' people) whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC unti ...
, a propylaea, propylea or propylaia (; Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
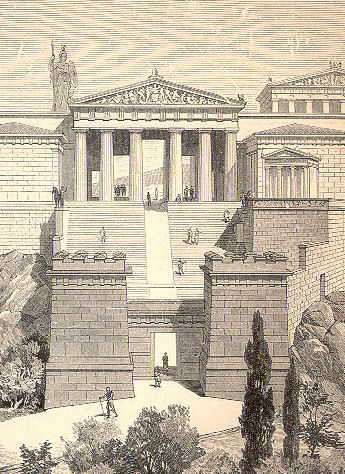
: προπύλαια) is a monumental gateway. They are seen as a partition, specifically for separating the secular and religious pieces of a city. The prototypical Greek example is the propylaea that serves as the entrance to the Acropolis of Athens
The Acropolis of Athens is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historical significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. Th ...
. In this case, the propylaea is built wider than the Acropolis of Athens in order to allow chariots through. The construction of it was part of Pericles great rebuilding program for Athens in c. 437 BCE. The project of the propylaea began once the Parthenon was almost done. It was overseen by Mnesicles (an Athenian architect). Though the work was suspended due to the Peloponnesian War, the important pieces of Mnesicles’ vision were able to come through (World History Encyclopedia). The Greek Revival
The Greek Revival was an architectural movement which began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe and the United States and Canada, but a ...
Brandenburg Gate of Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
and the Propylaea in Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and Ha ...
both evoke the central portion of the Athens propylaea. The architecture for the propylaea is unique in that it uses horizontal beams across the roof. These beams were supported by marble girders, which were supported by iron bars. The only other known use of metal in Greek architecture for structural purposes is the Temple of Zeus at Agrigento (World History Encyclopedia).
Etymology
The Greek word προπύλαιον ''propylaeon'' (''propylaeum'' is theLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
version) is the union of the prefix προ- ''pro-'', "before, in front of" plus the plural of πύλη ''pyle'' "gate," meaning literally "that which is before the gates," but the word has come to mean simply "gate building."
Propylaea of the Athenian Acropolis
The Propylaea was the monumental gateway to the Acropolis commissioned by the Athenian leaderPericles
Pericles (; grc-gre, Περικλῆς; c. 495 – 429 BC) was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Pelo ...
in order to rebuild the Acropolis at the conclusion of the Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the ...
.
Propylaea outside the Greco-Roman world
The oldest known freestanding propylaeum is the one located at the palace area in Pasargadae, anAchaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
capital.
A covered passage, called "the Propylaeum", used to face the Palace of Darius at Susa.
In the 18th Century, the Athenian Propylaea inspired Carl Gotthard Langhans in construction of the Brandenburg Gate in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
.
See also
* Portal (architecture) *Triumphal arch
A triumphal arch is a free-standing monumental structure in the shape of an archway with one or more arched passageways, often designed to span a road. In its simplest form a triumphal arch consists of two massive piers connected by an arch, cro ...
*Gate tower
A gate tower (german: Torturm) is a tower built over or next to a major gateway.
Usually it is part of a medieval fortification. This may be a town or city wall, fortress, castle or castle chapel. The gate tower may be built as a twin tower on ...
Notes
References
* Berve, H.; Gruben, G.; and Hirmer, M. ''Greek Temples, Theaters, and Shrines'' (New York, 1963). A general look at selected Greek structures. * Dinsmoor, William Bell (1922), "Structural Iron in Greek Architecture," '' American Journal of Archaeology,'' XXVI * Dinsmoor, W. B., ''The Architecture of Ancient Greece'' (New York, 1975 - but actually a reprint of the 1950 publication). A general book on Greek architecture; dated in many areas but valuable for the Propylaea. * Dinsmoor, W. B., Jr., ''The Propylaia I: The Predecessors'' (Princeton, 1980). A careful study of the predecessors of the Propylaea. * Eiteljorg, Harrison, II, ''The Entrance to the Acropolis Before Mnesicles'' (Dubuque, 1993). A careful study of the predecessors of the Propylaea, with very different conclusions from those of Dinsmoor above. * Lawrence, A. W., ''Greek Architecture'' (Baltimore, 1973). A general book on Greek architecture. * Robertson, D.S. ''Greek and Roman Architecture (Cambridge, 1969). A general book on Greek and Roman architecture. Available in paper, this may be the best place to begin for those with no knowledge of ancient architecture. * Travlos, J., ''Pictorial Dictionary of Ancient Athens'' (London, 1971). An encyclopedic approach to the monuments of Athens. * The Perseus Project An electronic resource that provides quick information, but some of the information about the Propylaea was incorrect when the site was last checked. Several good photographs of the Propylaea are available through the Perseus project. * Cartwright, Mark. “Propylaea.” ''World History Encyclopedia'',External links
{{Commons category, Propylaea (architecture), PropylaeaPropylaea.org
– leads to a variety of material, some scholarly, but many photographs as well Acropolis of Athens Ancient Greek buildings and structures in Athens Ancient Greek culture Types of gates