Projections Of Population Growth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Population projections are attempts to show how the
Population projections are attempts to show how the  Because of
Because of
 Fertility is expressed as the
Fertility is expressed as the


World Population to 2300
'. 2004. Executive Summary, p. 2. By contrast, a 2014 projection by the United Nations Population Division predicted a population close to 11 billion by 2100 without any declining trend in the foreseeable future.

 Population projections are attempts to show how the
Population projections are attempts to show how the human population
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
statistics might change in the future. These projections are an important input to forecasts
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared (resolved) against what happens. For example, a company might estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the actual ...
of the population's impact on this planet and humanity's future well-being. Models of population growth take trends in human development Human development may refer to:
* Development of the human body
* Developmental psychology
* Human development (economics)
* Human Development Index, an index used to rank countries by level of human development
* Human evolution
Human evoluti ...
, and apply projections into the future. These models use trend-based-assumptions about how populations will respond to economic, social and technological forces to understand how they will affect fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Fertili ...
and mortality, and thus population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
.
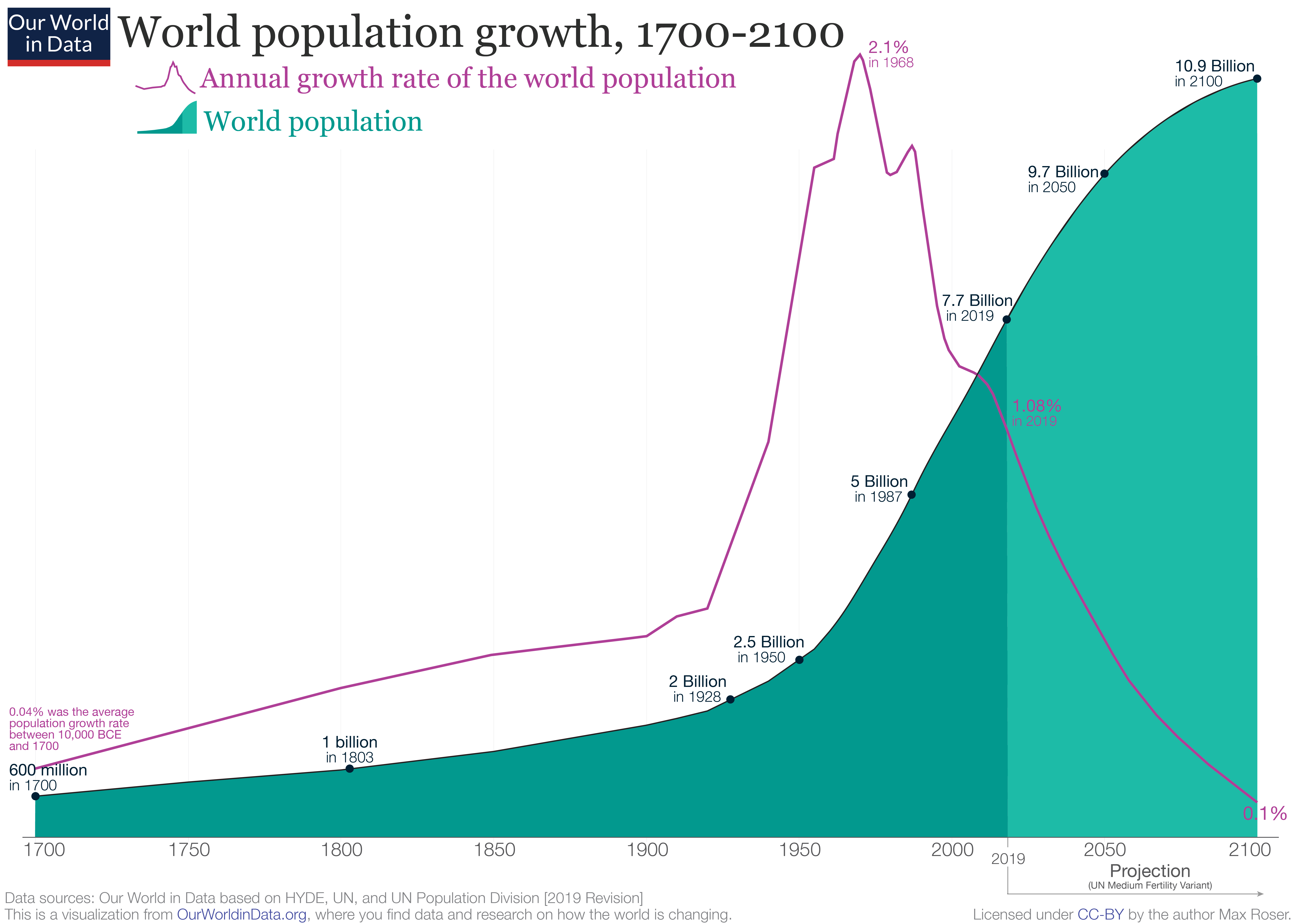
The 2019 projections from the United Nations Population Division show that annual world population growth peaked at 2.1% in 1968, has since dropped to 1.1%, and could drop even further to 0.1% by 2100, which would be a growth rate not seen since pre-industrial revolution days. Based on this, the UN Population Division projects the world population, which is 7.8 billion , to level out around 2100 at 10.9 billion (the median line), assuming a continuing decrease in the global average fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
from 2.5 births per woman during the 2015–2020 period to 1.9 in 2095–2100, according to the medium-variant projection. A 2014 projection has the population continuing to grow into the next century.
However, estimates outside of the United Nations have put forward alternative models based on additional downward pressure on fertility (such as successful implementation of education and family planning goals in the Sustainable Development Goals
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) or Global Goals are a collection of 17 interlinked objectives designed to serve as a "shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future".United Nations (2017) R ...
) which could result in peak population during the 2060-2070 period rather than later.
According to the UN, about two-thirds of the predicted growth in population between 2020 and 2050 will take place in Africa. It is projected that 50% of births in the 5-year period 2095-2100 will be in Africa. Other organizations project lower levels of population growth in Africa based particularly on improvement in women's education and successfully implementing family planning.
By 2100, the UN projects the population in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
will reach 3.8 billion, IHME
Ihme (in its upper course: Wennigser Mühlbach) is a river of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Leine.
The Ihme is long. Its source is in the village , a district of Wennigsen. After about , the Ihme reaches the city of Hano ...
projects 3.1 billion, and IIASA
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an independent international research institute located in Laxenburg, near Vienna, in Austria. Through its research programs and initiatives, the institute conducts policy-o ...
is the lowest at 2.6 billion. In contrast to the UN projections, the models of fertility developed by IHME and IIASA incorporate women's educational attainment, and in the case of IHME, also assume successful implementation of family planning.
population momentum Population momentum is a consequence of the demographic transition. Population momentum explains why a population will continue to grow even if the fertility rate declines. Population momentum occurs because it is not only the number of children per ...
the global population will continue to grow, although at a steadily slower rate, for the remainder of this century, but the main driver of long-term future population growth will be the evolution of the global average fertility rate.
Table of UN projections
The United Nation's Population Division publishes high & low estimates (by gender) & density.History of population projections
Walter Greiling projected in the 1950s that world population would reach a peak of about nine billion, in the 21st century, and then stop growing after a readjustment of theThird World
The term "Third World" arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Western European nations and their allies represented the " First ...
and a sanitation of the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
.
Estimates published in the 2000s tended to predict that the population of Earth would stop increasing around 2070. In a 2004 long-term prospective report, the United Nations Population Division
The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA) is part of the United Nations Secretariat and is responsible for the follow-up to major United Nations Summits and Conferences, as well as services to the United Nations Ec ...
projected the world population would peak at 7.85 billion in 2075. After reaching this maximum, it would decline slightly and then resume a slow increase, reaching a level of 5.11 billion by 2300, about the same as the projected 2050 figure.
This prediction was revised in the 2010s, to the effect that no maximum will likely be reached in the 21st century. The main reason for the revision was that the ongoing rapid population growth in Africa had been underestimated. A 2014 paper by demographers from several universities and the United Nations Population Division forecast that the world's population would reach about 10.9 billion in 2100 and continue growing thereafter. In 2017 the UN predicted a decline of global population growth rate from +1.0% in 2020 to +0.5% in 2050 and to +0.1% in 2100.
Jørgen Randers
Jørgen Randers (born 22 May 1945) is a Norwegian academic, professor emeritus of climate strategy at the BI Norwegian Business School, and practitioner in the field of future studies.
, one of the authors of the seminal 1972 long-term simulations in ''The Limits to Growth
''The Limits to Growth'' (''LTG'') is a 1972 report that discussed the possibility of exponential economic and population growth with finite supply of resources, studied by computer simulation. The study used the World3 computer model to simula ...
'', offered an alternative scenario in a 2012 book, arguing that traditional projections insufficiently take into account the downward impact of global urbanization on fertility. Randers' "most likely scenario" predicts a peak in the world population in the early 2040s at about 8.1 billion people, followed by decline.
Drivers of population change
The population of a country or area grows or declines through the interaction of three demographic drivers: fertility, mortality, and migration.Fertility
total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
(TFR), a measure of the number of children on average that a woman will bear in her lifetime. With longevity
The word " longevity" is sometimes used as a synonym for "life expectancy" in demography. However, the term ''longevity'' is sometimes meant to refer only to especially long-lived members of a population, whereas ''life expectancy'' is always d ...
trending towards uniform and stable values worldwide, the main driver of future population growth will be the evolution of the fertility rate.
Where fertility is high, demographers generally assume that fertility will decline and eventually stabilize at about two children per woman.
During the period 2015–2020, the average world fertility rate was 2.5 children per woman, about half the level in 1950-1955 (5 children per woman). In the medium variant, global fertility is projected to decline further to 2.2 in 2045-2050 and to 1.9 in 2095–2100.
Mortality
If themortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of de ...
is relatively high and the resulting life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
is therefore relatively low, changes in mortality can have a material impact on population growth. Where the mortality rate is low and life expectancy has therefore risen, a change in mortality will have much less of an effect.
Because child mortality
Child mortality is the mortality of children under the age of five. The child mortality rate, also under-five mortality rate, refers to the probability of dying between birth and exactly five years of age expressed per 1,000 live births.
It en ...
has declined substantially over the last several decades, global life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
at birth, which is estimated to have risen from 47 years in 1950–1955 to 67 years in 2000–2005, is expected to keep rising to reach 77 years in 2045–2050. In the more Developed regions, the projected increase is from 79 years today to 83 years by mid-century. Among the Least Developed countries, where life expectancy today is just under 65 years, it is expected to be 71 years in 2045–2050.
The population of 31 countries or areas, including Ukraine, Romania, Japan and most of the successor states of the Soviet Union, is expected to be lower in 2050 than in 2005.
Migration
Migration can have a significant effect on population change. Global South-South migration accounts for 38% of total migration, and Global South-North for 34%. For example, the United Nations reports that during the period 2010–2020, fourteen countries will have seen a net inflow of more than one million migrants, while ten countries will have seen a net outflow of similar proportions. The largest migratory outflows have been in response to demand for workers in other countries (Bangladesh, Nepal and the Philippines) or to insecurity in the home country (Myanmar, Syria and Venezuela). Belarus, Estonia, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Japan, the Russian Federation, Serbia and Ukraine have experienced a net inflow of migrants over the decade, helping to offset population losses caused by a negativenatural increase
In Demography, the rate of natural increase (RNI), also known as natural population change, is defined as the birth rate minus the death rate of a particular population, over a particular time period. It is typically expressed either as a number ...
(births minus deaths).
World population
2050
The median scenario of the UN 2019 World Population Prospects predicts the following populations per region in 2050 (compared to population in 2000), in billions:After 2050
Projections of population reaching more than one generation into the future are highly speculative: Thus, the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs report of 2004 projected the world population to peak at 9.22 billion in 2075 and then stabilise at a value close to 9 billion;United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs.World Population to 2300
'. 2004. Executive Summary, p. 2. By contrast, a 2014 projection by the United Nations Population Division predicted a population close to 11 billion by 2100 without any declining trend in the foreseeable future.
United Nations projections
The UN Population Division report of 2019 projects world population to continue growing, although at a steadily decreasing rate, and to reach 10.9 billion in 2100 with a growth rate at that time of close to zero. This projected growth of population, like all others, depends on assumptions about vital rates. For example, the UN Population Division assumes that Total fertility rate (TFR) will continue to decline, at varying paces depending on circumstances in individual regions, to a below-replacement level of 1.9 by 2100. Between now (2020) and 2100, regions with TFR currently below this rate, e.g. Europe, will see TFR rise. Regions with TFR above this rate, will see TFR continue to decline.
Other projections
* A 2020 study published byThe Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles, ...
from researchers funded by the Global Burden of Disease Study
The Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD) is a comprehensive regional and global research program of disease burden that assesses mortality and disability from major diseases, injuries, and risk factors. GBD is a collaboration of over 3600 research ...
promotes a lower growth scenario, projecting that world population will peak in 2064 at 9.7 billion and then decline to 8.8 billion in 2100. This projection assumes further advancement of women's rights
Women's rights are the rights and entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countries, ...
globally. In this case TFR is assumed to decline more rapidly than the UN's projection, to reach 1.7 in 2100.
*An analysis from the Wittgenstein Center IIASA predicts global population to peak in 2070 at 9.4 billion and then decline to 9.0 billion in 2100.
*The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) and the Insurance Institute of South Africa (IIASA) project lower fertility in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) in 2100 than the UN. By 2100, the UN projects the population in SSA will reach 3.8 billion, IHME projects 3.1 billion, and IIASA projects 2.6 billion. IHME and IIASA incorporate women's educational attainment in their models of fertility, and in the case of IHME, also consider met need for family planning.
Other assumptions can produce other results. Some of the authors of the 2004 UN report assumed that life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
would rise slowly and continuously. The projections in the report assume this with no upper limit, though at a slowing pace depending on circumstances in individual countries. By 2100, the report assumed life expectancy to be from 66 to 97 years, and by 2300 from 87 to 106 years, depending on the country. Based on that assumption, they expect that rising life expectancy will produce small but continuing population growth by the end of the projections, ranging from 0.03 to 0.07 percent annually. The hypothetical feasibility (and wide availability) of life extension
Life extension is the concept of extending the human life expectancy, lifespan, either modestly through improvements in medicine or dramatically by increasing the maximum lifespan beyond its generally-settled oldest people, limit of 125 years.
S ...
by technological means would further contribute to long term (beyond 2100) population growth.
Evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life fo ...
also suggests the demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory which refers to the historical shift from high birth rates and high death rates in societies with minimal technology, education (especially of women) and economic development, to l ...
may reverse itself and global population may continue to grow in the long term. In addition, recent evidence suggests birth rates may be rising in the 21st century in the developed world.
Growth regions
The table below shows that from 2020 to 2050, the bulk of the world's population growth is predicted to take place in Africa: of the additional 1.9 billion people projected between 2020 and 2050, 1.2 billion will be added in Africa, 0.7 billion in Asia and zero in the rest of the world. Africa's share of global population is projected to grow from 17% in 2020 to 26% in 2050 and 39% by 2100, while the share of Asia will fall from 59% in 2020 to 55% in 2050 and 43% in 2100. The strong growth of the African population will happen regardless of the rate of decrease of fertility, because of the exceptional proportion of young people already living today. For example, the UN projects that the population ofNigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
will surpass that of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
by about 2050.
Thus the population of the More Developed regions is slated to remain mostly unchanged, at 1.3 billion for the remainder of the 21st century. All population growth comes from the Less Developed regions.
The table below breaks out the UN's future population growth predictions by region
The UN projects that between 2020 and 2100 there will be declines in population growth in all six regions; that by 2100 three of them will be undergoing population decline, and the world will have reached zero population growth
Zero population growth, sometimes abbreviated ZPG, is a condition of demographic balance where the number of people in a specified population neither grows nor declines; that is, the number of births plus in-migrants equals the number of death ...
.
Most populous nations by 2050 and 2100
The UN Population Division has calculated the future population of the world's countries, based on current demographic trends. Current (2020)world
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the worl ...
population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ...
is 7.8 billion. The 2019 report projects world population in 2050 to be 9.7 billion people, and possibly as high as 11 billion by the next century, with the following estimates for the top 14 countries in 2020, 2050, and 2100:
From 2017 to 2050, the nine highlighted countries are expected to account for half of the world's projected population increase: India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
, the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territor ...
, and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, listed according to the expected size of their contribution to that projected population growth.
Population projections of the largest metropolitan areas
Largeurban areas
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
are hubs of economic development and innovation, with larger cities underpinning regional economies and local and global sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livi ...
initiatives. Currently, 757 million humans live in the 101 largest cities; these cities are home to 11% of the world's population. By the end of the century, the world population is projected to grow, with estimates ranging from 6.9 billion to 13.1 billion; the percentage of people living in the 101 largest cities is estimated to be 15% to 23%.
The following 101 metropolitan areas with the largest population projections for the years 2025, 2050, 2075, and 2100, according to professors Daniel Hoornweg and Kevin Pope, are listed below.
See also
*Population projection
Population projection, in the field of demography, is an estimate of a future population.
In contrast with intercensal estimates and censuses, which usually involve some sort of field data gathering, projections usually involve mathematical mod ...
* Population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
* Estimates of historical world population
This article lists current estimates of the world population in history. In summary, estimates for the progression of world population since the Late Middle Ages are in the following ranges:
Estimates for pre-modern times are necessarily fraugh ...
* Human overpopulation
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
* Pledge two or fewer (campaign for smaller families)
* List of sovereign states and dependencies by total fertility rate
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby unio ...
* List of countries by number of births
The following list sorts sovereign states and dependent territories and by the total number of births. Figures are from the 2022 revision of the United Nations World Population Prospects report, for the calendar year 2021.
List of countries by n ...
References
{{Navboxes , list = {{Human impact on the environment {{Population {{Population country lists {{biological organisation {{Globalization , state = autocollapse Population statistics Human overpopulation Population ecology Environmental controversies