Progesterone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Progesterone (P4) is an
 Progesterone has key effects via non-genomic signalling on human sperm as they migrate through the female tract before
Progesterone has key effects via non-genomic signalling on human sperm as they migrate through the female tract before
 In mammals, progesterone, like all other
In mammals, progesterone, like all other
 In women, progesterone levels are relatively low during the preovulatory phase of the
In women, progesterone levels are relatively low during the preovulatory phase of the
 Progesterone is a naturally occurring pregnane
Progesterone is a naturally occurring pregnane
 The 16-DPA intermediate is important to the synthesis of many other medically important steroids. A very similar approach can produce 16-DPA from
The 16-DPA intermediate is important to the synthesis of many other medically important steroids. A very similar approach can produce 16-DPA from

 A total synthesis of progesterone was reported in 1971 by W.S. Johnson. The synthesis begins with reacting the phosphonium salt 7 with phenyl lithium to produce the
A total synthesis of progesterone was reported in 1971 by W.S. Johnson. The synthesis begins with reacting the phosphonium salt 7 with phenyl lithium to produce the
Progesterone MS Spectrum
* * {{Navboxes , title = Biological activity , titlestyle = background:#ccccff , list1 = {{GABAA receptor positive modulators {{Glucocorticoid receptor modulators {{Mineralocorticoid receptor modulators {{Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators {{Progesterone receptor modulators {{Sigma receptor modulators {{Xenobiotic-sensing receptor modulators 5α-Reductase inhibitors 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors Alkene derivatives Antimineralocorticoids Diketones GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Glucocorticoids Glycine receptor antagonists Neurosteroids Hepatotoxins Hormones of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis Hormones of the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad axis Hormones of the hypothalamic-pituitary-prolactin axis Hormones of the ovary Hormones of the placenta Hormones of the suprarenal cortex Hormones of the brain Hormones of the pregnant female Human female endocrine system Human hormones Pregnane X receptor agonists Pregnanes Progestogens Prolactin releasers Sex hormones Sigma antagonists Steroid hormones Total synthesis
endogenous
Endogenous substances and processes are those that originate from within a living system such as an organism, tissue, or cell.
In contrast, exogenous substances and processes are those that originate from outside of an organism.
For example, ...
steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
and progestogen sex hormone
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effect ...
involved in the menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs ...
, pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
, and embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
s, including the sex hormone
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effect ...
s and the corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term ''neurosteroid'' was co ...
.
In addition to its role as a natural hormone, progesterone is also used as a medication, such as in combination with estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
for contraception
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
, to reduce the risk of uterine or cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal ...
, in hormone replacement therapy, and in feminizing hormone therapy
Feminizing hormone therapy, also known as transfeminine hormone therapy, is hormone therapy and sex reassignment therapy to change the secondary sex characteristics of transgender people from masculine or androgynous to feminine. It is a co ...
. It was first prescribed in 1934.
Biological activity
Progesterone is the most important progestogen in the body. As a potentagonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
of the nuclear progesterone receptor (nPR) (with an affinity of KD = 1 nM) the resulting effects on ribosomal transcription plays a major role in regulation of female reproduction. In addition, progesterone is an agonist of the more recently discovered membrane progesterone receptors (mPRs), of which the expression has regulation effects in reproduction function (oocyte maturation
Oogenesis, ovogenesis, or oögenesis is the differentiation of the ovum (egg cell) into a cell competent to further develop when fertilized. It is developed from the primary oocyte by maturation. Oogenesis is initiated in the embryonic stage.
O ...
, labor, and sperm motility) and cancer although additional research is required to further define the roles. It also functions as a ligand of the PGRMC1 (progesterone receptor membrane component 1) which impacts tumor progression, metabolic regulation, and viability control of nerve cells
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
. Moreover, progesterone is also known to be an antagonist of the sigma
Sigma (; uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; grc-gre, σίγμα) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used a ...
σ1 receptor, a negative allosteric modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, and a potent antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR). Progesterone prevents MR activation by binding to this receptor with an affinity exceeding even those of aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays a c ...
and glucocorticoids such as cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the '' zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal g ...
and corticosterone
Corticosterone, also known as 17-deoxycortisol and 11β,21-dihydroxyprogesterone, is a 21-carbon steroid hormone of the corticosteroid type produced in the cortex of the adrenal glands. It is of minor importance in humans, except in the very rar ...
, and produces antimineralocorticoid effects, such as natriuresis, at physiological concentrations. In addition, progesterone binds to and behaves as a partial agonist
In pharmacology, partial agonists are drugs that bind to and activate a given receptor, but have only partial efficacy at the receptor relative to a full agonist. They may also be considered ligands which display both agonistic and antagonis ...
of the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), albeit with very low potency ( EC50 >100-fold less relative to cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the '' zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal g ...
).
Progesterone, through its neurosteroid
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term ''neurosteroid'' was co ...
active metabolite An active metabolite is an active form of a drug after it has been processed by the body.
Metabolites of drugs
An active metabolite results when a drug is metabolized by the body into a modified form which continues to produce effects in the body ...
s such as 5α-dihydroprogesterone
5α-Dihydroprogesterone (5α-DHP, allopregnanedione, or 5α-pregnane-3,20-dione) is an endogenous progestogen and neurosteroid that is synthesized from progesterone. It is also an intermediate in the synthesis of allopregnanolone and isopregnano ...
and allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone is a naturally occurring neurosteroid which is made in the body from the hormone progesterone. As a medication, allopregnanolone is referred to as brexanolone, sold under the brand name Zulresso, and used to treat postpartum ...
, acts indirectly as a positive allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor.
Progesterone and some of its metabolites, such as 5β-dihydroprogesterone, are agonists of the pregnane X receptor
In the field of molecular biology, the pregnane X receptor (PXR), also known as the steroid and xenobiotic sensing nuclear receptor (SXR) or nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2 (NR1I2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ' ...
(PXR), albeit weakly so ( EC50 >10 μM). In accordance, progesterone induces several hepatic cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various co ...
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s, such as CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules ( xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from ...
, especially during pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
when concentrations are much higher than usual. Perimenopausal women have been found to have greater CYP3A4 activity relative to men and postmenopausal women, and it has been inferred that this may be due to the higher progesterone levels present in perimenopausal women.
Progesterone modulates the activity of CatSper
The cation channels of sperm also known as Catsper channels or CatSper, are ion channels that are related to the two-pore channels and distantly related to TRP channels. The four members of this family form voltage-gated Ca2+ channels that ...
(cation channels of sperm) voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Since eggs release progesterone, sperm may use progesterone as a homing signal to swim toward eggs (chemotaxis
Chemotaxis (from '' chemo-'' + '' taxis'') is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemica ...
). As a result, it has been suggested that substances that block the progesterone binding site on CatSper channels could potentially be used in male contraception
Male contraceptives, also known as male birth control, are methods of preventing pregnancy that solely involve the male physiology. The most common kinds of male contraception include condoms, outercourse, and vasectomy. In domestic animals, cast ...
.
Biological function
Hormonal interactions
Progesterone has a number of physiological effects that are amplified in the presence ofestrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
s. Estrogens through estrogen receptors (ERs) induce or upregulate
In the biological context of organisms' production of gene products, downregulation is the process by which a cell decreases the quantity of a cellular component, such as RNA or protein, in response to an external stimulus. The complementary pro ...
the expression of the PR. One example of this is in breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.
In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and sec ...
tissue, where estrogens allow progesterone to mediate lobuloalveolar
A mammary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity") is a small cavity or sac found in the mammary gland. Mammary alveoli are the site of milk production and storage in the mammary gland. Mammary alveoli cluster into g ...
development.
Elevated levels of progesterone potently reduce the sodium-retaining activity of aldosterone, resulting in natriuresis and a reduction in extracellular fluid volume. Progesterone withdrawal, on the other hand, is associated with a temporary increase in sodium retention (reduced natriuresis, with an increase in extracellular fluid volume) due to the compensatory increase in aldosterone production, which combats the blockade of the mineralocorticoid receptor by the previously elevated level of progesterone.
Reproductive system
 Progesterone has key effects via non-genomic signalling on human sperm as they migrate through the female tract before
Progesterone has key effects via non-genomic signalling on human sperm as they migrate through the female tract before fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
occurs, though the receptor(s) as yet remain unidentified. Detailed characterisation of the events occurring in sperm in response to progesterone has elucidated certain events including intracellular calcium transients and maintained changes, slow calcium oscillations, now thought to possibly regulate motility. It is produced by the ovaries. Progesterone has also been shown to demonstrate effects on octopus spermatozoa.
Progesterone is sometimes called the "hormone of pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
", and it has many roles relating to the development of the fetus:
* Progesterone converts the endometrium to its secretory stage to prepare the uterus for implantation. At the same time progesterone affects the vaginal epithelium and cervical mucus
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during ...
, making it thick and impenetrable to sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
. Progesterone is anti- mitogenic in endometrial epithelial cells, and as such, mitigates the tropic effects of estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
. If pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels will decrease, leading, in the woman, to menstruate
Menstruation (also known as a period, among other colloquial terms) is the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina. The menstrual cycle is characterized by the rise and fall of ho ...
. Normal menstrual bleeding is progesterone-withdrawal bleeding. If ovulation does not occur and the corpus luteum does not develop, levels of progesterone may be low, leading to anovulatory dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
* During implantation and gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pr ...
, progesterone appears to decrease the maternal immune response to allow for the acceptance of the pregnancy.
* Progesterone decreases contractility of the uterine smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit ...
. This effect contributes to prevention of preterm labor.
* A drop in progesterone levels is possibly one step that facilitates the onset of labor.
*In addition, progesterone inhibits lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The proces ...
during pregnancy. The fall in progesterone levels following delivery is one of the triggers for milk production.
The fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal dev ...
metabolizes placental progesterone in the production of adrenal
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
steroids.
Breasts
Lobuloalveolar development
Progesterone plays an important role in breast development in women. In conjunction withprolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secreted from the pi ...
, it mediates lobuloalveolar
A mammary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity") is a small cavity or sac found in the mammary gland. Mammary alveoli are the site of milk production and storage in the mammary gland. Mammary alveoli cluster into g ...
maturation of the mammary gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in ...
s during pregnancy to allow for milk production and thus lactation
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The proces ...
and breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that bre ...
of offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by a single organism or, in the case of sexual reproduction, two organisms. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny in a more general way. This ca ...
following parturition (childbirth). Estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
induces expression of the PR in breast tissue and hence progesterone is dependent on estrogen to mediate lobuloalveolar development. It has been found that is a critical downstream mediator of progesterone-induced lobuloalveolar maturation. RANKL knockout mice show an almost identical mammary phenotype to PR knockout mice, including normal mammary ductal development but complete failure of the development of lobuloalveolar structures.
Ductal development
Though to a far lesser extent than estrogen, which is the major mediator of mammary ductal development (via the ERα), progesterone may be involved in ductal development of the mammary glands to some extent as well. PR knockout mice or mice treated with the PR antagonistmifepristone
Mifepristone, also known as RU-486, is a medication typically used in combination with misoprostol to bring about a medical abortion during pregnancy and manage early miscarriage. This combination is 97% effective during the first 63 days of ...
show delayed although otherwise normal mammary ductal development at puberty. In addition, mice modified to have overexpression of PRA display ductal hyperplasia, and progesterone induces ductal growth in the mouse mammary gland. Progesterone mediates ductal development mainly via induction of the expression of amphiregulin, the same growth factor that estrogen primarily induces the expression of to mediate ductal development. These animal findings suggest that, while not essential for full mammary ductal development, progesterone seems to play a potentiating or accelerating role in estrogen-mediated mammary ductal development.
Breast cancer risk
Progesterone also appears to be involved in the pathophysiology ofbreast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
, though its role, and whether it is a promoter or inhibitor of breast cancer risk, has not been fully elucidated. Most progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic'' progestogen. Pro ...
s, or synthetic Synthetic things are composed of multiple parts, often with the implication that they are artificial. In particular, 'synthetic' may refer to:
Science
* Synthetic chemical or compound, produced by the process of chemical synthesis
* Synthetic ...
progestogens, like medroxyprogesterone acetate, have been found to increase the risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women in combination with estrogen as a component of menopausal hormone therapy. The combination of natural oral progesterone or the atypical progestin dydrogesterone with estrogen has been associated with less risk of breast cancer than progestins plus estrogen. However, this may simply be an artifact of the low progesterone levels produced with oral progesterone. More research is needed on the role of progesterone in breast cancer.
Skin health
The estrogen receptor, as well as the progesterone receptor, have been detected in theskin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, including in keratinocytes and fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells ...
s. At menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
and thereafter, decreased levels of female sex hormone
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effect ...
s result in atrophy, thinning, and increased wrinkling
A wrinkle, also known as a rhytid, is a fold, ridge or crease in an otherwise smooth surface, such as on skin or fabric. Skin wrinkles typically appear as a result of ageing processes such as glycation, habitual sleeping positions, loss of bo ...
of the skin and a reduction in skin elasticity, firmness, and strength. These skin changes constitute an acceleration in skin aging and are the result of decreased collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whol ...
content, irregularities in the morphology of epidermal skin cells, decreased ground substance between skin fibers, and reduced capillaries and blood flow. The skin also becomes more dry during menopause, which is due to reduced skin hydration Hydration may refer to:
* Hydrate, a substance that contains water
* Hydration enthalpy, energy released through hydrating a substance
* Hydration reaction, a chemical addition reaction where a hydroxyl group and proton are added to a compound
* ...
and surface lipids (sebum production). Along with chronological aging and photoaging, estrogen deficiency in menopause is one of the three main factors that predominantly influences skin aging.
Hormone replacement therapy, consisting of systemic treatment with estrogen alone or in combination with a progestogen, has well-documented and considerable beneficial effects on the skin of postmenopausal women. These benefits include increased skin collagen content, skin thickness and elasticity, and skin hydration and surface lipids. Topical estrogen has been found to have similar beneficial effects on the skin. In addition, a study has found that topical 2% progesterone cream significantly increases skin elasticity and firmness and observably decreases wrinkles in peri- and postmenopausal women. Skin hydration and surface lipids, on the other hand, did not significantly change with topical progesterone. These findings suggest that progesterone, like estrogen, also has beneficial effects on the skin, and may be independently protective against skin aging.
Sexuality
Libido
Progesterone and itsneurosteroid
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term ''neurosteroid'' was co ...
active metabolite An active metabolite is an active form of a drug after it has been processed by the body.
Metabolites of drugs
An active metabolite results when a drug is metabolized by the body into a modified form which continues to produce effects in the body ...
allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone is a naturally occurring neurosteroid which is made in the body from the hormone progesterone. As a medication, allopregnanolone is referred to as brexanolone, sold under the brand name Zulresso, and used to treat postpartum ...
appear to be importantly involved in libido in females.
Homosexuality
Dr. Diana Fleischman, of the University of Portsmouth, and colleagues looked for a relationship between progesterone and sexual attitudes in 92 women. Their research, published in the Archives of Sexual Behavior found that women who had higher levels of progesterone scored higher on a questionnaire measuring homoerotic motivation. They also found that men who had high levels of progesterone were more likely to have higher homoerotic motivation scores after affiliative priming compared to men with low levels of progesterone.Nervous system
Progesterone, likepregnenolone
Pregnenolone (P5), or pregn-5-en-3β-ol-20-one, is an endogenous steroid and precursor/metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of most of the steroid hormones, including the progestogens, androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocor ...
and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), belongs to an important group of endogenous steroids called neurosteroid
Neurosteroids, also known as neuroactive steroids, are endogenous or exogenous steroids that rapidly alter neuronal excitability through interaction with ligand-gated ion channels and other cell surface receptors. The term ''neurosteroid'' was co ...
s. It can be metabolized within all parts of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
.
Neurosteroids are neuromodulators, and are neuroprotective, neurogenic, and regulate neurotransmission and myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can ...
ation. The effects of progesterone as a neurosteroid are mediated predominantly through its interactions with non-nuclear PRs, namely the mPRs and PGRMC1, as well as certain other receptors, such as the σ1 and nACh receptors.
Brain damage
Previous studies have shown that progesterone supports the normal development of neurons in the brain, and that the hormone has a protective effect on damaged brain tissue. It has been observed in animal models that females have reduced susceptibility to traumatic brain injury and this protective effect has been hypothesized to be caused by increased circulating levels ofestrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
and progesterone in females.
Proposed mechanism
The mechanism of progesterone protective effects may be the reduction of inflammation that follows brain trauma and hemorrhage. Damage incurred by traumatic brain injury is believed to be caused in part by mass depolarization leading to excitotoxicity. One way in which progesterone helps to alleviate some of this excitotoxicity is by blocking the voltage-dependent calcium channels that triggerneurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neu ...
release. It does so by manipulating the signaling pathways of transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
s involved in this release. Another method for reducing the excitotoxicity is by up-regulating the GABAA, a widespread inhibitory neurotransmitter receptor.
Progesterone has also been shown to prevent apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
in neurons, a common consequence of brain injury. It does so by inhibiting enzymes involved in the apoptosis pathway specifically concerning the mitochondria, such as activated caspase 3 and cytochrome c
The cytochrome complex, or cyt ''c'', is a small hemeprotein found loosely associated with the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. It belongs to the cytochrome c family of proteins and plays a major role in cell apoptosis. Cytochrome c is hig ...
.
Not only does progesterone help prevent further damage, it has also been shown to aid in neuroregeneration
Neuroregeneration refers to the regrowth or repair of nervous tissues, cells or cell products. Such mechanisms may include generation of new neurons, glia, axons, myelin, or synapses. Neuroregeneration differs between the peripheral nervous syst ...
. One of the serious effects of traumatic brain injury includes edema. Animal studies show that progesterone treatment leads to a decrease in edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
levels by increasing the concentration of macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
s and microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
sent to the injured tissue. This was observed in the form of reduced leakage from the blood brain barrier
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the ...
in secondary recovery in progesterone treated rats. In addition, progesterone was observed to have antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubrica ...
properties, reducing the concentration of oxygen free radicals faster than without. There is also evidence that the addition of progesterone can also help remyelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can ...
ate damaged axons
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
due to trauma, restoring some lost neural signal conduction. Another way progesterone aids in regeneration includes increasing the circulation of endothelial progenitor cells in the brain. This helps new vasculature to grow around scar tissue which helps repair the area of insult.
Addiction
Progesterone enhances the function ofserotonin receptor
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory ne ...
s in the brain, so an excess or deficit of progesterone has the potential to result in significant neurochemical issues. This provides an explanation for why some people resort to substances that enhance serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and va ...
activity such as nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and '' Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is use ...
, alcohol, and cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternative ...
when their progesterone levels fall below optimal levels.
* Sex differences in hormone levels may induce women to respond differently than men to nicotine. When women undergo cyclic changes or different hormonal transition phases (menopause, pregnancy, adolescence), there are changes in their progesterone levels. Therefore, females have an increased biological vulnerability to nicotine's reinforcing effects compared to males and progesterone may be used to counter this enhanced vulnerability. This information supports the idea that progesterone can affect behavior.
* Similar to nicotine, cocaine also increases the release of dopamine in the brain. The neurotransmitter is involved in the reward center and is one of the main neurotransmitters involved with substance abuse and reliance. In a study of cocaine users, it was reported that progesterone reduced craving and the feeling of being stimulated by cocaine. Thus, progesterone was suggested as an agent that decreases cocaine craving by reducing the dopaminergic properties of the drug.
Societal
In a 2012 University of Amsterdam study of 120 women, women's luteal phase (higher levels of progesterone, and increasing levels of estrogen) was correlated with lower level of competitive behavior in gambling and math contest scenarios, while their premenstrual phase (sharply-decreasing levels of progesterone, and decreasing levels of estrogen) was correlated with a higher level of competitive behavior.Other effects
* Progesterone also has a role in skin elasticity and bone strength, in respiration, in nerve tissue and infemale sexuality
Human female sexuality encompasses a broad range of behaviors and processes, including female sexual identity and Human sexual activity, sexual behavior, the physiological, psychological, social, cultural, political, and spiritual or religious ...
, and the presence of progesterone receptors in certain muscle and fat tissue may hint at a role in sexually dimorphic proportions of those.
* During pregnancy, progesterone is said to decrease uterine irritability.
* During pregnancy, progesterone helps to suppress immune responses of the mother to fetal antigens, which prevents rejection of the fetus.
* Progesterone raises epidermal growth factor-1
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a protein that stimulates cell growth and differentiation by binding to its receptor, EGFR. Human EGF is 6-k Da and has 53 amino acid residues and three intramolecular disulfide bonds.
EGF was originally desc ...
(EGF-1) levels, a factor often used to induce proliferation, and used to sustain cultures, of stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of ...
s.
* Progesterone increases core temperature (thermogenic function) during ovulation.
* Progesterone reduces spasm and relaxes smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit ...
. Bronchi are widened and mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
regulated. (PRs are widely present in submucosal tissue.)
* Progesterone acts as an antiinflammatory agent and regulates the immune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which coul ...
.
* Progesterone reduces gall-bladder activity.
* Progesterone normalizes blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
clotting and vascular tone, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
levels, cell oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements ...
levels, and use of fat stores for energy.
* Progesterone may affect gum health, increasing risk of gingivitis (gum inflammation).
* Progesterone appears to prevent endometrial cancer
Endometrial cancer is a cancer that arises from the endometrium (the lining of the uterus or womb). It is the result of the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. The first sign is most ...
(involving the uterine lining) by regulating the effects of estrogen.
* Progesterone plays an important role in the signaling of insulin release and pancreatic function, and may affect the susceptibility to diabetes or gestational diabetes.
Biochemistry
Biosynthesis
steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s, is synthesized from pregnenolone
Pregnenolone (P5), or pregn-5-en-3β-ol-20-one, is an endogenous steroid and precursor/metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of most of the steroid hormones, including the progestogens, androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocor ...
, which itself is derived from cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell memb ...
.
Cholesterol undergoes double oxidation to produce 22''R''-hydroxycholesterol and then 20α,22''R''-dihydroxycholesterol. This vicinal diol is then further oxidized with loss of the side chain starting at position C22 to produce pregnenolone. This reaction is catalyzed by cytochrome
Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central Fe atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of ...
P450scc.
The conversion of pregnenolone to progesterone takes place in two steps. First, the 3β-hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydrox ...
group is oxidized to a keto group and second, the double bond is moved to C4, from C5 through a keto/enol
In organic chemistry, alkenols (shortened to enols) are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is represented as an alkene ( olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond (). T ...
tautomer
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hy ...
ization reaction. This reaction is catalyzed by 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/δ5-4-isomerase.
Progesterone in turn is the precursor of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone
Aldosterone is the main mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It is essential for sodium conservation in the kidney, salivary glands, sweat glands, and colon. It plays a c ...
, and after conversion to 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, of cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, in the glucocorticoid class of hormones. When used as a medication, it is known as hydrocortisone.
It is produced in many animals, mainly by the '' zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal g ...
and androstenedione
Androstenedione, or 4-androstenedione (abbreviated as A4 or Δ4-dione), also known as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous weak androgen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of estrone and of testosterone from dehy ...
. Androstenedione can be converted to testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristi ...
, estrone, and estradiol, highlighting the critical role of progesterone in testosterone synthesis.
Pregnenolone and progesterone can also be synthesized by yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
.
Approximately 25 mg of progesterone is secreted from the ovaries per day in women, while the adrenal glands produce about 2 mg of progesterone per day.
Distribution
Progesterone binds extensively toplasma protein
Blood-proteins, also termed plasma proteins, are proteins present in blood plasma. They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other bl ...
s, including albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Album ...
(50–54%) and transcortin (43–48%). It has similar affinity for albumin relative to the PR.
Metabolism
Themetabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run ...
of progesterone is rapid and extensive and occurs mainly in the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
, though enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s that metabolize progesterone are also expressed widely in the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
, skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, and various other extrahepatic tissues. Progesterone has an elimination half-life
Biological half-life (also known as elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration ( Cmax) to half of Cmax in the b ...
of only approximately 5 minutes in circulation. The metabolism of progesterone is complex, and it may form as many as 35 different unconjugated metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, ...
s when it is ingested orally. Progesterone is highly susceptible to enzymatic reduction via reductase
A reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes a reduction reaction.
Examples
* 5α-Reductase
* 5β-Reductase
* Dihydrofolate reductase
* HMG-CoA reductase
* Methemoglobin reductase
* Ribonucleotide reductase
* Thioredoxin reductase
* ''E. coli' ...
s and hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases due to its double bond (between the C4 and C5 positions) and its two ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double b ...
s (at the C3 and C20 positions).
The major metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical ...
of progesterone is reduction by 5α-reductase
5α-Reductases, also known as 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenases, are enzymes involved in steroid metabolism. They participate in three metabolic pathways: bile acid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism. There are three isozymes o ...
and 5β-reductase into the dihydrogenated 5α-dihydroprogesterone
5α-Dihydroprogesterone (5α-DHP, allopregnanedione, or 5α-pregnane-3,20-dione) is an endogenous progestogen and neurosteroid that is synthesized from progesterone. It is also an intermediate in the synthesis of allopregnanolone and isopregnano ...
and 5β-dihydroprogesterone, respectively. This is followed by the further reduction of these metabolites via 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase into the tetrahydrogenated allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone is a naturally occurring neurosteroid which is made in the body from the hormone progesterone. As a medication, allopregnanolone is referred to as brexanolone, sold under the brand name Zulresso, and used to treat postpartum ...
, pregnanolone
Pregnanolone, also known as eltanolone, is an endogenous inhibitory neurosteroid which is produced in the body from progesterone. It is closely related to allopregnanolone, which has similar properties.
Biological activity
Pregnanolone is a ...
, isopregnanolone
Isopregnanolone, also known as isoallopregnanolone and epiallopregnanolone, as well as sepranolone (), and as 3β-hydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one or 3β,5α-tetrahydroprogesterone (3β,5α-THP), is an endogenous neurosteroid and a natural 3β-epimer of ...
, and epipregnanolone
Epipregnanolone, also known as 3β-hydroxy-5β-pregnan-20-one, 3β,5β-tetrahydroprogesterone, or 3β,5β-THP, is an endogenous neurosteroid. It acts as a negative allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor and reverses the effects of potentiato ...
. Subsequently, 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 20β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
In enzymology, a 3alpha(or 20beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
: androstan-3alpha,17beta-diol + NAD+ \rightleftharpoons 17beta-hydroxyandrostan-3-one + NADH + H+
Thus, the two substrates of ...
reduce these metabolites to form the corresponding hexahydrogenated pregnanediols (eight different isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
Is ...
s in total), which are then conjugated via glucuronidation
Glucuronidation is often involved in drug metabolism of substances such as drugs, pollutants, bilirubin, androgens, estrogens, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, fatty acid derivatives, retinoids, and bile acids. These linkages involve gl ...
and/or sulfation, released from the liver into circulation, and excreted by the kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
s into the urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellul ...
. The major metabolite of progesterone in the urine is the 3α,5β,20α isomer of pregnanediol glucuronide, which has been found to constitute 15 to 30% of an injection of progesterone. Other metabolites of progesterone formed by the enzymes in this pathway include 3α-dihydroprogesterone, 3β-dihydroprogesterone, 20α-dihydroprogesterone
20α-Dihydroprogesterone (20α-DHP), also known as 20α-hydroxyprogesterone (20α-OHP), is a naturally occurring, endogenous progestogen. It is a metabolite of progesterone, formed by the 20α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases (20α-HSDs) AKR1C1, ...
, and 20β-dihydroprogesterone, as well as various combination products of the enzymes aside from those already mentioned. Progesterone can also first be hydroxylated (see below) and then reduced. Endogenous progesterone is metabolized approximately 50% into 5α-dihydroprogesterone in the corpus luteum, 35% into 3β-dihydroprogesterone in the liver, and 10% into 20α-dihydroprogesterone.
Relatively small portions of progesterone are hydroxylated via 17α-hydroxylase (CYP17A1) and 21-hydroxylase (CYP21A2) into 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 11-deoxycorticosterone
11-Deoxycorticosterone (DOC), or simply deoxycorticosterone, also known as 21-hydroxyprogesterone, as well as desoxycortone (INN), deoxycortone, and cortexone, is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland that possesses mineralocorticoid ...
(21-hydroxyprogesterone), respectively, and pregnanetriols are formed secondarily to 17α-hydroxylation. Even smaller amounts of progesterone may be also hydroxylated via 11β-hydroxylase (CYP11B1) and to a lesser extent via aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) into 11β-hydroxyprogesterone
11β-Hydroxyprogesterone (11β-OHP), also known as 21-deoxycorticosterone, as well as 11β-hydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, is a naturally occurring, endogenous steroid and derivative of progesterone. It is a potent mineralocorticoid. Syntheses of 1 ...
. In addition, progesterone can be hydroxylated in the liver by other cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various co ...
enzymes which are not steroid-specific. 6β-Hydroxylation, which is catalyzed mainly by CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules ( xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from ...
, is the major transformation, and is responsible for approximately 70% of cytochrome P450-mediated progesterone metabolism. Other routes include 6α-, 16α-, and 16β-hydroxylation. However, treatment of women with ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral among others, is an antiandrogen and antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin infections such as tinea, cutaneous ca ...
, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, had minimal effects on progesterone levels, producing only a slight and non-significant increase, and this suggests that cytochrome P450 enzymes play only a small role in progesterone metabolism.
Levels
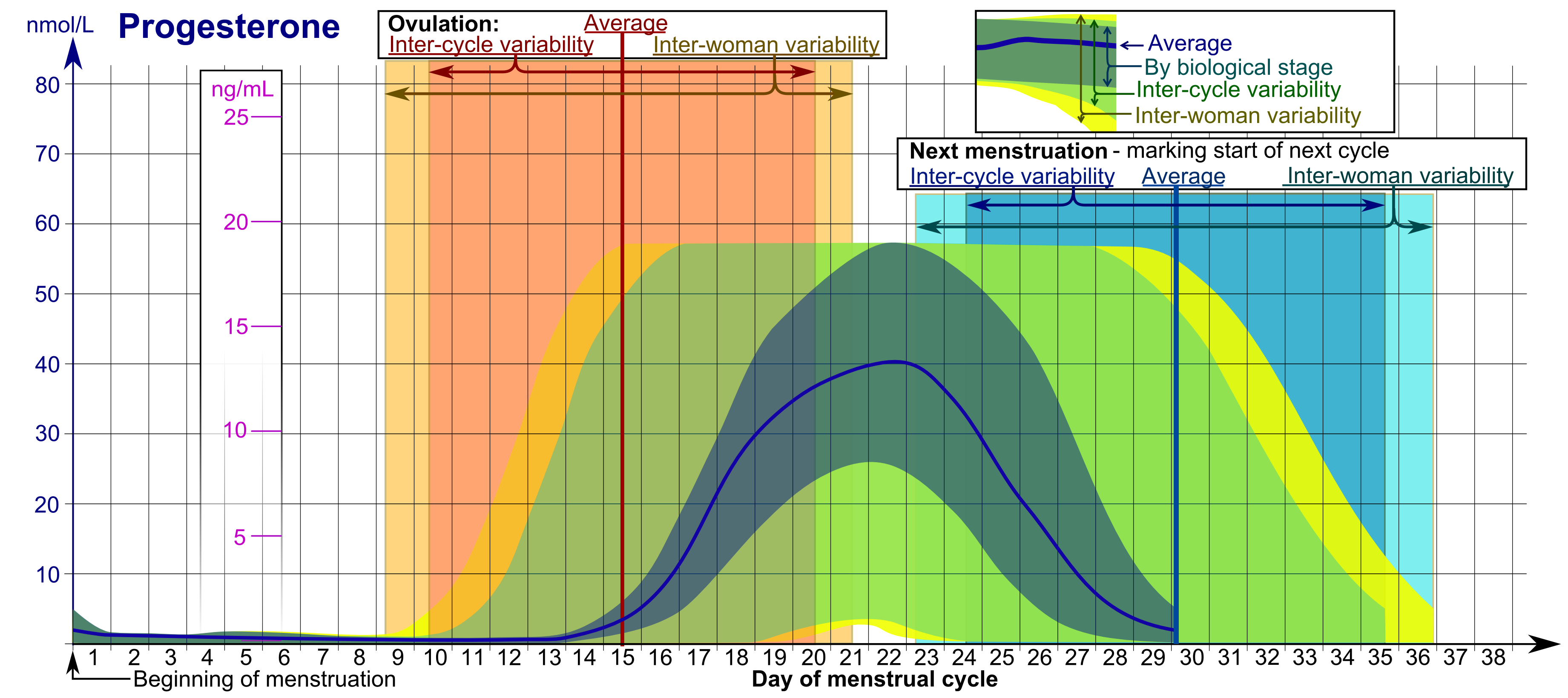
 In women, progesterone levels are relatively low during the preovulatory phase of the
In women, progesterone levels are relatively low during the preovulatory phase of the menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs ...
, rise after ovulation, and are elevated during the luteal phase, as shown in the diagram above. Progesterone levels tend to be less than 2 ng/mL prior to ovulation and greater than 5 ng/mL after ovulation. If pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
occurs, human chorionic gonadotropin
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo (syncytiotrophoblast initially), which eventually forms the placenta after implantatio ...
is released, maintaining the corpus luteum and allowing it to maintain levels of progesterone. Between 7 and 9 weeks, the placenta begins to produce progesterone in place of the corpus luteum in a process called the luteal-placental shift.
After the luteal-placental shift, progesterone levels start to rise further and may reach 100 to 200 ng/mL at term. Whether a decrease in progesterone levels is critical for the initiation of labor has been argued and may be species-specific. After delivery of the placenta and during lactation, progesterone levels are very low.
Progesterone levels are low in children and postmenopausal women. Adult males have levels similar to those in women during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
Ranges
Blood test results should always be interpreted using the reference ranges provided by the laboratory that performed the results. Example reference ranges are listed below.
Sources
Animal
Progesterone is produced in high amounts in theovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
(by the corpus luteum) from the onset of puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a ...
to menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often d ...
, and is also produced in smaller amounts by the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex ...
s after the onset of adrenarche in both males and females. To a lesser extent, progesterone is produced in nervous tissue
Nervous tissue, also called neural tissue, is the main tissue component of the nervous system. The nervous system regulates and controls body functions and activity. It consists of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) comprising the bra ...
, especially in the brain, and in adipose (fat) tissue, as well.
During human pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
, progesterone is produced in increasingly high amounts by the ovaries and placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mate ...
. At first, the source is the corpus luteum that has been "rescued" by the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo (syncytiotrophoblast initially), which eventually forms the placenta after implantatio ...
(hCG) from the conceptus. However, after the 8th week, production of progesterone shifts to the placenta. The placenta utilizes maternal cholesterol as the initial substrate, and most of the produced progesterone enters the maternal circulation, but some is picked up by the fetal circulation and used as substrate for fetal corticosteroids. At term the placenta produces about 250 mg progesterone per day.
An additional animal source of progesterone is milk products. After consumption of milk products the level of bioavailable progesterone goes up.
Plants
In at least one plant, '' Juglans regia'', progesterone has been detected. In addition, progesterone-likesteroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
s are found in '' Dioscorea mexicana''. ''Dioscorea mexicana'' is a plant that is part of the yam family native to Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
. It contains a steroid called diosgenin
Diosgenin, a phytosteroid sapogenin, is the product of hydrolysis by acids, strong bases, or enzymes of saponins, extracted from the tubers of '' Dioscorea'' wild yam species, such as the Kokoro. The sugar-free ( aglycone) product of such hy ...
that is taken from the plant and is converted into progesterone. Diosgenin and progesterone are also found in other ''Dioscorea
''Dioscorea'' is a genus of over 600 species of flowering plants in the family Dioscoreaceae, native throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. The vast majority of the species are tropical, with only a few species extendi ...
'' species, as well as in other plants that are not closely related, such as fenugreek
Fenugreek (; ''Trigonella foenum-graecum'') is an annual plant in the family Fabaceae, with leaves consisting of three small obovate to oblong leaflets. It is cultivated worldwide as a semiarid crop. Its seeds and leaves are common ingredients ...
.
Another plant that contains substances readily convertible to progesterone is ''Dioscorea pseudojaponica
''Dioscorea'' is a genus of over 600 species of flowering plants in the family Dioscoreaceae, native throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. The vast majority of the species are tropical, with only a few species extending ...
'' native to Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the no ...
. Research has shown that the Taiwanese yam contains saponins — steroids that can be converted to diosgenin and thence to progesterone.
Many other ''Dioscorea'' species of the yam family contain steroidal substances from which progesterone can be produced. Among the more notable of these are '' Dioscorea villosa'' and ''Dioscorea polygonoides
''Dioscorea'' is a genus of over 600 species of flowering plants in the family Dioscoreaceae, native throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. The vast majority of the species are tropical, with only a few species extend ...
''. One study showed that the ''Dioscorea villosa'' contains 3.5% diosgenin. ''Dioscorea polygonoides
''Dioscorea'' is a genus of over 600 species of flowering plants in the family Dioscoreaceae, native throughout the tropical and warm temperate regions of the world. The vast majority of the species are tropical, with only a few species extend ...
'' has been found to contain 2.64% diosgenin as shown by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), ...
. Many of the ''Dioscorea'' species that originate from the yam family grow in countries that have tropical and subtropical climates.
Medical use
Progesterone is used as amedication
A medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and ...
. It is used in combination with estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal ac ...
s mainly in hormone therapy
Hormone therapy or hormonal therapy is the use of hormones in medical treatment. Treatment with hormone antagonists may also be referred to as hormonal therapy or antihormone therapy. The most general classes of hormone therapy are oncologic ho ...
for menopausal symptom
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showi ...
s and low sex hormone levels in women. It is also used in women to support pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but ...
and fertility
Fertility is the capability to produce offspring through reproduction following the onset of sexual maturity. The fertility rate is the average number of children born by a female during her lifetime and is quantified demographically. Ferti ...
and to treat gynecological disorders. Progesterone has been shown to prevent miscarriage in women with 1) vaginal bleeding early in their current pregnancy and 2) a previous history of miscarriage. Progesterone can be taken by mouth, through the vagina, and by injection into muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of mus ...
or fat, among other routes.
Chemistry
 Progesterone is a naturally occurring pregnane
Progesterone is a naturally occurring pregnane steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
and is also known as pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione. It has a double bond ( 4-ene) between the C4 and C5 positions and two ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double b ...
groups (3,20- dione), one at the C3 position and the other at the C20 position.
Synthesis
Progesterone is commercially produced by semisynthesis. Two main routes are used: one from yamdiosgenin
Diosgenin, a phytosteroid sapogenin, is the product of hydrolysis by acids, strong bases, or enzymes of saponins, extracted from the tubers of '' Dioscorea'' wild yam species, such as the Kokoro. The sugar-free ( aglycone) product of such hy ...
first pioneered by Marker in 1940, and one based on soy phytosterol
Phytosterols are phytosteroids, similar to cholesterol, that serve as structural components of biological membranes of plants. They encompass plant sterols and stanols. More than 250 sterols and related compounds have been identified. Free phyt ...
s scaled up in the 1970s. Additional (not necessarily economical) semisyntheses of progesterone have also been reported starting from a variety of steroids. For the example, cortisone can be simultaneously deoxygenated at the C-17 and C-21 position by treatment with iodotrimethylsilane in chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with formula C H Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to PTFE. It is also a precursor to various ...
to produce 11-keto-progesterone (ketogestin), which in turn can be reduced at position-11 to yield progesterone.
Marker semisynthesis
An economicalsemisynthesis
Semisynthesis, or partial chemical synthesis, is a type of chemical synthesis that uses chemical compounds isolated from natural sources (such as microbial cell cultures or plant material) as the starting materials to produce novel compounds with ...
of progesterone from the plant steroid diosgenin
Diosgenin, a phytosteroid sapogenin, is the product of hydrolysis by acids, strong bases, or enzymes of saponins, extracted from the tubers of '' Dioscorea'' wild yam species, such as the Kokoro. The sugar-free ( aglycone) product of such hy ...
isolated from yams was developed by Russell Marker in 1940 for the Parke-Davis
Parke-Davis is a subsidiary of the pharmaceutical company Pfizer. Although Parke, Davis & Co. is no longer an independent corporation, it was once America's oldest and largest drug maker, and played an important role in medical history. In 19 ...
pharmaceutical company. This synthesis is known as the Marker degradation.
 The 16-DPA intermediate is important to the synthesis of many other medically important steroids. A very similar approach can produce 16-DPA from
The 16-DPA intermediate is important to the synthesis of many other medically important steroids. A very similar approach can produce 16-DPA from solanine
Solanine is a glycoalkaloid poison found in species of the nightshade family within the genus '' Solanum'', such as the potato (''Solanum tuberosum''), the tomato (''Solanum lycopersicum''), and the eggplant (''Solanum melongena''). It can occ ...
.
Soy semisynthesis
Progesterone can also be made from the stigmasterol found insoybean oil
Soybean oil (British English: soyabean oil) is a vegetable oil extracted from the seeds of the soybean (''Glycine max''). It is one of the most widely consumed cooking oils and the second most consumed vegetable oil. As a drying oil, processe ...
also. c.f. Percy Julian.

Total synthesis
 A total synthesis of progesterone was reported in 1971 by W.S. Johnson. The synthesis begins with reacting the phosphonium salt 7 with phenyl lithium to produce the
A total synthesis of progesterone was reported in 1971 by W.S. Johnson. The synthesis begins with reacting the phosphonium salt 7 with phenyl lithium to produce the phosphonium ylide
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent. Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Most of ...
8. The ylide 8 is reacted with an aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl gro ...
to produce the alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic ...
9. The ketal protecting groups of 9 are hydrolyzed to produce the diketone 10, which in turn is cyclized to form the cyclopentenone 11. The ketone of 11 is reacted with methyl lithium to yield the tertiary alcohol 12, which in turn is treated with acid to produce the tertiary cation 13. The key step of the synthesis is the π-cation cyclization of 13 in which the B-, C-, and D-rings of the steroid are simultaneously formed to produce 14. This step resembles the cationic cyclization reaction used in the biosynthesis of steroids and hence is referred to as ''biomimetic''. In the next step the enol
In organic chemistry, alkenols (shortened to enols) are a type of reactive structure or intermediate in organic chemistry that is represented as an alkene ( olefin) with a hydroxyl group attached to one end of the alkene double bond (). T ...
orthoester is hydrolyzed to produce the ketone 15. The cyclopentene A-ring is then opened by oxidizing with ozone to produce 16. Finally, the diketone 17 undergoes an intramolecular aldol condensation by treating with aqueous potassium hydroxide to produce progesterone.
History
George W. Corner
George Washington Corner FRS FRSE (12 December 1889 – 28 September 1981) was an American physician, embryologist and pioneer of the contraceptive pill. He received an outstanding ten honorary degrees from various universities. He played a criti ...
and Willard M. Allen discovered the hormonal action of progesterone in 1929. By 1931–1932, nearly pure crystalline material of high progestational activity had been isolated from the corpus luteum of animals, and by 1934, pure crystalline progesterone had been refined and obtained and the chemical structure
A chemical structure determination includes a chemist's specifying the molecular geometry and, when feasible and necessary, the electronic structure of the target molecule or other solid. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of ...
of progesterone was determined. This was achieved by Adolf Butenandt at the ''Chemisches Institut'' of Technical University in Danzig, who extracted this new compound from several thousand liters of urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellul ...
.
Chemical synthesis
As a topic of chemistry, chemical synthesis (or combination) is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In mod ...
of progesterone from stigmasterol and pregnanediol was accomplished later that year. Up to this point, progesterone, known generically as corpus luteum hormone, had been being referred to by several groups by different names, including corporin, lutein, luteosterone, and progestin. In 1935, at the time of the Second International Conference on the Standardization of Sex Hormones in London, England
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major se ...
, a compromise was made between the groups and the name progesterone (progestational steroidal ketone) was created.
Veterinary use
The use of progesterone tests in dog breeding to pinpoint ovulation is becoming more widely used. There are several tests available but the most reliable test is a blood test with blood drawn by a veterinarian and sent to a lab for processing. Results can usually be obtained with 24 to 72 hours. The rationale for using progesterone tests is that increased numbers begin in close proximity to preovulatory surge in gonadotrophins and continue through ovulation and estrus. When progesterone levels reach certain levels they can signal the stage of estrus the female is. Prediction of birth date of the pending litter can be very accurate if ovulation date is known. Puppies deliver with a day or two of 9 weeks gestation in most cases. It is not possible to determine pregnancy using progesterone tests once a breeding has taken place, however. This is due to the fact that, in dogs, progesterone levels remain elevated throughout the estrus period.References
External links
Progesterone MS Spectrum
* * {{Navboxes , title = Biological activity , titlestyle = background:#ccccff , list1 = {{GABAA receptor positive modulators {{Glucocorticoid receptor modulators {{Mineralocorticoid receptor modulators {{Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators {{Progesterone receptor modulators {{Sigma receptor modulators {{Xenobiotic-sensing receptor modulators 5α-Reductase inhibitors 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibitors Alkene derivatives Antimineralocorticoids Diketones GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Glucocorticoids Glycine receptor antagonists Neurosteroids Hepatotoxins Hormones of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis Hormones of the hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad axis Hormones of the hypothalamic-pituitary-prolactin axis Hormones of the ovary Hormones of the placenta Hormones of the suprarenal cortex Hormones of the brain Hormones of the pregnant female Human female endocrine system Human hormones Pregnane X receptor agonists Pregnanes Progestogens Prolactin releasers Sex hormones Sigma antagonists Steroid hormones Total synthesis