Prise De La Bastille on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Storming of the Bastille (french: Prise de la Bastille ) occurred in
 News of Necker's dismissal reached Paris on the afternoon of Sunday, 12 July. The Parisians generally presumed that the dismissal marked the start of a coup by conservative elements. Liberal Parisians were further enraged by the fear that a concentration of Royal troops—brought in from frontier garrisons to
News of Necker's dismissal reached Paris on the afternoon of Sunday, 12 July. The Parisians generally presumed that the dismissal marked the start of a coup by conservative elements. Liberal Parisians were further enraged by the fear that a concentration of Royal troops—brought in from frontier garrisons to
 The regiment of
The regiment of
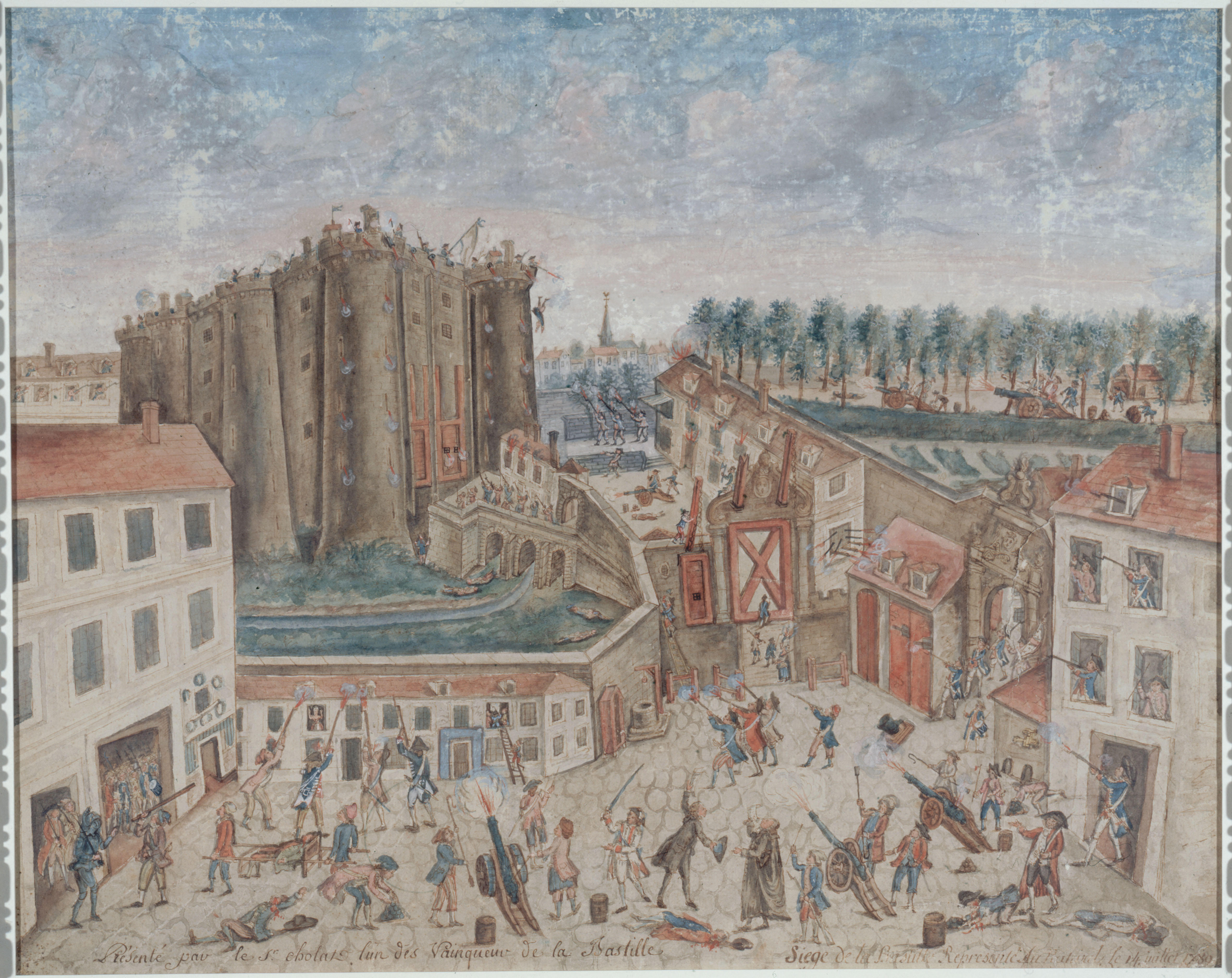


 On the morning of 14 July 1789, the city of Paris was in a state of alarm. The partisans of the Third Estate in France, now under the control of the Bourgeois Militia of Paris (soon to become Revolutionary France's National Guard), had earlier stormed the
On the morning of 14 July 1789, the city of Paris was in a state of alarm. The partisans of the Third Estate in France, now under the control of the Bourgeois Militia of Paris (soon to become Revolutionary France's National Guard), had earlier stormed the  Returning to the Hôtel de Ville, the mob accused the ''prévôt dès marchands'' (roughly, mayor)
Returning to the Hôtel de Ville, the mob accused the ''prévôt dès marchands'' (roughly, mayor)  The King first learned of the storming only the next morning through the
The King first learned of the storming only the next morning through the
Place de la Bastille
– official French website
Thomas Jefferson's letter to John Jay recounting the storming of the Bastille
{{DEFAULTSORT:Storming Of The Bastille 1789 events of the French Revolution 18th century in Paris Conflicts in 1789 Attacks on government buildings and structures Attacks on buildings and structures in Paris Riots and civil disorder in France Insurgencies in Paris
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, on 14 July 1789, when revolutionary insurgents stormed and seized control of the medieval armoury
An arsenal is a place where arms and ammunition are made, maintained and repaired, stored, or issued, in any combination, whether privately or publicly owned. Arsenal and armoury (British English) or armory (American English) are most ...
, fortress
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
, and political prison
A political prisoner is someone imprisoned for their political activity. The political offense is not always the official reason for the prisoner's detention.
There is no internationally recognized legal definition of the concept, although n ...
known as the Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was sto ...
. At the time, the Bastille represented royal authority in the centre of Paris. The prison contained only seven inmates at the time of its storming, but was seen by the revolutionaries as a symbol of the monarchy's abuse of power; its fall was the flashpoint of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
.
In France, 14 July is a national holiday National holiday may refer to:
* National day, a day when a nation celebrates a very important event in its history, such as its establishment
*Public holiday, a holiday established by law, usually a day off for at least a portion of the workforce, ...
, usually called Bastille Day
Bastille Day is the common name given in English-speaking countries to the national day of France, which is celebrated on 14 July each year. In French, it is formally called the (; "French National Celebration"); legally it is known as (; "t ...
in English. However, the expression Bastille Day is properly incorrect, as the event celebrated during the national holiday is the Fête de la Fédération
The (Festival of the Federation) was a massive holiday festival held throughout France in 1790 in honour of the French Revolution, celebrating the Revolution itself, as well as National Unity.
It commemorated the revolution and events of 1789 ...
of 1790, which was itself the 1st anniversary of the Bastille Day.
Background
During the reign ofLouis XVI
Louis XVI (''Louis-Auguste''; ; 23 August 175421 January 1793) was the last King of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. He was referred to as ''Citizen Louis Capet'' during the four months just before he was ...
France faced a major economic crisis
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the p ...
. This crisis was caused in part by the cost of intervening in the American Revolution and exacerbated by a regressive system of taxation, as well as poor harvests in the late 1780s. On 5 May 1789, the Estates-General convened to deal with this issue, but were held back by archaic protocols and the conservatism of the Second Estate, representing the nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many e ...
who made up less than 2% of France's population.
On 17 June 1789, the Third Estate
The estates of the realm, or three estates, were the broad orders of social stratification, social hierarchy used in Christendom (Christian Europe) from the Middle Ages to early modern Europe. Different systems for dividing society members into ...
, with its representatives drawn from the commoners, reconstituted itself as the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repre ...
, a body whose purpose was the creation of a French constitution. The king initially opposed this development but was forced to acknowledge the authority of the assembly, which renamed itself the National Constituent Assembly on 9 July.
Paris, close to insurrection and in François Mignet
François Auguste Marie Mignet (, 8 May 1796 – 24 March 1884) was a French journalist and historian of the French Revolution.
Biography
He was born in Aix-en-Provence (Bouches-du-Rhône), France. His father was a locksmith from the Vendée ...
's words, "intoxicated with liberty and enthusiasm", showed wide support for the Assembly. The press published the Assembly's debates; political debate spread beyond the Assembly itself into the public squares and halls of the capital. The Palais-Royal
The Palais-Royal () is a former royal palace located in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. The screened entrance court faces the Place du Palais-Royal, opposite the Louvre. Originally called the Palais-Cardinal, it was built for Cardinal ...
and its grounds became the site of an ongoing meeting. The crowd, on the authority of the meeting at the Palais-Royal, broke open the prisons of the ''Abbaye'' to release some grenadiers
A grenadier ( , ; derived from the word ''grenade'') was originally a specialist soldier who threw hand grenades in battle. The distinct combat function of the grenadier was established in the mid-17th century, when grenadiers were recruited from ...
of the French guards
The French Guards (french: Régiment des Gardes françaises) were an elite infantry regiment of the French Royal Army. They formed a constituent part of the Maison militaire du roi de France ("Military Household of the King of France") under the ...
, reportedly imprisoned for refusing to fire on the people. The Assembly recommended the imprisoned guardsmen to the clemency of the king; they returned to prison for a token one-day period and received a pardon. The rank and file of the regiment, previously considered reliable, now leaned toward the popular cause.
Necker's dismissal
On 11 July 1789, Louis XVI—acting under the influence of the conservative nobles of hisprivy council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mon ...
—dismissed and banished his finance minister, Jacques Necker
Jacques Necker (; 30 September 1732 – 9 April 1804) was a Genevan banker and statesman who served as finance minister for Louis XVI. He was a reformer, but his innovations sometimes caused great discontent. Necker was a constitutional monarchi ...
(who had been sympathetic to the Third Estate) and completely reconstituted the ministry. The marshals Victor-François, duc de Broglie, la Galissonnière, the duc de la Vauguyon, the Baron Louis de Breteuil, and the intendant Foulon Foulon is a French surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Celia Foulon (born 1979), French rower
* Daam Foulon (born 1999), Belgian footballer
* Emmanuel Foulon (1871–1945), Belgian archer
* Gwenn Foulon (born 1998), French footballe ...
, took over the posts of Puységur, Armand Marc, comte de Montmorin
Armand Marc, Count of Montmorin de Saint Herem (13 October 17452 September 1792) was a French statesman. He was Minister of Foreign Affairs and the Navy under Louis XVI.
Biography
He belonged to a junior branch of a noble family of Auvergne. He ...
, La Luzerne, Saint-Priest, and Necker.
 News of Necker's dismissal reached Paris on the afternoon of Sunday, 12 July. The Parisians generally presumed that the dismissal marked the start of a coup by conservative elements. Liberal Parisians were further enraged by the fear that a concentration of Royal troops—brought in from frontier garrisons to
News of Necker's dismissal reached Paris on the afternoon of Sunday, 12 July. The Parisians generally presumed that the dismissal marked the start of a coup by conservative elements. Liberal Parisians were further enraged by the fear that a concentration of Royal troops—brought in from frontier garrisons to Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
, Sèvres
Sèvres (, ) is a commune in the southwestern suburbs of Paris, France. It is located from the centre of Paris, in the Hauts-de-Seine department, Île-de-France region. The commune, which had a population of 23,251 as of 2018, is known for i ...
, the Champ de Mars
The Champ de Mars (; en, Field of Mars) is a large public greenspace in Paris, France, located in the seventh ''arrondissement'', between the Eiffel Tower to the northwest and the École Militaire to the southeast. The park is named after the ...
, and Saint-Denis—would attempt to shut down the National Constituent Assembly, which was meeting in Versailles. Crowds gathered throughout Paris, including more than ten thousand at the Palais-Royal. Camille Desmoulins
Lucie-Simplice-Camille-Benoît Desmoulins (; 2 March 17605 April 1794) was a French journalist and politician who played an important role in the French Revolution. Desmoulins was tried and executed alongside Georges Danton when the Committee o ...
successfully rallied the crowd by "mounting a table, pistol in hand, exclaiming: Citizens, there is no time to lose; the dismissal of Necker is the knell of a Saint Bartholomew
Bartholomew (Aramaic: ; grc, Βαρθολομαῖος, translit=Bartholomaîos; la, Bartholomaeus; arm, Բարթողիմէոս; cop, ⲃⲁⲣⲑⲟⲗⲟⲙⲉⲟⲥ; he, בר-תולמי, translit=bar-Tôlmay; ar, بَرثُولَماو� ...
for patriots! This very night all the Swiss and German battalions will leave the Champ de Mars
The Champ de Mars (; en, Field of Mars) is a large public greenspace in Paris, France, located in the seventh ''arrondissement'', between the Eiffel Tower to the northwest and the École Militaire to the southeast. The park is named after the ...
to massacre us all; one resource is left; to take arms''!'"
The Swiss and German regiments referred to were among the foreign mercenary
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any o ...
troops who made up a significant portion of the pre-revolutionary Royal Army, and were seen as being less likely to be sympathetic to the popular cause than ordinary French soldiers. By early July, approximately half of the 25,000 regular troops in Paris and Versailles were drawn from these foreign regiments. The French regiments included in the concentration appear to have been selected either because of the proximity of their garrisons to Paris or because their colonels were supporters of the reactionary "court party" opposed to reform.
During the public demonstrations that started on 12 July, the multitude displayed busts of Necker and of Louis Philippe II, Duke of Orléans
Louis Philippe II, Duke of Orléans (Louis Philippe Joseph; 13 April 17476 November 1793), was a major French noble who supported the French Revolution.
Louis Philippe II was born at the Château de Saint-Cloud to Louis Philippe I, Duke of Char ...
, then marched from the Palais Royal through the theater district before continuing westward along the boulevards. The crowd clashed with the Royal German Cavalry Regiment ("Royal-Allemand") between the Place Vendôme
The Place Vendôme (), earlier known as Place Louis-le-Grand, and also as Place Internationale, is a square in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France, located to the north of the Tuileries Gardens and east of the Église de la Madeleine. It is ...
and the Tuileries Palace
The Tuileries Palace (french: Palais des Tuileries, ) was a royal and imperial palace in Paris which stood on the right bank of the River Seine, directly in front of the Louvre. It was the usual Parisian residence of most French monarchs, from ...
. From atop the Champs-Élysées
The Avenue des Champs-Élysées (, ; ) is an avenue in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France, long and wide, running between the Place de la Concorde in the east and the Place Charles de Gaulle in the west, where the Arc de Triomphe is lo ...
, Charles Eugene, Prince of Lambesc
Charles Eugène of Lorraine (25 September 1751 – 2 November 1825) was the head of and last male member of the House of Guise, the cadet branch of the House of Lorraine which dominated France during the Wars of Religion, remained prominent as '' p ...
(Marshal of the Camp, Proprietor of the Royal Allemand-Dragoons) unleashed a cavalry charge that dispersed the remaining protesters at Place Louis XV—now Place de la Concorde
The Place de la Concorde () is one of the major public squares in Paris, France. Measuring in area, it is the largest square in the French capital. It is located in the city's eighth arrondissement, at the eastern end of the Champs-Élysées.
...
. The Royal commander, Baron de Besenval, fearing the results of a blood bath amongst the poorly armed crowds or defections among his own men, then withdrew the cavalry towards Sèvres.
Meanwhile, unrest was growing among the people of Paris who expressed their hostility against state authorities by attacking customs posts blamed for causing increased food and wine prices. The people of Paris started to plunder
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. ...
any place where food, guns, and supplies might be hoarded. That night, rumors spread that supplies were hoarded at Saint-Lazare, a huge property of the clergy, which functioned as a convent, hospital, school, and even a jail. An angry mob broke in and plundered the property, seizing 52 wagons of wheat, which were taken to the public market. That same day multitudes of people plundered many other places including weapon arsenals. Royal troops did nothing to stop the spreading of social chaos in Paris during those days.
Armed conflict
 The regiment of
The regiment of Gardes Françaises
The French Guards (french: Régiment des Gardes françaises) were an elite infantry regiment of the French Royal Army. They formed a constituent part of the Maison militaire du roi de France ("Military Household of the King of France") under the ...
(French Guards) formed the permanent garrison of Paris and, with many local ties, was favourably disposed towards the popular cause. This regiment had remained confined to its barracks during the initial stages of the mid-July disturbances. With Paris becoming the scene of a general riot, Charles Eugene, not trusting the regiment to obey his order, posted sixty dragoons to station themselves before its depot in the Chaussée d'Antin
''Chaussee'' is an historic term used in German-speaking countries for early, Road metal, metalled, rural highways, designed by road engineers, as opposed to the hitherto, traditional, unpaved country roads. The term is no longer used in modern ro ...
. The officers of the French Guards made ineffectual attempts to rally their men. The rebellious citizenry had now acquired a trained military contingent. As word of this spread, the commanders of the royal forces encamped on the Champ de Mars became doubtful of the dependability of even the foreign regiments.
The future "Citizen King", Louis-Philippe, duc d 'Orléans, witnessed these events as a young officer and was of the opinion that the soldiers would have obeyed orders if put to the test. He also commented in retrospect that the officers of the French Guards had neglected their responsibilities in the period before the uprising, leaving the regiment too much to the control of its non-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enli ...
s. However, the uncertain leadership of Besenval led to a virtual abdication of royal authority in central Paris. On the morning of 13 July, the electors of Paris met and agreed to the recruitment of a "bourgeois militia" of 48,000 men from the sixty voting districts of Paris, to restore order. Their identifying cockades were of blue and red, the colours of Paris. Lafayette was elected commander of this group on 14 July and subsequently changed its name to the National Guard. He added the colour white, the colour of the King, to the cockade on 27 July, to make the famous French tri-colour.
Storming the Bastille (14 July 1789)



Hôtel des Invalides
The Hôtel des Invalides ( en, "house of invalids"), commonly called Les Invalides (), is a complex of buildings in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, France, containing museums and monuments, all relating to the military history of France, as ...
without meeting significant opposition. Their intention had been to gather the weapons held there (29,000 to 32,000 muskets, but without powder or shot). The commandant at the Invalides had in the previous few days taken the precaution of transferring 250 barrels of gunpowder to the Bastille for safer storage.
At this point, the Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was sto ...
was nearly empty, housing only seven prisoners: four forgers arrested under warrants issued by the Grand Châtelet The Grand Châtelet was a stronghold in Ancien Régime Paris, on the right bank of the Seine, on the site of what is now the Place du Châtelet; it contained a court and police headquarters and a number of prisons.
The original building on the s ...
court; James F.X. Whyte, an Irish born "lunatic" suspected of spying and imprisoned at the request of his family; Auguste-Claude Tavernier, who had tried to assassinate Louis XV
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved (french: le Bien-Aimé), was King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reache ...
thirty years before; and one "deviant" aristocrat suspected of murder, the Comte de Solages, imprisoned by his father using a ''lettre de cachet
''Lettres de cachet'' (; ) were letters signed by the king of France, countersigned by one of his ministers, and closed with the royal seal. They contained orders directly from the king, often to enforce arbitrary actions and judgments that co ...
'' (while the Marquis de Sade
Donatien Alphonse François, Marquis de Sade (; 2 June 1740 – 2 December 1814), was a French nobleman, revolutionary politician, philosopher and writer famous for his literary depictions of a libertine sexuality as well as numerous accusat ...
had been transferred out ten days earlier).
The high cost of maintaining a garrisoned medieval fortress, for what was seen as having a limited purpose, had led to a decision being made shortly before the disturbances began to replace it with an open public space. Amid the tensions of July 1789, the building remained as a symbol of royal tyranny
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to rep ...
.
The regular garrison consisted of 82 ''invalides'' (veteran soldiers no longer suitable for service in the field). It had however been reinforced on 7 July by 32 grenadier
A grenadier ( , ; derived from the word '' grenade'') was originally a specialist soldier who threw hand grenades in battle. The distinct combat function of the grenadier was established in the mid-17th century, when grenadiers were recruited fr ...
s of the Swiss
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
* Swiss people
Places
* Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
* Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss Internation ...
Salis-Samade Regiment from the regular troops on the Champ de Mars
The Champ de Mars (; en, Field of Mars) is a large public greenspace in Paris, France, located in the seventh ''arrondissement'', between the Eiffel Tower to the northwest and the École Militaire to the southeast. The park is named after the ...
.Christopher J. Tozzi, p. 54 "Nationalizing France's Army. Foreign, Black and Jewish Troops in the French Military, 1715–1831, The walls mounted 18 eight-pound guns and 12 smaller pieces. The governor was Bernard-René de Launay, son of a previous governor and actually born within the Bastille.
The official list of ''vainqueurs de la Bastille'' (conquerors of the Bastille) subsequently compiled has 954 names, and the total of the crowd was probably fewer than one thousand. A breakdown of occupations included in the list indicates that the majority were local artisans, together with some regular army deserters and a few distinctive categories, such as 21 wine merchants.
The crowd gathered outside the fortress around mid-morning, calling for the pulling back of the seemingly threatening cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder ...
from the embrasures of the towers and walls and the release of the arms and gunpowder stored inside. Two representatives from the Hotel de Ville (municipal authorities from the Town Hall) were invited into the fortress and negotiations began, while another was admitted around noon with definite demands. The negotiations dragged on while the crowd grew and became impatient. Around 1:30 pm, the crowd surged into the undefended outer courtyard. A small party climbed onto the roof of a building next to the gate to the inner courtyard of the fortress and broke the chains on the drawbridge
A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of moveable bridge typically at the entrance to a castle or tower surrounded by a moat. In some forms of English, including American English, the word ''drawbridge'' commonly refers to all types of moveable ...
, crushing one ''vainqueur'' as it fell. Soldiers of the garrison called to the people to withdraw, but amid the noise and confusion these shouts were misinterpreted as encouragement to enter. Gunfire began, apparently spontaneously, turning the crowd into a mob. The crowd seems to have felt that they had been intentionally drawn into a trap and the fighting became more violent and intense, while attempts by deputies to organise a cease-fire were ignored by the attackers.
The firing continued, and after 3:00 pm, the attackers were reinforced by mutinous ''gardes françaises'', along with two cannons each of which was reportedly fired about six times. A substantial force of Royal Army troops encamped on the Champ de Mars did not intervene. With the possibility of mutual carnage suddenly apparent, Governor de Launay ordered the garrison to cease firing at 5:00 pm. A letter written by de Launay offering surrender but threatening to explode the powder stocks held if the garrison were not permitted to evacuate the fortress unharmed, was handed out to the besiegers through a gap in the inner gate. His demands were not met, but Launay nonetheless capitulated, as he realised that with limited food stocks and no water supply his troops could not hold out much longer. He accordingly opened the gates, and the ''vainqueurs'' swept in to take over the fortress at 5:30 pm.
Ninety-eight attackers and one defender had died in the actual fighting or subsequently from wounds, a disparity accounted for by the protection provided to the garrison by the fortress walls. Launay was seized and dragged towards the Hôtel de Ville in a storm of abuse. Outside the Hôtel, a discussion as to his fate began. The badly beaten Launay shouted "Enough! Let me die!" and kicked a pastry cook named Dulait in the groin. Launay was then stabbed repeatedly and died. An English traveller, Doctor Edward Rigby, reported what he saw, " eperceived two bloody heads raised on pikes, which were said to be the heads of the Marquis de Launay, Governor of the Bastille, and of Monsieur Flesselles, Prévôt des Marchands. It was a chilling and a horrid sight! ... Shocked and disgusted at this scene, eretired immediately from the streets."
The three officers of the permanent Bastille garrison were also killed by the crowd; surviving police reports detail their wounds and clothing.
Three of the ''invalides'' of the garrison were lynched plus two of the Swiss regulars of the Salis-Samade Regiment. The remaining Swiss were protected by the French Guards and eventually released to return to their regiment. Their officer, Lieutenant Louis de Flue of the Salis-Samade Regiment wrote a detailed report on the defense of the Bastille, which was incorporated in the logbook of the Salis-Samade and has survived."Relation de la prise de la Bastille le 14 juillet 1789 par un de ses défenseurs", in ''Revue Rétrospective'', vol. 4 (Paris: M. J. Taschereau, 1834) It is (perhaps unfairly) critical of the dead Marquis de Launay, whom Flue accuses of weak and indecisive leadership. The blame for the fall of the Bastille would rather appear to lie with the inertia of the commanders of the 5,000 Royal Army troops encamped on the Champ de Mars, who did not act when either the nearby Hôtel des Invalides or the Bastille were attacked.
 Returning to the Hôtel de Ville, the mob accused the ''prévôt dès marchands'' (roughly, mayor)
Returning to the Hôtel de Ville, the mob accused the ''prévôt dès marchands'' (roughly, mayor) Jacques de Flesselles
Jacques de Flesselles (; 11 November 173014 July 1789) was a French official and one of the early victims of the French Revolution.
Early life
Jacques de Flesselles was born in Paris in 1730 of a family of middle-class origins, which had recentl ...
of treachery, and he was assassinated on the way to an ostensible trial at the Palais-Royal.
 The King first learned of the storming only the next morning through the
The King first learned of the storming only the next morning through the Duke of La Rochefoucauld
The title of Duke de La Rochefoucauld is a French peerage belonging to one of the most famous families of the French nobility, whose origins go back to lord Rochefoucauld in Charente in the 10th and 11th centuries (with official evidence of nobil ...
. "Is it a revolt?" asked Louis XVI. The duke replied: "No sire, it's not a revolt; it's a revolution." Indeed, the storming of the Bastille is occasionally suggested to be the founding point of the Revolution in national discourse. In his book ''The French Revolution: From Enlightenment to Tyranny'', however, historian Ian Davidson argued that Louis XVI capitulating to the Third Estate at Versailles has a better claim to being the founding event, noting that the "bourgeois Revolutionaries" of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Château de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
had a major role in steering the future of the revolution, using parliamentary and political mechanisms, for the next three years. Nonetheless, the fall of the Bastille marks the first time the regular citizens of Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
, the ''sans-culottes
The (, 'without breeches') were the common people of the lower classes in late 18th-century France, a great many of whom became radical and militant partisans of the French Revolution in response to their poor quality of life under the . The ...
'', made a major intervention into the Revolution's affairs. For this stage of the Revolution, the ''sans-culotte'' were allies to the "bourgeois Revolutionaries".
14 to 15 July – immediate reaction
At Versailles, the Assembly were for a few hours ignorant of most of the Paris events. The representatives remained however concerned that the Marshal de Broglie might still unleash a pro-Royalist coup to force them to adopt the order of 23 June, and then dissolve the Assembly. Noailles apparently was first to bring reasonably accurate news of the Paris events to Versailles. M. Ganilh and Bancal-des-Issarts, dispatched to the Hôtel de Ville, confirmed his report. By the morning of 15 July, the outcome appeared clear to the king as well, and he and his military commanders backed down. The twenty-three regiments of Royal troops concentrated around Paris were dispersed to their frontier garrisons. TheMarquis de la Fayette
Marie-Joseph Paul Yves Roch Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de La Fayette (6 September 1757 – 20 May 1834), known in the United States as Lafayette (, ), was a French aristocrat, freemason and military officer who fought in the American Revolutio ...
took up command of the National Guard at Paris; Jean-Sylvain Bailly
Jean Sylvain Bailly (; 15 September 1736 – 12 November 1793) was a French astronomer, mathematician, freemason, and political leader of the early part of the French Revolution. He presided over the Tennis Court Oath, served as the mayor of Pa ...
– leader of the Third Estate and instigator of the Tennis Court Oath
On 20 June 1789, the members of the French Third Estate took the Tennis Court Oath (french: Serment du Jeu de Paume) in the tennis court which had been built in 1686 for the use of the Versailles palace. Their vow "not to separate and to reasse ...
– became the city's mayor under a new governmental structure known as the ''Commune de Paris
The Paris Commune (french: Commune de Paris, ) was a revolutionary government that seized power in Paris, the capital of France, from 18 March to 28 May 1871.
During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defended ...
''. The king announced that he would recall Necker and return from Versailles to Paris; on 17 July, in Paris, he accepted a tricolour
A tricolour () or tricolor () is a type of flag or banner design with a triband design which originated in the 16th century as a symbol of republicanism, liberty, or revolution. The flags of France, Italy, Romania, Mexico, and Ireland were ...
cockade
A cockade is a knot of ribbons, or other circular- or oval-shaped symbol of distinctive colours which is usually worn on a hat or cap.
Eighteenth century
In the 18th and 19th centuries, coloured cockades were used in Europe to show the allegia ...
from Bailly and entered the Hôtel de Ville to cries of "Long live the King" and "Long live the Nation".
Aftermath
Political
Immediately after the violence of 14 July members of the nobility – little assured by the apparent and, as it was to prove, temporary reconciliation of king and people – started to flee the country as ''émigré
An ''émigré'' () is a person who has emigrated, often with a connotation of political or social self-exile. The word is the past participle of the French ''émigrer'', "to emigrate".
French Huguenots
Many French Huguenots fled France followi ...
s''. Among the first to leave were the comte d'Artois (the future Charles X of France
Charles X (born Charles Philippe, Count of Artois; 9 October 1757 – 6 November 1836) was King of France from 16 September 1824 until 2 August 1830. An uncle of the uncrowned Louis XVII and younger brother to reigning kings Louis XVI and Lou ...
) and his two sons, the prince de Condé
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The ...
, the prince de Conti
The title of Prince of Conti (French: ''prince de Conti'') was a French noble title, assumed by a cadet branch of the princely house of Bourbon-Condé.
History
The title derives its name from Conty, a small town in northern France, c. 35 k ...
, the Polignac family, and (slightly later) Charles Alexandre de Calonne
Charles Alexandre de Calonne (20 January 173430 October 1802), titled Count of Hannonville in 1759, was a French statesman, best known for his involvement in the French Revolution.
Realizing that the Parlement de Paris would never agree to reform ...
, the former finance minister. They settled at Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
, where Calonne, as agent for the count d'Artois and the prince de Condé, began plotting civil war within the kingdom and agitating for a European coalition against France.
The news of the successful insurrection at Paris spread throughout France. In accord with principles of popular sovereignty
Popular sovereignty is the principle that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. Popular sovereignty, being a principle, does not imply any ...
and with complete disregard for claims of royal authority, the people established parallel structures of municipalities for civic government and militias for civic protection. In rural areas, many went beyond this: some burned title-deeds and no small number of châteaux, as the "Great Fear
The Great Fear (french: Grande Peur) was a general panic that took place between 22 July to 6 August 1789, at the start of the French Revolution. Rural unrest had been present in France since the worsening grain shortage of the spring, ...
" spread across the countryside during the weeks of 20 July to 5 August, with attacks on wealthy landlords impelled by the belief that the aristocracy was trying to put down the revolution.
On 16 July 1789, two days after the Storming of the Bastille, John Frederick Sackville
John Frederick Sackville, 3rd Duke of Dorset, KG (25 March 174519 July 1799) was the only son of Lord John Philip Sackville, second son of Lionel Sackville, 1st Duke of Dorset. His mother was the former Lady Frances Leveson-Gower. He succeeded ...
, British ambassador to France, reported to Secretary of State for Foreign Affairs
The secretary of state for foreign, Commonwealth and development affairs, known as the foreign secretary, is a minister of the Crown of the Government of the United Kingdom and head of the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office. Seen as ...
Francis Osborne, 5th Duke of Leeds
Francis Godolphin Osborne, 5th Duke of Leeds, (29 January 1751 – 31 January 1799), styled Marquess of Carmarthen until 1789, was a British politician. He notably served as Foreign Secretary under William Pitt the Younger from 1783 to 1791. H ...
, "Thus, my Lord, the greatest revolution that we know anything of has been effected with, comparatively speaking—if the magnitude of the event is considered—the loss of very few lives. From this moment we may consider France as a free country, the King a very limited monarch, and the nobility as reduced to a level with the rest of the nation."
On 22 July 1789 the populace lynched Controller-General of Finances The Controller-General or Comptroller-General of Finances (french: Contrôleur général des finances) was the name of the minister in charge of finances in France from 1661 to 1791. It replaced the former position of Superintendent of Finances (''S ...
Joseph Foullon de Doué and his son-in-law Louis Bénigne François Bertier de Sauvigny. Both had held official positions under the monarchy.
About 900 people who claimed to have stormed the Bastille received certificates (''Brevet de vainqueur de la Bastille'') from the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repre ...
in 1790, and a number of these still exist.
Demolition of Bastille
Although there were arguments that the Bastille should be preserved as a monument to liberation or as a depot for the new National Guard, the Permanent Committee of Municipal Electors at the Paris Town Hall gave the construction entrepreneurPierre-François Palloy
Pierre-François Palloy (23 January 1755 – 1835), self-styled as ''Palloy Patriote'' (Palloy the Patriot), was an entrepreneurial building contractor remembered for the demolition of the Bastille.
Life
Palloy was born in 1755 in Paris. Both his ...
the commission of disassembling the building. Palloy commenced work immediately, employing about 1,000 workers. The demolition of the fortress itself, the melting down of its clock portraying chained prisoners, and the breaking up of four statues were all carried out within five months.
In 1790, Lafayette
Lafayette or La Fayette may refer to:
People
* Lafayette (name), a list of people with the surname Lafayette or La Fayette or the given name Lafayette
* House of La Fayette, a French noble family
** Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de Lafayette (1757� ...
gave the wrought-iron, one-pound and three-ounce key to the Bastille to U.S. President George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
. Washington displayed it prominently at government facilities and events in New York and in Philadelphia until shortly before his retirement in 1797. The key remains on display at Washington's residence of Mount Vernon
Mount Vernon is an American landmark and former plantation of Founding Father, commander of the Continental Army in the Revolutionary War, and the first president of the United States George Washington and his wife, Martha. The estate is on ...
.
Palloy also took bricks from the Bastille and had them carved into replicas of the fortress, which he sold, along with medals allegedly made from the chains of prisoners. Pieces of stone from the structure were sent to every district in France, and some have been located. Various other pieces of the Bastille also survive, including stones used to build the Pont de la Concorde bridge over the Seine, and one of the towers, which was found buried in 1899 and is now at Square Henri-Galli in Paris, as well as the clock bells and pulley system, which are now in the Musée d’Art Campanaire. The building itself is outlined in brick on the location where it once stood, as is the moat in the Paris Metro
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Sin ...
stop below it, where a piece of the foundation is also on display.
Notes
References
Citations
Works cited
* * * * * *Additional sources
*Further reading
* * Alpaugh, Micah. "A Self-Defining Bourgeoisie in the Early French Revolution: The ''Milice bourgeoise,'' the Bastille Days of 1789, and their Aftermath", ''Journal of Social History'' 47, no. 3 (Spring 2014), 696–720. * * * Sewell, William H. "Historical Events as Transformations of Structures: Inventing Revolution at the Bastille", ''Theory and Society'' 25, no. 6 (Dec. 1996), 841–81.External links
Place de la Bastille
– official French website
Thomas Jefferson's letter to John Jay recounting the storming of the Bastille
{{DEFAULTSORT:Storming Of The Bastille 1789 events of the French Revolution 18th century in Paris Conflicts in 1789 Attacks on government buildings and structures Attacks on buildings and structures in Paris Riots and civil disorder in France Insurgencies in Paris