Prince Of Wales's Feathers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Prince of Wales's feathers is the
 The ostrich feathers heraldic motif is generally traced back to Edward, the Black Prince (1330–1376), eldest son and
The ostrich feathers heraldic motif is generally traced back to Edward, the Black Prince (1330–1376), eldest son and  The feathers had first appeared at the time of the marriage of King
The feathers had first appeared at the time of the marriage of King  King
King

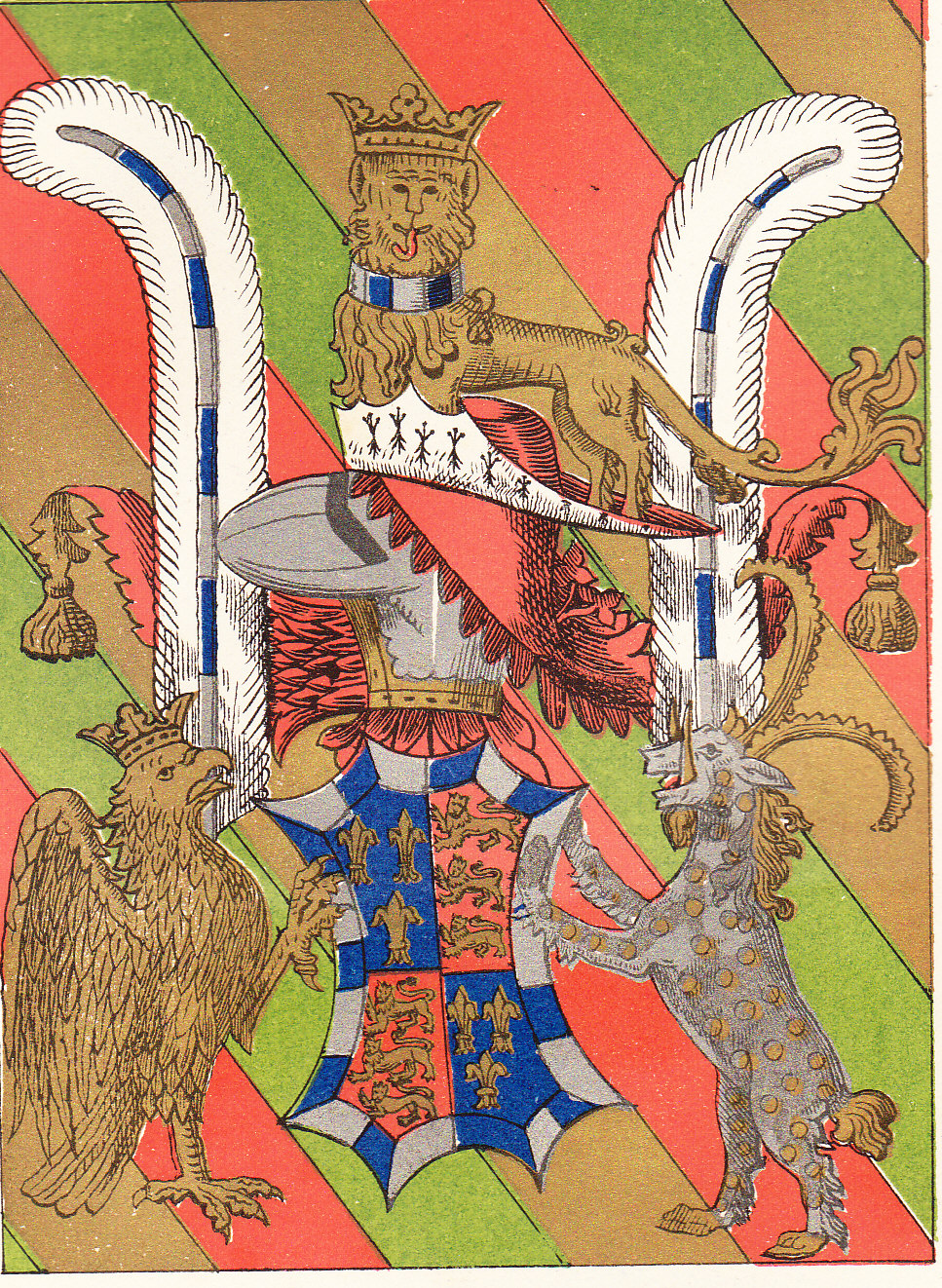 John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster, the Black Prince's second younger brother, used ostrich feathers in several contexts, including on a shield very similar to the Black Prince's "shield for peace", although in Gaunt's case the feathers were ermine. Single ostrich feather supporters were also used by John Beaufort, 1st Duke of Somerset (1404-1444) (as shown in his Garter stall plate in St George's Chapel), the second son of John Beaufort, 1st Earl of Somerset (1371-1410), the eldest of the four legitimized children of John of Gaunt by his mistress
John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster, the Black Prince's second younger brother, used ostrich feathers in several contexts, including on a shield very similar to the Black Prince's "shield for peace", although in Gaunt's case the feathers were ermine. Single ostrich feather supporters were also used by John Beaufort, 1st Duke of Somerset (1404-1444) (as shown in his Garter stall plate in St George's Chapel), the second son of John Beaufort, 1st Earl of Somerset (1371-1410), the eldest of the four legitimized children of John of Gaunt by his mistress
 The first Prince of Wales to use the badge in its modern form (i.e. three white feathers encircled by a coronet, and with the motto ') was Prince Arthur (1486–1502), eldest son of Henry VII, at the beginning of the 16th century. It was also widely used by Prince Edward, son of
The first Prince of Wales to use the badge in its modern form (i.e. three white feathers encircled by a coronet, and with the motto ') was Prince Arthur (1486–1502), eldest son of Henry VII, at the beginning of the 16th century. It was also widely used by Prince Edward, son of

 The feathers are used as the logo of two shooting clubs at Oxford University: the Oxford University Pistol Club (OUPC), and the Oxford University Rifle Club (OURC).
The feathers are used as the logo of two shooting clubs at Oxford University: the Oxford University Pistol Club (OUPC), and the Oxford University Rifle Club (OURC).
heraldic badge
A heraldic badge, emblem, impresa, device, or personal device worn as a badge indicates allegiance to, or the property of, an individual, family or corporate body. Medieval forms are usually called a livery badge, and also a cognizance. They are ...
of the Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the rule ...
, during the use of the title by the English and later British monarchy. It consists of three white ostrich feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premie ...
s emerging from a gold coronet
A coronet is a small crown consisting of ornaments fixed on a metal ring. A coronet differs from other kinds of crowns in that a coronet never has arches, and from a tiara in that a coronet completely encircles the head, while a tiara doe ...
. A ribbon below the coronet bears the motto (, "I serve"). As well as being used in royal heraldry
Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings (known as armory), as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known bran ...
, the badge is sometimes used to symbolise Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, particularly in Welsh rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
and Welsh regiments of the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkha ...
.
Bearers of the motif
The badge has no connection with the native Princes of Wales.Edward the Black Prince / House of Plantagenet
heir apparent
An heir apparent, often shortened to heir, is a person who is first in an order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person; a person who is first in the order of succession but can be displaced by the b ...
of King Edward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring ...
. The Black Prince bore (as an alternative to his differenced royal arms
The royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom, or the royal arms for short, is the arms of dominion of the British monarch, currently King Charles III. These arms are used by the King in his official capacity as monarch of the United Kingdom. Varia ...
) a shield of ''Sable, three ostrich feathers argent'', described as his "shield for peace", probably meaning the shield he used for jousting. These arms appear several times on his chest tomb
Funerary art is any work of art forming, or placed in, a repository for the remains of the dead. The term encompasses a wide variety of forms, including cenotaphs ("empty tombs"), tomb-like monuments which do not contain human remains, and com ...
in Canterbury Cathedral
Canterbury Cathedral in Canterbury, Kent, is one of the oldest and most famous Christian structures in England. It forms part of a World Heritage Site. It is the cathedral of the Archbishop of Canterbury, currently Justin Welby, leader of the ...
, alternating with his paternal royal arms (the royal arms of King Edward III differenced by ''a label of three points argent''). The Black Prince also used heraldic badges of one or more ostrich feathers in various other contexts.
 The feathers had first appeared at the time of the marriage of King
The feathers had first appeared at the time of the marriage of King Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
to Philippa of Hainault, and Edward III himself occasionally used ostrich feather badges. It is therefore likely that the Black Prince inherited the badge from his mother,Scott-Giles 1929, p. 89. descended from the Counts of Hainault, whose eldest son bore the title "Count of Ostrevent", the ostrich (french: link=no, autruche, Old French
Old French (, , ; Modern French: ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France from approximately the 8th to the 14th centuries. Rather than a unified language, Old French was a linkage of Romance dialects, mutually intel ...
spellings including ''ostruce'') feathers being possibly an heraldic pun on that name.Pinches and Pinches 1974, p. 59.Siddons 2009, p. 178. Alternatively, the badge may have derived from the Counts of Luxembourg, from whom Philippa was also descended, who had used the badge of an ostrich. Sir Roger de Clarendon, an illegitimate son of the Black Prince by his mistress Edith Willesford, bore arms of ''Or, on a bend sable three ostrich feathers argent'';
 King
King Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Wales, and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father ...
, the Black Prince's legitimate son, used ostrich feather badges in several colours and awarded augmented arms with ostrich feather supporters to Thomas de Mowbray, 1st Duke of Norfolk (1366-1399), the second son of John de Mowbray, 4th Baron Mowbray, and Elizabeth de Segrave, ''suo jure'' Lady Segrave, daughter and heiress of John de Segrave, 4th Baron Segrave
John Segrave, 4th Baron Segrave (4 May 1315 – 1 April 1353) was an English peer and landowner in Leicestershire and Yorkshire. His family title of Baron Segrave is drawn from a village now spelled Seagrave, which uses a coat of arms imitated fr ...
, by Margaret, Duchess of Norfolk, daughter and heiress of Thomas of Brotherton, 1st Earl of Norfolk
Thomas of Brotherton, 1st Earl of Norfolk (1 June 13004 August 1338), was the fifth son of King Edward I of England (1239–1307), and the eldest child by his second wife, Margaret of France, the daughter of King Philip III of France. He was, ...
, a son of King Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vas ...
.
Legendary origins
According to a longstanding legend, the Black Prince obtained the badge from the blind KingJohn of Bohemia
John the Blind or John of Luxembourg ( lb, Jang de Blannen; german: link=no, Johann der Blinde; cz, Jan Lucemburský; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King o ...
, against whom he fought at the Battle of Crécy
The Battle of Crécy took place on 26 August 1346 in northern France between a French army commanded by King PhilipVI and an English army led by King EdwardIII. The French attacked the English while they were traversing northern France du ...
in 1346. After the battle, the prince is said to have gone to the body of the dead king, and taken his helmet with its ostrich feather crest, afterwards incorporating the feathers into his arms, and adopting King John's motto, "'", as his own. The story first appears in writing in 1376, the year of the Black Prince's death. There is, however, no sound historical basis for it, and no evidence for King John having used either the motto or the crest (he actually bore a crest of vultures' wings).
Since a key factor in the English army's victory at Crécy was the use of Welsh archers, it is also sometimes said to have been Edward's pride in the men of Wales which led him to adopt a symbol alluding to their assistance. The mediaeval German motto "'" ("I serve") is a near-homophone
A homophone () is a word that is pronounced the same (to varying extent) as another word but differs in meaning. A ''homophone'' may also differ in spelling. The two words may be spelled the same, for example ''rose'' (flower) and ''rose'' (pa ...
for the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
phrase "'" meaning "Your Man", which might have helped endear the young Black Prince to the Welsh soldiers in particular. Again, however, there is no historical evidence to support this theory. In 1917, during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, it was rumoured that the motto might be formally changed to "''Eich Dyn''" to avoid the use of German.
John of Gaunt / House of Lancaster
 John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster, the Black Prince's second younger brother, used ostrich feathers in several contexts, including on a shield very similar to the Black Prince's "shield for peace", although in Gaunt's case the feathers were ermine. Single ostrich feather supporters were also used by John Beaufort, 1st Duke of Somerset (1404-1444) (as shown in his Garter stall plate in St George's Chapel), the second son of John Beaufort, 1st Earl of Somerset (1371-1410), the eldest of the four legitimized children of John of Gaunt by his mistress
John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster, the Black Prince's second younger brother, used ostrich feathers in several contexts, including on a shield very similar to the Black Prince's "shield for peace", although in Gaunt's case the feathers were ermine. Single ostrich feather supporters were also used by John Beaufort, 1st Duke of Somerset (1404-1444) (as shown in his Garter stall plate in St George's Chapel), the second son of John Beaufort, 1st Earl of Somerset (1371-1410), the eldest of the four legitimized children of John of Gaunt by his mistress Katherine Swynford
Katherine Swynford, Duchess of Lancaster (born Katherine de Roet, – 10 May 1403), also spelled Katharine or Catherine, was the third wife of John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster, the fourth (but third surviving) son of King Edward III.
Daughte ...
.
King Henry IV, of the House of Lancaster
The House of Lancaster was a cadet branch of the royal House of Plantagenet. The first house was created when King Henry III of England created the Earldom of Lancasterfrom which the house was namedfor his second son Edmund Crouchback in 126 ...
, the son of John of Gaunt by his first wife Blanche of Lancaster, used a badge of a single ostrich feather entwined by a scroll inscribed with the motto "Ma Sovereyne". His eldest son and successor King Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
used ostrich feathers as a secondary royal badge at various times, as did Henry IV's younger sons Thomas of Lancaster, 1st Duke of Clarence who used an ermine ostrich feather with a label; John of Lancaster, 1st Duke of Bedford who used an ostrich feather with the "Sovereygne" scroll; and Humphrey of Lancaster, 1st Duke of Gloucester
Humphrey of Lancaster, Duke of Gloucester (3 October 139023 February 1447) was an English prince, soldier, and literary patron. He was (as he styled himself) "son, brother and uncle of kings", being the fourth and youngest son of Henry IV of E ...
who used an ostrich feather semée of fleurs-de-lis
The fleur-de-lis, also spelled fleur-de-lys (plural ''fleurs-de-lis'' or ''fleurs-de-lys''), is a lily (in French, and mean 'flower' and 'lily' respectively) that is used as a decorative design or symbol.
The fleur-de-lis has been used in the ...
. Similar badges were used by other royal princes.
House of Tudor
 The first Prince of Wales to use the badge in its modern form (i.e. three white feathers encircled by a coronet, and with the motto ') was Prince Arthur (1486–1502), eldest son of Henry VII, at the beginning of the 16th century. It was also widely used by Prince Edward, son of
The first Prince of Wales to use the badge in its modern form (i.e. three white feathers encircled by a coronet, and with the motto ') was Prince Arthur (1486–1502), eldest son of Henry VII, at the beginning of the 16th century. It was also widely used by Prince Edward, son of Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
and afterwards Edward VI
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first E ...
, although he was never formally invested as Prince of Wales. Feathers continued to be used as lesser royal badges, by Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is sometimes referred to as the "Virgin Queen".
Eli ...
among others, until the end of the century.
House of Stuart and successors
Only from the beginning of the 17th century did the badge become exclusively associated with the Prince of Wales. It has formed thedexter
Dexter may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Dexter, the main character of the American animated series '' Dexter's Laboratory'' that aired from 1996 to 2003
* Dexter, a fictional character in the British web series ''Diary of a Bad Man''
* Dext ...
badge of the heraldic achievement of the Prince of Wales since at least 1901, blazoned ''A plume of three ostrich feathers argent enfiled by a coronet composed of fleurs-de-lys and crosses patée or alternately with motto Ich Dien''. (See coat of arms of the Prince of Wales).
Modern uses of the badge

Military uses
The plaque of HMS ''Norfolk'' has beneath a single, crowned, feather. The badge is thecap badge
A cap badge, also known as head badge or hat badge, is a badge worn on uniform headgear and distinguishes the wearer's nationality and/or organisation. The wearing of cap badges is a convention commonly found among military and police forces, as w ...
of the Royal Welsh, an amalgamation of three Welsh regiments, the Royal Welch Fusiliers, the Royal Regiment of Wales and the Territorial Army's Royal Welsh Regiment
The Royal Welsh Regiment was an infantry regiment of the Territorial Army in the United Kingdom. It existed from 1999, until it was re-designated as the 3rd Battalion, The Royal Welsh in 2006.
History
The regiment was formed in 1999 as part of th ...
. Previously it was the cap badge of the Prince of Wales' Own Civil Service Rifles, whose motto was also .
The badge also appears as an element on the regimental badges of many other regiments of Commonwealth armies which have a historical connection with the Prince of Wales:
* The Royal Scots Dragoon Guards (Carabiniers and Greys) (as arm badge)
* Royal Marines Band Service Commando Training Centre Lympstone (part of cap badge)
* 9th/12th Royal Lancers (Prince of Wales')
*The Princess of Wales' Royal Regiment
Princess is a regal rank and the feminine equivalent of prince (from Latin ''princeps'', meaning principal citizen). Most often, the term has been used for the consort of a prince, or for the daughter of a king or prince.
Princess as a subst ...
(Queen's and Royal Hampshires) (part of cap badge)
* The Staffordshire Regiment (The Prince of Wales') (part of cap badge)
* 2nd King Edward VII's Own Gurkha Rifles (The Sirmoor Rifles)
* The Royal Wiltshire Yeomanry (Prince of Wales' Own) (part of cap badge)
*The Cheshire Yeomanry (Earl of Chester's)
The Cheshire Yeomanry was a yeomanry regiment that can trace its history back to 1797 when Sir John Leicester of Tabley raised a county regiment of light cavalry in response to the growing fears of invasion from Napoleonic France. Its lineage i ...
*2 Squadron Honourable Artillery Company (squadron badge)
*4th Battalion 8 Punjab Regiment
Fourth or the fourth may refer to:
* the ordinal form of the number 4
* ''Fourth'' (album), by Soft Machine, 1971
* Fourth (angle), an ancient astronomical subdivision
* Fourth (music), a musical interval
* ''The Fourth'' (1972 film), a Sovie ...
* 4th/19th Prince of Wales' Light Horse Regiment
* The Royal Regiment of Canada (part of cap badge)
*Ceylon Light Infantry
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
* Bengal Engineer Group
*The Princess of Wales' Own Regiment
The Princess of Wales' Own Regiment (PWOR) is a Primary Reserve infantry regiment of the Canadian Army.
Lineage
File:PWOR Regt Colour.jpg, Regimental colour
File:PWOR Camp Flag.jpg, Camp flag .
* Originated on 16 January, 1863, as the ''14th ...
(part of cap badge)
*The Royal Monmouthshire Royal Engineers (part of cap badge)
*2 Engineers (Pak Army) From 1805 Princess of Wales' Own
*The Royal Hussars (PWO) From 1969 to 1992
*Prince of Wales Royal Indian Military College since 1922 currently known as Rashtriya Indian Military College
*
*One South African Infantry Battalion
Sporting uses
The feathers have traditionally been worn on the jerseys of players in the Welsh rugby union team, being sewn on jerseys of players representing Welsh clubs before a national team or union existed. It has since been adopted as the logo of theWelsh Rugby Union
The Welsh Rugby Union (WRU; cy, Undeb Rygbi Cymru) is the governing body of rugby union in the country of Wales, recognised by the sport's international governing body, World Rugby.
The WRU is responsible for the running of rugby in Wales, o ...
(WRU). In the 1990s, the WRU modified the form of the badge they used to copyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educatio ...
the design. The new logo is more stylised, with "WRU" in place of "'". As the logo of the WRU, the Prince of Wales' feathers are also represented in one of the quarters of the British and Irish Lions' badge.
The Welsh Rugby League has stuck to the traditional three feathers with "'' RL''" ("''RL''" standing for "rugby league") written underneath.
Surrey County Cricket Club
Surrey County Cricket Club (Surrey CCC) is a first-class club in county cricket, one of eighteen in the domestic cricket structure of England and Wales. It represents the historic county of Surrey, including areas that now form South London. ...
were granted permission in 1915 to use the feathers for their badge. Their home ground, The Oval
The Oval, currently known for sponsorship reasons as the Kia Oval, is an international cricket ground in Kennington, located in the borough of Lambeth, in south London. The Oval has been the home ground of Surrey County Cricket Club since ...
, is on land owned by the Prince of Wales.
The feathers appear on the badge of Wrexham Association Football Club.
The emblem of Lingfield Park Racecourse
Lingfield Park Racecourse (commonly referred to as Lingfield) is a horse racing course at Lingfield in Surrey, United Kingdom. It is owned by the ARC Racing and Leisure Group, formerly Arena Leisure Plc.
Lingfield is best known as a winter ...
, in Surrey incorporates the feathers, having been opened in 1890 by the Prince of Wales (latterly Edward VII)
 The feathers are used as the logo of two shooting clubs at Oxford University: the Oxford University Pistol Club (OUPC), and the Oxford University Rifle Club (OURC).
The feathers are used as the logo of two shooting clubs at Oxford University: the Oxford University Pistol Club (OUPC), and the Oxford University Rifle Club (OURC).
Other uses
Prince Edward School, Harare, Zimbabwe was given permission by Edward VIII, then Prince of Wales to use the badge - with the motto "Tot Facienda Parum Factum" as its emblem. TheCarlton Club
The Carlton Club is a private members' club in St James's, London. It was the original home of the Conservative Party before the creation of Conservative Central Office. Membership of the club is by nomination and election only.
History
T ...
uses the feathered coronet badge as its emblem, without the motto.
Prince of Wales' College, Moratuwa
Prince of Wales' College ( Sinhala: වේල්ස් කුමර විද්යාලය ''Wels Kumara Vidyalaya'', Tamil: பிரின்ஸ் ஆஃப் வேல்ஸ் கல்லூரி) is a selective entry boys' school s ...
, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, has used the feathers since the inception of the school in 1876.
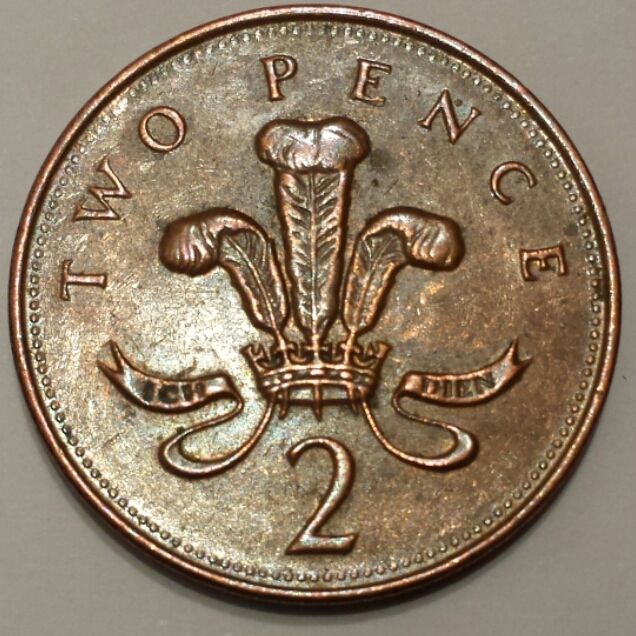
The badge appeared on the reverse of the British two pence coins minted between 1971 and 2008, many of which remain in circulation. The badge appears as a provenance mark on those silver coins minted using Welsh mined silver in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries.
During the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I (" Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of r ...
, most coins minted by Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
at his various provincial wartime mints carry the feathers. The feathers appear on these coins because Charles I had no access to the Royal Mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's oldest company and the official maker of British coins.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly owned by HM Treasury, His Majesty's Treasury and is un ...
in London and instead transferred the Aberystwyth Mint (originally established to coin Welsh silver) to Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , also ) is a market town, civil parish, and the county town of Shropshire, England, on the River Severn, north-west of London; at the 2021 census, it had a population of 76,782. The town's name can be pronounced as either 'Sh ...
and then Oxford as an emergency measure. All the Civil War provincial mints are therefore in effect sub-branches of the Aberystwyth mint.
The badge was until 1985 on the coat of arms of Penang
The Coat of arms of Penang is largely based on the coat of arms of Penang first granted to the Settlement (now State) of Penang, then in the Federation of Malaya, by a Royal Warrant of King George VI dated 11 September 1949.
Between 1911 ( ...
, a state in present-day Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federal constitutional monarchy consists of thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two regions: Peninsular Malaysia and Borneo's East Mal ...
, which was founded in 1786 as the settlement of Prince of Wales Island.
The badge is inscribed on the foundation stone, laid on 25 February 1927, of Patna Medical College and Hospital
Patna Medical College and Hospital (abbreviated as PMCH) was established in 1925 and originally known as Prince of Wales Medical College, is a medical college located in Patna, the state capital of Bihar, India.
It is located on the southern b ...
, in Patna, Bihar, India, established in 1925 as the Prince of Wales Medical College. The motto "''Ich dien''" is still widely used within the institution.
The badge is used by a society in Malta called "The Prince of Wales Philharmonic Society". The scope of this organisation is mainly one related to music but is also linked to the feast of St. Dominic in Vittoriosa in Malta. Malta was a colony of the British Crown for 200 years, and there exist a variety of clubs and organisations bearing the name of royal personalities.
From 1932 until its abolition in 1965, the Municipal Borough of Barnes, Surrey, used feathers based on those of the Prince of Wales on its coat of arms, in honour of the fact that the then Prince of Wales (afterwards Edward VIII, and later Duke of Windsor) had been born in the borough.
Norfolk County Council was given special consent by King Edward VII to use the badge on its arms, in recognition of Sandringham House, which was one of the King's favourite residences. Edward held the title Prince of Wales for 59 years, making him at the time the longest-serving holder.
A derivative of the badge is that used by the Prince's Trust, a charitable organisation that helps young people.
Many pubs in the UK pub names, are named The Prince of Wales's Feathers, the Prince's Feathers or simply the Feathers, particularly in areas associated with royal estates.
See also
* Coat of arms of the Prince of Wales * ''Dieu et mon droit'' * Flag of Wales * Fleur-de-lis * ''Honi soit qui mal y pense'' * Rashtriya Indian Military College * Royal badges of England * Royal Welsh * Royal standards of CanadaReferences
Bibliography
* * * {{Princes of Wales British monarchy English heraldry Rugby league in Wales Rugby union in Wales National symbols of the United Kingdom National symbols of Wales Princes of Wales, Feathers Ostriches Edward the Black Prince Heraldic badges