Powertrain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A drivetrain (also frequently spelled as drive train or sometimes drive-train) is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In
A drivetrain (also frequently spelled as drive train or sometimes drive-train) is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In
 *
*
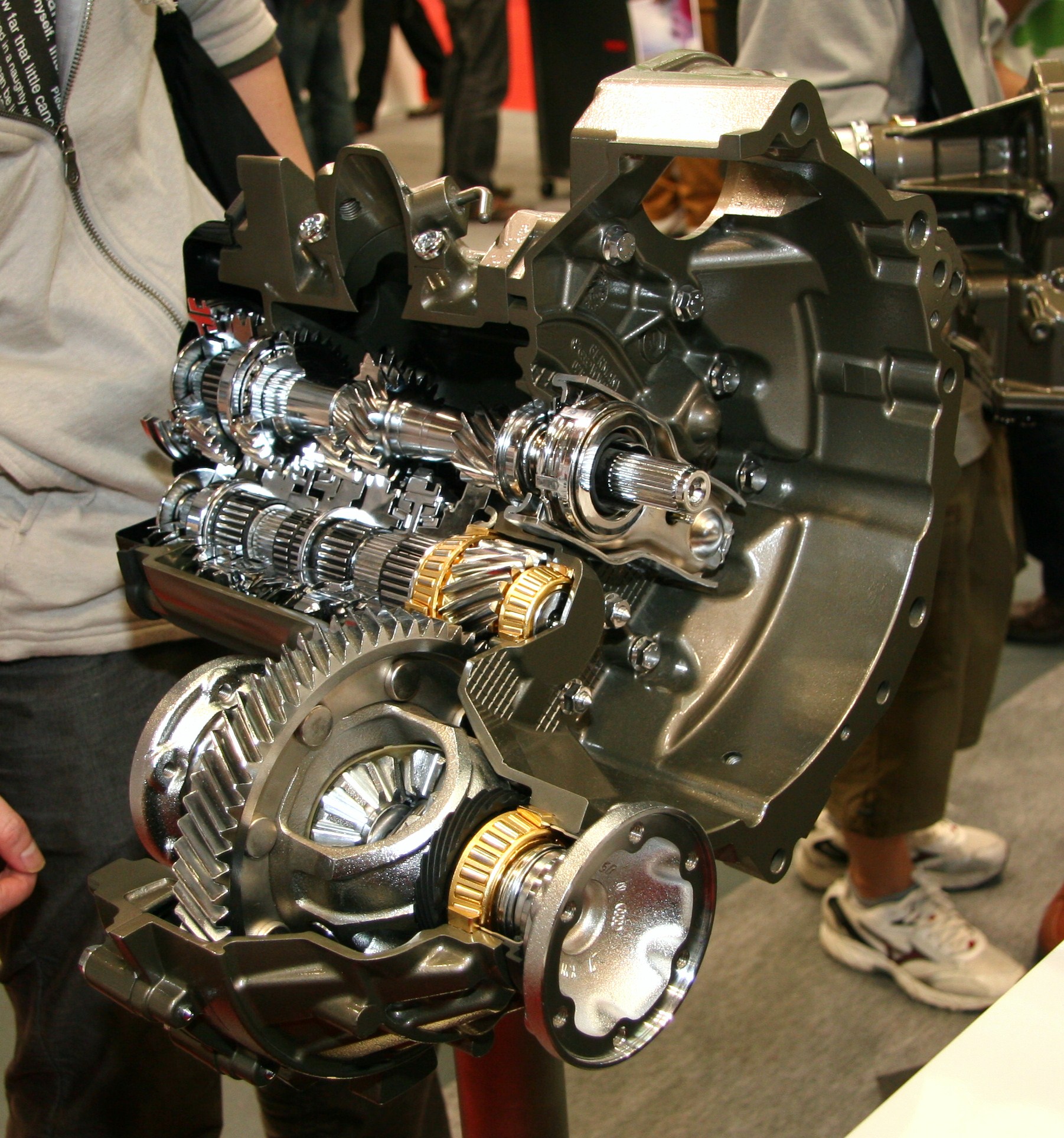 * Clutch
*
* Clutch
*
 * Clutch
* Gearbox
* Transfer box
*
* Clutch
* Gearbox
* Transfer box
*
 The final drive is the last in the set of components which delivers torque to the
The final drive is the last in the set of components which delivers torque to the
 A drivetrain (also frequently spelled as drive train or sometimes drive-train) is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In
A drivetrain (also frequently spelled as drive train or sometimes drive-train) is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering
Automotive engineering, along with aerospace engineering and naval architecture, is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software, and safety engineering as applied to the design, manufac ...
, the drivetrain is the components of a motor vehicle that deliver power to the drive wheel
A drive wheel is a wheel of a motor vehicle that transmits force, transforming torque into tractive force from the tires to the road, causing the vehicle to move. The powertrain delivers enough torque to the wheel to overcome stationary for ...
s. This excludes the engine or motor that generates the power. In marine applications, the drive shaft will drive a propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon ...
, thruster, or waterjet rather than a drive axle, while the actual engine might be similar to an automotive engine. Other machinery, equipment and vehicles may also use a drivetrain to deliver power from the engine(s) to the driven components.
In contrast, the powertrain is considered to include both the engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power ...
and/or motor(s) as well as the drivetrain.
Function
The function of the drivetrain is to couple the engine that produces the power to the driving wheels that use this mechanical power to rotate the axle. This connection involves physically linking the two components, which may be at opposite ends of the vehicle and so requiring a longpropeller shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect ...
or drive shaft. The operating speed of the engine and wheels are also different and must be matched by the correct gear ratio
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission ...
. As the vehicle speed changes, the ideal engine speed must remain approximately constant for efficient operation and so this gearbox ratio must also be changed, either manually, automatically or by an automatic continuous variation
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a continuous variation (that is a change without jump) of the argument induces a continuous variation of the value of the function. This means that there are no abrupt changes in value ...
.
Automotive components
The precise components of the drivetrain vary, according to the type of vehicle. Some typical examples:Manual transmission car
 *
* Flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, assu ...
** Dual mass flywheel ''still rare''
* Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts ...
* Gearbox
Propulsion transmission is the mode of transmitting and controlling propulsion power of a machine. The term ''transmission'' properly refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive vehicles), diffe ...
** Overdrive ''Since the adoption of 5 speeds has become standard ''
* Propeller shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect ...
* Rear axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearing ...
** Final drive
A drivetrain (also frequently spelled as drive train or sometimes drive-train) is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering, the drivetrain is the components o ...
** Differential
Automatic transmission car
*Torque converter
A torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that transfers rotating power from a prime mover, like an internal combustion engine, to a rotating driven load. In a vehicle with an automatic transmission, the torque converter connects the pow ...
* Transmission
* Propeller shaft
* Rear axle
** Spool
** Differential
Front-wheel drive car
 * Clutch
*
* Clutch
* Transaxle
A transaxle is a single mechanical device which combines the functions of an automobile's transmission, axle, and differential into one integrated assembly. It can be produced in both manual and automatic versions.
Engine and drive at the s ...
** Gearbox
** Final drive
** Differential
** Drive shafts and constant-velocity joint
Constant-velocity joints (also known as homokinetic or CV joints) are mechanical joints which allow a drive shaft to transmit power through a variable angle, at constant rotational speed, without an appreciable increase in friction or play. Th ...
s to each wheel
Four-wheel drive off-road vehicle
Transmission brake
A transmission brake or driveline parking brake is an inboard vehicle brake that is applied to the drivetrain rather than to the wheels.
Historically, some early cars used transmission brakes as the normal driving brake and often had wheel brake ...
* Propeller shaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft (Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to connect ...
s, to front and rear
* Front and rear axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, beari ...
s
** Final drive
** Locking differential
** Portal gear
Final drive
 The final drive is the last in the set of components which delivers torque to the
The final drive is the last in the set of components which delivers torque to the drive wheel
A drive wheel is a wheel of a motor vehicle that transmits force, transforming torque into tractive force from the tires to the road, causing the vehicle to move. The powertrain delivers enough torque to the wheel to overcome stationary for ...
s. In a road vehicle, it incorporates the differential. In a railway vehicle, it sometimes incorporates the reversing gear. Examples include the Self-Changing Gears RF 28 (used in many first-generation diesel multiple units of British Railways) and RF 11 used in the British Rail Class 03
The British Rail Class 03 locomotive was, together with the similar British Rail Class 04, Class 04, one of British Railways' most successful 0-6-0 diesel-mechanical shunters. 230 were built at Doncaster Works, Doncaster and Swindon Works, Swind ...
and British Rail Class 04
The British Rail Class 04 is a 0-6-0 diesel-mechanical shunting locomotive class, built between 1952 and 1962 and was the basis for the later Class 03 built in the British Railways workshops.
History
The prototype locomotive was built in ...
diesel shunting locomotives.
In a motor vehicle
A motor vehicle, also known as motorized vehicle or automotive vehicle, is a self-propelled land vehicle, commonly wheeled, that does not operate on rails (such as trains or trams) and is used for the transportation of people or cargo.
The ...
, the powertrain consists of the source of propulsion (e.g. the engine or electric motor) and the drivetrain system which transfers this energy into forward movement of the vehicle.
Powertrain
Definition
The powertrain consists of the prime mover (e.g. an internal combustion engine and/or one or more traction motors) and the drivetrain - all of the components that convert the prime mover's power into movement of the vehicle (e.g. the transmission,driveshaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft ( Australian English), propeller shaft (prop shaft), or Cardan shaft (after Girolamo Cardano) is a component for transmitting mechanical power and torque and rotation, usually used to conne ...
s, differential and axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, beari ...
s); whereas the drivetrain does not include the power source and consists of the transmission, driveshafts, differential and axles.
Power sources
Most passenger cars and commercial vehicles are powered by either aninternal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal co ...
, electric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate forc ...
(s) or a combination of the two.
The most common types of internal combustion engines are:
* petrol engine
A petrol engine (gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine designed to run on petrol (gasoline). Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as '' ...
s
* diesel engine
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-ca ...
s
* ethanol blends (such as E85 and E10)
* liquefied petroleum gas
Most purely electric vehicles use batteries for energy storage and are referred to as battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, wi ...
s.
Vehicles with both internal combustion engines and electric motors are called ''hybrid vehicles''. If a hybrid vehicle includes a charging socket, it is considered to be a plug-in hybrid
A plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) is a hybrid electric vehicle whose battery pack can be recharged by plugging a charging cable into an external electric power source, in addition to internally by its on-board internal combustion engin ...
, while vehicles that do not include a charging socket (therefore relying on the engine or regenerative braking
Regenerative braking is an energy recovery mechanism that slows down a moving vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form that can be either used immediately or stored until needed. In this mechanism, the electric traction m ...
to charge the batteries) are considered to be mild hybrid
Mild hybrids (also known as power-assist hybrids, battery-assisted hybrid vehicles or BAHVs) are generally cars with an internal combustion engine equipped with an electric machine (one motor/generator in a parallel hybrid configuration) allowing ...
s.
Powered vessels
Aircraft
Railway locomotives
Other
See also
References
{{Authority control Automotive technologies