Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK, German: ''Potsdam-Institut für Klimafolgenforschung'') is a German government-funded research institute addressing crucial scientific questions in the fields of
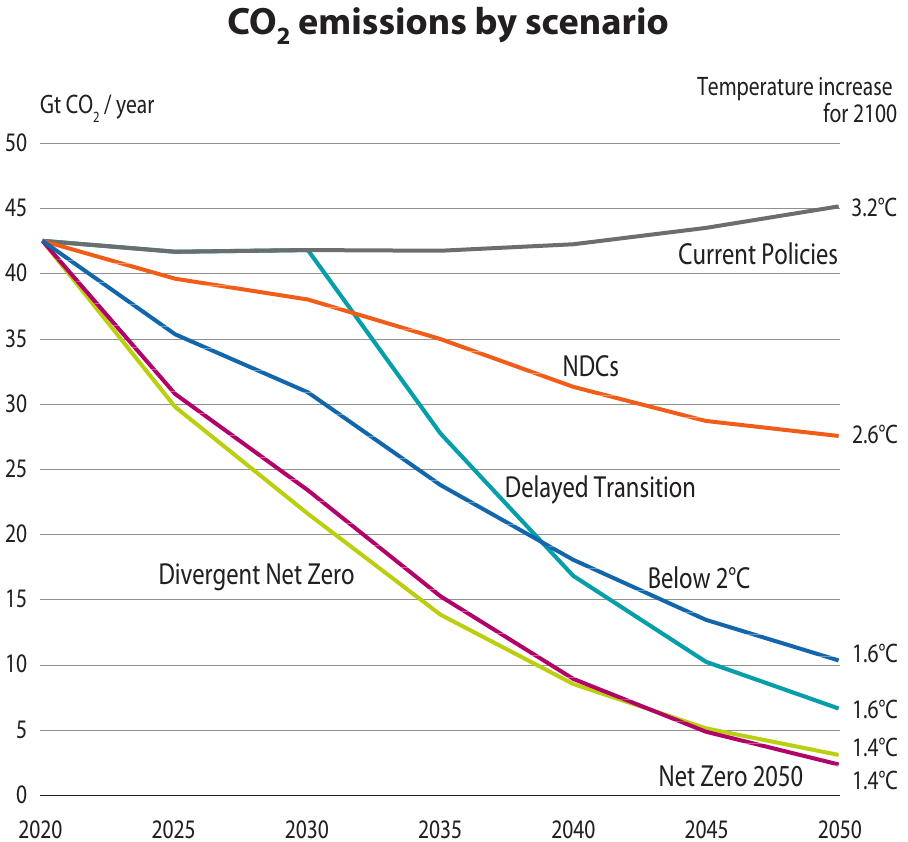 Research Department 3 (RD3) aims to provide an integrated perspective on climate change mitigation and climate change impact pathways to inform societies’ choices. Climate protection may have costs, but unabated climate change can have strong adverse effects on economic development; loss of
Research Department 3 (RD3) aims to provide an integrated perspective on climate change mitigation and climate change impact pathways to inform societies’ choices. Climate protection may have costs, but unabated climate change can have strong adverse effects on economic development; loss of
Sachbericht 2020
/ref>
Researchers refine assessment of tipping elements of the climate system
regarding
''Some Like It Hot!''
Bill McKibben 9 May 2013
''Turn Down the Heat: Why a 4ºC Warmer World Must Be Avoided''
a report for the World Bank by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and Climate Analytics; November 2012, 58 pp., available at climatechange.worldbank.org
Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
{{Authority control Climate change organizations Environmental research institutes Research institutes in Germany Organisations based in Potsdam
global change
Global change in broad sense refers to planetary-scale changes in the Earth system. It is most commonly use to encompass the variety of changes connected to the rapid increase in human activities which started around mid-20th century, i.e. the ...
, climate impacts, and sustainable development. Ranked among the top environmental think tank
A think tank, or policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, military, technology, and culture. Most think tanks are non-governmenta ...
s worldwide, it is one of the leading research institutions and part of a global network of scientific and academic institutions working on questions of global environmental change. It is a member of the Leibniz Association
The Leibniz Association (German: ''Leibniz-Gemeinschaft'' or ''Wissenschaftsgemeinschaft Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz'') is a union of German non-university research institutes from various disciplines.
As of 2020, 96 non-university research insti ...
, whose institutions perform research on subjects of high relevance to society.
History
PIK was founded in 1992 byHans Joachim Schellnhuber
Hans Joachim "John" Schellnhuber (born 7 June 1950) is a German atmospheric physicist, climatologist and founding director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and former chair of the German Advisory Council on Global ...
, who became the institute's first director. In 2018 he was succeeded by two joint directors – the climate economist Ottmar Edenhofer, and Earth scientist Johan Rockström , formerly director of the Stockholm Resilience Centre. About 400 people work at the institute that is located on Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream o ...
's historic Telegrafenberg. Researchers from the natural and social sciences analyze the Earth system, assess climate risks and develop policies and solution pathways towards a manageable climate future.
Organization
The Potsdam Institute is part of theLeibniz Association
The Leibniz Association (German: ''Leibniz-Gemeinschaft'' or ''Wissenschaftsgemeinschaft Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz'') is a union of German non-university research institutes from various disciplines.
As of 2020, 96 non-university research insti ...
. Its board consists of three directors, Ottmar Edenhofer, Johan Rockström and Bettina Hörstrup, who is the administrative director. PIK has four research departments (RDs) and seven Future Labs.
Research Departments
Earth System Analysis (RD 1)
Research Department 1 (RD1) provides the Earth system science foundation of PIK. It focuses on the understanding and modelling of the physical and biogeochemical processes that govern the Earth system (i.e. Oceans, Atmosphere and Biosphere) and its response to human interference. RD1 research is guided by four major themes that PIK helped to establish: *Tipping points in the climate system
In climate science, a tipping point is a critical threshold that, when crossed, leads to large and often irreversible changes in the climate system. If tipping points are crossed, they are likely to have severe impacts on human society. Tippin ...
: Non-linear Earth system processes and threshold behavior.
* Planetary boundaries
Planetary boundaries is a concept highlighting human-caused perturbations of Earth systems making them relevant in a way not accommodated by the environmental boundaries separating the three ages within the Holocene epoch. Crossing a planetary ...
: Definition, quantification and operationalization of planetary boundaries and their interactions.
* Earth trajectories: Dynamics and modes of operation of the Earth system (for example circulation changes, feedback systems) under natural and human forcing, and the resulting long- and short-term trajectories.
* Extreme events: Development of an understanding of the dynamical mechanisms and changing statistics of extreme weather
Extreme weather or extreme climate events includes unexpected, unusual, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Often, extreme events are based on a loca ...
events on a warming Earth.Climate Resilience (RD 2)
RD2 strives to improve the understanding ofclimate resilience
Climate resilience is defined as the "capacity of social, economic and ecosystems to cope with a hazardous event or trend or disturbance".IPCC, 2022Summary for Policymakers .-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, M. Tignor, ...
, i.e. resilience of social and ecological systems to climate change, in various sectors and across multiple spatial scales. As a general framing for RD2 research, resilience entails aspects of persistence —the capacity of systems to resist and absorb short-term shocks, yet remain within critical thresholds; adaptability—the capacity to recover, adjust to changing external drivers, and thereby remain on the current trajectory; and transformability —the capacity to cross thresholds, if necessary, into new, robust long-term development trajectories.
* Climate change impacts and their socio-economic consequences related to land use, agriculture, forests, hydrological systems, human health and well-being, and urban areas;
* Adaptive capacity of societies and ecosystems across scales at different levels of global warming;
* Synergies between climate change adaptation and mitigation to improve climate resilience and achieve sustainable human development.
Transformation Pathways (RD 3)
 Research Department 3 (RD3) aims to provide an integrated perspective on climate change mitigation and climate change impact pathways to inform societies’ choices. Climate protection may have costs, but unabated climate change can have strong adverse effects on economic development; loss of
Research Department 3 (RD3) aims to provide an integrated perspective on climate change mitigation and climate change impact pathways to inform societies’ choices. Climate protection may have costs, but unabated climate change can have strong adverse effects on economic development; loss of biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
is amplified by climate change, but could also be increased by certain mitigation strategies relying on the use of land; climate protection might create winners and losers, but climate change itself will have strong distributional impacts and affect low income groups disproportionately.
* Development of integrated climate protection and climate impact pathways. Evaluation of mitigation strategies and remaining impacts with regard to socio-economic development, distributional effects and planetary integrity.
* Societal impacts of climate change. Assessment of climate change as a potential driver of migration, displacement
Displacement may refer to:
Physical sciences
Mathematics and Physics
* Displacement (geometry), is the difference between the final and initial position of a point trajectory (for instance, the center of mass of a moving object). The actual path ...
, and conflict.
* Sustainable land use. Evaluation of land-use transformation pathways exploiting mitigation potential while at the same time ensuring biosphere integrity.
* Sustainable energy use. Exploration of transformation pathways towards sustainable and carbon-neutral energy use taking into account their resource use and environmental footprint.
* Policy strategies for climate protection pathways. Analysis of regulatory and economic climate policy instruments with regard to their efficiency and distributional implications.
Complexity Science (RD 4)
This RD is devoted toMachine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
, Nonlinear Methods and decision strategies. Of particular focus are:
* Climate phenomena and extremes: Prediction and modelling with complex networks, statistical physics
Statistical physics is a branch of physics that evolved from a foundation of statistical mechanics, which uses methods of probability theory and statistics, and particularly the mathematical tools for dealing with large populations and approxim ...
, and machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
.
* Abrupt climate transitions: Detection and prediction with advanced time series analysis, numerical modelling, and analytical concepts.
* Socio-economic and infrastructure networks: Understanding dynamics through new modelling and stability concepts.
* Climate decisions: Uncovering principles and modelling interactions using econometrics
Econometrics is the application of statistical methods to economic data in order to give empirical content to economic relationships. M. Hashem Pesaran (1987). "Econometrics," '' The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics'', v. 2, p. 8 p. 8 ...
, game theory, and machine learning.
Future Labs
Six of the FutureLabs are time-limited and will be evaluated after five years. One permanent FutureLab has been established that aims to strengthen the institute's efforts in capacity building activities as well as its social metabolism research endeavors.FutureLab on Social Metabolism & Impacts (Permanent Future Lab)
Human societies depend on a continuous throughput of materials and energy for their reproduction. Raw materials must be extracted from the environment, transformed into goods and services (e.g. food, housing and mobility) and eventually all materials are released back to the environment as emissions and waste. Free energy and socially organized human labor are required to keep this social metabolism going.FutureLab on Public Economics and Climate Finance
The research within this Future Lab is undertaken against the background of the question how we can reconcile short-term human well-being with long-term environmental sustainability. It aims to provide scientific advances and policy-relevant insights regarding the economics of theglobal commons Global commons is a term typically used to describe international, supranational, and global resource domains in which common-pool resources are found. Global commons include the earth's shared natural resources, such as the high oceans, the at ...
– which include natural commons, such as the atmosphere, land, and forests, as well as social commons, such as health care and education systems, basic infrastructures and a stable financial system.
FutureLab on Security, Ethnic Conflicts and Migration
With this FutureLab, PIK kick-started dedicated research on the implications of climate change for human security and conflict, accounting for the potential roles of human migration anddisplacement
Displacement may refer to:
Physical sciences
Mathematics and Physics
* Displacement (geometry), is the difference between the final and initial position of a point trajectory (for instance, the center of mass of a moving object). The actual path ...
as drivers, outcomes, or mediating factors.
FutureLab on Game Theory and Networks of Interacting Agents
In this cross-institutional FutureLab between PIK and theMercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change
The Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC) conducts research and fosters dialogue about how the global commons, such as the atmosphere and the oceans, might be used and shared by many yet nevertheless be protected. ...
(MCC), established in January 2019 and hosted by PIK's Research Department 4, a small team of interdisciplinary researchers explores and develops cutting-edge modeling and analysis methods for complex decision situations with several decision makers, and applies these to problems in national and international climate policy and sustainable management.
FutureLab on Earth Resilience in the Anthropocene
In theAnthropocene
The Anthropocene ( ) is a proposed geological epoch dating from the commencement of significant human impact on Earth's geology and ecosystems, including, but not limited to, anthropogenic climate change.
, neither the International Commissio ...
, with exponential rise in human pressures such as greenhouse gas emissions and land-use change, there is an increasing risk of crossing critical thresholds and thereby degrading hard-wired biophysical processes that regulate the state of the entire Earth system. There is an urgent need for understanding and quantifying the state of the self-regulatory and regenerative capacities of our planetary life-support system, in short Earth system resilience.
FutureLab on Inequality, Human Well-Being and Development
This FutureLab analyses the role of inequality, human well-being and development for understanding the impacts of and responses to climate change from an economic perspective.Partners
PIK provides scientific advice to international organizations like theWorld Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
and the International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster glo ...
, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of ...
, the International Organization for Migration
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) is a United Nations agency that provides services and advice concerning migration to governments and migrants, including internally displaced persons, refugees, and migrant workers.
The IOM w ...
as well as to regional bodies like the Federal Government of Germany
The Federal Cabinet or Federal Government (german: link=no, Bundeskabinett or ') is the chief executive body of the Federal Republic of Germany. It consists of the Federal Chancellor and cabinet ministers. The fundamentals of the cabinet's or ...
and the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
. PIK scientists also contribute to the reports of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). From 2008 to 2015, the IPCC working group Climate Change mitigation was co-chaired by the institute's co-director and chief economist Ottmar Edenhofer. In the IPCC's sixth assessment cycle (2016–2022) PIK researchers have contributed their expertise to the Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C
The Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C (SR15) was published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) on 8 October 2018. The report, approved in Incheon, South Korea, includes over 6,000 scientific references, and was prep ...
(2017) and the Special Report on Climate Change and Land (2019). Several PIK researchers are chapter authors for the Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), to be published in 2021–2022.
PIK’s further scientific networks include:
* The Earth League
* The Earth Commission
* Food System Economics Commission
* German Advisory Council on Global Change (WGBU)
* German Advisory Council on the Environment (SRU)
* German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina
The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (german: Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina – Nationale Akademie der Wissenschaften), short Leopoldina, is the national academy of Germany, and is located in Halle (Saale). Founded ...
* United Nations Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN)
Financing
PIK is a non-profit and a member of theLeibniz Association
The Leibniz Association (German: ''Leibniz-Gemeinschaft'' or ''Wissenschaftsgemeinschaft Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz'') is a union of German non-university research institutes from various disciplines.
As of 2020, 96 non-university research insti ...
and is funded to a roughly equal extent by the Federal Republic of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between ...
and the Federal State of Brandenburg. In 2020, the institute received around 12.4 million euros in institutional funding. Additional project funding from external sources amounted to around 14.4 million euros, mostly from public sources such as European Union research programmes or the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft)./ref>
See also
*Climatic Research Unit
The Climatic Research Unit (CRU) is a component of the University of East Anglia and is one of the leading institutions concerned with the study of natural and anthropogenic climate change.
With a staff of some thirty research scientists and s ...
* NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
Goddard Institute for Space Studies
The Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) is a laboratory in the Earth Sciences Division of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center affiliated with the Columbia University Earth Institute.
The institute is located at Columbia University in N ...
* NCAR
The US National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR ) is a US federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) managed by the nonprofit University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) and funded by the National Science Foundatio ...
Community Climate System Model The Community Climate System Model (CCSM) is a coupled general circulation model (GCM) developed by the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) with funding from the National Science Foundation (NSF), the Department of Energy (DoE), ...
* Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
* ''Earth for All'' initiative
References
Further reading
*USA Today
''USA Today'' (stylized in all uppercase) is an American daily middle-market newspaper and news broadcasting company. Founded by Al Neuharth on September 15, 1982, the newspaper operates from Gannett's corporate headquarters in Tysons, Virgi ...
br> Stories about: Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact ResearchResearchers refine assessment of tipping elements of the climate system
regarding
Tipping point (climatology)
In climate science, a tipping point is a critical threshold that, when crossed, leads to large and often irreversible changes in the climate system. If tipping points are crossed, they are likely to have severe impacts on human society. Tippin ...
23 June 2011 ''Some Like It Hot!''
Bill McKibben 9 May 2013
New York Review of Books
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator ...
review o''Turn Down the Heat: Why a 4ºC Warmer World Must Be Avoided''
a report for the World Bank by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and Climate Analytics; November 2012, 58 pp., available at climatechange.worldbank.org
External links
Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research
{{Authority control Climate change organizations Environmental research institutes Research institutes in Germany Organisations based in Potsdam