Pomerania During The Early Middle Ages on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pomerania during the Early Middle Ages covers the
 Pomerelia has also been settled by Slavs in the 7th and 8th century. Based on archeological and linguistic findings, two hypotheses have been put forth: one posits that these settlers moved northward along the
Pomerelia has also been settled by Slavs in the 7th and 8th century. Based on archeological and linguistic findings, two hypotheses have been put forth: one posits that these settlers moved northward along the
 By the 9th to 11th century the region was recorded as inhabited by various tribes belonging to the Lechitic group of the
By the 9th to 11th century the region was recorded as inhabited by various tribes belonging to the Lechitic group of the
Another chronicle written in 1113 by
 In the Middle Ages, Pomeranians, Liutizians and
In the Middle Ages, Pomeranians, Liutizians and

 Scandinavian settlements at the Pomeranian coast include
Scandinavian settlements at the Pomeranian coast include  A merchants' settlement has also been suggested near Arkona, but no archeological evidence supports this theory.
A merchants' settlement has also been suggested near Arkona, but no archeological evidence supports this theory.

 In 936, the area west of the
In 936, the area west of the
"Henry I and the Beginnings of the Saxon Empire."
''The English Historical Review'', Vol. 83, No. 326. (Jan., 1968), pp 1–32. In 983, the area regained independence in an uprising initiated by the Liutizian federation.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.27, The margraves and bishops upheld their claims, but were not able to reinforce them despite various expeditions.Werner Buchholz, ''Pommern'', Siedler, 1999, pp.28,29, A similar pagan reaction in
History of Pomerania
The history of Pomerania starts shortly before 1000 AD with ongoing conquests by newly arrived Polans rulers. Before that, the area was recorded nearly 2000 years ago as Germania, and in modern-day times Pomerania is split between Germany and ...
from the 7th to the 11th centuries.
The southward movement of Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
during the migration period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
had left territory later called Pomerania largely depopulated by the 7th century.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.26, Between 650 and 850 AD, West Slavic tribes settled in Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, pp.29ff The tribes between the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
and the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
were collectively known as Pomeranians, and those west of the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
as Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Hither Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, a loose monarchic c ...
and later Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
. A distinct Slavic tribe, the Rani
''Rani'' in Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia, sometimes spelled ''Ranee'', is a Hindu/Sanskrit feminine given name. The term is the female form of the term for princely rulers in South and Southeast Asia and applies equally to the wife of a ...
, was based on the island of Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
and the adjacent mainland.Werner Buchholz, ''Pommern'', Siedler, 1999, pp.22,23, In the 8th and 9th centuries, Slavic- Scandinavian emporia were set up along the coastline as powerful centers of craft and trade.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, pp.15ff,
In 936, the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
set up the Billung
The House of Billung was a dynasty of Saxon noblemen in the 9th through 12th centuries.
The first known member of the house was Count Wichmann, mentioned as a Billung in 811. Oda, the wife of Count Liudolf, oldest known member of the Liudol ...
and Northern march
The Northern March or North March (german: Nordmark) was created out of the division of the vast '' Marca Geronis'' in 965. It initially comprised the northern third of the ''Marca'' (roughly corresponding to the modern state of Brandenburg) and ...
es in Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, West ...
, divided by the Peene
The Peene () is a river in Germany.
Geography
The Westpeene, with the Ostpeene as its longer tributary, and the Kleine Peene/Teterower Peene (with a ''Peene '' without specification (or ''Nordpeene'') as its smaller and shorter affluent) flo ...
river. The Liutician federation regain independence in an uprising of 983 but succumbed to internal conflicts and disintegrated in the course of the 11th century.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, pp.261,345ff In late 960s, Polish Piasts acquired parts of eastern Pomerania, where the short-lived Diocese of Kołobrzeg (Kolberg) was installed in 1000 AD. The Pomeranians regained independence during the Pomeranian uprising of 1005.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.32, :pagan reaction of 1005Werner Buchholz, ''Pommern'', Siedler, 1999, p.25, : pagan uprising that also ended the Polish suzerainty in 1005Jürgen Petersohn, ''Der südliche Ostseeraum im kirchlich-politischen Kräftespiel des Reichs, Polens und Dänemarks vom 10. bis 13. Jahrhundert: Mission, Kirchenorganisation, Kultpolitik'', Böhlau, 1979, p.43, . 1005/13Oskar Eggert, ''Geschichte Pommerns'', Pommerscher Buchversand, 1974: 1005-1009Roderich Schmidt, ''Das historische Pommern: Personen, Orte, Ereignisse'', Böhlau, 2007, p.101, . 1005/13A. P. Vlasto, ''Entry of Slavs Christendom'', CUP Archive, 1970, p.129, : abandoned 1004 - 1005 in face of violent oppositionNora Berend, ''Christianization and the Rise of Christian Monarchy: Scandinavia, Central Europe and Rus' C. 900-1200'', Cambridge University Press, 2007, p.293, , David Warner, ''Ottonian Germany: The Chronicon of Thietmar of Merseburg'', Manchester University Press, 2001, p.358, , Michael Borgolte, Benjamin Scheller, ''Polen und Deutschland vor 1000 Jahren: Die Berliner Tagung über den"akt von Gnesen"'', Akademie Verlag, 2002, p.282, , Michael Müller-Wille, ''Rom und Byzanz im Norden: Mission und Glaubenswechsel im Ostseeraum während des 8.-14. Jahrhunderts: internationale Fachkonferenz der deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft in Verbindung mit der Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur, Mainz: Kiel, 18.-25. 9. 1994'', 1997, p.105, ,
During the first half of the 11th century, the Liuticians participated in the Holy Roman Empire's wars against Piast Poland
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in the early 12th ce ...
.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, pp.356ff The alliance broke off when Poland was defeated,Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.359 and the Liutician federation broke apart in 1057 during a civil war.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.365 The Liutician capital was destroyed by the Germans in 1068/69,Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.366 making way for the subsequent eastward expansion of their western neighbor, the Obodrite state. In 1093, the Luticians,Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.379 Pomeranians and Rani had to pay tribute to Obodrite prince Henry.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.367
Migration period
The pattern of settlement in Pomerania started to change in the 3rd century. The prospering material cultures of theRoman Iron Age
The archaeology of Northern Europe studies the prehistory of Scandinavia and the adjacent North European Plain,
roughly corresponding to the territories of modern Sweden, Norway, Denmark, northern Germany, Poland and the Netherlands.
The regi ...
decayed. Only in some areas a continuity of these cultures is observed until the 5th and 6th centuries.
These changes are associated with the migration period, when Germanic tribes migrated towards the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
.
Slavic Pomeranians
The 5th century marks the climax of an era that is characterized by a gap between the latest Germanic and the earliest Slavic archaeological findings inPomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, that researchers until today cannot explain sufficiently.
Origin debate
The origins of theSlavic tribes
This is a list of Slavic peoples and Slavic tribes reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500.
Ancestors
*Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers)
** Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of Ba ...
in Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
are subject to an ongoing debate. One school of thought, particularly popular among German researchers, sees the origins of these Slavs east of the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
and postulates a westward migration from there during the 6th and 7th centuries. It does not explain, however, the enormous increase in both the inhabited area and the numbers of the settlers. The second school of thought, popular among Polish researchers, seeks to prove an archeological continuity from the cultures of the Roman Iron Age
The archaeology of Northern Europe studies the prehistory of Scandinavia and the adjacent North European Plain,
roughly corresponding to the territories of modern Sweden, Norway, Denmark, northern Germany, Poland and the Netherlands.
The regi ...
to the medieval Slavic culture. The third hypothesis postulates that parts of the Veneti were assimilated by the Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
while the rest became Slavs. No consensus on the subject has emerged.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, pp.26,27
First appearance of Slavic cultures
The first appearance of Slavs in the area is still unclear and is related to the question of the general ethnogenesis of the Slavs. According to German historiography, Slavic immigration took place between 650 and 850 AD, reaching first the southern parts of the mainland,Usedom
Usedom (german: Usedom , pl, Uznam ) is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
It is north of the Szczeci ...
and Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the ...
in the late 8th century, and Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
in the 9th century. On the other hand, Polish historiography has stressed linkages between Roman-era cultures and later, clearly Slavic, populations.
The first archeological records of Slavs in the Oder area are ceramics of the Sukow type dated back to the 6th or the beginning 7th century.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.29 The Sukow
Sukow is a municipality in the Ludwigslust-Parchim district, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; nds, Mäkelborg-Vörpommern), also known by its anglicized name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a state in the north- ...
type is also known as Sukow-Szeligi group, Deez type, and Dziedzice type. These findings are associated with the first wave of immigrants from what is now Southwestern Poland. For some areas, continuous settlement from the Roman to the Slavic era is suggested on the basis of analyses of pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametop ...
name transitions. Farther Pomerania and Pomerelia appear to have been unsettled in this period. Archeological research in Pomerelia is less extensive than that of Farther Pomerania. It has been previously suggested that subsequent appearances of new material cultures were due to other waves of immigration, but it is presently interpreted as a mere technology transfer not involving mass migration.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.17,
Slavic Feldberg type ceramics, found in a region comprising the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
area up to the Persante (Parseta) river, as well as Mecklenburg and Brandenburg, are dated back to the 7th and 8th century. Feldberg ceramics dominate west of the Oder since the mid-8th century, except for Northwestern Pomerania.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.13, This ceramic type is associated by some researchers with subsequent waves of migration from Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
, Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
and Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
.
The Bavarian Geographer The epithet "Bavarian Geographer" ( la, Geographus Bavarus) is the conventional name for the anonymous author of a short Latin medieval text containing a list of the tribes in Central- Eastern Europe, headed ().
The name "Bavarian Geographer" was ...
's anonymous medieval document, compiled in 830 in Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the ...
, contains a list of the tribes in Central-Eastern Europe east of the Elbe. It mentions among others the Uuilci (Veleti) with 95 civitas
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (; plural ), according to Cicero in the time of the late Roman Republic, was the social body of the , or citizens, united by law (). It is the law that binds them together, giving them responsibilities () on th ...
, the Nortabtrezi (Obotrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ...
) with 53 civitas, the Milzane (Milceni
The Milceni or Milzeni ( cs, Milčané; german: Milzener; pl, Milczanie) were a West Slavs, West Slavic tribe, who settled in the present-day Upper Lusatia region. They were first mentioned in the middle of the 9th century AD by the Bavarian Geogr ...
) with 30 civitas, and the Hehfeldi (Hevelli
The Hevelli or Hevellians/ Navellasîni (sometimes ''Havolane''; german: Heveller or ''Stodoranen''; pl, Hawelanie or ''Stodoranie''; cs, Havolané or ''Stodorané'') were a tribe of the Polabian Slavs, who settled around the middle Havel river ...
) with 14 civitas.
 Pomerelia has also been settled by Slavs in the 7th and 8th century. Based on archeological and linguistic findings, two hypotheses have been put forth: one posits that these settlers moved northward along the
Pomerelia has also been settled by Slavs in the 7th and 8th century. Based on archeological and linguistic findings, two hypotheses have been put forth: one posits that these settlers moved northward along the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river, and another views them as the Veleti moving westward from the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
delta.
Slavic settlement extended to Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, West ...
in the 9th century and possibly as early as the 8th century. Dense Slavic settlement before the 9th century is especially unlikely for the northern areas, where findings of Feldberg ceramics are very rare. Freesendorf ceramics however, which became popular in the course of the 9th century, are found abundantly in northwestern Pomerania, too.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.14,
Soon after the Slavic settlement, Gords fortified with walls of wood and clay were built. One of the oldest ''gards'' is the stronghold of Dragovit, king of the Veleti, that was targeted by an expedition led by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
in 789 and is thought to be at modern ''Vorwerk'' near Demmin
Demmin () is a town in the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It was the capital of the former district of Demmin.
Geography
Demmin lies on the West Pomeranian plain at the confluence of the rivers ...
. The Slavs modeled their burghs and armament following West Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
an standards, yet in the 8th and 9th century, the density of burghs in Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
and Pomerania became exceptionally high compared with other territories.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.18,
Tribal and territorial organization
West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic la ...
. The small tribes dwelling west of the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
river were known collectively as "Veleti" (Wilzi), since the late 10th century as "Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
" (Lutici), the tribes further east as "Pomeranians". Another distinct tribe, the Rani
''Rani'' in Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia, sometimes spelled ''Ranee'', is a Hindu/Sanskrit feminine given name. The term is the female form of the term for princely rulers in South and Southeast Asia and applies equally to the wife of a ...
, lived on the island of Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
and the adjacent mainland. These tribes spoke Polabian (Veleti, Rani) and closely related Pomeranian (Pomeranians) dialects. A Frankish document titled ''Bavarian Geographer The epithet "Bavarian Geographer" ( la, Geographus Bavarus) is the conventional name for the anonymous author of a short Latin medieval text containing a list of the tribes in Central- Eastern Europe, headed ().
The name "Bavarian Geographer" was ...
'' (ca 845) mentions the tribes of Volinians (''Velunzani''), Pyritzans The Prissani or Pyritzans ( pl, Pyrzyczanie) were a medieval tribe in Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Prissani" with 70 civitas by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845.Johannes Hoops, Herbert Jankuhn, Heinrich Beck, Reallexikon der germanische ...
(''Prissani''), Ukrani
250px, ''Burgwallinsel'', a former Ukrian Oberuckersee.html"_;"title="burgh_on_an_isle_in_Lake_Oberuckersee">burgh_on_an_isle_in_Lake_Oberuckersee_
The_Ukrani_or_UkriansOberuckersee.html"_;"title="burgh_on_an_isle_in_Lake_Oberuckersee">burgh_o ...
(''Ukri'') and Veleti (''Wiltzi'') around the lower Oder.
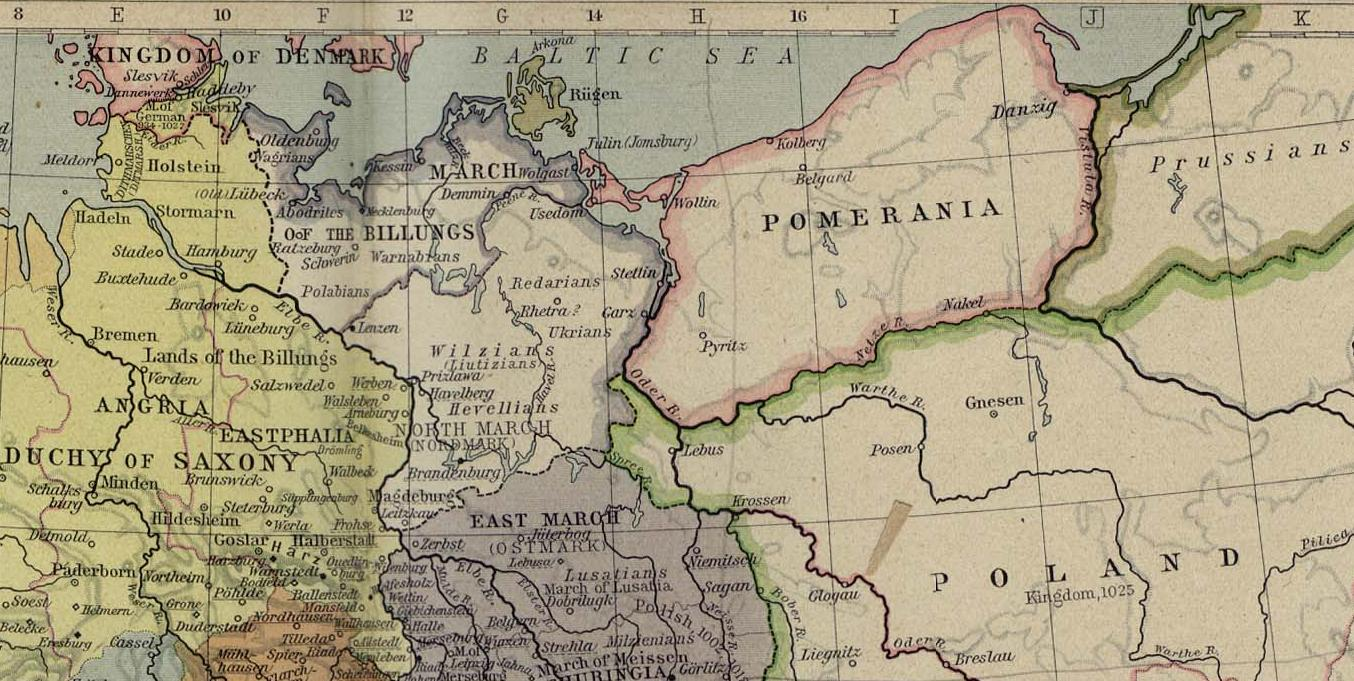
From the 9th to the 11th century, at least ten Pomeranian tribes dwelled between the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
and Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river. They are not known by name except for the Volinians and Pyritzans The Prissani or Pyritzans ( pl, Pyrzyczanie) were a medieval tribe in Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Prissani" with 70 civitas by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845.Johannes Hoops, Herbert Jankuhn, Heinrich Beck, Reallexikon der germanische ...
. It is not known if these tribes ever formed any kind of a tribal union. It is also possible that on the two sides of the river, the tribes were split from the beginning into eastern and western Pomeranian groups, with the latter possibly related to the Veleti.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.30
The settlements of the distinct tribes were separated from each other and from their neighbors by vast woodlands. In 1124, it took Otto of Bamberg
Otto of Bamberg (1060 or 1061 – 30 June 1139) was a German missionary and papal legate who converted much of medieval Pomerania to Christianity. He was the bishop of Bamberg from 1102 until his death. He was canonized in 1189.
Early life
T ...
three days to cross the woods separating the Pomeranians from the neighboring Poles.
Among the various Pomeranian tribes, the territory of the Volinians was the smallest, but also the most densely settled, with about one settlement for every four square kilometers, around 1000 AD. In contrast, the other tribe explicitly mentioned in contemporary chronicles, was that of the Pyritzans The Prissani or Pyritzans ( pl, Pyrzyczanie) were a medieval tribe in Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Prissani" with 70 civitas by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845.Johannes Hoops, Herbert Jankuhn, Heinrich Beck, Reallexikon der germanische ...
, who inhabited the area around Pyritz and Stargard
Stargard (; 1945: ''Starogród'', 1950–2016: ''Stargard Szczeciński''; formerly German language, German: ''Stargard in Pommern'', or ''Stargard an der Ihna''; csb, Stôrgard) is a city in northwestern Poland, located in the West Pomeranian V ...
but whose settlements numbered roughly only one for every twenty kilometers. The center of the Volinian territory was a town located at the site of the modern town of Wolin (Wollin) on Wolin (Wollin) island. Russian, Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, and Scandinavian merchants lived in the town.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, pp.30,31,
The Lutici tribes in 983 formed the Liutizian federation, comprising the Circipanes
Circipania (german: Circipanien, Zirzipanien) was a medieval territory in what is now northeastern Germany. The name derives from Latin ''circum'' (around) and ''Pane'' (the Peene River). The region was enclosed roughly by the upper Recknitz, Tr ...
, Kessinians, Redarians
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
, and Tollensians The Tollensians ( la, Tholenzi, pl, Dołężanie, Tolężanie, Dolency, Doleczanie) were a West Slavic tribe inhabiting the shores of the lower and middle Tollense (Dołęża) river, after which they were named. They were part of the Veleti/ Lutic ...
, probably also the Hevelli
The Hevelli or Hevellians/ Navellasîni (sometimes ''Havolane''; german: Heveller or ''Stodoranen''; pl, Hawelanie or ''Stodoranie''; cs, Havolané or ''Stodorané'') were a tribe of the Polabian Slavs, who settled around the middle Havel river ...
and Rani
''Rani'' in Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia, sometimes spelled ''Ranee'', is a Hindu/Sanskrit feminine given name. The term is the female form of the term for princely rulers in South and Southeast Asia and applies equally to the wife of a ...
. The Volinians also played an important role.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.31, They were at various times both ally and military target of the Holy Roman Empire and Poland. The federation declined in the 1050s due to internal struggles (''see below'').
There are sparse records of dukes in this area, but no records about the extension of their duchies or any dynastic relations. The first written record of any local Pomeranian ruler is the 1046 mention of ZemuzilJan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.33, (in Polish literature also called ''Siemomysł'') at an imperial meeting. A "dux Pomorie" is recorded for the year 997 in a 13th-century vitae of Adalbert of Prague
Adalbert of Prague ( la, Sanctus Adalbertus, cs, svatý Vojtěch, sk, svätý Vojtech, pl, święty Wojciech, hu, Szent Adalbert (Béla); 95623 April 997), known in the Czech Republic, Poland and Slovakia by his birth name Vojtěch ( la, ...
, most probably seated in Gdańsk (Danzig).De s. Adalberto episcopo Pragensi, dMGH SS XV, c. 12, p. 1182Another chronicle written in 1113 by
Gallus Anonymus
''Gallus Anonymus'' ( Polonized variant: ''Gall '') is the name traditionally given to the anonymous author of ''Gesta principum Polonorum'' (Deeds of the Princes of the Poles), composed in Latin between 1112 and 1118.
''Gallus'' is generally rega ...
mentions several dukes of Pomerania: Swantibor, Gniewomir, and an unnamed duke besieged in Kołobrzeg
Kołobrzeg ( ; csb, Kòlbrzég; german: Kolberg, ), ; csb, Kòlbrzég , is a port city in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in north-western Poland with about 47,000 inhabitants (). Kołobrzeg is located on the Parsęta River on the south coast ...
. A mention of a battle between the Pomeranians, Poles and Hungarians in the '' Gesta Hunnorum et Hungarorum'', taken as historical by earlier historians, has been identified as medieval folklore, since the author Simon de Keza mixed up historical events with legends. This 13th-century chronicle reports that the later Hungarian king Bela I had fled to Mieszko II of Poland
Mieszko II Lambert (; c. 990 – 10/11 May 1034) was King of Poland from 1025 to 1031, and Duke from 1032 until his death.
He was the second son of Bolesław I the Brave, but the eldest born from his third wife Emnilda of Lusatia. He was proba ...
(mistaken for Casimir I), and defeated a Pomeranian duke ("Pomoranie ducem") in a duel. The Annals of Pegau (''Annales Pegaviensis''), written in 1150, mention a Wilk de Posduwc
Wilk is a surname of English and Polish-language origin.
In Poland, the surname means wolf and is pronounced . It has 35,000 bearers in Poland and ranks about 60th on the list of the most popular Polish surnames (fifth in Podkarpackie Voivodeshi ...
(Wolf of Pasewalk
Pasewalk () is a town in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district, in the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in Germany. Located on the Uecker river, it is the capital of the former Uecker-Randow district, and the seat of the Uecker-Randow-Tal '' Amt'' ...
) as one of the grandfathers of the founder of Pegau Abbey
The Abbey of St. James in Pegau was a Benedictine monastery in the town of Pegau
Pegau () is a town in the Leipzig district in Saxony, Germany, situated in a fertile plain, on the White Elster, 18 m. S.W. from Leipzig by the railway to Zeitz.
...
and later margrave of Meissen
This article lists the margraves of Meissen, a march and territorial state on the eastern border of the Holy Roman Empire.
History
King Henry the Fowler, on his 928-29 campaign against the Slavic Glomacze tribes, had a fortress erected on a ...
, Wiprecht von Groitzsch, born 1050. The annals say that Wilk held a "Pomeranorum primatum". Since the oldest parts of these annals are regarded to resemble "legendary tales", it is uncertain whether Wilk is a historical or legendary figure. Pomeranian historian Adolf Hofmeister
Adolf (also spelt Adolph or Adolphe, Adolfo and when Latinised Adolphus) is a given name used in German-speaking countries, Scandinavia, the Netherlands and Flanders, France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Latin America and to a lesser extent in vari ...
proposed that the record might nevertheless have a grain of truth in it, but in this case sees Wilk not as a universal ruler of Pomerania, but as a local or subordinate prince.

Languages
The western Slavs included the ancestors of the peoples known later asPoles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in ...
, Pomeranians, Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, ...
, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 mi ...
and Polabians. The northern so-called Lechitic group includes, along with Polish, the dead Polabian and Pomeranian language
), East Low German, East Pomeranian dialect
The Pomeranian language ( Polish: ''pomorszczyzna'' or ''język pomorski'', German: ''Pomoranisch'' or ''die pomoranische Sprache'') is in the Pomeranian group of Lechitic languages ( Polish: ''grupa ...
s. The languages of the southern part of the Polabian area, preserved as relics today in Upper and Lower Lusatia
Lower Lusatia (; ; ; szl, Dolnŏ Łużyca; ; ) is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the sou ...
, occupy a place between the Lechitic and Czecho-Slovak groups.
According to The Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
:
: " Lekhitic languages, also spelled Lechitic , group of West Slavic languages composed of Polish, Kashubian and its archaic variant Slovincian, and the extinct Polabian language
The Polabian language was a West Slavic language that was spoken by the Polabian Slavs (german: Wenden) in present-day northeastern Germany around the Elbe (''Łaba/Laba/Labe'' in Slavic) river, from which derives its name ("po Labe" – ''u ...
. All these languages except Polish are sometimes classified as a Pomeranian subgroup. In the early Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, before their speakers had become Germanized, Pomeranian languages and dialects were spoken along the Baltic in an area extending from the lower Vistula River
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
to the lower Oder River
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows t ...
. Kashubian and Slovincian survived into the 20th century; there were still a considerable number of native speakers of Kashubian in Poland and Canada in the 1990s. The extinct Polabian language, which bordered the Sorbian dialects in eastern Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, was spoken by the Slavic population of the Elbe River
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of ...
region until the 17th or 18th century; a dictionary and some phrases written in the language exist".
Religion
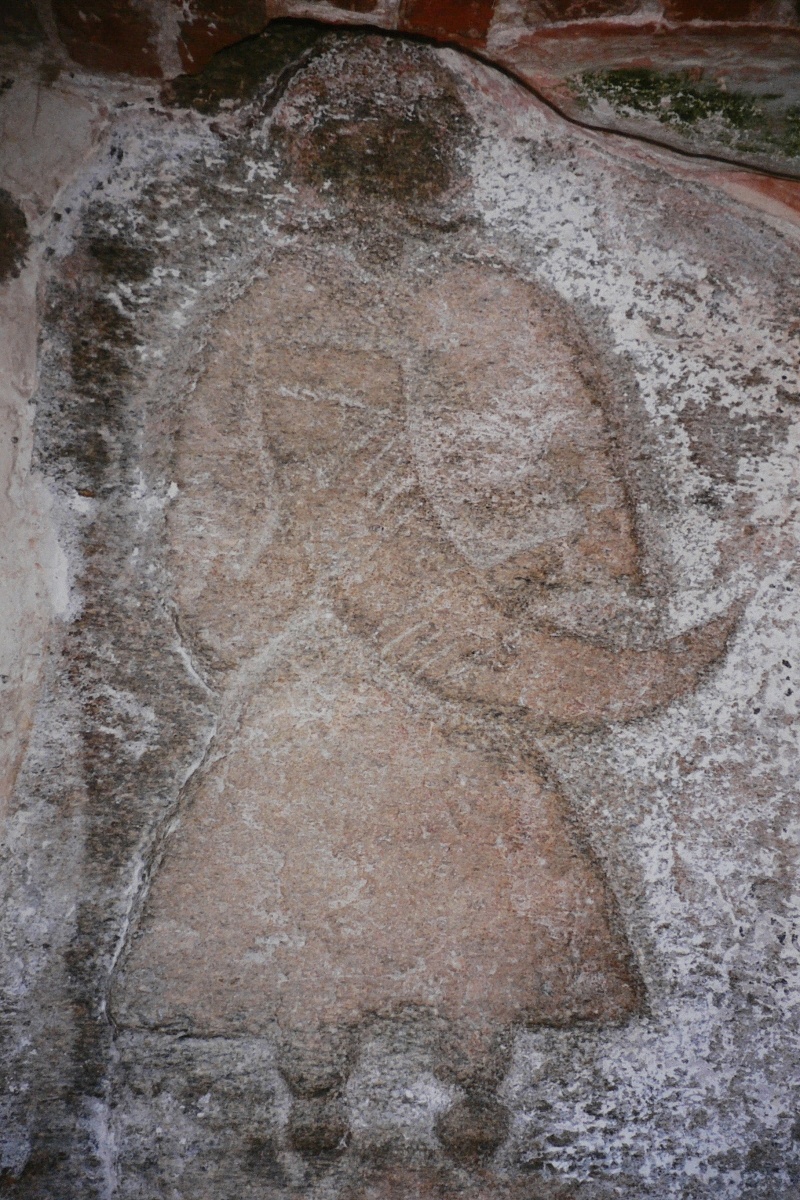
 In the Middle Ages, Pomeranians, Liutizians and
In the Middle Ages, Pomeranians, Liutizians and Rani
''Rani'' in Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia, sometimes spelled ''Ranee'', is a Hindu/Sanskrit feminine given name. The term is the female form of the term for princely rulers in South and Southeast Asia and applies equally to the wife of a ...
worshipped gods of the Slavic mythology
Slavic mythology or Slavic religion is the religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and the 13th century. The South Slavs, who likely settled in the Bal ...
:
: The gods were worshipped in temples, sacred grove
Sacred groves or sacred woods are groves of trees and have special religious importance within a particular culture. Sacred groves feature in various cultures throughout the world. They were important features of the mythological landscape and ...
s, sacred trees and sacred springs. The priesthood was a powerful class of the society. The elders held their assemblies in the sacred places. Important decisions were made only after asking an oracle
An oracle is a person or agency considered to provide wise and insightful counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. As such, it is a form of divination.
Description
The word ...
.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.47,
Among oracles were horse oracles in Szczecin and Arkona.
Major temple sites were:
* Arkona ( Swantewit temple)
*Charenza
Charenza, also Karentia or Karenz, later also Gharense, was a medieval '' Slavic burgwall'' on the island of Rügen in the Baltic Sea. It was the administrative centre of the Rani tribe and of the Principality of Rugia. Today, the remnants are ca ...
(numerous temples, e.g. Porenut, Rugievit)
* Gützkow
*Wolgast
Wolgast (; csb, Wòłogòszcz) is a town in the district of Vorpommern-Greifswald, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated on the bank of the river (or strait) Peenestrom, vis-a-vis the island of Usedom on the Baltic coast that can b ...
(Jarovit
Yarovit, Iarovit (or Yerovit, Ierovit) is a Polabian god of war, worshipped in Vologošč ( Circipanians) and Hobolin ( Hobolians; modern Havelberg). Sources give only a brief description of his cult, his main temple was located in Vologošč, ...
temple)
*Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the ...
(worship an idol referred to as "The iron lance of Caesar")
*Szczecin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
, two to four temples,Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.45, most notably the temple of Triglaw
Triglav ( "Three-headed one") is the god of the Pomeranians and probably some of the Polabian Slavs, worshipped in Szczecin, Wolin and probably Brenna (now Brandenburg). His cult is confirmed in the biographies of St. Otto of Bamberg. His cul ...
, a three-headed god and a sacred walnut tree
Scandinavian settlements and emporia
Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Germ ...
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
n settlements were set up along the southern coast of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
, primarily for trade purposes. Their appearance coincides with the settlement and consolidation of the Slavic tribes in the respective areas. Scandinavians had contacts with the Slavs since their very immigration, these first contacts were soon followed by both the construction of Scandinavian emporia and Slavic burghs in their vicinity.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.15,
The Scandinavian settlements were larger than the early Slavic ones, their craftsmen had a considerably higher productivity, and in contrast to the early Slavs, the Scandinavians were capable of seafaring. It is not known whether or not the emporia were somehow integrated into the emerging tribal organizations of the Slavs, yet it is taken for certain that they were very important centers of power.
Their importance for trade with the Slavic world however was limited to the coastal regions and their hinterlands - while imported goods associated with Scandinavian trade have been found in the areas between Baltic coast, Mecklenburg Lake District
The Mecklenburg Lake Plateau or Mecklenburg Lakeland
- Federal Ministry of Economics ...
and Pomeranian lake chain, evidence for contacts to distant Slavic areas further south is missing.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, pp.16,17,
- Federal Ministry of Economics ...
 Scandinavian settlements at the Pomeranian coast include
Scandinavian settlements at the Pomeranian coast include Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the ...
(on the isle of Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the ...
), Ralswiek (on the isle of Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
), Altes Lager Menzlin
Altes Lager (German for "Old Camp") is a site south of the village of Menzlin near Anklam, Western Pomerania, Germany. The site, on the banks of the river Peene, was an important Viking trading-post during the Viking Age. At that time, Pomerani ...
(at the lower Peene
The Peene () is a river in Germany.
Geography
The Westpeene, with the Ostpeene as its longer tributary, and the Kleine Peene/Teterower Peene (with a ''Peene '' without specification (or ''Nordpeene'') as its smaller and shorter affluent) flo ...
river),Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, pp.pp.237ff,244ff and Bardy-Świelubie near modern Kołobrzeg
Kołobrzeg ( ; csb, Kòlbrzég; german: Kolberg, ), ; csb, Kòlbrzég , is a port city in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in north-western Poland with about 47,000 inhabitants (). Kołobrzeg is located on the Parsęta River on the south coast ...
.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, pp.15,16, Menzlin was set up in the mid-8th century. In Wollin, seaside fortifications have been dated back to the beginning 10th century, yet remnants of older fortifications were also found, probably pointing to an earlier burgh with an adjacent open settlement. Wollin and Ralswiek began to prosper in the course of the 9th century.
Bardy-Świelubie differs from other emporia: The location is rather far from the coastline, and Bardy was built before 800, making it one of the earliest Slavic burghs in the coastal area. Archaeological findings indicate participation in Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
trade, but evidence of non-Slavic presence is missing. In the 9th century, Scandinavians (men and women) settled the site, as is evident from the adjacent Hügelgrab grave field in Świelubie. The exact site of the settlement, whether inside or close to the burgh, is not yet determined. A Slavic burgh as a predecessor for a Scandinavian settlement is not observed elsewhere, with the possible, but not yet evident exception of Wollin.
Reric
Reric or Rerik was one of the Viking Age multi-ethnic Slavic- Scandinavian emporia on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, located near Wismar in the present-day German state of Mecklenburg-VorpommernOle Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reri ...
, formerly located at Rerik
Rerik (, formerly Alt-Gaarz) is a town in the Rostock district, in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It is situated on the Baltic Sea coast, 19 km west of Bad Doberan, and 27 km northeast of Wismar. In 1938, Rerik was named afte ...
on the Fischland-Darß-Zingst peninsula in Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, West ...
, has recently been identified as Groß Strömkendorf on the eastern coast of Wismar Bay
The Bay of WismarKohl, Horst; Marcinek, Joachim and Nitz, Bernhard (1986). ''Geography of the German Democratic Republic'', VEB Hermann Haack, Gotha, p. 47. . or more commonly Wismar Bay or ''Wismarbucht'' is a well sheltered multi-sectioned bay ...
in Mecklenburg.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.12, Reric was set up around the year 700, but following later warfare between Obodrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ( ...
and Danes
Danes ( da, danskere, ) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
Danes generally regard t ...
, the merchants were resettled to Haithabu.
The exact ethnic composition of the settlements cannot be determined, it is thought that they had a multi-ethnic character - besides Scandinavians, a Slavic and Frisian presence has been suggested.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.16, Scandinavian presence is evident in artefacts, burial rites, and the type of houses.
Early emporia like Menzlin and Dierkow Dierkow near Rostock, Mecklenburg, was a Viking Age Slavic- Scandinavian settlement at the southern Baltic coast in the late 8th and early 9th century.
(just west of the Pomeranian border, near Rostock
Rostock (), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (german: link=no, Hanse- und Universitätsstadt Rostock), is the largest city in the German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state ...
) reached their peak already in the 9th century, no imported goods are found from the 10th century. Bardy-Świelubie was vacated in the late 9th century, when the Slavic settlement of Kołobrzeg
Kołobrzeg ( ; csb, Kòlbrzég; german: Kolberg, ), ; csb, Kòlbrzég , is a port city in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in north-western Poland with about 47,000 inhabitants (). Kołobrzeg is located on the Parsęta River on the south coast ...
became the new center of the region. Ralswiek made it into the new millennium, but at the time when written chronicles reported the site in the 12th century it had lost all its importance. Wollin was destroyed by the Danes in the 12th century.
Scandinavian arrowheads from the 8th and 9th centuries were found between the coast and the lake chains in the Mecklenburgian and Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
n hinterlands, pointing at periods of warfare between the Scandinavians and Slavs.
Jomsvikings
Jomsborg (Jomsburg) was the name given by several medieval Scandinavian sources to a stronghold on thePomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
n coast. It was set up by Danish king Harald Bluetooth
Harald "Bluetooth" Gormsson ( non, Haraldr Blátǫnn Gormsson; da, Harald Blåtand Gormsen, died c. 985/86) was a king of Denmark and Norway.
He was the son of King Gorm the Old and of Thyra Dannebod. Harald ruled as king of Denmark from c. 958 ...
and Styrbjörn in the course of Harald's internal struggles with his son, Sweyn Forkbeard
Sweyn Forkbeard ( non, Sveinn Haraldsson tjúguskegg ; da, Svend Tveskæg; 17 April 963 – 3 February 1014) was King of Denmark from 986 to 1014, also at times King of the English and King of Norway. He was the father of King Harald II of ...
, in the 970s or 980s, and housed a garrison of soldiers known as Jomsvikings. Jomsborg is believed today to be identical with Vineta, Jumne and Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the ...
. Harald is reported to have died in Jomsborg after he was wounded trying to regain his power with a Jomsviking and Norman fleet. Sweyn was captured by the Jomsvikings and held hostage in Jomsborg, until a peace was negotiated and Sweyn as well as Harald's body were sent back to Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
.

Trade, robbery, and piracy
Scandinavian emporia and major Slavic burghs were set up primarily at junctions of long-distance trade routes. Such trade routes ran along theVistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river, reaching the coast at Truso
Truso was a Viking Age port of trade (emporium) set up by the Scandinavians at the banks of the Nogat delta branch of the Vistula River, close to a bay (the modern Drużno lake), where it emptied into the shallow and brackish Vistula Lagoon. This ...
and Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
; along the western bank of the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
, coming from the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
area and Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The ...
and forking north of Schwedt
Schwedt (or Schwedt/Oder; ) is a town in Brandenburg, in northeastern Germany. With the official status of a ''Große Kreisstadt, Große kreisangehörige Stadt'' (major district town), it is the largest town of the Uckermark (district), Uckermark ...
with the eastern fork running through Szczecin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
and reaching the sea at Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the ...
, while the western fork ran through Menzlin and reached the sea at Wolgast
Wolgast (; csb, Wòłogòszcz) is a town in the district of Vorpommern-Greifswald, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated on the bank of the river (or strait) Peenestrom, vis-a-vis the island of Usedom on the Baltic coast that can b ...
and Usedom
Usedom (german: Usedom , pl, Uznam ) is a Baltic Sea island in Pomerania, divided between Germany and Poland. It is the second largest Pomeranian island after Rügen, and the most populous island in the Baltic Sea.
It is north of the Szczeci ...
.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, pp.146,147 Routes from Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
and the western parts of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
met at Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; nds, label=Low Saxon, Meideborg ) is the capital and second-largest city of the German state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is situated at the Elbe river.
Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archdiocese of Magdebu ...
, which in turn was connected to Mecklenburg and Reric
Reric or Rerik was one of the Viking Age multi-ethnic Slavic- Scandinavian emporia on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, located near Wismar in the present-day German state of Mecklenburg-VorpommernOle Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reri ...
by a northern route, with Demmin
Demmin () is a town in the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It was the capital of the former district of Demmin.
Geography
Demmin lies on the West Pomeranian plain at the confluence of the rivers ...
and Menzlin by a northeastern route, and with the Oder route by an eastern route running through the Uckermark
The Uckermark () is a historical region in northeastern Germany, straddles the Uckermark District of Brandenburg and the Vorpommern-Greifswald District of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Its traditional capital is Prenzlau.
Geography
The region is nam ...
. Another trade route connected Mecklenburg and Reric with Usedom and Wollin, running through Werle, Lüchow
Lüchow (Wendland) () is a city in northeastern Lower Saxony, in Germany. It is the seat of the ''Samtgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Lüchow (Wendland), and is the capital of the district Lüchow-Dannenberg. Situated approximately 13&nb ...
, Dargun, Demmin
Demmin () is a town in the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It was the capital of the former district of Demmin.
Geography
Demmin lies on the West Pomeranian plain at the confluence of the rivers ...
and Menzlin.
From the coastal emporia, these routes were connected to sea trade routes of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.148 Vessels build for seafaring were also able to navigate in the lower Recknitz river, Peenestrom and lower Peene
The Peene () is a river in Germany.
Geography
The Westpeene, with the Ostpeene as its longer tributary, and the Kleine Peene/Teterower Peene (with a ''Peene '' without specification (or ''Nordpeene'') as its smaller and shorter affluent) flo ...
river up to Demmin
Demmin () is a town in the Mecklenburgische Seenplatte district, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany. It was the capital of the former district of Demmin.
Geography
Demmin lies on the West Pomeranian plain at the confluence of the rivers ...
, and Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
river up to Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. S ...
.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.150 Already in the 9th century, wooden and waterproof containers were in use that were easy to transport by carriage as well as by ship.
Trade, robbery, and piracy did not exclude each other, but were then two sides of the same coin. Whether one traded or stole depended on one's own military strength or protection compared to the abilities of the encountered party.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, pp.149,150 Slavic piracy, especially from Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
and Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the ...
, climaxed in the 11th century. Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, being the major target, launched several expeditions to stop this piracy, such as an expedition directed at Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the ...
and the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
estuary led by king Magnus
Magnus, meaning "Great" in Latin, was used as cognomen of Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus in the first century BC. The best-known use of the name during the Roman Empire is for the fourth-century Western Roman Emperor Magnus Maximus. The name gained wid ...
in 1043, and several expeditions initiated by Eric Ejegod, father of Canute Lavard, in the late 11th century.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.29,
Major trade items were livestock, especially horses; wheat, honey, wax, and salt; grind and millstones; jewelry and luxury articles like pearls and items made from glass, semi-precious stones, gold, silver and amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In M ...
; weapons, and slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, pp.135-141 Acquisition of loot and capture of people for slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
were primary war aims in the many campaigns and expeditions of the Slavic tribes and invaders from outside Pomerania. Also, merchants' caravans did not only engage in slave trade, but also captured people to sell them as slaves.
If not exchanging goods with an equal value, one used linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
, iron and silver for payment.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, pp.127,128 Iron was cast to non-functional daggers, spades, and axes, while silver was either used minted to coins, or as chopped silver items (including jewelry and coins). Before 950, silver coins originated primarily in Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Pl ...
, after 950 these were used together with western European coins, which since the late 10th century largely replaced the Arabic ones.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.143 Also, coins minted in Haithabu were abundantly used in the western regions of Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
up to the lower Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
region.
Billung and Northern marches (936–983)
Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
River was incorporated in the March of the Billungs (north of the Peene
The Peene () is a river in Germany.
Geography
The Westpeene, with the Ostpeene as its longer tributary, and the Kleine Peene/Teterower Peene (with a ''Peene '' without specification (or ''Nordpeene'') as its smaller and shorter affluent) flo ...
River) and the Northern March
The Northern March or North March (german: Nordmark) was created out of the division of the vast '' Marca Geronis'' in 965. It initially comprised the northern third of the ''Marca'' (roughly corresponding to the modern state of Brandenburg) and ...
(south of the Peene River) of the Holy Roman Empire. The respective bishoprics were the Diocese of Hamburg-Bremen and Diocese of Magdeburg. In the Battle of Recknitz ("Raxa") in 955, German and Rani
''Rani'' in Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia, sometimes spelled ''Ranee'', is a Hindu/Sanskrit feminine given name. The term is the female form of the term for princely rulers in South and Southeast Asia and applies equally to the wife of a ...
forces commanded by Otto I of Germany
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
suppressed an Obodrite revolt in the Billung march, instigated by Wichmann the Younger and his brother Egbert the One-Eyed
Egbert the One-Eyed (german: Ekbert der Einäugige) (died 4 April 994) was the second son of Wichmann the Elder and the younger brother of Wichmann the Younger. He was thus of the elder line of the Billung family. His nickname derives from the fact ...
Leyser, Karl"Henry I and the Beginnings of the Saxon Empire."
''The English Historical Review'', Vol. 83, No. 326. (Jan., 1968), pp 1–32. In 983, the area regained independence in an uprising initiated by the Liutizian federation.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn vom 9. Bis ins 13. Jahrhundert: Beiträge einer internationalen Konferenz, Leipzig, 4.-6. Dezember 1997, Franz Steiner Verlag, 2001, p.27, The margraves and bishops upheld their claims, but were not able to reinforce them despite various expeditions.Werner Buchholz, ''Pommern'', Siedler, 1999, pp.28,29, A similar pagan reaction in
Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
between 976Heidger Brandt, Niels Lund, Haithabu und die grossen dänischen Ringburgen: Analysen und Antworten zu den offenen Fragen der Dänischen und Schleswig-holsteinischen Geschichte des 10. Jahrhunderts, Books on Demand, 2004, pp.198,201, and 986, initiated by Sven Forkbeard, forced his father Harald Bluetooth
Harald "Bluetooth" Gormsson ( non, Haraldr Blátǫnn Gormsson; da, Harald Blåtand Gormsen, died c. 985/86) was a king of Denmark and Norway.
He was the son of King Gorm the Old and of Thyra Dannebod. Harald ruled as king of Denmark from c. 958 ...
to exile to Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the ...
.
Polish gains and formation of the Diocese of Kołobrzeg
The first Polish dukeMieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and ...
invaded Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
and acquired the town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an o ...
of Kołobrzeg
Kołobrzeg ( ; csb, Kòlbrzég; german: Kolberg, ), ; csb, Kòlbrzég , is a port city in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in north-western Poland with about 47,000 inhabitants (). Kołobrzeg is located on the Parsęta River on the south coast ...
and the adjacent areas in the 960s.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.32, He also fought the Volinians, but despite a won battle in 967, he did not succeed in expanding his Pomeranian gains.Paul W. Knoll, Frank Schaer, annotaded Gesta Principum Polonorum: The Deeds of the Princes of the Poles by Gallus, Central European University Press, 2003, p.32, His son and successor Bolesław I continued to campaign in Pomerania, but also failed to subdue the Volinians and the lower Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
areas.
During the Congress of Gniezno
The Congress of Gniezno ( pl, Zjazd gnieźnieński, german: Akt von Gnesen or ''Gnesener Übereinkunft'') was an amicable meeting between the Polish Duke Bolesław I the Brave and Emperor Otto III, which took place at Gniezno in Poland on 11 Ma ...
in 1000 AD, Bolesław created the first, yet short-lived bishopric in Pomerania Diocese of Kolobrzeg (Kolberg), subordinate to the Archdiocese of Gniezno
The Archdiocese of Gniezno ( la, Archidioecesis Gnesnensis, pl, Archidiecezja Gnieźnieńska) is the oldest Latin Catholic archdiocese in Poland, located in the city of Gniezno.Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
bishop Reinbern, which was destroyed when Pomeranians revolted in 1005. Of all Liutizians, the Volinians were especially devoted to participation in the wars between the Holy Roman Empire and Poland from 1002 to 1018 to prevent Bolesław I from reinstating his rule in Pomerania.
German-Lutician alliance
In the aftermath of the uprising of 983, Holy Roman EmperorOtto III
Otto III (June/July 980 – 23 January 1002) was Holy Roman Emperor from 996 until his death in 1002. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto III was the only son of the Emperor Otto II and his wife Theophanu.
Otto III was crowned as King of ...
sought to reinstate his marches and upheld good relations with Piast Poland
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in the early 12th ce ...
, which was to be integrated in a reorganized empire ("'' renovatio imperii Romanorum''").Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.356 These plans, reaching a climax with the Congress of Gniezno
The Congress of Gniezno ( pl, Zjazd gnieźnieński, german: Akt von Gnesen or ''Gnesener Übereinkunft'') was an amicable meeting between the Polish Duke Bolesław I the Brave and Emperor Otto III, which took place at Gniezno in Poland on 11 Ma ...
in 1000 AD, were thwarted by Otto's death in 1002, the subsequent rapid expansion of the Piast realm, and the resulting change in Polish politics. After conquering Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
, parts of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
and Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
, Bolesław I of Poland refused to give his oath to Otto's successor, Henry II, and instead allied with German dukes and margraves opposing Henry. Thus, Henry, for a tribute, offered an alliance to the Luticians when he met with their representatives at a Hoftag in Merseburg
Merseburg () is a town in central Germany in southern Saxony-Anhalt, situated on the river Saale, and approximately 14 km south of Halle (Saale) and 30 km west of Leipzig. It is the capital of the Saalekreis district. It had a dioces ...
on March 28, 1003.
Parts of the German clergy and nobility however did not approve this alliance, because it thwarted their ambitions to reintegrate the Lutician territories in their marches and bishoprics.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.358 Among those who disapproved was Thietmar of Merseburg
Thietmar (also Dietmar or Dithmar; 25 July 9751 December 1018), Prince-Bishop of Merseburg from 1009 until his death, was an important chronicler recording the reigns of German kings and Holy Roman Emperors of the Ottonian (Saxon) dynasty. Two ...
, a contemporary chronicler whom we own the reports of the subsequent events.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.357 During the expedition to Poland in 1005, the Christian German army was "shocked" when the pagan Luticians showed up carrying their idols with them. Many of the nobles now ordered by Henry to fight Bolesław were just years before involved with the German-Polish alliance by fighting the Luticians and arranging marriages with the House of Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branc ...
. In another expedition in 1017, when Hermann Billung
Hermann Billung (900 or 912 – 27 March 973) was the margrave of the Billung March from 936 until his death. The first of the Saxon House of Billung, Hermann was a trusted lieutenant of Emperor Otto I.
Though never Duke of Saxony himself, w ...
commanded an army comprising several Lutician units, one of Billung's men threw a rock at an idol of a Lutician goddess, with the consequence that Henry had to pay the Luticians twelve punds of silver.Joachim Herrmann, ''Die Slawen in Deutschland'', Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985, p.361 Bolesław on the other hand prepared an anti-Lutician alliance which he termed "brotherhood in Christo", but at the same time tried to bribe the Luticians and have them carry out attacks on the empire. In 1007, Luticians reported a bribery case to Henry, while in 1010, Hevelli
The Hevelli or Hevellians/ Navellasîni (sometimes ''Havolane''; german: Heveller or ''Stodoranen''; pl, Hawelanie or ''Stodoranie''; cs, Havolané or ''Stodorané'') were a tribe of the Polabian Slavs, who settled around the middle Havel river ...
an renegades were caught by Henry's troops, indicating that the German and Polish offers at least to some degree divided the Luticians.
In 1012, the German-Lutician alliance of 1003 was renewed in Amberg
Amberg () is a town in Bavaria, Germany. It is located in the Upper Palatinate, roughly halfway between Regensburg and Bayreuth. In 2020, over 42,000 people lived in the town.
History
The town was first mentioned in 1034, at that time under ...
. In 1017, after an idol of a Lutician goddess got lost when German and Lutician units crossed the Mulde river during a flood, the Luticians left the expeditions and held an assembly on whether or not continue the alliance after this omen - though they eventually decided in favor of the alliance, an inner division of the Luticians in this case was evident again.
The alliance broke off, when Henry's successor, Konrad II managed to subdue Poland, then led by Bolesław's successor, Mieszko II. Starting in 1129, several imperial campaigns with Danish and Kievian participation resulted in the Peace of Merseburg, concluded in 1033. With the Polish threat, the primary precondition for the German-Lutician alliance was thus eliminated, and hostilities started the same year.
Lutician decline and Obodrite expansion
In 1056/57, the Lutician federation fell apart during a civil war ("''Lutizischer Bruderkrieg''"). The expanding Obodrite state, then led byGottschalk Gottschalk or Godescalc ( Old High German) is a male German name that can be translated literally as "servant of God". Latin forms include ''Godeschalcus'' and ''Godescalcus''.
Given name
*Godescalc of Benevento, 8th-century Lombard duke
*Godescalc ...
and supported by Danish Sven Estridson
Sven (in Danish and Norwegian, also Svend and also in Norwegian most commonly Svein) is a Scandinavian first name which is also used in the Low Countries and German-speaking countries. The name itself is Old Norse for "young man" or "young ...
, Gottschalk's father-in-law, and Saxon duke Bernhard II, engaged in the Lutician war and incorporated the Kessinian territory and Circipania
Circipania (german: Circipanien, Zirzipanien) was a medieval territory in what is now northeastern Germany. The name derives from Latin ''circum'' (around) and ''Pane'' (the Peene River). The region was enclosed roughly by the upper Recknitz, Tr ...
in 1057. While the Obodrite state was temporarily weakened by a revolt in 1066 that cost Gottschalk's life, Burchard I, bishop of Halberstadt invaded the Lutician area in the winter of 1067/68, raided their capital Rethra, captured the holy steed, Rethra's most important Svarozic oracle, and rode it to Halberstadt
Halberstadt ( Eastphalian: ''Halverstidde'') is a town in the German state of Saxony-Anhalt, the capital of Harz district. Located north of the Harz mountain range, it is known for its old town center that was greatly destroyed by Allied bomb ...
. In the winter of 1069, Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry IV (german: Heinrich IV; 11 November 1050 – 7 August 1106) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1084 to 1105, King of Germany from 1054 to 1105, King of Italy and Burgundy from 1056 to 1105, and Duke of Bavaria from 1052 to 1054. He was the ...
again raided and looted the area.
However, inner quarrels hindered the empire to pursue further conquests, and in 1073, Henry IV as well as his Saxon opponents offered alliances to the Luticians outbidding each other with favourable conditions and benefits. As a result, the Luticians allied with neither party, but instead started another civil war over which alliance they should conclude. In addition, Bolesław II of Poland Boleslav or Bolesław may refer to:
In people:
* Boleslaw (given name)
In geography:
*Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland
*Bolesław, Olkusz County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland
*Bolesław, Silesian Voivodeship, Pol ...
also canvassed the Luticians for joining an anti-German coalition with Denmark. As a consequence, Lutician military power was completely exhausted in the course of the 11th century. In 1093, Helmold of Bosau
Helmold of Bosau (ca. 1120 – after 1177) was a Saxon historian of the 12th century and a priest at Bosau near Plön. He was a friend of the two bishops of Oldenburg in Holstein, Vicelinus (died 1154) and Gerold (died 1163), who did much to ...
reported that among others the Luticians, Pomeranians and Rani
''Rani'' in Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia, sometimes spelled ''Ranee'', is a Hindu/Sanskrit feminine given name. The term is the female form of the term for princely rulers in South and Southeast Asia and applies equally to the wife of a ...
had to pay tribute to Obodrite prince Henry.
References
Bibliography
* Werner Buchholz et al., ''Pommern'', Siedler, 1999/2002, , 576 pages; this book is part of the ''Deutsche Geschichte im Osten Europas'' series and primarily covers the history of theDuchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
and Province of Pomerania from the 12th century to 1945, and Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, West ...
after 1945.
* Jan Maria Piskorski et al. (Werner Buchholz, Jörg Hackmann, Alina Hutnikiewicz
Alina is a female given name of European origin. It is particularly common in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. It may be derived from the name Adelina. Alina was one of the top 10 most popular names in Switzerland and one of the top 50 most ...
, Norbert Kersken, Hans-Werner Rautenberg, Wlodzimierz Stepinski, Zygmunt Szultka, Bogdan Wachowiak, Edward Wlodarczyk), ''Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten'', Zamek Ksiazat Pomorskich, 1999, . This book is a co-edition of several German and Polish experts on Pomeranian history and covers the history of Pomerania, except for Pomerelia, from the earliest appearance of humans in the area until the end of the second millennium. It is also available in a Polish version, .
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pomerania During The Early Middle Ages
1
Medieval Denmark
Medieval Sweden
History of Prussia
Jomsvikings
Early medieval Poland
de:Geschichte Pommerns