Po Valley on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
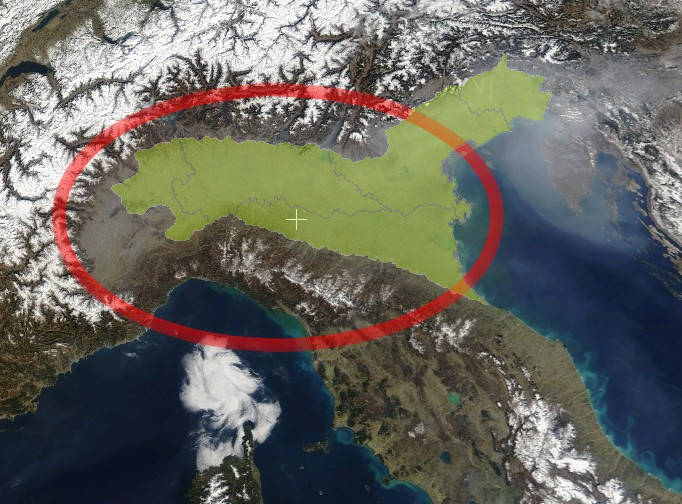

 The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of
The Po Valley, Po Plain, Plain of the Po, or Padan Plain ( it, Pianura Padana , or ''Val Padana'') is a major geographical feature of
 The Po Valley and the Adriatic overlay a
The Po Valley and the Adriatic overlay a


 The Po Valley is often regarded as a
The Po Valley is often regarded as a
 The Po Valley has a range from
The Po Valley has a range from 
 By 196 BC, Rome was master of the woody plains and soon displaced the Etruscans, dotting the region with bustling colonies, clearing the land, fighting the last rebel tribes and gradually imposing its own civilisation.
By 196 BC, Rome was master of the woody plains and soon displaced the Etruscans, dotting the region with bustling colonies, clearing the land, fighting the last rebel tribes and gradually imposing its own civilisation.
 In 1494, the ruinous
In 1494, the ruinous


Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative region ...
. It extends approximately in an east-west direction, with an area of including its Venetic
Venetic is an extinct Indo-European language, usually classified into the Italic subgroup, that was spoken by the Veneti people in ancient times in northeast Italy (Veneto and Friuli) and part of modern Slovenia, between the Po Delta and ...
extension not actually related to the Po river basin; it runs from the Western Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
to the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
. The flatlands of Veneto
Veneto (, ; vec, Vèneto ) or Venetia is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about five million, ranking fourth in Italy. The region's capital is Venice while the biggest city is Verona.
Veneto was part of the Roman Empire unt ...
and Friuli are often considered apart since they do not drain into the Po, but they effectively combine into an unbroken plain, making it the largest in Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alb ...
. It has a population of 17 million, or a third of Italy's total population.
The plain is the surface of an in-filled system of ancient canyons (the "Apennine Foredeep") extending from the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
in the south to the Alps in the north, including the northern Adriatic. In addition to the Po and its affluents, the contemporary surface may be considered to include the Savio, Lamone
Lamone is a municipality in the district of Lugano in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland.
History
Lamone is first mentioned in 854 as ''Namonni''. In 1295 it was mentioned as ''Lamono''.
A prehistoric stone bowl was discovered on San Zeno h ...
and Reno
Reno ( ) is a city in the northwest section of the U.S. state of Nevada, along the Nevada-California border, about north from Lake Tahoe, known as "The Biggest Little City in the World". Known for its casino and tourism industry, Reno is th ...
to the south, and the Adige, Brenta, Piave and Tagliamento of the Venetian Plain to the north, among the many streams that empty into the north Adriatic from the west and north.
Geo-political definitions of the valley depend on the defining authority. The Po Basin Water Board ('), authorized in 1989 by Law no. 183/89 to oversee "protection of lands, water rehabilitation, the use and management of hydro resources for the national economic and social development, and protection of related environment" within the Po basin, has authority in several administrative regions of north Italy, including the plain north of the Adriatic and the territory south of the lower Po, as shown in the regional depiction included with this article. The law defines the Po basin as "the territory from which rainwater or snow and glacier melt flows on the surface, gathers in streams of water either directly or via tributaries...". The United Nations Environment Program includes the Alps and Apennines as far as the sources of the tributaries of the Po but excludes Veneto and that portion of Emilia-Romagna south of the lower Po; that is, it includes the region drained by the Po but only the Po and its tributaries.
The altitude of the valley through which the Po flows, exclusive of its tributaries, varies from approximately below sea level in the Polesine subregion (the delta around Ferrara
Ferrara (, ; egl, Fràra ) is a city and ''comune'' in Emilia-Romagna, northern Italy, capital of the Province of Ferrara. it had 132,009 inhabitants. It is situated northeast of Bologna, on the Po di Volano, a branch channel of the main stream ...
) to about at the river's origin in the southern Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
ese province of Cuneo
Cuneo ( Italian), or Coni ( Piedmontese), is a province in the southwest of the Piedmont region of Italy. To the west it borders on the French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur (departments of Alpes-Maritimes, Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and H ...
, also known as the ''Provincia granda''. The valley is crossed by a number of affluents running down from the Alps in the north and from the Apennines in the south. The Po's major affluents include the Tanaro
The Tanaro (; pms, Tane ; ; la, Tanarus), is a long river in northwestern Italy. The river begins in the Ligurian Alps, near the border with France, and is the most significant right-side tributary to the Po in terms of length, size of dra ...
, Scrivia, Trebbia
The Trebbia (stressed ''Trèbbia''; la, Trebia) is a river predominantly of Liguria and Emilia Romagna in northern Italy. It is one of the four main right-bank tributaries of the river Po, the other three being the Tanaro, the Secchia and t ...
, Panaro and Secchia in the south, Dora Riparia
The Dora Riparia (; pms, Dòira Rivaira; french: Doire Ripaire or ''Doire''; la, Duria minor) is an alpine river, a left-hand tributary of the Po. It is long (of which 5 km in France), with a drainage basin. It originates in the Cottia ...
, Dora Baltea, Sesia
The Sesia (Latin ''Sesites'' or ''Sessites'') is a river in Piedmont, north-western Italy, tributary to the Po.
Geography
Its sources are the glaciers of Monte Rosa at the border with Switzerland. It flows through the Alpine valley Valsesia a ...
, Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
(draining Lake Maggiore), Lambro, Adda (draining Lake Como), Oglio
The Oglio (; Latin ''Ollius'', or ''Olius''; Lombard ''Òi''; Cremonese ''Ùi'') is a left-side tributary of the river Po in Lombardy, Italy. It is long.
In the hierarchy of the Po's tributaries, with its of length, it occupies the 2nd ...
(draining Lake Iseo) and Mincio (draining Lake Garda
Lake Garda ( it, Lago di Garda or ; lmo, label= Eastern Lombard, Lach de Garda; vec, Ƚago de Garda; la, Benacus; grc, Βήνακος) is the largest lake in Italy.
It is a popular holiday location in northern Italy, about halfway between ...
and called Sarca in its upper reaches) in the north.
Geology
foreland basin
A foreland basin is a structural basin that develops adjacent and parallel to a mountain belt. Foreland basins form because the immense mass created by crustal thickening associated with the evolution of a mountain belt causes the lithosphere ...
and a system of deeply buried ancient canyons surviving from the tectonic collision of an offshore land mass, Tyrrhenis, with the mainland, an incident within the collision of the African and Eurasian plates. Since the Messinian (7–5 mya) the system has been filling with sediment mainly from the older Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
but also from the Alps. The shoreline of the Adriatic depends on a balance between the sedimentation rate and isostatic factors. Until about 1950, the Po delta was prograding into the Adriatic. After that time due to human alteration of geologic factors, such as the sedimentation rate, the delta has been degrading and the coastline subsiding, resulting in ongoing contemporaneous crises in the city of Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, where much irreplaceable art and architecture is likely to be lost due to soaring sea level in the next centuries. Where the land surface now dips below sea level the river must run at a relative elevation between dikes.
The Malossa gas condensate field was discovered in 1973 and produces at depths of from the Upper Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest per ...
Dolomia Principale dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
and the Lower Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
Zandobbio dolomite, capped by the Lower Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
Marne di Bruntino marl.
Geography


 The Po Valley is often regarded as a
The Po Valley is often regarded as a syncline
In structural geology, a syncline is a fold with younger layers closer to the center of the structure, whereas an anticline is the inverse of a syncline. A synclinorium (plural synclinoriums or synclinoria) is a large syncline with superimpose ...
, or dip in the crust due to compression at the edges. Regardless of whether this concept accurately describes its geology, the valley is manifestly a sediment-filled trough, or virtual syncline, continuous with the deeps of the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
. The surface terrain is therefore divided into two overall types of landform
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, ...
: the plain, or flat surface of the fill, and the anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is t ...
at the edges, taking the form of hilly country in which the outcrops of the original rock are visible along with alluvial fans formed from the outwash of the more severe anticlinal terrain; that is, the Apennines and the Alps.
The valley is broadly divided into an upper, drier part, often not particularly suited for agriculture, and a lower, very fertile, and well-irrigated section, known in Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
and western Emilia as ''la Bassa'', "the low (plain)". The upper areas of the Po valley take local names which reflect in their meanings their being modestly suited for farming. So we have the Piedmontese ''vaude'' and ''baragge'', the Lombard ''brughiere'' and ''Groane'', or, exiting from the Po valley proper, the Friulian ''magredi'', areas remote from easily reachable water tables and covered with dense woods or dry soils.
This specific meaning for "lower plain" derive from a geologic feature called the ''fontanili'' ("spring") line or zone, a band of springs around the Val Po, heaviest on the north, on the lowermost slopes of the anticline. It varies from a few kilometres to as much as wide. The fontanili line is the outcrop, or intersection, of the anticline's water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
with the surface at the edge of the ''bassa''. The rock above the line is porous. Surface water in the intermittent streams of the mountains tends to disappear below ground only to spring out again in the spring zone. The spring zone is often called "the middle valley."
Surface runoff water (the Po and its affluents) is not of much value to the valley's dense population for drinking and other immediate uses, being unreliable, often destructive, and heavily polluted by sewage and fertilizers. Its main anthropic value is for hydro-electric power, irrigation, and industrial transport. The cost of purifying it for human consumption makes that process less feasible. The fresh drinking water comes from hundreds of thousands of wells concentrated especially in the fontanili zone. The major settlements, therefore, are also in that zone, which has become the centre of economic development and industry in Italy, and now is an almost continuous megalopolis stretching from Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
to Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into pr ...
.
The ''bassa Padana'' was settled and farmed earliest, in Etruscan and Roman times. After the collapse of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
(5th century AD), lack of maintenance of the irrigation systems associated with a cooling climate phase (i.e. the so-called Migration Period or The Dark Age Cold Period) led to the progressive waterlogging of the Po Valley and the natural depressions on the right side of the Po River
The Po ( , ; la, Padus or ; Ancient Ligurian: or ) is the longest river in Italy. It flows eastward across northern Italy starting from the Cottian Alps. The river's length is either or , if the Maira, a right bank tributary, is included. T ...
turned in vast swamp basins. The waterlogging process of the area continued until the 10th century influencing the human sustenance and settling practices. According to historical-archaeological data, indeed, the wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (Anoxic waters, anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in t ...
s were exploited for fishing as well as for transport by boat while the early medieval sites settled on the fluvial ridges, in topographically higher and strategic position in the surrounding swampy meadows.
The Po Valley has been completely turned to agriculture since the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, when efforts from monastic orders, feudal lords and free communes converged. The older and smaller cities deriving from ancient times are still located there.
According to historical maps and documents the land reclamation of the Po Valley reached its peak during the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
(15th–16th centuries) and continued in the Modern Age (17th–18th centuries), with the last marsh areas only being reclaimed in the 20th century: channels and drainage system are still active and allow the Po Valley to be drained and be cultivatable.
Climate and vegetation
humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(Köppen: ''Dfa'') to humid subtropical (Köppen: ''Cfa''), or ''continental temperate'' (cool-humid with fog in winter and warm-moist in summer) climate in other classification. The conformation of the plain, surrounded by the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
and the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
, and the influence of the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
cause high levels of relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
throughout the year. The climate of the Po Valley becomes increasingly warmer and more humid farther south and east.
Winters are cool and damp, with January mean temperatures ranging between (1981–2010 averages). Fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
and mist
Mist is a phenomenon caused by small droplets of water suspended in the cold air, usually by condensation. Physically, it is an example of a dispersion. It is most commonly seen where water vapor in warm, moist air meets sudden cooling, such a ...
are frequent, although the urban heat effect has made winters less foggy and cold than before in some areas. Snow can occasionally occur and prolonged winter droughts increasingly deny sufficient moisture to the soil. Summers are hot and humid, with July mean temperatures ranging between (1971–2000 averages). Frequent thunderstorms and sudden hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
storms have the potential to produce large hail, dump large quantities of rain, and be highly destructive to crops. The largest hail is produced by intense supercell thunderstorms, with significant agricultural costs. Tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, alt ...
es are also not uncommon in the plains of the valley. For these climatological considerations the Friuli Venezia Giulia
(man), it, Friulana (woman), it, Giuliano (man), it, Giuliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_t ...
is an important extension beyond the Po River plain itself, as these are situated downwind of the mountains and upwind of moisture sources from nearby seas. Spring and autumn are well-marked and pleasant. Both winter and summer are less mild in the lower parts along the Po, while the Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to th ...
and the great lakes moderate the local climate in their proximity.
Rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
varies between and is equally distributed during the year, though in recent years the climate tends to become somewhat drier, especially in summer. Rainfall maximums are reached during autumn and spring. Winds are usually weak, although sudden bursts of foehn
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the lee (downwind side) of a mountain range.
It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of ...
or thunderstorms can sweep the air clean. The almost enclosed nature of the Padan basin, indeed, added to the crushing weight of road traffic, makes it prone to a high level of pollution in winter, when cold air clings to the soil. The natural potential vegetation of the Po basin is a mixed broadleaf forest of pedunculate oak, poplars, European hornbeam
''Carpinus betulus'', the European or common hornbeam, is a species of tree in the birch family Betulaceae, native to Western Asia and central, eastern, and southern Europe, including southern England. It requires a warm climate for good growth, ...
, alders, elderberry, elms, willows, maples, ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non-gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
, and other central-European trees. The largest remaining fragments of forest are located around the Ticino River and are protected by a Biosphere Reserve.

History
Prehistory and antiquity
The Po Valley has had traces of inhabitation since at least 780,000 years ago, when the first big glaciation of pleistocene took place. Sites like Monte Poggiolo may have served as refuges of human populations fleeing the terribly cold conditions of northern Europe during the subsequent glaciations along pleistocene. The valley was covered by sea level in warm times, but glaciations could cause a lower sea level that allowed big mammals and humans to migrate from Africa and the Middle East to central and western Europe through an empty and open Po valley, avoiding the barrier of the Alps, reaching the Loire Valley, and Iberian Peninsula, and then, when glaciation retreated, the rest of continental Europe. Urban development began in the Po Valley much later than in southern Italy or Greece. The first known ancient inhabitants of the thick forests and swamps were theLigurians
The Ligures (singular Ligur; Italian: liguri; English: Ligurians) were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day north-western Italy, is named.
Ancient Liguria corresponded more or less to the current Italian reg ...
, an Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
people. After the progressive immigration in the 7th century BC of Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
peoples known as the Insubres
The Insubres or Insubri were an ancient Celtic population settled in Insubria, in what is now the Italian region of Lombardy. They were the founders of Mediolanum ( Milan). Though completely Gaulish at the time of Roman conquest, they were the r ...
(hence the name of Insubria sometimes being given to northwestern Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
), the southern and central regions were conquered and colonised here and there by a pre-Indo-European people, the Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roug ...
, who left names such as Parma
Parma (; egl, Pärma, ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, music, art, prosciutto (ham), cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,292 inhabitants, Parma is the second m ...
, Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the c ...
and Felsina, the ancient name of Bologna
Bologna (, , ; egl, label= Emilian, Bulåggna ; lat, Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different na ...
. The Etruscan domination left significant marks and introduced urban civilisation, but was short-lived.
Its inhabitants, the Venetics, likely being a distinct group who, being skillful merchants, were, in time, also culturally influenced by both Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roug ...
and Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
.
 By 196 BC, Rome was master of the woody plains and soon displaced the Etruscans, dotting the region with bustling colonies, clearing the land, fighting the last rebel tribes and gradually imposing its own civilisation.
By 196 BC, Rome was master of the woody plains and soon displaced the Etruscans, dotting the region with bustling colonies, clearing the land, fighting the last rebel tribes and gradually imposing its own civilisation.
Middle Ages
The Gothic War andJustinian's plague
The plague of Justinian or Justinianic plague (541–549 AD) was the first recorded major outbreak of the first plague pandemic, the first Old World pandemic of plague, the contagious disease caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. The dise ...
devastated the Padan population. In this scenario of desolation, from which many people had fled to the mountains for safety (making them fairly populated till the 20th century) came the Germanic Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
, a warrior people who gave their name to almost the whole of the Po valley: Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
. In the Middle Ages the term was used to indicate all of northern Italy. The Lombards divided their domain in duchies, often contending for the throne; Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
and Friuli, in the extreme west and east end respectively, seem to have been the most powerful, whereas the capital soon shifted from Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
to Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the ...
. Monza also was an important town in that time, more so than ruined Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
. The Lombards' harsh, caste
Caste is a form of social stratification characterised by endogamy, hereditary transmission of a style of life which often includes an occupation, ritual status in a hierarchy, and customary social interaction and exclusion based on cultur ...
-like rule over the natives softened somewhat with their conversion from Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God ...
to Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
.
The Lombard kingdom
The Kingdom of the Lombards ( la, Regnum Langobardorum; it, Regno dei Longobardi; lmo, Regn di Lombard) also known as the Lombard Kingdom; later the Kingdom of (all) Italy ( la, Regnum totius Italiae), was an early medieval state established ...
was overthrown in 774 by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
and his Frankish armies, becoming a prized part of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
, forming the kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
, always with its capital in Pavia. The affirmation of large landownership from the eighth/ninth centuries accelerated the process of land reclamation and intensified land use, transforming the landscape of the Po Valley. After the chaotic feudal dissolution of the empire and much fighting among pretenders to the imperial crown, Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a ...
set the stage for the following phase of the region's history by adding the Po Valley to the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
of the Germanic nation in 962. In Veneto
Veneto (, ; vec, Vèneto ) or Venetia is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about five million, ranking fourth in Italy. The region's capital is Venice while the biggest city is Verona.
Veneto was part of the Roman Empire unt ...
, the lagoon capital of Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, emerged a great sea power in alliance with its old master, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. In time the Comuni emerged, as towns thrived in commerce. Soon Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
became the most powerful city of the central plain of Lombardy proper, and despite being razed in 1162, it was a Milan-driven Lombard League with Papal benediction that defeated emperor Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt ...
at the Battle of Legnano
The Battle of Legnano was a battle between the imperial army of Frederick Barbarossa and the troops of the Lombard League on May 29, 1176, near the town of Legnano in present-day Lombardy, in Italy. Although the presence of the enemy nearby w ...
in 1176.
Between the 10th and 13th centuries, concurrent with the Medieval Warm Period climate phase, the European population grew substantially, almost tripling (in Northern and Central Italy, the urban population doubled), and increasing the demand for cultivated lands. Cereals became a more significant constituent in the average diet and in the agrarian regime compared to the centuries before, leading populations to reconfigure the medieval natural landscape for agricultural purposes. In creating new land for cultivation and settlement, the European communities triggered a massive landscape transformation through woodland clearance, arable intensification, the development of irrigation systems and the drainage of wetlands. Land reclamations works profoundly modified many European regions. In Central Po Plain the earliest evidence of attempts to clear the forests and drain the wetlands is mentioned in historical documents from the late 8th century, but only from the 10th to 13th centuries were land and water management activities actually carried out widely.
Further civil wars escalated in the Guelph-Ghibelline reciprocate bloodbath of the 13th and 14th centuries. The Signorie came from spent out Communal institutions. With Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
's expansion on the eastern mainland in the first half of the 15th century and Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
's supremacy in the center and west the region (not significantly diminished by the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
of 1348) reached unprecedented peaks of prosperity. Vast areas were irrigated and cultivated with the most modern techniques available. The population averaged some 50 people per square kilometer, a very high standard for those times.
Early modern
 In 1494, the ruinous
In 1494, the ruinous Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
began between France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, which lasted for decades. Land changed hands frequently. Even Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
received some Italian-speaking lands in the north ( Canton Ticino, not technically a part of the Padan region), and the Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
domain was invaded, forcing Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
into neutrality as an independent power. In the end, Spain prevailed with Charles V's victory over Francis I of France
Francis I (french: François Ier; frm, Francoys; 12 September 1494 – 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin on ...
at the Battle of Pavia in 1525.
The Spanish domination was oppressive, adding its burden to the Counterreformation imposed by the archbishopric of Milan; Protestantism
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
was prevented from making inroads in the area. Burning at the stake
Death by burning (also known as immolation) is an execution and murder method involving combustion or exposure to extreme heat. It has a long history as a form of public capital punishment, and many societies have employed it as a punishment f ...
became common practice during witchhunts, especially in the neighboring Alpine lands. During this bleak period, however, Lombard industry recovered, especially the textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, different #Fabric, fabric types, etc. At f ...
branch, its pillar.
When the War of Spanish Succession traded Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
to Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, government and administration improved significantly. Though the peasantry began a century-long plunge into misery, cities prospered and grew.
When Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
entered the Po Valley during some of his brightest campaigns (1796 and 1800, culminating in the historical Battle of Marengo), he found an advanced country and made it into his Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
. With Napoleon's final defeat the Austrians came back, but they were no longer welcome. In the west, in Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, the Savoy dynasty
The House of Savoy ( it, Casa Savoia) was a royal dynasty that was established in 1003 in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, the family grew in power from ruling a small Alpine county north-west of Italy to absolute rule ...
would emerge to serve as a springboard for Italian unification.
Late modern and contemporary
The Risorgimento, after an unsuccessful start in 1848 and 1849, triumphed ten years later inLombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
, which was conquered by a Franco-Piedmontese army. In 1866 Veneto
Veneto (, ; vec, Vèneto ) or Venetia is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about five million, ranking fourth in Italy. The region's capital is Venice while the biggest city is Verona.
Veneto was part of the Roman Empire unt ...
joined young Italy, thanks to Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
's defeat of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. Poverty in the countryside increased emigration to the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
, a phenomenon which subsided in the central region towards the end of the 19th century, but persisted in Veneto
Veneto (, ; vec, Vèneto ) or Venetia is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about five million, ranking fourth in Italy. The region's capital is Venice while the biggest city is Verona.
Veneto was part of the Roman Empire unt ...
well into the 20th century. Industry grew rapidly, thanks to an abundance of water and literate manpower.
The World Wars did not significantly damage the area, despite the destruction caused by Allied aerial bombing
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The offici ...
of many cities and heavy frontline fighting in Romagna
Romagna ( rgn, Rumâgna) is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna, North Italy. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to th ...
. The Resistance protected the main industries, which the Third Reich was using for war production, preventing their destruction: on 25 April 1945 a general insurrection in the wake of the German defeat was a huge success. Most cities and towns, notably Milan and Turin, were freed by the partisans days before the Allies arrived.
After the war, the Padan area took the lead in the economic miracle
Economic miracle is an informal economic term for a period of dramatic economic development that is entirely unexpected or unexpectedly strong. Economic miracles have occurred in the recent histories of a number of countries, often those undergoing ...
of the 1950s and 60s. Since 1989, Lega Nord
Lega Nord (; acronym: LN), whose complete name is (), is a right-wing, federalist, populist and conservative political party in Italy. In the run-up of the 2018 general election, the party was rebranded as (), without changing its offici ...
, a federation of Northern regionalist parties, has promoted either secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics l ...
or larger autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one' ...
for the Padan area which they call '' Padania''.
Economy
The Po Valley is one of the most important industrial and agricultural areas in Europe. Hydroelectricity is produced by the flow of the Po. The river is extensively used for irrigation for the region's agriculture.Pollution
Po valley is considered the worst area in Europe for air quality. In March 2019, theEuropean Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (120 ...
(ESA) published images of nitrogen dioxide concentrations taken from the Sentinel-5P satellite. These images show a big red area, made of nitrogen dioxide and fine particles, situated above the Po Valley area, which incorporates the city of Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
, Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
, and Bologna
Bologna (, , ; egl, label= Emilian, Bulåggna ; lat, Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different na ...
. Milan and Turin share high levels of ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the l ...
and nitrogen oxides, which are mainly produced by cars' diesel and petrol engines. To shed light on the danger for humans living polluted environments, Chicago Energy Policy Institute has developed the Air Quality Life Index (AQLI), a system capable of analyzing air pollution worldwide. According to AQLI findings, Po valley air pollution affects inhabitants so hard that it cuts off about half a year of their life expectancy. The main reasons for the high amount of air pollution over the Po valley are strictly connected to livestock and factories. The so-called "NPK fertilizers", made of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, along with manure emissions from intensive breeding and high levels of nitrogen dioxide released by diesel and petrol engines are all accountable for this disastrous air condition in Northern Italy. The region of Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
produces also vast amounts of animal waste, a big contributor to pollution. It delivers more than 40 percent of Italy's milk production, for example, while over half of the Italian pig production is located in the Po Valley.
According to research published in The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal and one of the oldest of its kind. It is also the world's highest-impact academic journal. It was founded in England in 1823.
The journal publishes original research articles ...
Planetary Health in January 2021, which estimates the death rate associated with fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) pollution in 1000 European cities, Brescia
Brescia (, locally ; lmo, link=no, label= Lombard, Brèsa ; lat, Brixia; vec, Bressa) is a city and '' comune'' in the region of Lombardy, Northern Italy. It is situated at the foot of the Alps, a few kilometers from the lakes Garda and Iseo ...
and Bergamo
Bergamo (; lmo, Bèrghem ; from the proto- Germanic elements *''berg +*heim'', the "mountain home") is a city in the alpine Lombardy region of northern Italy, approximately northeast of Milan, and about from Switzerland, the alpine lakes Com ...
in Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
have the highest death rate from fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in Europe. Vicenza (Veneto
Veneto (, ; vec, Vèneto ) or Venetia is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about five million, ranking fourth in Italy. The region's capital is Venice while the biggest city is Verona.
Veneto was part of the Roman Empire unt ...
) and Saronno (Lombardy) are in fourth and eighth place, respectively, in a top ten of ten cities. Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
and Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
are also at the top of the European ranking – 3rd and 5th respectively – in terms of increased mortality from nitrogen dioxide, a gas that is produced mainly from traffic and in particular from diesel vehicles, while Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
, Treviso
Treviso ( , ; vec, Trevixo) is a city and '' comune'' in the Veneto region of northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Treviso and the municipality has 84,669 inhabitants (as of September 2017). Some 3,000 live within the Vene ...
, Padova, Como
Como (, ; lmo, Còmm, label= Comasco , or ; lat, Novum Comum; rm, Com; french: Côme) is a city and '' comune'' in Lombardy, Italy. It is the administrative capital of the Province of Como.
Its proximity to Lake Como and to the Alps ...
and Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
rank eleventh, fourteenth, fifteenth, seventeenth and twenty-third respectively.
The data show that many cities in the Po Valley suffer the most serious impact at European level due to poor air quality, first of all the metropolitan area of Milan, thirteenth in the ranking in terms of fine particulate impact, where any year 3967 premature deaths occur – approximately 9% of the total.
References
External links
* {{Authority control Geographical, historical and cultural regions of Italy Plains of Italy Landforms of Piedmont Landforms of Lombardy Landforms of Emilia-Romagna Landforms of Veneto