Plastic Film on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
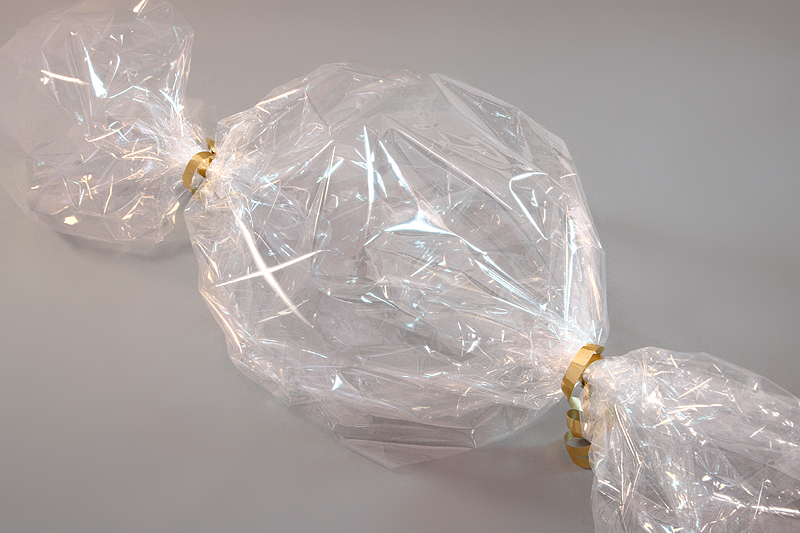

 Plastic film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a "sheet". These thin
Plastic film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a "sheet". These thin
 Plastic films are usually
Plastic films are usually

 Plastic film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a "sheet". These thin
Plastic film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a "sheet". These thin plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
membranes are used to separate areas or volumes, to hold items, to act as barriers, or as printable surfaces.
Plastic films are used in a wide variety of applications. These include: packaging
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a co ...
, plastic bags, label
A label (as distinct from signage) is a piece of paper, plastic film, cloth, metal, or other material affixed to a container or product, on which is written or printed information or symbols about the product or item. Information printed ...
s, building construction, landscaping, electrical fabrication, photographic film
Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin photographic emulsion, emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of th ...
, film stock for movies, video tape
Videotape is magnetic tape used for storing video and usually sound in addition. Information stored can be in the form of either an analog or digital signal. Videotape is used in both video tape recorders (VTRs) and, more commonly, videocassett ...
, etc.
Materials
Almost all plastics can be formed into a thin film. Some of the primary ones are: *Polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging ( plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bo ...
– The most common plastic film is made of one of the varieties of polyethylene: low-density polyethylene
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic made from the monomer ethylene. It was the first grade of polyethylene, produced in 1933 by Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) using a high pressure process via free radical polymerization. Its ...
, medium-density polyethylene
Medium-density polyethylene (MDPE) is a type of polyethylene defined by a density range of 0.926–0.940 g/cm3. It is less dense than HDPE, which is more common.
MDPE can be produced by chromium/silica catalysts, Ziegler-Natta catalysts or met ...
, high-density polyethylene
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or "polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density ratio, ...
, or linear low-density polyethylene
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) is a substantially linear polymer (polyethylene), with significant numbers of short branches, commonly made by copolymerization of ethylene with longer-chain olefins. Linear low-density polyethylene differs ...
.
* Polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins a ...
– Polypropylene can be made a cast film, biaxially oriented film (BOPP), or as a uniaxially oriented film.
* Polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
– BoPET
BoPET (biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate) is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and ar ...
is a biaxially oriented polyester film.
* Nylon
Nylon is a generic designation for a family of synthetic polymers composed of polyamides ( repeating units linked by amide links).The polyamides may be aliphatic or semi-aromatic.
Nylon is a silk-like thermoplastic, generally made from petro ...
– BOPA/BON is a Biaxially Oriented Polyamide/Nylon - (Commonly known as Nylon)
* Polyvinyl chloride – film can be with or without a Plasticizer
A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.
Plasticiz ...
* Cellulose acetate
In biochemistry, cellulose acetate refers to any acetate ester of cellulose, usually cellulose diacetate. It was first prepared in 1865. A bioplastic, cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some coatings, and ...
- an early bioplastic.
* Cellophane
Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Its low permeability to air, oils, greases, bacteria, and liquid water makes it useful for food packaging. Cellophane is highly permeable to water vapour, but may be coated ...
- made of regenerated cellulose.
* A variety of bioplastic
Bioplastics are plastic materials produced from renewable biomass sources, such as vegetable fats and oils, corn starch, straw, woodchips, sawdust, recycled food waste, etc. Some bioplastics are obtained by processing directly from natural bi ...
s and biodegradable plastics are available.
* Semiembossed film {{unreferenced, date=July 2013
Semiembossed film is used as a liner to the calendared rubber to retain the properties of rubber and also to prevent dust and other foreign matters from sticking to the rubber while calendaring and during storage. It ...
– Semiembossed film can be used as a liner to the calendered rubber to retain the properties of rubber and also to prevent dust and other foreign matters from sticking to the rubber while calendering and during storage
Processes
 Plastic films are usually
Plastic films are usually thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate ...
s and are formed by melting for forming the film.
* Cast – Plastics extrusion
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic fi ...
can cast film which is cooled or quenched then wound up on a roll.
* Extruded
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex c ...
film can be stretched, thinned, or oriented in one or two directions. Blown or tubular process forces air into an extruded ring to expand the film. Flat tenter frames stretch the extruded film before annealing.
* Calender rolls can be used to form film from hot polymers
* Solution deposition is another film forming process.
* Skiving is used to scrape off a film from a solid core (sometimes used to make PTFE thread seal tape
Thread seal tape (also known as PTFE tape, Teflon tape, or plumber's tape) is a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) film tape commonly used in plumbing for sealing pipe threads. The tape is sold cut to specific widths and wound on a spool, making it ...
)
* Coextrusion involves extruding two or more layers of dissimilar polymers into a single film
* Lamination
Lamination is the technique/process of manufacturing a material in multiple layers, so that the composite material achieves improved strength, stability, sound insulation, appearance, or other properties from the use of the differing materia ...
combines two or more films (or other materials) into a sandwich.
* Extrusion coating
Extrusion coating is the coating of a molten web of synthetic resin onto a substrate material. It is a versatile coating technique used for the economic application of various plastics, notably polyethylene, onto paperboard, corrugated fiberboa ...
is used to form a film onto another film or substrate
Further processing
Plastic films are typically formed into rolls byroll slitting
Roll slitting is a shearing operation that cuts a large roll of material into narrower rolls. There are two types of slitting: log slitting and rewind slitting. In log slitting the roll of material is treated as a whole (the 'log') and one or mo ...
. Often additional coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. Pow ...
or printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ea ...
operations are also used. Films can be modified by physical vapor deposition
Physical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings on substrates including metals, ceramics, glass, and polym ...
to make metallised film Metallised films (or metallized films) are polymer films coated with a thin layer of metal, usually aluminium. They offer the glossy metallic appearance of an aluminium foil at a reduced weight and cost. Metallised films are widely used for decorati ...
s. Films can be subjected to corona treatment
Corona treatment (sometimes referred to as air plasma) is a surface modification technique that uses a low temperature corona discharge plasma to impart changes in the properties of a surface. The corona plasma is generated by the application of ...
or plasma processing
Plasma processing is a plasma-based material processing technology that aims at modifying the chemical and physical properties of a surface.
Plasma processing techniques include:
*Plasma activation
* Plasma ashing
*Plasma cleaning
*Plasma electr ...
; films can have release agent
A release agent (also mold release agent, release coating, or mold release coating) is a chemical used to prevent other materials from bonding to surfaces. It can provide a solution in processes involving mold release, die-cast release, plastic r ...
s applied as needed.
See also
*Converters (industry)
Converting companies are companies that specialize in modifying or combining raw materials such as polyesters, adhesives, silicone, adhesive tapes, foams, plastics, felts, rubbers, liners and metals, as well as other materials, to create new pro ...
* Die cutting (web)
*Film base
A film base is a transparent substrate which acts as a support medium for the photosensitive emulsion that lies atop it. Despite the numerous layers and coatings associated with the emulsion layer, the base generally accounts for the vast majorit ...
*Film blowing machine
A film blowing machine involves one process used to make plastic film. Extruded tubular processing is most often used with polyethylene films but can be used with other polymers.
The film may be Laminate, laminating film, shrink film, Agriculture ...
*Heat sealer
A heat sealer is a machine used to seal products, packaging, and other thermoplastic materials using heat. This can be with uniform thermoplastic monolayers or with materials having several layers, at least one being thermoplastic. Heat sealing ...
* Journal of Plastic Film and Sheeting
*Overwrap
An overwrap or wrap is a method of sealing a contained product, typically as part of retail packaging. It is often made of plastic film (sometimes called polywrapping) or paper. The wrap is applied over the bare product or can be applied over ...
*Plastic welding
Plastic welding is welding for semi-finished plastic materials, and is described in ISO 472 as a process of uniting softened surfaces of materials, generally with the aid of heat (except solvent welding). Welding of thermoplastics is accomplishe ...
*Plastic wrap
Plastic wrap, cling film, Saran wrap, cling wrap, Glad wrap or food wrap is a thin plastic film typically used for sealing food items in containers to keep them fresh over a longer period of time. Plastic wrap, typically sold on rolls in boxes ...
*Shrink wrap
Shrink may refer to:
Common meanings
*Miniaturization
*Shrink, a slang term for:
** a psychiatrist
** a psychoanalyst
** a psychologist
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Shrink'' (album), album by German indie rock/electronica group The Notwist
...
*Stretch wrap
Stretch wrap or stretch film is a highly stretchable plastic film that is wrapped around items. The elastic recovery keeps the items tightly bound. In contrast, shrink wrap is applied loosely around an item and shrinks tightly with heat. While ...
*Thin film
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer (monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many ap ...
References
Standards by
ASTM International
ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, ...
: D882 – Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Thin Plastic Sheeting
:D1004 – Standard Test Method for Tear Resistance (Graves Tear) of Plastic Film and Sheeting
:D1204 – Standard Test Method for Linear Dimensional Changes of Nonrigid Thermoplastic Sheeting or Film at Elevated Temperature
:D1593 – Standard Specification for Nonrigid Vinyl Chloride Plastic Film and Sheeting
:D1709 – Standard Test Methods for Impact Resistance of Plastic Film by the Free Falling Dart Method
:D1894 – Standard Test Method for Static and Kinetic Coefficients of Friction of Plastic Film and Sheeting
:D1922 – Standard Test Method for Propagation Tear Resistance of Plastic Film and Thin Sheeting by Pendulum Method
:D1938 – Standard Test Method for Tear Propagation Resistance of Plastic Film and Thin Sheeting by a Single Tear Method
:D2103 – Standard Specification for Polyethylene Film and Sheeting
:D2582 – Standard Test Method for Puncture Propagation Tear Resistance of Plastic Film and Thin Sheeting
:D2673 – Standard Specification for Oriented Polypropylene Film
:D2732 – Standard Test Method for Unrestrained Linear Thermal Shrinkage of Plastic Film and Sheeting
:D2838 -Standard Test Method for Shrink Tension and Orientation Release Stress of Plastic Film and Thin Sheeting
:D2923 – Standard Test Method for Rigidity of Polyolefin Film and Sheeting
:D3420 – Standard Test Method for Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastic Film
:D3595 – Standard Specification for Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE) Extruded Plastic Sheet and Film
:D3664 – Standard Specification for Biaxially Oriented Polymeric Resin Film for Capacitors in Electrical Equipment
:D3985 – Standard Test Method for Oxygen Gas Transmission Rate Through Plastic Film and Sheeting Using a Coulometric Sensor
:D4321 – Standard Test Method for Package Yield of Plastic Film
:D5047 – Standard Specification for Polyethylene Terephthalate Film and Sheeting
:D6287 – Standard Practice for Cutting Film and Sheeting Test Specimens
:D6988 – Standard Guide for Determination of Thickness of Plastic Film Test Specimens
:D8136 - Standard Test Method for Determining Plastic Film Thickness and Thickness Variability Using a Non-Contact Capacitance Thickness Gauge
:E1870 – Standard Test Method for Odor and Taste Transfer from Polymeric Packaging Film
:F2029- Standard Practices for Making Heatseals for Determination of Heatsealability of Flexible Webs as Measured by Seal Strength
:F2622 – Standard Test Method for Oxygen Gas Transmission Rate Through Plastic Film and Sheeting Using Various Sensors
Books and general references
* Hawkins, William E, The Plastic Film and Foil Web Handling Guide CRC Press 2003 *Jenkins, W. A., and Osborn, K. R. Plastic Films: Technology and Packaging Applications, CRC Press 1992 * Yam, K. L., "Encyclopedia of Packaging Technology", John Wiley & Sons, 2009, {{plastics Packaging materials Plastics applications