Plantation house on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A plantation house is the main house of a
 In the
In the
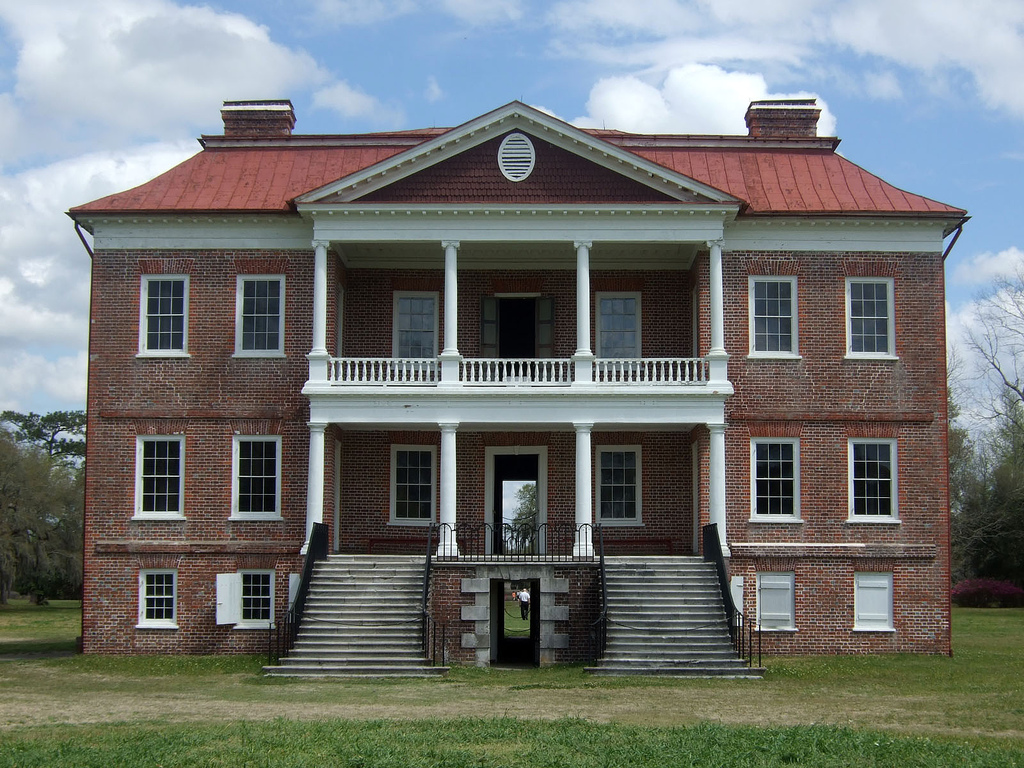 Most historical research has focused on the main houses of plantations, primarily because they were the most likely to survive and usually the most elaborate structures in the complex. Also, until fairly recent times, scholars and local historians usually focused on the life of the plantation owner, that is, the planter, and his or her family rather than the people they held as slaves. All romanticized notions aside, the plantation house was, at its most basic, a functioning
Most historical research has focused on the main houses of plantations, primarily because they were the most likely to survive and usually the most elaborate structures in the complex. Also, until fairly recent times, scholars and local historians usually focused on the life of the plantation owner, that is, the planter, and his or her family rather than the people they held as slaves. All romanticized notions aside, the plantation house was, at its most basic, a functioning  In colonial
In colonial  Large portions of the South outside of the original British colonies, such as in
Large portions of the South outside of the original British colonies, such as in  Rough vernacular architecture for early plantations was also true in
Rough vernacular architecture for early plantations was also true in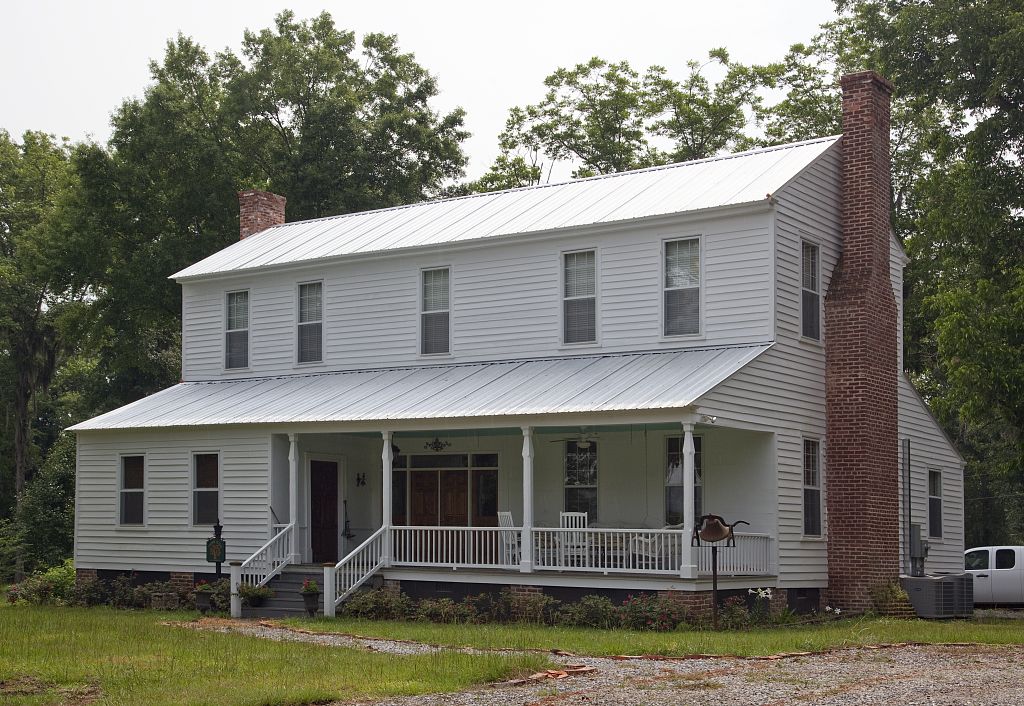  After the period of initial settlement, more refined folk house types came from the older portions of the South, especially the
After the period of initial settlement, more refined folk house types came from the older portions of the South, especially the  Jenrette, Richard Hampton (2005)
Jenrette, Richard Hampton (2005)
with Old Houses''
p. 179. Wyrick & Company. Another house type, the Creole cottage, came from the areas along the When the cotton boom years began in the 1830s, the United States was entering its second neoclassical phase, with
When the cotton boom years began in the 1830s, the United States was entering its second neoclassical phase, with 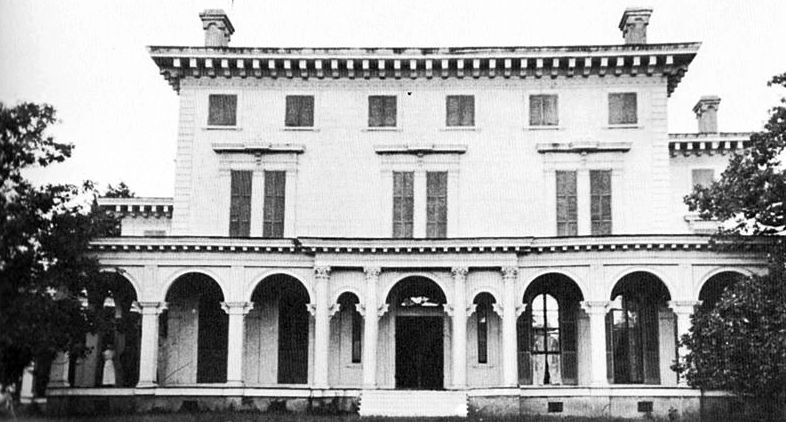 Earlier neoclassicism had often used ancient
Earlier neoclassicism had often used ancient  Greek Revival would remain a favorite architectural style in the agrarian South until well after the Civil War, but other styles had appeared in the nation about the same time as Greek Revival or soon afterward. These were primarily the
Greek Revival would remain a favorite architectural style in the agrarian South until well after the Civil War, but other styles had appeared in the nation about the same time as Greek Revival or soon afterward. These were primarily the
plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The ...
, often a substantial farmhouse
FarmHouse (FH) is a social fraternity founded at the University of Missouri on April 15, 1905. It became a national organization in 1921. Today FarmHouse has 33 active chapters and four associate chapters (formerly colonies) in the United State ...
, which often serves as a symbol for the plantation as a whole. Plantation houses in the Southern United States and in other areas are known as quite grand and expensive architectural works today, though most were more utilitarian, working farmhouses.
Antebellum American South
In theAmerican South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
, antebellum
Antebellum, Latin for "before war", may refer to:
United States history
* Antebellum South, the pre-American Civil War period in the Southern United States
** Antebellum Georgia
** Antebellum South Carolina
** Antebellum Virginia
* Antebellum a ...
plantations were centered on a " plantation house," the residence of the owner, where important business was conducted. Slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
and plantations had different characteristics in different regions of the South. As the Upper South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern and lower Midwestern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, econo ...
of the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / E ...
colonies developed first, historians
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the stu ...
of the antebellum South defined planters as those who held 20 enslaved people. Major planters held many more, especially in the Deep South as it developed.Peter Kolchin, ''American Slavery 1619–1877'', New York: Hill and Wang, 1993, xiii The majority of slaveholders held 10 or fewer enslaved people, often to labor domestically. By the late 18th century, most planters in the Upper South had switched from exclusive tobacco cultivation to mixed-crop production, both because tobacco had exhausted the soil and because of changing markets. The shift away from tobacco meant they had slaves in excess of the number needed for labor, and they began to sell them in the internal slave trade.
There was a variety of domestic architecture on plantations. The largest and wealthiest planter families, for instance, those with estates fronting on the James River
The James River is a river in the U.S. state of Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 to Chesape ...
in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
, constructed mansions in brick and Georgian style, e.g. Shirley Plantation
Shirley Plantation is an estate located on the north bank of the James River in Charles City County, Virginia, USA. It is located on scenic byway State Route 5, between Richmond and Williamsburg. It is the oldest active plantation in Virginia ...
. Common or smaller planters in the late 18th and 19th century had more modest wood-frame buildings, such as Southall Plantation in Charles City County.
 In the
In the Lowcountry
The Lowcountry (sometimes Low Country or just low country) is a geographic and cultural region along South Carolina's coast, including the Sea Islands. The region includes significant salt marshes and other coastal waterways, making it an import ...
of South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, by contrast, even before the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
, planters holding large rice plantations typically owned hundreds of enslaved people. In Charleston and Savannah, the elite also held numerous enslaved people to work as household servants. The 19th-century development of the Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the wa ...
for cotton cultivation depended on large plantations with much more acreage than was typical of the Upper South; and for labor, planters held hundreds of enslaved people.
Until December 1865 slavery was legal in parts of the United States. Most enslaved people labored in agricultural production, and ''planter'' was a term commonly used to describe a farmer with many enslaved humans.
The term planter has no universally-accepted definition, but academic historians have defined it to identify the elite class, "a landowning farmer of substantial means." In the " Black Belt" counties of Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = " Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,7 ...
and Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Missis ...
, the terms "planter" and "farmer" were often synonymous.Oakes, Ruling Race, 52. Robert Fogel and Stanley Engerman define large planters as owning over 50 enslaved people, and medium planters as owning between 16 and 50 enslaved humans.
In his study of Black Belt counties in Alabama, Jonathan Wiener defines planters by ownership of real property, rather than of enslaved people. A planter, for Wiener, owned at least $10,000 worth of real estate in 1850 and $32,000 worth in 1860, equivalent to about the top 8 percent of landowners. In his study of southwest Georgia, Lee Formwalt also defines planters in size of land holdings rather than enslaved people. Formwalt's planters are in the top 4.5 percent of land owners, translating into real estate worth $6,000 or more in 1850, $24,000 or more in 1860, and $11,000 or more in 1870. In his study of Harrison County, Texas
Harrison County is a county on the eastern border of the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 United States census, its population was 68,839. The county seat is Marshall. The county was created in 1839 and organized in 1842. It is named for Jon ...
, Randolph B. Campbell classifies large planters as owners of 20 enslaved humans, and small planters as owners of between ten and 19 enslaved humans. In Chicot and Phillips counties, Arkansas, Carl H. Moneyhon defines large planters as owners of twenty or more enslaved humans, and six hundred or more acres.
Plantation house in the Southern United States
 Most historical research has focused on the main houses of plantations, primarily because they were the most likely to survive and usually the most elaborate structures in the complex. Also, until fairly recent times, scholars and local historians usually focused on the life of the plantation owner, that is, the planter, and his or her family rather than the people they held as slaves. All romanticized notions aside, the plantation house was, at its most basic, a functioning
Most historical research has focused on the main houses of plantations, primarily because they were the most likely to survive and usually the most elaborate structures in the complex. Also, until fairly recent times, scholars and local historians usually focused on the life of the plantation owner, that is, the planter, and his or her family rather than the people they held as slaves. All romanticized notions aside, the plantation house was, at its most basic, a functioning farmhouse
FarmHouse (FH) is a social fraternity founded at the University of Missouri on April 15, 1905. It became a national organization in 1921. Today FarmHouse has 33 active chapters and four associate chapters (formerly colonies) in the United State ...
. Although some plantation houses were planned as grand mansion
A mansion is a large dwelling house. The word itself derives through Old French from the Latin word ''mansio'' "dwelling", an abstract noun derived from the verb ''manere'' "to dwell". The English word ''manse'' originally defined a property l ...
s and were built all at once from the ground up, many more began as fairly rudimentary structures that either stayed that way, were replaced, or were enlarged and improved over time as fortunes improved. In most areas of the South the earliest settlers constructed houses to provide basic shelter suited to their local climate, not to establish permanence or demonstrate wealth or power.
 In colonial
In colonial Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to it ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and S ...
, South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
, the earliest plantation houses tended to follow British-derived folk forms such as the hall and parlor house
A hall-and-parlor house is a type of vernacular house found in early-modern to 19th century England, as well as in colonial North America.
-type and central-passage house-type.
Grander structures during the later colonial period usually conformed to the neoclassically-influenced styles, although some very early and rare Jacobean structures survive in Virginia. And in the southern portion of what became the state of Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is border ...
, the plantations reflected French Colonial
French colonial architecture includes several styles of architecture used by the French during colonization. Many former French colonies, especially those in Southeast Asia, have previously been reluctant to promote their colonial architectur ...
architectural types, some with Spanish influences, that remained in trend well after the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or appr ...
in 1803. Following the Revolutionary War, Federal and Jeffersonian-type neoclassicism became dominant in formal plantation architecture.
 Large portions of the South outside of the original British colonies, such as in
Large portions of the South outside of the original British colonies, such as in Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to ...
and Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to t ...
, did not see extensive settlement until the early 1800s. Although large portions of Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = " Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,7 ...
and Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Missis ...
were settled at roughly the same time, there were areas of these states, along with portions of western Georgia and southeastern Tennessee, that did not see wide-scale settlement until after the Indian removal
Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi Riverspecifically, to a des ...
in the 1830s. Very little formal architecture existed within these newly settled areas, with most dwellings being of hewn logs into the 1840s. The dogtrot-type plan was common for many of these log houses. Rough vernacular architecture for early plantations was also true in
Rough vernacular architecture for early plantations was also true in Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage la ...
and Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
although in their river regions. Admitted to the Union in the mid-1840s, early architecture in Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to th ...
and Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by b ...
generally showed a stronger Spanish Colonial architectural influence, blended with French and British forms.
Some of the wealthiest planters never built grand residences. One example was noted by Albert J. Pickett, an early Alabama historian. In 1850 he visited Nicholas Davis, the owner of the prosperous Walnut Grove Plantation. Despite owning more than 100 slaves, he was still living in the large log house he had built after his migration from Virginia in 1817. He told Pickett that he "would not exchange (it) for a palace." Even Gaineswood, now a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
due to it being considered a lavish example of a plantation house, began as a two-story hewn-log dogtrot that was eventually enveloped within the brick mass of the house.
 After the period of initial settlement, more refined folk house types came from the older portions of the South, especially the
After the period of initial settlement, more refined folk house types came from the older portions of the South, especially the I-house
The I-house is a vernacular house type, popular in the United States from the colonial period onward. The I-house was so named in the 1930s by Fred Kniffen, a cultural geographer at Louisiana State University who was a specialist in folk archi ...
, thought by architectural scholars to be a descendant of the hall and parlor and the central-passage house-types. The central-passage house continued to be popular and could be either single-pile (one room deep) or double-pile (two rooms deep). If it had a porch, it was under a separate roof attached to the main house.
I-houses were always two stories high, always single-pile, with side gables or a hipped roof. They were at least two rooms wide, with latter examples usually having a central hall dividing them. In the South, they usually had full-width one-story shed extensions to the front and rear. These sheds could manifest as open porches, enclosed rooms, or a combination of the two. This I-house with sheds came to be commonly referred to as "Plantation Plain." It also proved to be one of the most adaptable folk house types to changing architectural tastes, with some even having neoclassical portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cult ...
es and other high-style elements added to them at a later date.
 Jenrette, Richard Hampton (2005)
Jenrette, Richard Hampton (2005)with Old Houses''
p. 179. Wyrick & Company. Another house type, the Creole cottage, came from the areas along the
Gulf Coast
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississ ...
and its associated rivers that were formerly part of New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spai ...
. It was always one-and-a-half stories, with a side-gabled roof, and often had upper floor dormer windows. However, it accommodated a full-width front porch under the main roof, with doors or jib-windows opening from all of the rooms onto the porch, and was usually raised high above the ground on a full raised basement or piers. It was a common form for many early plantation houses and town houses alike in the lower reaches of Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi.
Greek Revival architecture
The Greek Revival was an architectural movement which began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe and the United States and Canada, but ...
being the dominant style. By this point trained architects were also becoming more common, and several introduced the style to the South. Whereas the earlier Federal and Jeffersonian neoclassicism displayed an almost feminine lightness, academic Greek Revival was very masculine, with a heaviness not seen in the earlier styles.
 Earlier neoclassicism had often used ancient
Earlier neoclassicism had often used ancient Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
models and the Tuscan order, along with the Roman versions of the original three Greek orders. The original Greek orders were Doric, Ionic, and the Corinthian. The academic version of Greek Revival embraced the pure form of ancient Grecian architecture. Due to its popularity during a time of great wealth for many southern plantations, it was the Greek Revival that became permanently linked to the plantation legend. Though some houses were architect-designed, many, if not most, were designed by the owners or their carpenters from pattern books published by Asher Benjamin
Asher Benjamin (June 15, 1773July 26, 1845) was an American architect and author whose work transitioned between Federal architecture and the later Greek Revival architecture. His seven handbooks on design deeply influenced the look of cities and ...
, Minard Lafever
Minard Lafever (1798–1854) was an American architect of churches and houses in the United States in the early nineteenth century.
Life and career
Lafever began life as a carpenter around 1820. At this period in the United States there were no ...
, John Haviland
John Haviland (15 December 1792 – 28 March 1852) was an English-born American architect who was a major figure in American Neo-Classical architecture, and one of the most notable architects working from Philadelphia in the 19th century.
Biog ...
, and others. Greek Revival proved to very adaptable to the hot and humid climate of the South, with colloquial adaptations of the style seen from one region, and sometimes from one town, to another.
 Greek Revival would remain a favorite architectural style in the agrarian South until well after the Civil War, but other styles had appeared in the nation about the same time as Greek Revival or soon afterward. These were primarily the
Greek Revival would remain a favorite architectural style in the agrarian South until well after the Civil War, but other styles had appeared in the nation about the same time as Greek Revival or soon afterward. These were primarily the Italianate
The Italianate style was a distinct 19th-century phase in the history of Classical architecture. Like Palladianism and Neoclassicism, the Italianate style drew its inspiration from the models and architectural vocabulary of 16th-century Italia ...
and Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
. They were slower to be adopted in whole for domestic plantation architecture, but they can be seen in a fusion of stylistic influences. Houses that were basically Greek Revival in character sprouted Italianate towers, bracketed eaves, or adopted the asymmetrical massing characteristic of that style.
Although never as popular as Greek Revival, fully Gothic Revival and Italianate plantation houses began to appear by the 1850s, after being popularized by the books of men such as Alexander Jackson Davis
Alexander Jackson Davis, or A. J. Davis (July 24, 1803 – January 14, 1892), was an American architect, known particularly for his association with the Gothic Revival style.
Education
Davis was born in New York City and studied at t ...
, Andrew Jackson Downing, and Samuel Sloan. The Gothic Revival was usually expressed in wood as Carpenter Gothic. Italianate was the most popular of the two styles. It was also most commonly built using wood construction when used for plantation houses, although a few brick examples, such as Kenworthy Hall, have survived.
The outbreak of war in 1861 put an abrupt end to the building of grand mansions. Following the war and the end of Reconstruction
Reconstruction may refer to:
Politics, history, and sociology
*Reconstruction (law), the transfer of a company's (or several companies') business to a new company
*''Perestroika'' (Russian for "reconstruction"), a late 20th century Soviet Union ...
, the economy was drastically altered. Planters often did not have the funds for upkeep of their existing houses and new construction virtually ceased on most plantations. The new sharecropping method kept many plantations going, but the days of extravagance were over.
References
{{reflist Antebellum architecture Plantations Farmhouses Mansions