Pisces (constellation) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pisces is a constellation of the
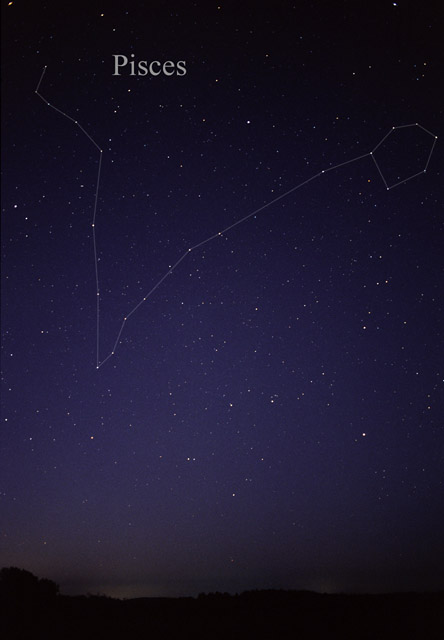 The
The
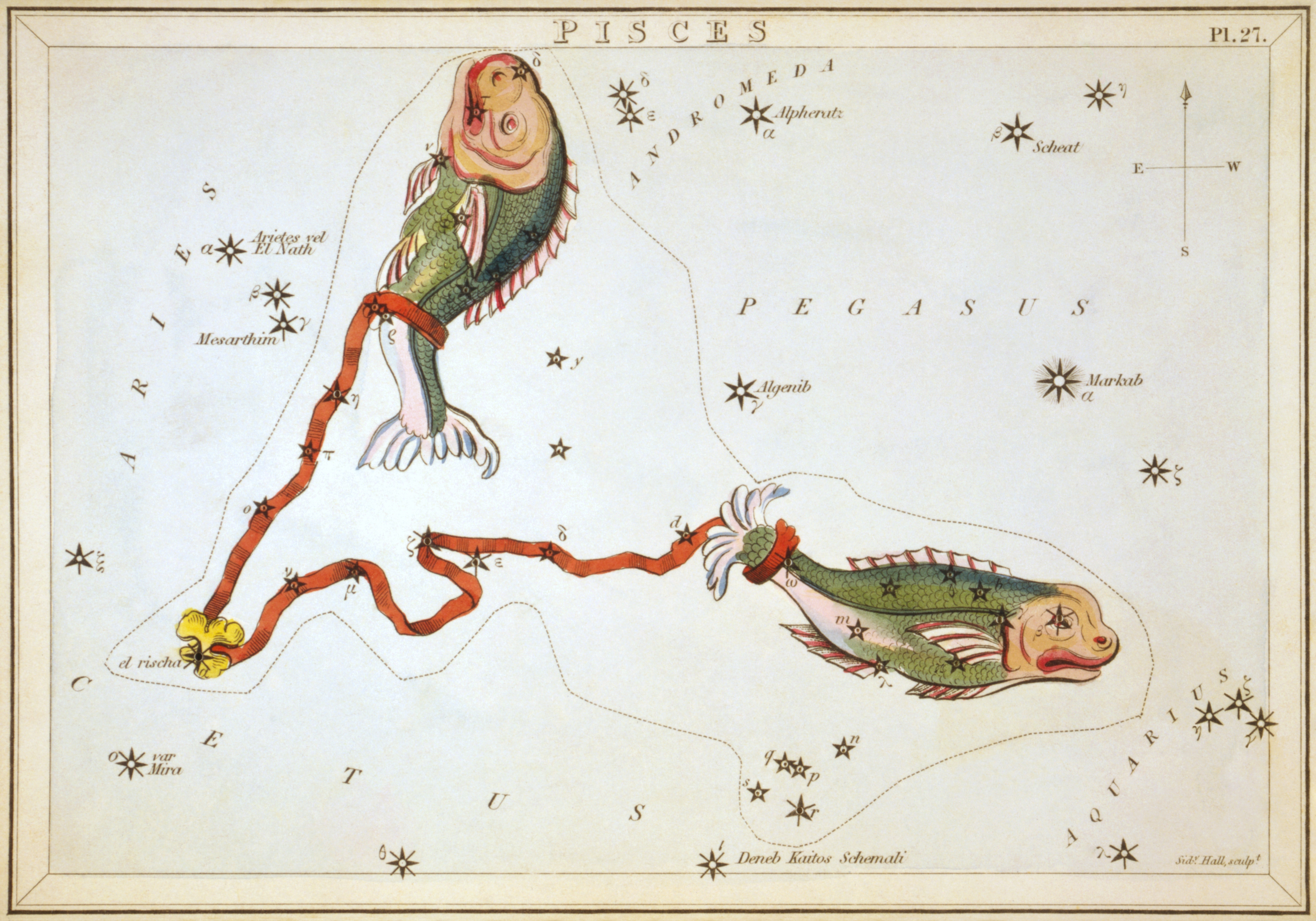 Pisces originates from some composition of the Babylonian constellations ''Šinunutu4'' "the great swallow" in current western Pisces, and ''Anunitum'' the "Lady of the Heaven" (supposedly
Pisces originates from some composition of the Babylonian constellations ''Šinunutu4'' "the great swallow" in current western Pisces, and ''Anunitum'' the "Lady of the Heaven" (supposedly
 In 1690, the astronomer
In 1690, the astronomer
Costellazioni Estinte (nate dal 1700 al 1800)
Sezione di Ricerca per la Cultura Astronomica It would host a natural but quite faint Asterism (astronomy), asterism in which the star 20 Psc is the head of the turtle. While Admiral Smyth mentioned the proposal, it was largely neglected by other astronomers, and it is now
The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Pisces
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (medieval and early modern images of Pisces)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pisces (Constellation) Constellations Equatorial constellations Constellations listed by Ptolemy
zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The pa ...
. Its vast bulk – and main asterism viewed in most European cultures per Greco-Roman antiquity as a distant pair of fishes connected by one cord each that join at an apex – are in the Northern celestial hemisphere. Its old astronomical symbol is (♓︎). Its name is Latin for "fishes". It is between Aquarius
Aquarius may refer to:
Astrology
* Aquarius (astrology), an astrological sign
* Age of Aquarius, a time period in the cycle of astrological ages
Astronomy
* Aquarius (constellation)
* Aquarius in Chinese astronomy
Arts and entertainment ...
, of similar size, to the southwest and Aries, which is smaller, to the east. The ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agains ...
and the celestial equator
The celestial equator is the great circle of the imaginary celestial sphere on the same plane as the equator of Earth. This plane of reference bases the equatorial coordinate system. In other words, the celestial equator is an abstract proj ...
intersect within this constellation and in Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
*Virgo (astrology), the sixth astrological sign of the zodiac
* Virgo (constellation), a constellation
*Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo
*Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy
* Virgo Su ...
. This means the sun passes directly overhead of the equator, on average, at approximately this point in the sky, at the March equinox
The March equinox or northward equinox is the equinox on the Earth when the subsolar point appears to leave the Southern Hemisphere and cross the celestial equator, heading northward as seen from Earth. The March equinox is known as the ve ...
.
Features
 The
The March equinox
The March equinox or northward equinox is the equinox on the Earth when the subsolar point appears to leave the Southern Hemisphere and cross the celestial equator, heading northward as seen from Earth. The March equinox is known as the ve ...
is currently located in Pisces, due south of ω Psc, and, due to precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In oth ...
, slowly drifting due west, just below the western fish towards Aquarius
Aquarius may refer to:
Astrology
* Aquarius (astrology), an astrological sign
* Age of Aquarius, a time period in the cycle of astrological ages
Astronomy
* Aquarius (constellation)
* Aquarius in Chinese astronomy
Arts and entertainment ...
.
Stars
* Alrescha ("the cord"), otherwise Alpha Piscium (α Psc), 309.8 lightyears, class A2, magnitude 3.62. Variable binary star. * Fumalsamakah ("mouth of the fish"), otherwise Beta Piscium (β Psc), 492 lightyears, class B6Ve, magnitude 4.48 * Delta Piscium (δ Psc), 305 lightyears, class K5III, magnitude 4.44. Like other stars near the ecliptic, Delta Piscium is subject to lunar occultations. * Epsilon Piscium (ε Psc), 190 lightyears, class K0III, magnitude 4.27. Has a candidate exoplanet. * Revati ("rich"), otherwise Zeta Piscium (ζ Psc), 148 lightyears, class A7IV, magnitude 5.21. Quintuple star system. * Alpherg ("emptying"), otherwise Eta Piscium (η Psc), 349 lightyears, class G7 IIIa, magnitude 3.62. It is aGamma Cassiopeiae variable A Gamma Cassiopeiae variable (γ Cassiopeiae variable) is a type of variable star, named for its prototype γ Cassiopeiae.
Variability
γ Cassiopeiae variables show irregular changes in brightness on a timescale of decades. These typically hav ...
with a weak magnetic field.
* Torcular ("thread"), otherwise Omicron Piscium (ο Psc), 258 lightyears, class K0III, magnitude 4.2. It is an evolved red giant star on the horizontal branch
The horizontal branch (HB) is a stage of stellar evolution that immediately follows the red-giant branch in stars whose masses are similar to the Sun's. Horizontal-branch stars are powered by helium fusion in the core (via the triple-alpha proce ...
.
* Omega Piscium
Omega Piscium (Omega Psc, ω Piscium, ω Psc) is a star approximately 106 light years away from Earth, in the constellation Pisces. It has a spectral type of F4IV, meaning it is a subgiant/dwarf star, and it has a temperatur ...
(ω Psc), 106 lightyears, class F4IV, magnitude 4.03. It is an F-type star that is either a subgiant
A subgiant is a star that is brighter than a normal main-sequence star of the same spectral class, but not as bright as giant stars. The term subgiant is applied both to a particular spectral luminosity class and to a stage in the evolution ...
or on the main sequence.
* Gamma Piscium
Gamma Piscium (Gamma Psc, γ Piscium, γ Psc) is a star approximately 138 light years away from Earth, in the zodiac constellation of Pisces. It is a yellow star with a spectral type of G8 III, meaning it has a surfac ...
(γ Psc), 138 lightyears, magnitude 3.70. The star hosts an exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first possible evidence of an exoplanet was noted in 1917 but was not recognized as such. The first confirmation of detection occurred in 1992. A different planet, init ...
which was discovered in 2021. It has a spectral type of G8 III.
* Van Maanen's Star
Van Maanen 2, or van Maanen's Star, is the closest known solitary white dwarf to the solar system. It is a dense, compact stellar remnant no longer generating energy and has equivalent to about 68% of the Sun's mass but only 1% of its r ...
is the closest-known solitary white dwarf to us, with a dim apparent magnitude. It is located about 2° to the south of the star Delta Piscium, with a relatively high proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more distan ...
of 2.978″ annually along a position angle
In astronomy, position angle (usually abbreviated PA) is the convention for measuring angles on the sky. The International Astronomical Union defines it as the angle measured relative to the north celestial pole (NCP), turning positive into the ...
of 155.538°. It is closer to the Sun than any other solitary white dwarf. It is too faint to be seen with the naked eye
Naked eye, also called bare eye or unaided eye, is the practice of engaging in visual perception unaided by a magnifying, light-collecting optical instrument, such as a telescope or microscope, or eye protection. Vision corrected to norma ...
. Like other white dwarfs, it is a very dense star: its mass has been estimated to be about 67% of the Sun's, yet it has only 1% of the Sun's radius. Based on log ''L''/ = −3.77. The outer atmosphere has a temperature of approximately 6,110 K, which is relatively cool for a white dwarf. As all white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
s steadily radiate away their heat over time, this temperature can be used to estimate its age, thought to be around 3 billion years. It was originally thought to be an F-type star before the properties of white dwarfs were known.
Due to the dimness of these stars, the constellation is essentially invisible in or near any major city due to light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive use of artificial lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting, during the day or night. Light po ...
.
Deep-sky objects
M74 is a loosely wound (type Sc)spiral galaxy
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''redshift
In physics, a redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation (such as light). The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and simultaneous increase in fr ...
0.0022). It has many clusters of young stars and the associated nebula
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in Latin; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regio ...
e, showing extensive regions of star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in The "medium" is present further soon.-->interstellar space
. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain
Pierre François André Méchain (; 16 August 1744 – 20 September 1804) was a French astronomer and surveyor who, with Charles Messier, was a major contributor to the early study of deep-sky objects and comets.
Life
Pierre Méchain was born i ...
, a French astronomer, in 1780. A type II-P supernova was discovered in the outer regions of M74 by Robert Evans in June 2003; the star that underwent the supernova was later identified as a red supergiant
Red supergiants (RSGs) are stars with a supergiant luminosity class ( Yerkes class I) of spectral type K or M. They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of volume, although they are not the most massive or luminous. Betelgeuse and Ant ...
with a mass of 8 solar mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass ...
es. It is the brightest member of the M74 Group.
NGC 488 is an isolated face-on prototypical spiral galaxy. Two supernovae have been observed in the galaxy.
NGC 520 is a pair of colliding galaxies located 105 million light-years away.
CL 0024+1654 is a massive galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-lar ...
that lenses the galaxy behind it, creating arc-shaped images of the background galaxy. The cluster is primarily made up of yellow elliptical and spiral galaxies, at a distance of 3.6 billion light-years from Earth (redshift 0.4), half as far away as the background galaxy, which is at a distance of 5.7 billion light-years (redshift 1.67).
History and mythology
 Pisces originates from some composition of the Babylonian constellations ''Šinunutu4'' "the great swallow" in current western Pisces, and ''Anunitum'' the "Lady of the Heaven" (supposedly
Pisces originates from some composition of the Babylonian constellations ''Šinunutu4'' "the great swallow" in current western Pisces, and ''Anunitum'' the "Lady of the Heaven" (supposedly Inanna
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
), at the place of the northern fish. In the first-millennium BC texts known as the ''Astronomical Diaries
The Babylonian astronomical diaries are a collection of Babylonian cuneiform texts that contain systematic records of astronomical observations and political events as well as predictions, based on astronomical observations. They also include oth ...
'', part of the constellation was also called DU.NU.NU (''Rikis-nu.mi'', "the fish cord or ribbon").
Greco-Roman period
Pisces is associated with the Greek legend thatAphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols incl ...
and her son Eros
In Greek mythology, Eros (, ; grc, Ἔρως, Érōs, Love, Desire) is the Greek god of love and sex. His Roman counterpart was Cupid ("desire").''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. In the ear ...
either shape-shifted into forms of fishes to escape, or were rescued by two fishes.
In the Greek version according to Hyginus
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Caesar Augustus. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Grammati ...
, Aphrodite and Eros while visiting Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
fled from the monster Typhon
Typhon (; grc, Τυφῶν, Typhôn, ), also Typhoeus (; grc, Τυφωεύς, Typhōeús, label=none), Typhaon ( grc, Τυφάων, Typháōn, label=none) or Typhos ( grc, Τυφώς, Typhṓs, label=none), was a monstrous serpentine giant an ...
by leaping into the Euphrates River
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
and transforming into fishes (''Poeticon astronomicon
''De Astronomica'', or the ''Astronomy'', also known as ''Poeticon Astronomicon'', is a book of stories whose text is attributed to "Hyginus", though the true authorship is disputed. During the Renaissance, the work was attributed to the Roman ...
'' 2.30, citing Diognetus Erythraeus). The Roman variant of the story has Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
and Cupid
In classical mythology, Cupid (Latin Cupīdō , meaning "passionate desire") is the god of desire, lust, erotic love, attraction and affection. He is often portrayed as the son of the love goddess Venus (mythology), Venus and the god of war Mar ...
(counterparts for Aphrodite and Eros) carried away from this danger on the backs of two fishes (Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom ...
'' Fasti'' 2.457ff).
There is also a different origin tale that Hyginus preserved in another work. According to this, an egg rolled into the Euphrates, and some fishes nudged this to shore, after which the doves sat on the egg until Aphrodite (thereafter called the Syrian Goddess) hatched out of it. The fishes were then rewarded by being placed in the skies as a constellation (''Fabulae
Gaius Julius Hyginus (; 64 BC – AD 17) was a Latin author, a pupil of the scholar Alexander Polyhistor, and a freedman of Caesar Augustus. He was elected superintendent of the Palatine library by Augustus according to Suetonius' ''De Grammati ...
'' 197). This story is also recorded by the Third Vatican Mythographer.
Modern period
 In 1690, the astronomer
In 1690, the astronomer Johannes Hevelius
Johannes Hevelius
Some sources refer to Hevelius as Polish:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Some sources refer to Hevelius as German:
*
*
*
*
*of the Royal Society
* (in German also known as ''Hevel''; pl, Jan Heweliusz; – 28 January 1687) was a councillor ...
in his ''Firmamentum Sobiescianum'' regarded the constellation Pisces as being composed of four subdivisions:
* Piscis Boreus (the North Fish): σ – 68 – 65 – 67 – ψ1 – ψ2 – ψ3 – χ – φ – υ – 91 – τ – 82 – 78 Psc.
* Linum Boreum (the North Cord): χ – ρ,94 – VX(97) – η – π – ο – α Psc.
* Linum Austrinum (the South Cord): α – ξ – ν – μ – ζ – ε – δ – 41 – 35 – ω Psc.
* Piscis Austrinus (the South Fish): ω – ι – θ – 7 – β – 5 – κ,9 – λ – TX(19) Psc.
" Piscis Austrinus" more often refers to a separate constellation in its own right.
In 1754, the astronomer John Hill (author) John Hill] proposed to sever a southern zone of Pisces as Testudo (the Turtle). 24 – 27 – YY(30) – 33 – 29 Psc.,Ciofi, Claudio; Torre, PietroCostellazioni Estinte (nate dal 1700 al 1800)
Sezione di Ricerca per la Cultura Astronomica It would host a natural but quite faint Asterism (astronomy), asterism in which the star 20 Psc is the head of the turtle. While Admiral Smyth mentioned the proposal, it was largely neglected by other astronomers, and it is now
obsolete
Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ...
.
Western folklore
The Fishes are in the German lore of Antenteh, who owned just a tub and a crude cabin when he met two magical fish. They offered him a wish, which he refused. However, his wife begged him to return to the fish and ask for a beautifully furnished home. This wish was granted, but her desires were not satisfied. She then asked to be a queen and have a palace, but when she asked to become a goddess, the fish became angry and took the palace and home, leaving the couple with the tub and cabin once again. The tub is sometimes recognized as theGreat Square of Pegasus
Pegasus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the winged horse Pegasus in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognised today.
...
.
In non-Western astronomy
The stars of Pisces were incorporated into several constellations inChinese astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the tw ...
. Wai-ping ("Outer Enclosure") was a fence that kept a pig farmer from falling into the marshes and kept the pigs where they belonged. It was represented by Alpha, Delta, Epsilon, Zeta, Mu, Nu, and Xi Piscium. The marshes were represented by the four stars designated Phi Ceti. The northern fish of Pisces was a part of the House of the Sandal, Koui-siou.
Astrology
Pisces is a dim zodiac constellation between Aquarius and Aries. While astrological sign, water sign Pisces is deemed to fix on ecliptical longitudes 330° to 0, when the sun figures at these it is now mostly inAquarius
Aquarius may refer to:
Astrology
* Aquarius (astrology), an astrological sign
* Age of Aquarius, a time period in the cycle of astrological ages
Astronomy
* Aquarius (constellation)
* Aquarius in Chinese astronomy
Arts and entertainment ...
, due to the precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In oth ...
from when the constellation and the sign coincided. Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In oth ...
results in Western astrology's zodiacal divisions, thus, not corresponding in the current era to the constellations
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the earliest constellation ...
that carry alike names while Jyotiṣa, widely used in Hindu and Jain culture, will assign events to the Sun's current background constellations.Johnsen (2004)
See also
*List of star names in Pisces
This is the list of the proper names for the stars in the constellation Pisces. (Used modern western astronomy and uranography only).
List
Etymologies
α Psc
* Alrescha (Al Rescha, Al Richa, Alrischa, Al Rischa, Alrisha, El Rischa):
: � ...
*Pisces (Chinese astronomy) The modern constellation Pisces (constellation), Pisces lies across two of the quadrants symbolized by the Black Tortoise, Black Tortoise of the North (北方玄武, ''Běi Fāng Xuán Wǔ'') and White Tiger (Chinese constellation), White Tiger of t ...
References
Sources
* * * * Richard Hinckley Allen, ''Star Names, Their Lore and Legend'',New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, Dover: various dates.
*
* Thomas Wm. Hamilton, ''Useful Star Names'', Strategic Books, 2008.
External links
The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Pisces
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (medieval and early modern images of Pisces)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pisces (Constellation) Constellations Equatorial constellations Constellations listed by Ptolemy