Phytophthora Nicotianae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Phytophthora nicotianae'' or black shank is an oomycete belonging to the order Peronosprales and family Peronosporaceae.

 Black Shank is a polycyclic soil borne disease, with the possibility of multiple disease cycles per growing season occurring from May to October. There are important structures this pathogen uses in its disease cycle. Chlamydospores are produced asexually and serve as long lived resting structures, surviving from four to six years. Chlamydospores are the primary survival structure, the primary inoculum, and are usually produced in abundance. These
Black Shank is a polycyclic soil borne disease, with the possibility of multiple disease cycles per growing season occurring from May to October. There are important structures this pathogen uses in its disease cycle. Chlamydospores are produced asexually and serve as long lived resting structures, surviving from four to six years. Chlamydospores are the primary survival structure, the primary inoculum, and are usually produced in abundance. These

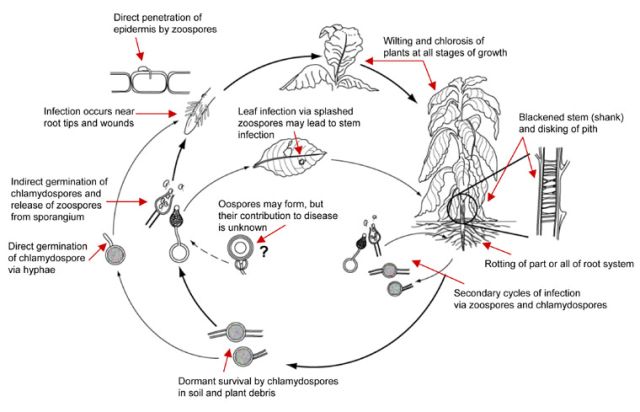 This pathogen thrives in temperatures ranging from . Disease is prominent in many agricultural productive regions and therefore is a major host to many warm environment crops. Black Shank needs water for germination and movement. Saturated soil optimizes disease spread because water is used for dissemination of motile zoospores and sporangia. Low-lying areas of the soil that remain wet for prolonged periods of time will have more disease. Splashing water from rain or
This pathogen thrives in temperatures ranging from . Disease is prominent in many agricultural productive regions and therefore is a major host to many warm environment crops. Black Shank needs water for germination and movement. Saturated soil optimizes disease spread because water is used for dissemination of motile zoospores and sporangia. Low-lying areas of the soil that remain wet for prolonged periods of time will have more disease. Splashing water from rain or

Hosts and symptoms
''Phytophthora nicotianae'' has a broad host range comprising 255genera
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclat ...
from 90 families. Hosts include tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus '' Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the on ...
, tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
, ornamentals, cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
, pepper, and citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to ...
plants. This pathogen can cause root rot, crown rot, fruit rot, leaf infection, and stem infection. Root rot symptoms are observed on tobacco, poinsettia, tomato, pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae. The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been cultivated for many centuri ...
, watermelon, and as well as African violet. Fruit rots occur on tomato, papaya
The papaya (, ), papaw, () or pawpaw () is the plant species ''Carica papaya'', one of the 21 accepted species in the genus '' Carica'' of the family Caricaceae. It was first domesticated in Mesoamerica, within modern-day southern Mexico and ...
, and eggplant
Eggplant ( US, Canada), aubergine ( UK, Ireland) or brinjal (Indian subcontinent, Singapore, Malaysia, South Africa) is a plant species in the nightshade family Solanaceae. ''Solanum melongena'' is grown worldwide for its edible fruit.
Mo ...
. Onion shows a leaf and stem infection. In tobacco Black Shank affects the roots and basal stem area, but all parts of the plant can become infected. Damping off symptoms can be observed in young seedlings. The first above ground symptom that will be observed is the wilting of plants, which leads to stunting. Roots will be blackened and decayed. In final stages of the disease the stem begins to turn black, hence the name Black Shank. As this happens, tobacco leaves turn brown and become not marketable. Another symptom is disk-like appearance of the pith, although this is not a definitive symptom as it may also be the result of lightning
Lightning is a naturally occurring electrostatic discharge during which two electrically charged regions, both in the atmosphere or with one on the ground, temporarily neutralize themselves, causing the instantaneous release of an average ...
strikes. On onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus '' Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the on ...
it causes the disease known as ''Phytophthora'' neck and bulb rot. Different stages of onion may be affected. Initially, tips of newly infected plants start to yellow and dry followed by softening of the "neck" of the plants that eventually fall over. Infected leaves may show grey lesions. Roots may become necrotic in late disease.

Disease cycle
 Black Shank is a polycyclic soil borne disease, with the possibility of multiple disease cycles per growing season occurring from May to October. There are important structures this pathogen uses in its disease cycle. Chlamydospores are produced asexually and serve as long lived resting structures, surviving from four to six years. Chlamydospores are the primary survival structure, the primary inoculum, and are usually produced in abundance. These
Black Shank is a polycyclic soil borne disease, with the possibility of multiple disease cycles per growing season occurring from May to October. There are important structures this pathogen uses in its disease cycle. Chlamydospores are produced asexually and serve as long lived resting structures, surviving from four to six years. Chlamydospores are the primary survival structure, the primary inoculum, and are usually produced in abundance. These spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, ...
s germinate in warm and moist soil to produce a germ tube that infects plants or produces a sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cy ...
. Another asexual structure and secondary inoculum, appearing ovoid, pear, or spherical in shape are called sporangium. These spores are produced and can either germinate directly or release motile zoospores within 24 hours of inoculation with the right conditions. Zoospores are kidney shaped with an anterior tinsel flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates.
A microorganism may have f ...
and a posterior whip like flagellum that helps to navigate toward root tips were infection occurs. Black Shank needs water for germination and movement because zoospores swim through soil pores and standing water. Splashing water from rain or irrigation can infect healthy plant leaves leading to more repeating secondary cycles. Zoospores move toward nutrient gradients around root tips and host wounds. Once the root surface is contacted, zoospores encyst and a germ tube will emerge penetrating the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water rel ...
. Infection leads to systemic rotting of the root system and wilting and chlorosis in the leaves. Another structure called hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one or ...
e is colorless, transparent, and coenocytic, but colonies may yellow with age. Also, there is much morphological variation in colony type with different isolates of ''P. nicotianae'' and the growth may differ when grown on different media. The hyphae are heterothallic and require two mating type
Mating types are the microorganism equivalent to sexes in multicellular lifeforms and are thought to be the ancestor to distinct sexes. They also occur in macro-organisms such as fungi.
Definition
Mating types are the microorganism equivalent to ...
s to produce oospores, the sexual survival structure. Many fields only contain one mating type, so the zoospores rarely germinate and rarely cause epidemics.
Environment

 This pathogen thrives in temperatures ranging from . Disease is prominent in many agricultural productive regions and therefore is a major host to many warm environment crops. Black Shank needs water for germination and movement. Saturated soil optimizes disease spread because water is used for dissemination of motile zoospores and sporangia. Low-lying areas of the soil that remain wet for prolonged periods of time will have more disease. Splashing water from rain or
This pathogen thrives in temperatures ranging from . Disease is prominent in many agricultural productive regions and therefore is a major host to many warm environment crops. Black Shank needs water for germination and movement. Saturated soil optimizes disease spread because water is used for dissemination of motile zoospores and sporangia. Low-lying areas of the soil that remain wet for prolonged periods of time will have more disease. Splashing water from rain or irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
can infect healthy plant leaves leading to more repeating secondary cycles. Soils that are not saturated will lead to little to no disease development, so water management is important. Optimum soil pH for development is between 6 and 7. Levels of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
and magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
in the soils can affect disease progress.
Management
Several kinds of management exist for the prevention and suppression of disease. A cultural method that can be effective in preventing disease is sanitation. Equipment should be cleaned after use in infested fields so the disease does not spread into uninfested fields. To disrupt chlamydospore germination crops should be grown in drained disease free soil. Also, avoid transplanting without thorough knowledge of the transplant. To limit spread of structures limit traffic in infected fields and always clean after exposure. Disease is favored by pH values greater than 6.2, so lowering the pH is an effective method for preventing germination. pH management can be difficult because tobacco cannot survive in very low pH soils. Soil pH 5.5 to 6 allow successful growth of tobacco and control of disease. The cultural control,Crop rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. It reduces reliance on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, and the probability of developing resistant ...
, is very effective at limiting disease. The longer an infected field is planted in a crop other than the initial infected crop, the lower the population will become. A minimum three-year rotation is recommended. Crop rotation is recommended in combination with resistant varieties as genetic controls. Burley Tobacco, Burley Tobacco hybrids, and Dark Tobacco are varieties of tobacco that are resistant to Black Shank. Resistance however is not reliable because a single variety has resistance to only a few races of Black Shank. Finding new lines of resistance is becoming increasingly important due to new discovered resistant races of the pathogen.
Chemical control is most successful if used with resistant varieties. Metalaxyl or mefenoxam are chemistries used to control ''Phytophthora nicotianae''. Ridomil Gold is an example a systemic pesticide with a Metalaxyl chemistry. Mefenoxam is twice as active as metalaxyl, but they both have the same mode of action. Successful chemical control is difficult because we are limited to these two chemistries that are basically identical. A study by A. S. Csinos and P. F. Bertrand found out at a rate of 3.36 kg/ha would not inhibit many of the common races used in their study. Overall, from their study they observed that Black Shank severity was increasing in Georgia due to Metalaxyl sensitivity and resistant races of Black Shank.
Importance
''Phytophthora nicotianae'' has a wide host range, affecting agriculture rich areas all over the world. In theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
this is a major pathogen of ornamentals, tobacco, and tomato. Black Shank is one of the most damaging and far reaching diseases of tobacco. In 1896, Black Shank was first described in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Gui ...
by Van Breda de Haan. Disease was observed near Georgia in 1915 and reached major tobacco growing areas of Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
and North Carolina
North Carolina () is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 28th largest and List of states and territories of the United ...
in the 1930s and 1940s. In North Carolina black shank can be found in every county that grows flue-cured tobacco
Flue-cured tobacco is a type of cigarette tobacco. Along with burley tobacco, it accounts for more than 90% of US tobacco production. Flue-cured farming is centered in North Carolina. Production was limited by national marketing quotas and acreag ...
and currently causes statewide losses of 1 to 2.5 percent per year. This pathogen thrives in warm climates, so it is destructive on crops grown in these areas. During favorable conditions, new generations of spores can be produced every 72 hours, so if this disease is not managed well it can be very destructive. Susceptible cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture ...
s in the right conditions can reach losses of 100 percent, because infected plants do not recover. Less than one propagule per gram of soil can lead to an epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time.
Epidemics of infectious ...
.

Pathogenesis
This pathogen causes secondary cycles of disease by mode of zoospores. Zoospores interact with the host by sensing and moving toward the nutrient gradients near the root tip and wounds of the plant. Without this means of sensing entry points there would be no secondary cycles of disease. Zoospores, chlamydospores, and sporangia produce a germ tube that directly penetrates the epidermis of the plant. Without this penetration device the pathogen would not be able to infect the plant. The pathogen interferes with transport by infecting the roots. Typically hyphae can be seen in the pith and cause blackening and necrosis. Infection can proceed rapidly once the pathogen has made an entrance into the plant. Once established, further reproduction of both chlamydospores and sporangia will occur within host tissues, amplifying the spread of disease within the host plant and spreading out into nearby plants. Upon death of the host, the decomposing infected tissues will release the pathogen back into the soil, in the form of chlamydospores and zoospores. A resting spore, the chlamydospores are capable of surviving in the soil for years, but it has been noted that cold winters cause an inhibitory effect on the survival rate. This results in less black shank infections where tobacco is grown in cooler, more northern climates. The action of ''P. nicotianae'' is amplified by the presence of root-knot nematodes, which through their own feeding habits, assist the pathogen in finding an entrance to the host. This pathogen synergy with root-knot nematodes has the ability to overcome much of the resistance of cultivars especially bred for ''P. nicotianae'' resistance.References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Phytophthora Nicotianae nicotianae Species described in 1896 Water mould plant pathogens and diseases Vegetable diseases