photoelectric sensor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
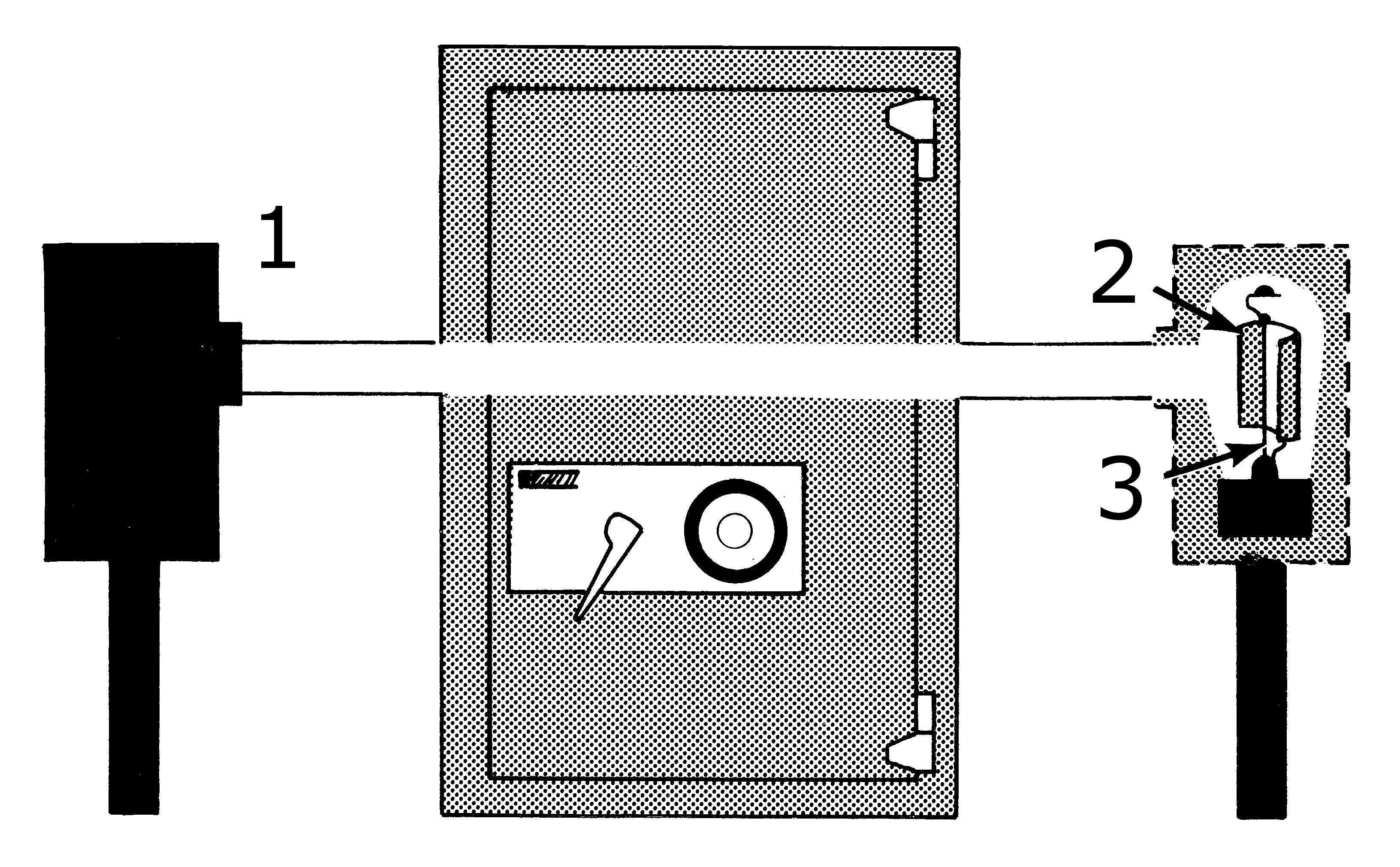 A photoelectric sensor is a device used to determine the distance, absence, or presence of an object by using a light transmitter, often
A photoelectric sensor is a device used to determine the distance, absence, or presence of an object by using a light transmitter, often

to Sensing'', 2002, Banner Engineering Corporation, P/N 120236Guide to sensing
{{Authority control Sensors
 A photoelectric sensor is a device used to determine the distance, absence, or presence of an object by using a light transmitter, often
A photoelectric sensor is a device used to determine the distance, absence, or presence of an object by using a light transmitter, often infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
, and a photoelectric
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid sta ...
receiver. They are largely used in industrial manufacturing. There are three different useful types: opposed (through-beam), retro-reflective, and proximity-sensing (diffused).
Types
A self-contained photoelectric sensor contains theoptics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultrav ...
, along with the electronics
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
. It requires only a power source. The sensor performs its own modulation, demodulation, amplification, and output switching. Some self-contained sensors provide such options as built-in control timers or counters. Because of technological progress, self-contained photoelectric sensors have become increasingly smaller.
Remote photoelectric sensors used for remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Eart ...
contain only the optical components of a sensor. The circuitry for power input, amplification, and output switching is located elsewhere, typically in a control panel. This allows the sensor, itself, to be very small. Also, the controls for the sensor are more accessible, since they may be bigger.
When space is restricted or the environment too hostile even for remote sensors, fibre optics
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means t ...
may be used. Fibre optics are passive mechanical sensing components. They may be used with either remote or self-contained sensors. They have no electrical circuitry and no moving parts, and can safely pipe light into and out of hostile environments.
Sensing modes
A through-beam arrangement consists of a receiver located within the line-of-sight of the transmitter. In this mode, an object is detected when the light beam is blocked from getting to the receiver from the transmitter. A retroreflective arrangement places the transmitter and receiver at the same location and uses a reflector to bounce the inverted light beam back from the transmitter to the receiver. An object is sensed when the beam is interrupted and fails to reach the receiver. A proximity-sensing (diffused) arrangement is one in which the transmitted radiation must reflect off the object in order to reach the receiver. In this mode, an object is detected when the receiver sees the transmitted source rather than when it fails to see it. As in retro-reflective sensors, diffuse sensor emitters and receivers are located in the same housing. But the target acts as the reflector so that detection of light is reflected off the disturbance object. The emitter sends out a beam of light (most often a pulsed infrared, visible red, or laser) that diffuses in all directions, filling a detection area. The target then enters the area and deflects part of the beam back to the receiver. Detection occurs and output is turned on or off when sufficient light falls on the receiver. Some photo-eyes have two different operational types, light operate and dark operate. The light operates photo eyes become operational when the receiver "receives" the transmitter signal. Dark operate photo eyes become operational when the receiver "does not receive" the transmitter signal. The detecting range of a photoelectric sensor is its "field of view", or the maximum distance from which the sensor can retrieve information, minus the minimum distance. A minimum detectable object is the smallest object the sensor can detect. More accurate sensors can often have minimum detectable objects of minuscule size.
Difference between modes
See also
*List of sensors
This is a list of sensors sorted by sensor type.
Acoustic, sound, vibration
* Geophone
* Hydrophone
*Microphone
* Pickup
*Seismometer
*Sound locator
Automotive
*Air flow meter
* AFR sensor
* Air–fuel ratio meter
*Blind spot monitor
*Crank ...
* Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, or ...
* Sensor
* Electric eye
An electric eye is a photodetector used for detecting obstruction of a light beam. An example is the door safety system used on garage door openers that use a light transmitter and receiver at the bottom of the door to prevent closing if there is ...
References
External links
to Sensing'', 2002, Banner Engineering Corporation, P/N 120236
{{Authority control Sensors