Phenazines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Phenazine is an
organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. Th ...
with the formula (C6H4)2N2. It is a dibenzo annulated
In organic chemistry annulation (from the Latin ''anellus'' for "little ring"; occasionally annelation) is a chemical reaction in which a new ring is constructed on a molecule.
:
Examples are the Robinson annulation, Danheiser annulation and cert ...
pyrazine, and the parent substance of many dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
stuffs, such as the toluylene red, indulines, and safranine
Safranin (Safranin O or basic red 2) is a biological stain used in histology and cytology. Safranin is used as a counterstain in some staining protocols, colouring cell nuclei red. This is the classic counterstain in both Gram stains and end ...
s (and the closely related eurhodines). Phenazine crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
lizes in yellow needles, which are only sparingly soluble in alcohol. Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular fo ...
dissolves it, forming a deep-red solution.
Synthesis
Classically phenazine are prepared by the reaction of nitrobenzene and aniline in the Wohl-Aue reaction. Other methods include: * pyrolysis of the bariumsalt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
of azobenzoate
* oxidation of aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ...
with lead oxide
* oxidation of dihydrophenazine, which is prepared by heating pyrocatechin with o-phenylenediamine.
* oxidation of ortho-aminodiphenylamine with lead peroxide
Lead(IV) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula PbO2. It is an oxide where lead is in an oxidation state of +4. It is a dark-brown solid which is insoluble in water. It exists in two crystalline forms. It has several important applicatio ...
.
Derivatives
* The more complex phenazines, such as the naphthophenazines, naphthazines, and naphthotolazines, may be prepared by condensing ortho-diamines with ortho-quinones or by theoxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or ...
of an ortho-diamine in the presence of α-naphthol Naphthol may refer to:
* 1-Naphthol
1-Naphthol, or α-naphthol, is a fluorescent organic compound with the formula . It is a white solid. It is an isomer of 2-naphthol differing by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. ...
, and by the decomposition of ortho-anilido-(-toluidido- et cetera)- azo compounds with dilute acids.
* If alkyl or aryl-ortho-diamines be used, azonium bases are obtained. The azines are mostly yellow in color, distill unchanged and are stable to oxidant
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxi ...
s. They add on alkyl iodides readily, forming alkyl azonium salts, anhydride formation also taking place between these hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydrox ...
groups. It dissolves in concentrated sulfuric acid with a yellowish-green fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, tha ...
.
* The rhodamines, which are closely related to the phthaleins, are formed by the condensation of the alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloa ...
metaaminophenols with phthalic anhydride in the presence of sulfuric acid. Their salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
s are fine red dyes. By the entrance of amino or hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydrox ...
groups into the molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and b ...
dyestuffs are formed. The mono-amino derivatives or eurhodines are obtained when the arylmonamines are condensed with orthoamino azo compounds; by condensing quinone dichlorimide or para-nitrosodimethyl aniline with monamines containing a free para position, or by oxidizing ortho-hydroxydiaminodipbenylamines. They are yellowish-red solids, which behave as weak bases, their salts undergoing hydrolytic
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysis i ...
dissociation in aqueous solution. When heated with concentrated hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the dige ...
the amino group is replaced by the hydroxyl group and the phenol
Phenol (also called carbolic acid) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group () bonded to a hydroxy group (). Mildly acidic, it r ...
ic eurhodols are produced.
Aminophenazine
Many aminophenazines are prominent dyes. Two of the first synthetic dyes are aminophenazines, these include induline and nigrosin. The symmetrical diaminophenazine is the parent substance of the important dyestuff neutral red (dimethyldiaminotoluphenazine). It is obtained by the oxidation of ortho-phenylenediamine withferric chloride
Iron(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . Also called ferric chloride, it is a common compound of iron in the +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous compound is a crystalline solid with a melting point of 307.6 °C. The col ...
.
In a related process, oxidation of a cold mixture of ''para''-aminodimethylaniline and ''meta''-toluylenediamine gives toluylene blue. This indamine is formed as an intermediate product and passing into the red when boiled; and also by the oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or ...
of dimethylparaphenylene diatnine with metatoluylene diamine. It crystallizes in orange-red needles and its alcoholic solution fluoresces strongly. It dyes silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from th ...
and mordanted cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor pe ...
a fine scarlet. It is known commercially as neutral red. For the phenazonium salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
s, see safranine
Safranin (Safranin O or basic red 2) is a biological stain used in histology and cytology. Safranin is used as a counterstain in some staining protocols, colouring cell nuclei red. This is the classic counterstain in both Gram stains and end ...
. Benzo innoline is an isomer of phenazine, to which it bears the same relation that phenanthrene bears to anthracene
Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes. Anthracene is co ...
.
Natural products
The known biological sources of phenazine compounds are mostly bacterial in nature. Some of the genera known to produce phenazines include '' Pseudomonas'' spp., ''Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positiv ...
'' spp., and ''Pantoea agglomerans
''Pantoea agglomerans'' is a Gram-negative bacterium that belongs to the family Erwiniaceae.
It was formerly called ''Enterobacter agglomerans'', or ''Erwinia herbicola'' and is a ubiquitous bacterium commonly isolated from plant surfaces, see ...
''. These phenazine natural products have been implicated in the virulence and competitive fitness of producing organisms. For example, the phenazine pyocyanin produced by ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic– facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. a ...
'' contributes to its ability to colonise the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients. Similarly, phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, produced by a number of Pseudomonads, increases survival in soil environments and has been shown to be essential for the biological control activity of certain strains.
While bacterial phenazines are principally involved in secondary metabolisms, methanophenazine in methanogenic archaea ( methanogens) is involved in primary metabolisms and are important electron carrier. Methanophenazine acts as the functional equivalent of menaquinones and ubiquinones in other organisms. Methanophenazine is only known phenazine of non-bacterial origin and also is the only phenazine that engages in primary metabolisms.
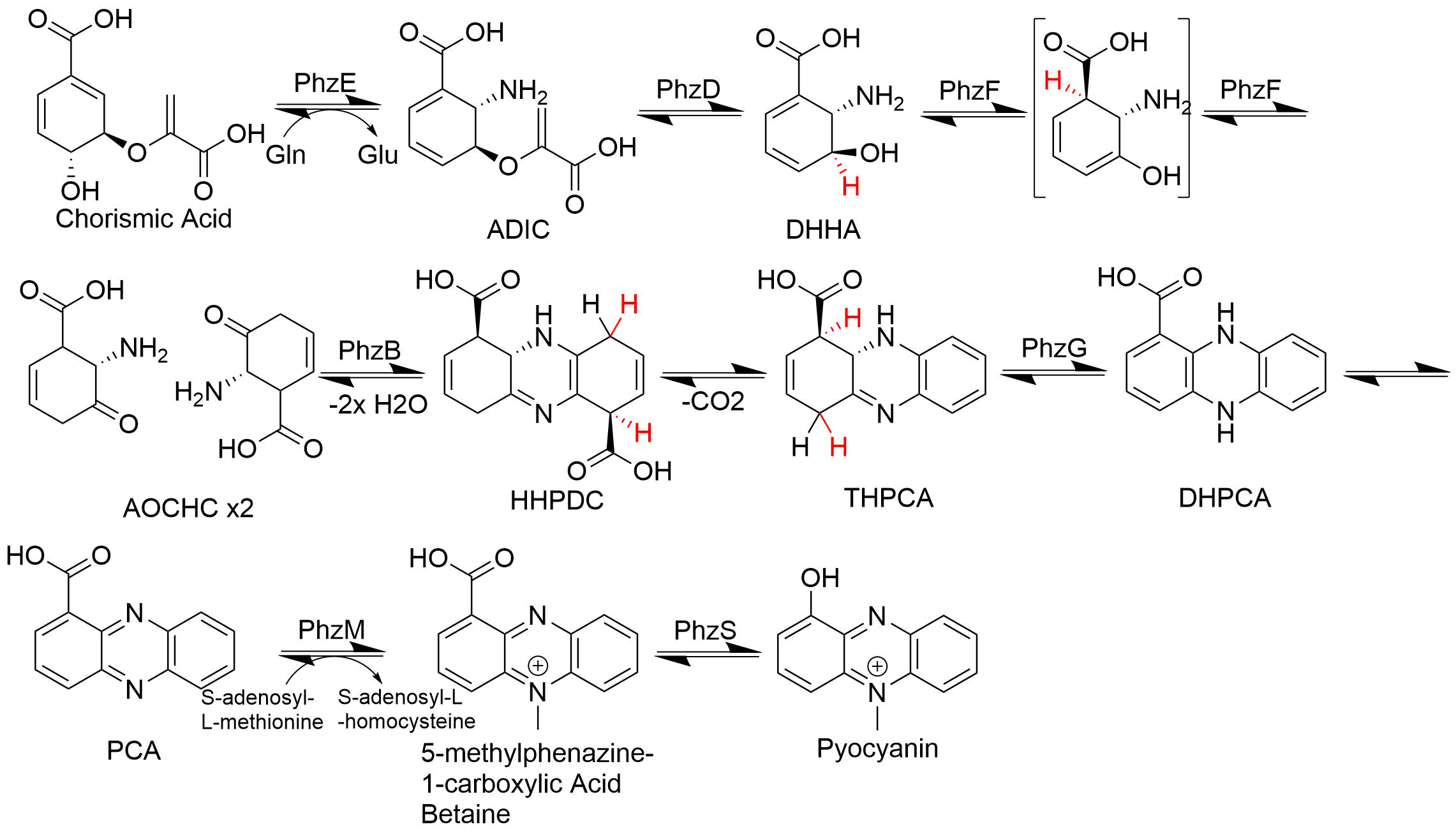
Biosynthesis
Phenazine biosynthesis branches off the shikimic acid pathway at a point subsequent to chorismic acid. Two molecules of this chorismate-derived intermediate are then brought together in a diagonally-symmetrical fashion to form the basic phenazine scaffold. Sequential modifications then lead to a variety of phenazine with differing biological activities. An example of phenazinic alkaloids are pyocyanin, saphenic acid and esmeraldins.
References
{{Authority control Azin dyes