People's Crusade on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The People's Crusade was the beginning phase of the

 Calling for a crusade at the
Calling for a crusade at the
 Peter gathered his army at
Peter gathered his army at
 In Zemun, the crusaders became suspicious, seeing Walter's sixteen suits of armor hanging from the walls, and eventually a dispute over the price of a pair of shoes in the market led to a riot, which then turned into an all-out assault on the city by the crusaders, in which 4,000 Hungarians were killed. The crusaders then fled across the river Sava to Belgrade, but only after skirmishing with Belgrade troops. The residents of Belgrade fled, and the crusaders pillaged and burned the city. Then they marched for seven days, arriving at
In Zemun, the crusaders became suspicious, seeing Walter's sixteen suits of armor hanging from the walls, and eventually a dispute over the price of a pair of shoes in the market led to a riot, which then turned into an all-out assault on the city by the crusaders, in which 4,000 Hungarians were killed. The crusaders then fled across the river Sava to Belgrade, but only after skirmishing with Belgrade troops. The residents of Belgrade fled, and the crusaders pillaged and burned the city. Then they marched for seven days, arriving at
Collected Accounts
* Duncalf, Frederic. "The Peasants Crusade." ''American Historical Review'' 26 (1921): pg. 440–53. * Cohn, Norman. ''The Pursuit of the Millennium''. * See also First Crusade – selected sources and further reading {{authority control 11th-century crusades Warfare of the Middle Ages First Crusade Conflicts in 1096 Wars involving the Sultanate of Rum
First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ...
whose objective was to retake the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
, and Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
in particular, from Islamic rule. After in 1095 the head of the Roman Catholic Church Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II ( la, Urbanus II; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening th ...
started to urge faithful Christians to undertake an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem, the People's Crusade was conducted for roughly six months from April to October 1096. It is also known as the Peasants' Crusade, Paupers' Crusade or the Popular Crusade as it was executed by a mainly untrained peasant army prior to the main church-organized crusade. It was led primarily by Peter the Hermit with forces of Walter Sans Avoir. The peasant army of this crusade was destroyed by the forces of the Seljuk Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
under Kilij Arslan at the Battle of Civetot in northwestern Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
.
The People's Crusade was the first, largest, and best documented of the popular crusades
The popular crusades were several movements "animated by crusading enthusiasm" but unsanctioned by the Church. They contrast with the "official crusades" authorised by the Papacy. While the latter consisted of professional armies led by apostoli ...
. The start of the more official and fully church-backed crusade, also called the "Princes' Crusade", started a few months later and was better organized, better armed, and better funded.
Background

Council of Clermont
The Council of Clermont was a mixed synod of ecclesiastics and laymen of the Catholic Church, called by Pope Urban II and held from 17 to 27 November 1095 at Clermont, Auvergne, at the time part of the Duchy of Aquitaine.
Pope Urban's speech ...
in 1095, Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II ( la, Urbanus II; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening th ...
planned the departure of the crusade for 15 August 1096. Nevertheless, a number of unexpected bands of peasants and low-ranking knights organized and set off for Jerusalem on their own. The peasant population had been afflicted by drought, famine, and disease for many years before 1096, and some of them seem to have envisioned the crusade as an escape from these hardships. Spurring them on had been a number of meteorological occurrences beginning in 1095 that seemed to be a divine blessing for the movement: a meteor shower
A meteor shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate, or originate, from one point in the night sky. These meteors are caused by streams of cosmic debris called meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at extr ...
, aurorae
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of bri ...
, a lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Ear ...
, and a comet, among other events. An outbreak of ergotism
Ergotism (pron. ) is the effect of long-term ergot poisoning, traditionally due to the ingestion of the alkaloids produced by the '' Claviceps purpurea'' fungus—from the Latin "club" or clavus "nail" and for "head", i.e. the purple club-he ...
had also occurred just before the Council of Clermont. Millenarianism
Millenarianism or millenarism (from Latin , "containing a thousand") is the belief by a religious, social, or political group or movement in a coming fundamental transformation of society, after which "all things will be changed". Millenarian ...
, the belief that the end of the world was imminent, popular in the early 11th century, experienced a resurgence in popularity. The response was beyond expectations: while Urban might have expected a few thousand knights, he ended up with a migration numbering up to 100,000 Crusaders of mostly unskilled fighters, including women and children.
A charismatic monk and powerful orator named Peter the Hermit of Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; pcd, Anmien, or ) is a city and commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme department in the region of Hauts-de-France. In 2021, the population of ...
was the spiritual leader of the movement. He was known for riding a donkey and dressing in simple clothing. He had vigorously preached the crusade throughout northern France and Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
. He claimed to have been appointed to preach by Christ himself (and supposedly had a divine letter to prove it), and it is likely that some of his followers thought he, not Urban, was the true originator of the crusading idea. It is often believed that Peter's army was a band of illiterate, incompetent peasants who had no idea where they were going, and who believed that every city of any size they encountered on their way was Jerusalem itself; this may have been true for some, but the long tradition of pilgrimages to Jerusalem ensured that the location and distance of the city were well known. While the majority were unskilled in fighting, there were some well-trained minor knights leading them, such as Walter Sans-Avoir (also mistakenly known as Walter the Penniless), who was experienced in warfare. A list of known members of Peter's army can be found in Riley-Smith, et al., ''A Database of Crusaders to the Holy Land''.
Massacre of Jews in Central Europe
In the late spring and summer of 1096, crusaders destroyed most of the Jewish communities along the Rhine in a series of unprecedentedly largepogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russian ...
s in France and Germany in which thousands of Jews were massacred, driven to suicide, or forced to convert to Christianity.Nikolas Jaspert, ''The Crusades''. Routledge, 2006: 39–40.Jonathan Phillips, ''Holy Warriors: A Modern History of the Crusades''. Random House, 2010: 9–10. Twelve Jews were murdered in Speyer
Speyer (, older spelling ''Speier'', French: ''Spire,'' historical English: ''Spires''; pfl, Schbaija) is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany with approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Located on the left bank of the river Rhine, Speyer lie ...
, where the Bishop saved the rest of the Jews, but in the Worms massacre some 800 were murdered. In Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
, over 1,000 Jews were murdered, as well as more in Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the ...
, Metz
Metz ( , , lat, Divodurum Mediomatricorum, then ) is a city in northeast France located at the confluence of the Moselle and the Seille rivers. Metz is the prefecture of the Moselle department and the seat of the parliament of the Grand ...
, Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
, and elsewhere. Others were subjected to forced baptism and conversion. The preacher Folkmar and Emicho of Flonheim were the main inciters and leaders of the massacre. The major chroniclers of the 1096 killings are Solomon bar Simson and Albert of Aachen Albert of Aix(-la-Chapelle) or Albert of Aachen; la, Albericus Aquensis; ''fl.'' c. 1100) was a historian of the First Crusade and the early Kingdom of Jerusalem. He was born during the later part of the 11th century, and afterwards became canon (p ...
. Norman Cohn, ''The Pursuit of the Millennium: Revolutionary Millenarians and Mystical Anarchists of the Middle Ages''. Oxford University Press, 1970: 69–70.
Estimates of the number of Jewish men, women, and children murdered or driven to suicide by crusaders vary, ranging from 2,000 to 12,000. Norman Cohn puts the number at between 4,000 and 8,000 from May to June 1096. Gedaliah ibn Yahya Gedaliah ibn Yahya ben Joseph (Hebrew: גדליה אבן יחיא בן יוסף; – 1587) was a 16th-century Italian Talmudist and Biblical chronologist chiefly known for his Biblical Chronology "Shalshelet HaḲabbalah".
Biography
Born in I ...
estimated that some 5,000 Jews were killed from April to June 1096. Edward H. Flannery's estimate is that 10,000 were murdered over the longer January-to-July period, "probably one-fourth to one-third of the Jewish population of Germany and Northern France at that time." The clergy and nobility of Europe condemned the killing of Jews, and forbade it on subsequent crusades.
Walter and the French
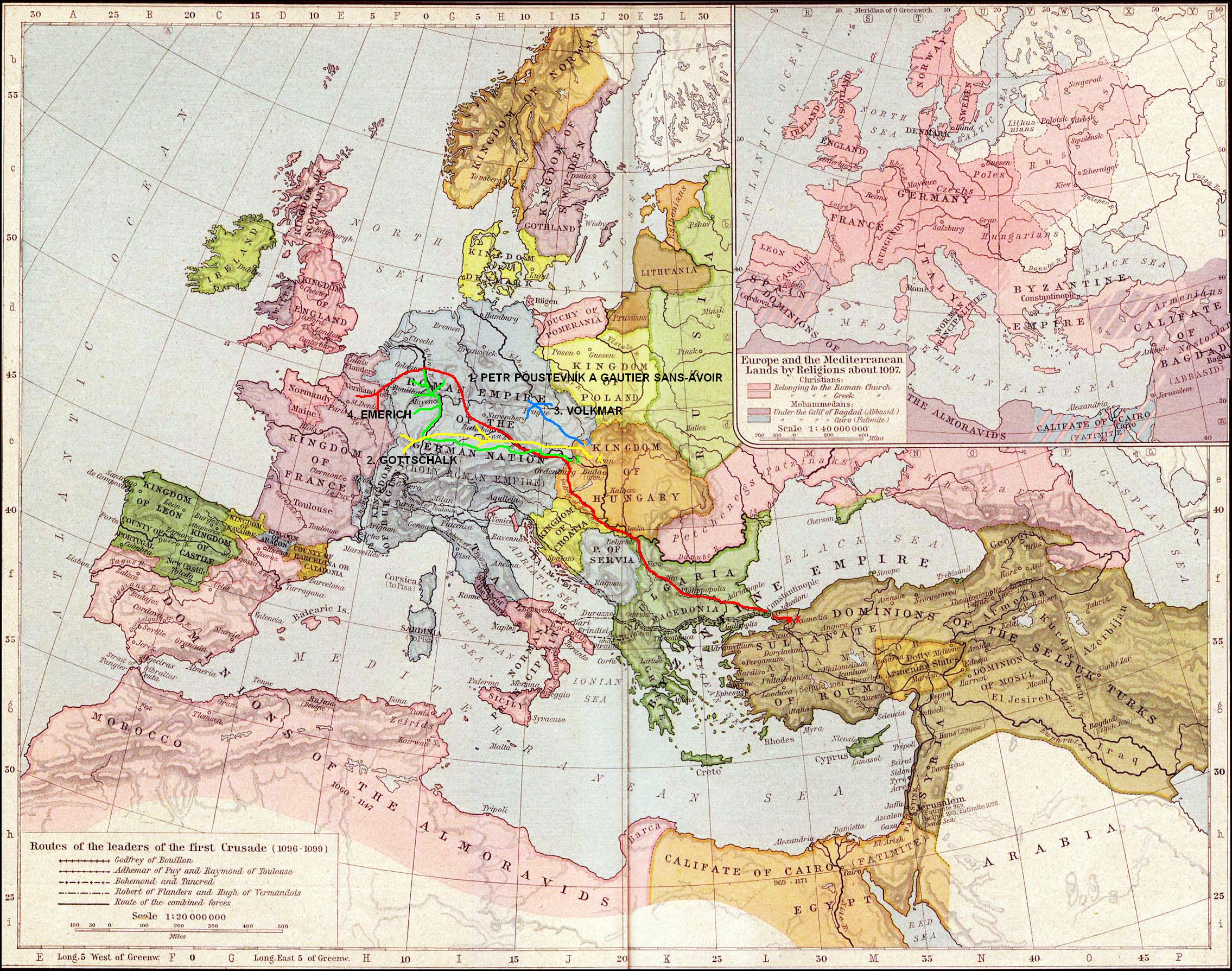
 Peter gathered his army at
Peter gathered his army at Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 millio ...
on 12 April 1096, planning to stop there and preach to the Germans and gather more crusaders. The French, however, were not willing to wait for Peter and the Germans and under the leadership of Walter Sans Avoir, a few thousand French crusaders left before Peter and reached Hungary on 8 May, passing through Hungary without incident and arriving at the river Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
at the border of the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
territory at Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 mi ...
. The Belgrade commander was taken by surprise, having no orders on what to do with them, and refused entry, forcing the crusaders to pillage the countryside for food. This resulted in skirmishes with the Belgrade garrison and, to make matters worse, sixteen of Walter's men had tried to rob a market in Zemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developme ...
across the river in Hungary and were stripped of their armor and clothing, which was hung from the castle walls. Eventually the crusaders were allowed to carry on to Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, whi ...
, where they were provided with food and waited to hear from Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
.
Cologne to Constantinople
Peter and the remaining crusaders left Cologne about 20 April. About 40,000 Crusaders departed immediately. Another group would follow soon after; this group committed theRhineland massacres
The Rhineland massacres, also known as the German Crusade of 1096 or ''Gzerot Tatnó'' ( he, גזרות תתנ"ו, "Edicts of 4856"), were a series of mass murders of Jews perpetrated by mobs of French and German Christians of the People's Cru ...
against Jewish populations and is sometimes referred to as the "German Crusade of 1096". When they reached the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
, part of the army decided to continue on by boat down the Danube, while the main body continued overland and entered Hungary at Sopron. There it continued through Hungary without incident and rejoined the Danube contingent at Zemun
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developme ...
on the Byzantine frontier.
 In Zemun, the crusaders became suspicious, seeing Walter's sixteen suits of armor hanging from the walls, and eventually a dispute over the price of a pair of shoes in the market led to a riot, which then turned into an all-out assault on the city by the crusaders, in which 4,000 Hungarians were killed. The crusaders then fled across the river Sava to Belgrade, but only after skirmishing with Belgrade troops. The residents of Belgrade fled, and the crusaders pillaged and burned the city. Then they marched for seven days, arriving at
In Zemun, the crusaders became suspicious, seeing Walter's sixteen suits of armor hanging from the walls, and eventually a dispute over the price of a pair of shoes in the market led to a riot, which then turned into an all-out assault on the city by the crusaders, in which 4,000 Hungarians were killed. The crusaders then fled across the river Sava to Belgrade, but only after skirmishing with Belgrade troops. The residents of Belgrade fled, and the crusaders pillaged and burned the city. Then they marched for seven days, arriving at Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, whi ...
on 3 July. There, the commander of Niš promised to provide escort for Peter's army to Constantinople as well as food, if he would leave right away. Peter obliged, and the next morning he set out. However, a few Germans got into a dispute with some locals along the road and set fire to a mill, which escalated out of Peter's control until Niš sent out its entire garrison against the crusaders. The crusaders were completely routed, losing about 10,000 (a quarter of their number), the remainder regrouping further on at Bela Palanka. When they reached Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
on 12 July they met their Byzantine escort, which brought them safely the rest of the way to Constantinople by 1 August.
Leadership breakdown
Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
Alexius I Komnenus, not knowing what else to do with such an unusual and unexpected army, quickly ferried all 30,000 across the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
by 6 August.J. Norwich, ''Byzantium: The Decline and Fall'', 34 It has since been debated whether he sent them away without Byzantine guides knowing full well that they could be slaughtered by the Turks, or whether they insisted on continuing into Asia Minor despite his warnings. In any case, it is known that Alexius warned Peter not to engage the Turks, whom he believed to be superior to Peter's motley army, and to wait for the main body of crusaders, which was still on the way.
Peter was rejoined by the French under Walter Sans Avoir and a number of bands of Italian crusaders who had arrived at the same time. Once in Asia Minor, they began to pillage towns and villages until they reached Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocle ...
, where an argument broke out between the Germans and Italians on one side and the French on the other. The Germans and Italians split off and elected a new leader, an Italian named Rainald, while for the French, Geoffrey Burel took command. Peter had effectively lost control of the crusade.
Even though Alexius had urged Peter to wait for the main army, Peter had lost much of his authority and the crusaders spurred each other on, moving more boldly against nearby towns until finally the French reached the edge of Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
, a Seljuk stronghold and provincial capital, where they pillaged the suburbs. The Germans, not to be outdone, marched with 6,000 crusaders on Xerigordos and captured the fortress to use as a base to raid the countryside. In response, the Turks, led by one of Kilij Arslan's generals, defeated the crusaders at the Siege of Xerigordos, many of whom were forced to drink the blood of donkeys and their own urine during the siege, since their water supply was cut. Some of the crusaders who were captured converted to Islam and were sent to Khorasan
Khorasan may refer to:
* Greater Khorasan, a historical region which lies mostly in modern-day northern/northwestern Afghanistan, northeastern Iran, southern Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan
* Khorasan Province, a pre-2004 province of Ira ...
, while others who refused to abandon their faith were killed.
Battle and outcome
Back at the main crusaders' camp, two Turkish spies had spread rumors that the Germans who had taken Xerigordos had also taken Nicaea, which caused excitement to get there as soon as possible to share in the looting. The Turks were waiting on the road to Nicaea. Peter the Hermit had gone back to Constantinople to arrange for supplies and was due back soon, and most of the leaders argued to wait for him to return (which he never did). However, Geoffrey Burel, who had popular support among the masses, argued that it would be cowardly to wait, and they should move against the Turks right away. His will prevailed and, on the morning of 21 October, the entire army of 20,000 marched out toward Nicaea, leaving women, children, the old and the sick behind at the camp. Three miles from the camp, where the road entered a narrow, wooded valley near the village of Dracon, the Turkish army was waiting. When approaching the valley, the crusaders marched noisily and were immediately subjected to a hail of arrows. Panic set in immediately and within minutes, the army was in full rout back to the camp. Most of the crusaders were slaughtered, including Walter Sans Avoir; however, women, children, and those who surrendered were spared. Three thousand, including Geoffrey Burel, were able to obtain refuge in an abandoned castle. Eventually the Byzantines under Constantine Katakalon sailed over and raised the siege; these few thousand returned to Constantinople, the only survivors of the People's Crusade.Skoulatos, Basile (1980). Les personnages byzantins de I'Alexiade: Analyse prosopographique et synthese (in French). p. 64In popular culture
James Michener's novel ''The Source'' contains an episode ("Volkmar") set during the People's Crusade.References
* Peter the Hermit and the People's CrusadeCollected Accounts
* Duncalf, Frederic. "The Peasants Crusade." ''American Historical Review'' 26 (1921): pg. 440–53. * Cohn, Norman. ''The Pursuit of the Millennium''. * See also First Crusade – selected sources and further reading {{authority control 11th-century crusades Warfare of the Middle Ages First Crusade Conflicts in 1096 Wars involving the Sultanate of Rum