Pelvic Inflammatory Disease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pelvic inflammatory disease, also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder (PID), is an
 Symptoms in PID range from none to severe. If there are symptoms,
Symptoms in PID range from none to severe. If there are symptoms,

 Upon a pelvic examination, cervical motion, uterine, or adnexal tenderness will be experienced. Mucopurulent cervicitis and or urethritis may be observed. In severe cases more testing may be required such as laparoscopy, intra-abdominal bacteria sampling and culturing, or tissue biopsy.
Laparoscopy can visualize "violin-string"
Upon a pelvic examination, cervical motion, uterine, or adnexal tenderness will be experienced. Mucopurulent cervicitis and or urethritis may be observed. In severe cases more testing may be required such as laparoscopy, intra-abdominal bacteria sampling and culturing, or tissue biopsy.
Laparoscopy can visualize "violin-string"
CDC
{{Authority control Abdominal pain Sexually transmitted diseases and infections Bacterial diseases Chlamydia infections Infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Inflammatory diseases of female pelvic organs Mycoplasma Gonorrhea
infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
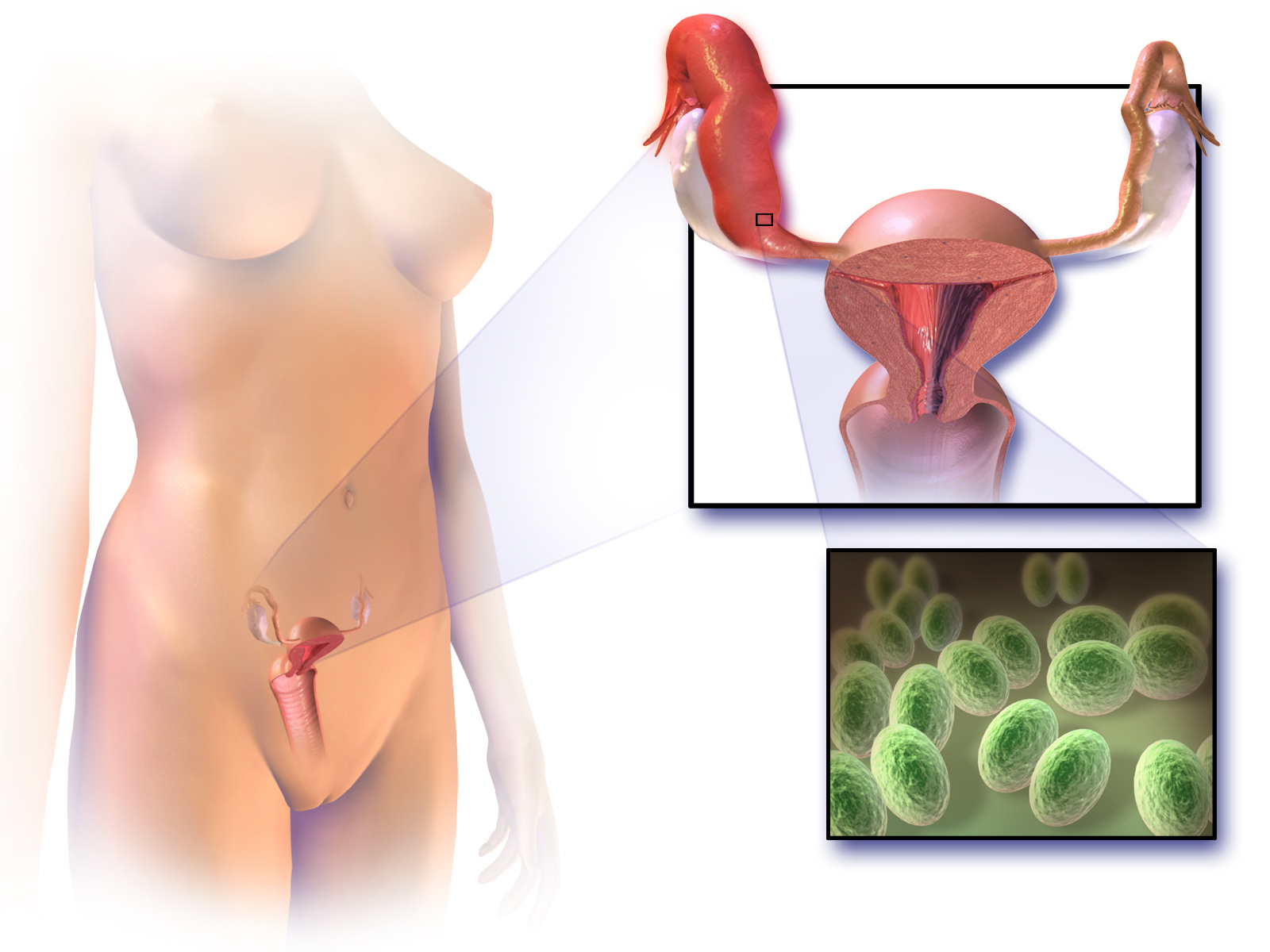
of the upper part of the female reproductive system, namely the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
, fallopian tubes
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In ot ...
, and ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no symptoms. Signs and symptoms, when present, may include lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, burning with urination, pain with sex, bleeding after sex, or irregular menstruation. Untreated PID can result in long-term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
.
The disease is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. Infections by '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' or '' Chlamydia trachomatis'' are present in 75 to 90 percent of cases. Often, multiple different bacteria are involved. Without treatment, about 10 percent of those with a chlamydial infection
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several we ...
and 40 percent of those with a gonorrhea infection
Gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Infected men may experience pain or burning with ...
will develop PID. Risk factors are generally similar to those of sexually transmitted infections and include a high number of sexual partners and drug use. Vaginal douching may also increase the risk. The diagnosis is typically based on the presenting signs and symptoms. It is recommended that the disease be considered in all women of childbearing age who have lower abdominal pain. A definitive diagnosis of PID is made by finding pus involving the fallopian tubes during surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pa ...
. Ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
may also be useful in diagnosis.
Efforts to prevent the disease include not having sex or having few sexual partners and using condoms. Screening women at risk for chlamydial infection followed by treatment decreases the risk of PID. If the diagnosis is suspected, treatment is typically advised. Treating a woman's sexual partners should also occur. In those with mild or moderate symptoms, a single injection of the antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and join ...
along with two weeks of doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus ...
and possibly metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vaginosis. It is ...
by mouth is recommended. For those who do not improve after three days or who have severe disease, intravenous antibiotics should be used.
Globally, about 106 million cases of chlamydia and 106 million cases of gonorrhea occurred in 2008. The number of cases of PID, however, is not clear. It is estimated to affect about 1.5 percent of young women yearly. In the United States, PID is estimated to affect about one million people each year. A type of intrauterine device (IUD) known as the Dalkon shield led to increased rates of PID in the 1970s. Current IUDs are not associated with this problem after the first month.
Signs and symptoms
 Symptoms in PID range from none to severe. If there are symptoms,
Symptoms in PID range from none to severe. If there are symptoms, fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a temperature above the normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature set point. There is not a single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature with sources using val ...
, cervical motion tenderness, lower abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues.
Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a m ...
, new or different discharge, painful intercourse
Dyspareunia ( ) is painful sexual intercourse due to medical or psychological causes. The term ''dyspareunia'' covers both female dyspareunia and male dyspareunia, but many discussions that use the term without further specification concern the f ...
, uterine tenderness, adnexal tenderness, or irregular menstruation may be noted.
Other complications include endometritis
Endometritis is inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). Symptoms may include fever, lower abdominal pain, and abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. It is the most common cause of infection after childbirth. It is also pa ...
, salpingitis
Salpingitis is an infection causing inflammation in the Fallopian tubes (also called ''salpinges''). It is often included in the umbrella term of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), along with endometritis, oophoritis, myometritis, parametritis, an ...
, tubo-ovarian abscess
A tubo-ovarian abscess (TOA) is one of the late complications of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and can be life-threatening if the abscess ruptures and results in sepsis. It consists of an encapsulated or confined pocket of pus with defined b ...
, pelvic peritonitis, periappendicitis, and perihepatitis
Perihepatitis is inflammation of the serous or peritoneal coating of the liver.
Perihepatitis is often caused by one of the inflammatory disorders of the female upper genital tract, known collectively as pelvic inflammatory disease.
Some patien ...
.
Complications
PID can cause scarring inside the reproductive system, which can later cause serious complications, including chronic pelvic pain, infertility, ectopic pregnancy (the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in adult females), and other complications of pregnancy. Occasionally, the infection can spread to theperitoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mes ...
causing inflammation and the formation of scar tissue on the external surface of the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
( Fitz-Hugh–Curtis syndrome).
Cause
''Chlamydia trachomatis'' and ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' are usually the main cause of PID. Data suggest that PID is often polymicrobial. Isolated anaerobes and facultative microorganisms have been obtained from the upper genital tract. ''N. gonorrhoeae'' has been isolated from fallopian tubes, facultative and anaerobic organisms were recovered from endometrial tissues. The anatomical structure of the internal organs and tissues of the female reproductive tract provides a pathway for pathogens to ascend from the vagina to the pelvic cavity thorough the infundibulum. The disturbance of the naturally occurring vaginal microbiota associated withbacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a disease of the vagina caused by excessive growth of bacteria. Common symptoms include increased vaginal discharge that often smells like fish. The discharge is usually white or gray in color. Burning with urinati ...
increases the risk of PID.
''N. gonorrhoea'' and ''C. trachomati''s are the most common organisms. The least common were infections caused exclusively by anaerobes and facultative organisms. Anaerobes and facultative bacteria were also isolated from 50 percent of the patients from whom ''Chlamydia'' and ''Neisseria'' were recovered; thus, anaerobes and facultative bacteria were present in the upper genital tract of nearly two-thirds of the PID patients. PCR and serological tests have associated extremely fastidious organism with endometritis, PID, and tubal factor infertility. Microorganisms associated with PID are listed below.
Rarely cases of PID have developed in people who have stated they have never had sex.
Bacteria
*'' Chlamydia trachomatis'' *'' Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' *'' Prevotella'' spp. *'' Streptococcus pyogenes'' *''Prevotella bivia
''Prevotella bivia'' is a species of bacteria in the genus ''Prevotella''. It is gram-negative. It is one cause of pelvic inflammatory disease.
Other ''Prevotella'' spp. are members of the oral and vaginal microbiota, and are recovered fro ...
''
*'' Prevotella disiens''
*''Bacteroides
''Bacteroides'' is a genus of Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic bacteria. ''Bacteroides'' species are non endospore-forming bacilli, and may be either motile or nonmotile, depending on the species. The DNA base composition is 40–48% GC. Unus ...
'' spp.
*'' Peptostreptococcus asaccharolyticus''
*'' Peptostreptococcus anaerobius''
*'' Gardnerella vaginalis''
*''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
''
*Group B streptococcus
''Streptococcus agalactiae'' (also known as group B streptococcus or GBS) is a gram-positive coccus (round bacterium) with a tendency to form chains (as reflected by the genus name ''Streptococcus''). It is a beta-hemolytic, catalase-negative, a ...
* α-hemolytic streptococcus
*Coagulase-negative staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillales. Under the microscope, they appear spherical (cocci), and form in grape-like clusters. ''Staphylococcus'' species are facultati ...
*'' Atopobium vaginae''
*'' Acinetobacter'' spp.
*'' Dialister'' spp.
*'' Fusobacterium gonidiaformans''
*''Gemella
''Gemella'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria that thrive best at high partial pressure of CO2.
Description
A Gemella species was first described as Neisseria hemolysans in 1938. It was reclassified as a new genus in 1960 when strains wer ...
'' spp.
*'' Leptotrichia'' spp.
*'' Mogibacterium'' spp.
*'' Porphyromonas'' spp.
*'' Sphingomonas'' spp.
*'' Veillonella'' spp.
*'' Cutibacterium acnes''
*'' Mycoplasma genitalium''
*'' Mycoplasma hominis''
*'' Ureaplasma'' spp.
Diagnosis

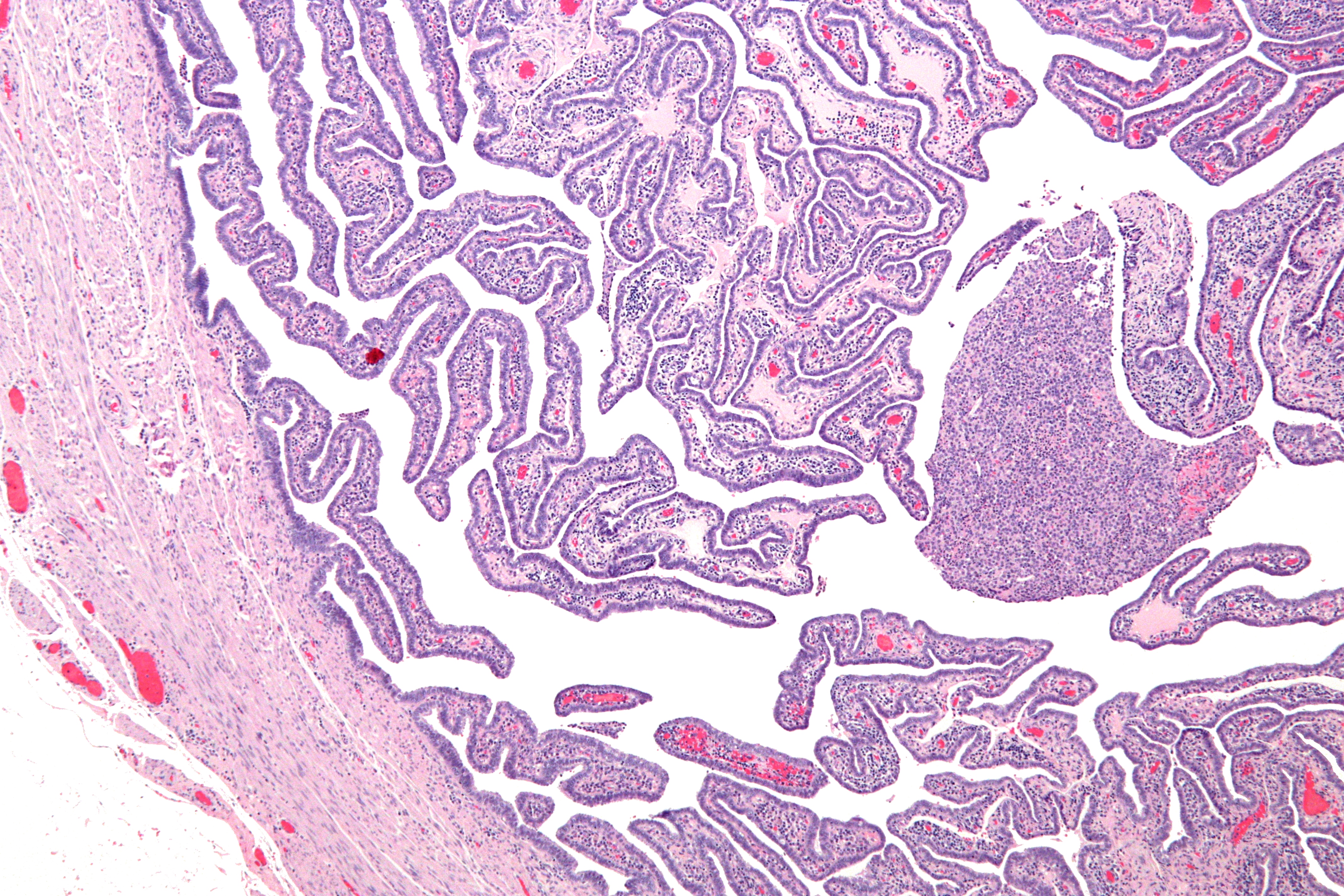
 Upon a pelvic examination, cervical motion, uterine, or adnexal tenderness will be experienced. Mucopurulent cervicitis and or urethritis may be observed. In severe cases more testing may be required such as laparoscopy, intra-abdominal bacteria sampling and culturing, or tissue biopsy.
Laparoscopy can visualize "violin-string"
Upon a pelvic examination, cervical motion, uterine, or adnexal tenderness will be experienced. Mucopurulent cervicitis and or urethritis may be observed. In severe cases more testing may be required such as laparoscopy, intra-abdominal bacteria sampling and culturing, or tissue biopsy.
Laparoscopy can visualize "violin-string" adhesion
Adhesion is the tendency of dissimilar particles or surfaces to cling to one another ( cohesion refers to the tendency of similar or identical particles/surfaces to cling to one another).
The forces that cause adhesion and cohesion can ...
s, characteristic of Fitz-Hugh–Curtis perihepatitis and other abscesses that may be present.
Other imaging methods, such as ultrasonography, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic imaging (MRI), can aid in diagnosis. Blood tests can also help identify the presence of infection: the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), the C-reactive protein (CRP) level, and chlamydial and gonococcal DNA probes.
Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), direct fluorescein tests (DFA), and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) are highly sensitive tests that can identify specific pathogens present. Serology testing for antibodies is not as useful since the presence of the microorganisms in healthy people can confound interpreting the antibody titer levels, although antibody levels can indicate whether an infection is recent or long-term.
Definitive criteria include histopathologic
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία ''-logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. S ...
evidence of endometritis, thickened filled Fallopian tubes
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (singular salpinx), are paired tubes in the human female that stretch from the uterus to the ovaries. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In ot ...
, or laparoscopic findings. Gram stain/smear becomes definitive in the identification of rare, atypical and possibly more serious organisms. Two thirds of patients with laparoscopic evidence of previous PID were not aware they had PID, but even asymptomatic PID can cause serious harm.
Laparoscopic identification is helpful in diagnosing tubal disease; a 65 percent to 90 percent positive predictive value
The positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV respectively) are the proportions of positive and negative results in statistics and diagnostic tests that are true positive and true negative results, respectively. The PPV and NPV des ...
exists in patients with presumed PID.
Upon gynecologic ultrasound
Gynecologic ultrasonography or gynecologic sonography refers to the application of medical ultrasonography to the female pelvic organs (specifically the uterus, the ovaries, and the fallopian tubes) as well as the bladder, the adnexa, and the re ...
, a potential finding is ''tubo-ovarian complex'', which is edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels tight, the area ma ...
tous and dilated pelvic structures as evidenced by vague margins, but without abscess formation.
Differential diagnosis
A number of other causes may produce similar symptoms including appendicitis, ectopic pregnancy, hemorrhagic or ruptured ovarian cysts, ovarian torsion, and endometriosis and gastroenteritis, peritonitis, and bacterial vaginosis among others. Pelvic inflammatory disease is more likely to reoccur when there is a prior history of the infection, recent sexual contact, recent onset of menses, or anIUD
An intrauterine device (IUD), also known as intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD or ICD) or coil, is a small, often T-shaped birth control device that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. IUDs are one form of long-acting reversi ...
(intrauterine device) in place or if the partner has a sexually transmitted infection.
Acute pelvic inflammatory disease is highly unlikely when recent intercourse has not taken place or an IUD is not being used. A sensitive serum pregnancy test is typically obtained to rule out ectopic pregnancy. Culdocentesis
Culdocentesis is a medical procedure involving the extraction of fluid from the pouch of Douglas (a rectouterine pouch posterior to the vagina) through a needle. It can be one diagnostic technique used in identifying pelvic inflammatory disease (i ...
will differentiate hemoperitoneum (ruptured ectopic pregnancy or hemorrhagic cyst) from pelvic sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
(salpingitis, ruptured pelvic abscess, or ruptured appendix).
Pelvic and vaginal ultrasounds are helpful in the diagnosis of PID. In the early stages of infection, the ultrasound may appear normal. As the disease progresses, nonspecific findings can include free pelvic fluid, endometrial thickening, uterine cavity distension by fluid or gas. In some instances the borders of the uterus and ovaries appear indistinct. Enlarged ovaries accompanied by increased numbers of small cysts correlates with PID.
Laparoscopy is infrequently used to diagnose pelvic inflammatory disease since it is not readily available. Moreover, it might not detect subtle inflammation of the fallopian tubes, and it fails to detect endometritis. Nevertheless, laparoscopy is conducted if the diagnosis is not certain or if the person has not responded to antibiotic therapy after 48 hours.
No single test has adequate sensitivity and specificity to diagnose pelvic inflammatory disease. A large multisite U.S. study found that cervical motion tenderness as a minimum clinical criterion increases the sensitivity of the CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georg ...
diagnostic criteria from 83 percent to 95 percent. However, even the modified 2002 CDC criteria do not identify women with subclinical disease.
Prevention
Regular testing for sexually transmitted infections is encouraged for prevention. The risk of contracting pelvic inflammatory disease can be reduced by the following: * Using barrier methods such as condoms; see human sexual behaviour for other listings. * Seeking medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of PID. * Using hormonal combined contraceptive pills also helps in reducing the chances of PID by thickening the cervical mucosal plug & hence preventing the ascent of causative organisms from the lower genital tract. * Seeking medical attention after learning that a current or former sex partner has, or might have had a sexually transmitted infection. * Getting a STI history from your current partner and strongly encouraging they be tested and treated before intercourse. * Diligence in avoiding vaginal activity, particularly intercourse, after the end of a pregnancy (delivery, miscarriage, orabortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pre ...
) or certain gynecological procedures, to ensure that the cervix closes.
* Reducing the number of sexual partners.
* Sexual monogamy
Monogamy ( ) is a form of dyadic relationship in which an individual has only one partner during their lifetime. Alternately, only one partner at any one time ( serial monogamy) — as compared to the various forms of non-monogamy (e.g., pol ...
.
* Abstinence
Treatment
Treatment is often started without confirmation of infection because of the serious complications that may result from delayed treatment. Treatment depends on the infectious agent and generally involves the use ofantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
therapy although there is no clear evidence of which antibiotic regimen is more effective and safe in the management of PID. If there is no improvement within two to three days, the patient is typically advised to seek further medical attention. Hospitalization sometimes becomes necessary if there are other complications. Treating sexual partners for possible STIs can help in treatment and prevention.
For women with PID of mild to moderate severity, parenteral and oral therapies appear to be effective. It does not matter to their short- or long-term outcome whether antibiotics are administered to them as inpatients or outpatients. Typical regimens include cefoxitin or cefotetan
Cefotetan is an injectable antibiotic of the cephamycin type for prophylaxis and treatment of bacterial infections. It is often grouped together with second-generation cephalosporins and has a similar antibacterial spectrum, but with additional an ...
plus doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus ...
, and clindamycin plus gentamicin. An alternative parenteral regimen is ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, salmonellosis, and endocarditis. It may also be used to prevent group B str ...
/ sulbactam plus doxycycline. Erythromycin-based medications can also be used. A single study suggests superiority of azithromycin over doxycycline. Another alternative is to use a parenteral regimen with ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and join ...
or cefoxitin plus doxycycline. Clinical experience guides decisions regarding transition from parenteral to oral therapy, which usually can be initiated within 24–48 hours of clinical improvement.
Prognosis
Even when the PID infection is cured, effects of the infection may be permanent. This makes early identification essential. Treatment resulting in cure is very important in the prevention of damage to thereproductive system
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are ...
. Formation of scar tissue due to one or more episodes of PID can lead to tubal blockage, increasing the risk of the inability to get pregnant and long-term pelvic/abdominal pain. Certain occurrences such as a post pelvic operation, the period of time immediately after childbirth ( postpartum), miscarriage or abortion
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pre ...
increase the risk of acquiring another infection leading to PID.
Epidemiology
Globally about 106 million cases of chlamydia and 106 million cases of gonorrhea occurred in 2008. The number of cases of PID; however, is not clear. It is estimated to affect about 1.5 percent of young women yearly. In the United States PID is estimated to affect about one million people yearly. Rates are highest with teenagers and first time mothers. PID causes over 100,000 women to become infertile in the US each year.References
External links
CDC
{{Authority control Abdominal pain Sexually transmitted diseases and infections Bacterial diseases Chlamydia infections Infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Inflammatory diseases of female pelvic organs Mycoplasma Gonorrhea