Paul Samuelson on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Paul Anthony Samuelson (May 15, 1915 – December 13, 2009) was an American
''
 Samuelson was born in
Samuelson was born in
''
"Statistical Entropy in General Equilibrium Theory"
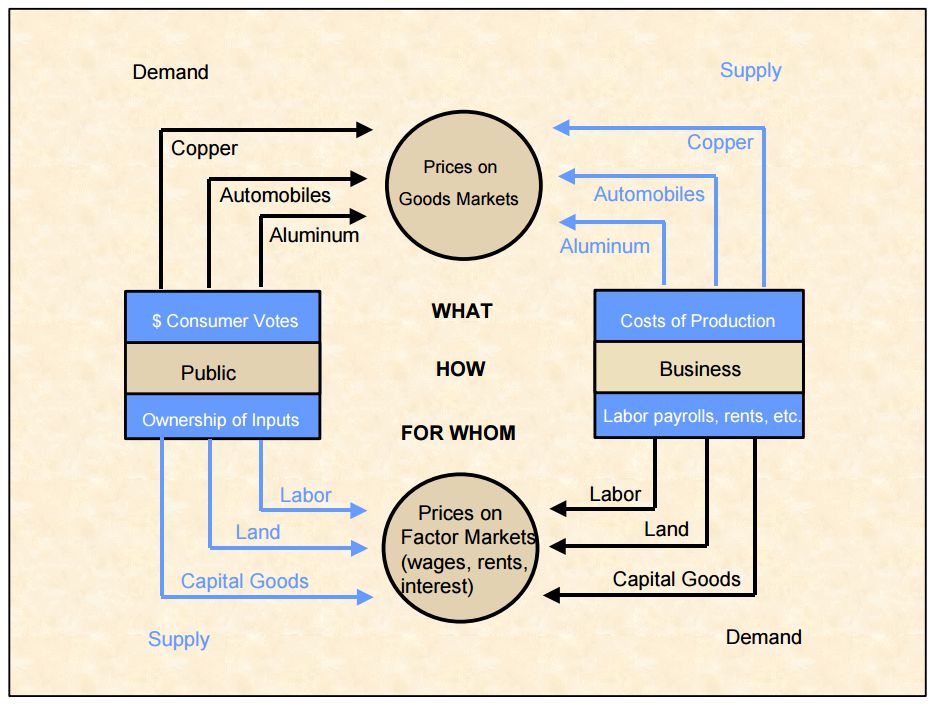
(p. 3). Department of Economics, Florida International University. The book proposes to: * examine underlying analogies between central features in theoretical and applied economics and * study how '' operationally meaningful theorems'' can be derived with a small number of ''analogous methods'' (p. 3), in order to derive "a general theory of economic theories" (Samuelson, 1983, p. xxvi). The book showed how these goals could be parsimoniously and fruitfully achieved, using the language of the mathematics applied to diverse subfields of economics. The book proposes two general hypotheses as sufficient for its purposes: * ''maximizing behavior'' of ''agents'' (including ''consumers'' as to utility and ''business firms'' as to profit) and * economic ''systems'' (including a market and an economy) in ''stable equilibrium''. In the first tenet, his views presented the idea that all actors, whether firms or consumers, are striving to maximize something. They could be attempting to maximize profits, utility, or wealth, but it did not matter because their efforts to improve their well-being would provide a basic model for all actors in an economic system. His second tenet was focused on providing insight on the workings of equilibrium in an economy. Generally in a market, supply would equal demand. However, he urged that this might not be the case and that the important thing to look at was a system's natural resting point. ''Foundations'' presents the question of how an equilibrium would react when it is moved from its optimal point. Samuelson was also influential in providing explanations on how the changes in certain factors can affect an economic system. For example, he could explain the economic effect of changes in taxes or new technologies. In the course of analysis, '' comparative statics'', (the analysis of changes in equilibrium of the system that result from a parameter change of the system) is formalized and clearly stated. The chapter on welfare economics "attempt(s) to give a brief but fairly complete survey of the whole field of welfare economics" (Samuelson, 1947, p. 252). It also exposits on and develops what became commonly called the
Elements of Economics
'.
56–66
* * Samuelson, Paul A. (1958), ''Linear Programming and Economic Analysis'' with
links.
* * * ''The Collected Scientific Papers of Paul A. Samuelson'', MIT Press. Preview links for vol. 1–3 below. Contents links for vol. 4–7. . :Samuelson, Paul A. (1966), Vol
1
→ via
2
→ via
3
→ via
4
→ via
5
→ via
Description
→ via :Samuelson, Paul A. (2011), Vol
6
1986–2009
Description
→ via
7
1986–2009.
Paul A. Samuelson Papers, 1933–2010
Rubenstein Library,
pp. 5-12.
* Samuelson, Paul A. (2007), ''Inside the Economist's Mind: Conversations with Eminent Economists'' with William A. Barnett, Blackwell Publishing, * Samuelson, Paul A. (2002), ''Paul Samuelson and the Foundations of Modern Economics'', Transaction Publishers, *Samuelson, Paul A. (2004), Macroeconomics *Samuelson, Paul A. (2004), Microeconomics
Description
arrow-scrollable preview
* * . * . * . * .
by Professor Assar Lindbeck, Stockholm School of Economics, Award Ceremony, The Bank of Sweden Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel, 1970
''A History of Economic Thought'' biography
2004 *
Yale Honorands biography, May 2005
''MIT News'', December 13, 2009 * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Samuelson, Paul 1915 births 2009 deaths Nobel laureates in Economics American Nobel laureates 20th-century American writers 21st-century American non-fiction writers 20th-century American economists 21st-century American economists American people of Polish-Jewish descent Fellows of the Econometric Society Harvard University alumni Jewish American writers Jewish American social scientists Kennedy administration personnel MIT School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences faculty Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences National Medal of Science laureates Writers from Gary, Indiana Trade economists University of Chicago alumni Neo-Keynesian economists Presidents of the Econometric Society People from Belmont, Massachusetts Presidents of the American Economic Association Economists from Massachusetts Economists from Indiana Corresponding Fellows of the British Academy Hyde Park Academy High School alumni Burials at Mount Auburn Cemetery Members of the American Philosophical Society
economist
An economist is a professional and practitioner in the social sciences, social science discipline of economics.
The individual may also study, develop, and apply theories and concepts from economics and write about economic policy. Within this ...
who was the first American to win the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences
The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, officially the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel ( sv, Sveriges riksbanks pris i ekonomisk vetenskap till Alfred Nobels minne), is an economics award administered ...
. When awarding the prize in 1970, the Swedish Royal Academies stated that he "has done more than any other contemporary economist to raise the level of scientific analysis in economic theory". "In a career that spanned seven decades, he transformed his field, influenced millions of students and turned MIT into an economics powerhouse" Economic historian Randall E. Parker has called him the "Father of Modern Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics anal ...
", and ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' considers him to be the "foremost academic economist of the 20th century".
Samuelson was likely the most influential economist of the latter half of the 20th century."Paul Samuelson: The last of the great general economists died on December 13th, aged 94"''
The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Eco ...
'', December 17, 2009 In 1996, when he was awarded the National Medal of Science, considered to be America's top science-honor, President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and again ...
commended Samuelson for his "fundamental contributions to economic science" for over 60 years. Samuelson considered mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
to be the "natural language" for economists and contributed significantly to the mathematical foundations of economics with his book '' Foundations of Economic Analysis''. He was author of the best-selling economics textbook of all time: '' Economics: An Introductory Analysis'', first published in 1948. It was the second American textbook that attempted to explain the principles of Keynesian economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output ...
. It is now in its 19th edition, having sold nearly 4 million copies in 40 languages. James Poterba, former head of MIT's Department of Economics, noted that by his book, Samuelson "leaves an immense legacy, as a researcher and a teacher, as one of the giants on whose shoulders every contemporary economist stands".
He entered the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the b ...
at age 16, during the depths of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
, and received his PhD PHD or PhD may refer to:
* Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), an academic qualification
Entertainment
* '' PhD: Phantasy Degree'', a Korean comic series
* '' Piled Higher and Deeper'', a web comic
* Ph.D. (band), a 1980s British group
** Ph.D. (Ph.D. al ...
in economics from Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
. After graduating, he became an assistant professor of economics at Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of th ...
(MIT) when he was 25 years of age and a full professor at age 32. In 1966, he was named Institute Professor, MIT's highest faculty honor. He spent his career at MIT, where he was instrumental in turning its Department of Economics into a world-renowned institution by attracting other noted economists to join the faculty, including later winners of the Nobel Prize Robert Solow
Robert Merton Solow, GCIH (; born August 23, 1924) is an American economist whose work on the theory of economic growth culminated in the exogenous growth model named after him. He is currently Emeritus Institute Professor of Economics at th ...
, Franco Modigliani
Franco Modigliani (18 June 1918 – 25 September 2003) was an Italian-American economist and the recipient of the 1985 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics. He was a professor at University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, Carnegie Mellon Un ...
, Robert C. Merton, Joseph Stiglitz
Joseph Eugene Stiglitz (; born February 9, 1943) is an American New Keynesian economist, a public policy analyst, and a full professor at Columbia University. He is a recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (2001) and the J ...
, and Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American economist, who is Distinguished Professor of Economics at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York, and a columnist for ''The New York Times''. In 2008, Krugman was t ...
.
He served as an advisor to Presidents John F. Kennedy and Lyndon B. Johnson, and was a consultant to the United States Treasury
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States, where it serves as an executive department. The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and ...
, the Bureau of the Budget and the President's Council of Economic Advisers
The Council of Economic Advisers (CEA) is a United States agency within the Executive Office of the President established in 1946, which advises the President of the United States on economic policy. The CEA provides much of the empirical rese ...
. Samuelson wrote a weekly column for ''Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly online news magazine co-owned 50 percent each by Dev Pragad, its president and CEO, and Johnathan Davis (businessman), Johnathan Davis, who has no operational role at ''Newsweek''. Founded as a weekly print m ...
'' magazine along with Chicago School economist Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and the ...
, where they represented opposing sides: Samuelson, as a self described "Cafeteria Keynesian", claimed taking the Keynesian perspective but only accepting what he felt was good in it. By contrast, Friedman represented the monetarist
Monetarism is a school of thought in monetary economics that emphasizes the role of governments in controlling the amount of money in circulation. Monetarist theory asserts that variations in the money supply have major influences on natio ...
perspective. Together with Henry Wallich
Henry Christopher Wallich (; June 10, 1914 – September 15, 1988) was a German American economist who served as a member of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors from 1974 to 1986. He previously served as a member of the Council of the Economi ...
, their 1967 columns earned the magazine a Gerald Loeb Special Award The Gerald Loeb Award is given annually for multiple categories of business reporting. Special awards were occasionally given for distinguished business journalism that doesn't necessarily fit into other categories.
Gerald Loeb Special Award winner ...
in 1968.
Samuelson worked in many theoretical fields, including: consumer theory; welfare economics; capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
; finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of f ...
, particularly the efficient-market hypothesis; public finance, particularly optimal allocation; international economics, particularly the Balassa–Samuelson effect
The Balassa–Samuelson effect, also known as Harrod–Balassa–Samuelson effect (Kravis and Lipsey 1983), the Ricardo–Viner–Harrod–Balassa–Samuelson–Penn–Bhagwati effect (Samuelson 1994, p. 201), or productivity biased purchasi ...
and the Heckscher–Ohlin model
The Heckscher–Ohlin model (, H–O model) is a general equilibrium mathematical model of international trade, developed by Eli Heckscher and Bertil Ohlin at the Stockholm School of Economics. It builds on David Ricardo's theory of comparative a ...
; macroeconomics
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
For example, using interest rates, taxes, and ...
, particularly the overlapping generations model
The overlapping generations (OLG) model is one of the dominating frameworks of analysis in the study of macroeconomic dynamics and economic growth. In contrast, to the Ramsey–Cass–Koopmans neoclassical growth model in which individuals are ...
; and market economics.
Biography
 Samuelson was born in
Samuelson was born in Gary, Indiana
Gary is a city in Lake County, Indiana, United States. The city has been historically dominated by major industrial activity and is home to U.S. Steel's Gary Works, the largest steel mill complex in North America. Gary is located along th ...
, on May 15, 1915, to Frank Samuelson, a pharmacist
A pharmacist, also known as a chemist (Commonwealth English) or a druggist (North American and, archaically, Commonwealth English), is a healthcare professional who prepares, controls and distributes medicines and provides advice and instructi ...
, and Ella ''née
A birth name is the name of a person given upon birth. The term may be applied to the surname, the given name, or the entire name. Where births are required to be officially registered, the entire name entered onto a birth certificate or birth re ...
'' Lipton. His family, he later said, was "made up of upwardly mobile Jewish immigrants from Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
who had prospered considerably in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
, because Gary was a brand new steel-town when my family went there". In 1923, Samuelson moved to Chicago where he graduated from Hyde Park High School (now Hyde Park Career Academy). He then studied at the University of Chicago
The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the b ...
and received his Bachelor of Arts
Bachelor of arts (BA or AB; from the Latin ', ', or ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for an undergraduate program in the arts, or, in some cases, other disciplines. A Bachelor of Arts degree course is generally completed in three or four yea ...
degree there in 1935. He said he was born as an economist, at 8.00am on January 2, 1932, in the University of Chicago classroom. The lecture mentioned as the cause was on the British economist Thomas Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus (; 13/14 February 1766 – 29 December 1834) was an English cleric, scholar and influential economist in the fields of political economy and demography.
In his 1798 book ''An Essay on the Principle of Population'', Mal ...
, who most famously studied population growth and its effects. Samuelson felt there was a dissonance between neoclassical economics
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good ...
and the way the system seemed to behave; he said Henry Simons and Frank Knight were a big influence on him. He next completed his Master of Arts
A Master of Arts ( la, Magister Artium or ''Artium Magister''; abbreviated MA, M.A., AM, or A.M.) is the holder of a master's degree awarded by universities in many countries. The degree is usually contrasted with that of Master of Science. Tho ...
degree in 1936, and his Doctor of Philosophy
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, Ph.D., or DPhil; Latin: or ') is the most common degree at the highest academic level awarded following a course of study. PhDs are awarded for programs across the whole breadth of academic fields. Because it is ...
in 1941 at Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of highe ...
. He won the David A. Wells prize in 1941 for writing the best doctoral dissertation at Harvard University in economics, for a thesis titled "Foundations of Analytical Economics", which later turned into '' Foundations of Economic Analysis''. As a graduate student at Harvard, Samuelson studied economics under Joseph Schumpeter, Wassily Leontief, Gottfried Haberler, and the "American Keynes" Alvin Hansen
Alvin Harvey Hansen (August 23, 1887 – June 6, 1975) was an American economist who taught at the University of Minnesota and was later a chair professor of economics at Harvard University. Often referred to as "the American Keynes", he was a w ...
. Samuelson moved to MIT as an assistant professor in 1940 and remained there until his death.
Samuelson's family included many well-known economists, including brother Robert Summers, sister-in-law Anita Summers, brother-in-law Kenneth Arrow
Kenneth Joseph Arrow (23 August 1921 – 21 February 2017) was an American economist, mathematician, writer, and political theorist. He was the joint winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with John Hicks in 1972.
In economi ...
and nephew Larry Summers.
During his seven decades as an economist, Samuelson's professional positions included:
* Assistant professor of economics at MIT, 1940; associate professor, 1944.
* Member of the Radiation Laboratory 1944–45.
* Professor of international economic relations (part-time) at the Fletcher School of Law and Diplomacy in 1945.
* Guggenheim Fellowship from 1948 to 1949
* Professor of economics at MIT beginning in 1947 and Institute Professor beginning in 1962.
* Vernon F. Taylor Visiting Distinguished Professor at Trinity University (Texas) in spring 1989.
Death
Samuelson died after a brief illness on December 13, 2009, at the age of 94. His death was announced by theMassachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of th ...
. James M. Poterba, an economics professor at MIT and the president of the National Bureau of Economic Research, commented that Samuelson "leaves an immense legacy, as a researcher and a teacher, as one of the giants on whose shoulders every contemporary economist stands". Susan Hockfield, the president of MIT, said that Samuelson "transformed everything he touched: the theoretical foundations of his field, the way economics was taught around the world, the ethos and stature of his department, the investment practices of MIT, and the lives of his colleagues and students"."Economics revolutionary Paul Samuelson dies aged 94"''
The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a national British daily broadsheet newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed across the United Kingdom and internationally.
It was f ...
'', December 14, 2009
Fields of interest
As professor of economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Samuelson worked in many fields, including: * Consumer theory, where he pioneered therevealed preference
Revealed preference theory, pioneered by economist Paul Anthony Samuelson in 1938, is a method of analyzing choices made by individuals, mostly used for comparing the influence of policies on consumer behavior. Revealed preference models assume th ...
approach, which is a method by which one can discern a consumer's utility function
As a topic of economics, utility is used to model worth or value. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness as part of the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosoph ...
, by observing their behavior. Rather than postulate a utility function
As a topic of economics, utility is used to model worth or value. Its usage has evolved significantly over time. The term was introduced initially as a measure of pleasure or happiness as part of the theory of utilitarianism by moral philosoph ...
or a preference ordering, Samuelson imposed conditions directly on the choices made by individuals – their preferences as revealed by their choices.
* Welfare economics, in which he popularised the Lindahl–Bowen–Samuelson conditions (criteria for deciding whether an action will improve welfare) and demonstrated in 1950 the insufficiency of a national-income index to reveal which of two social options was uniformly outside the other's (feasible) possibility function (''Collected Scientific Papers'', v. 2, ch. 77; Fischer, 1987, p. 236).
* Capital theory, where he is known for 1958 consumption loans model and a variety of turnpike theorems and involved in Cambridge capital controversy
The Cambridge capital controversy, sometimes called "the capital controversy"Brems (1975) pp. 369-384 or "the two Cambridges debate", was a dispute between proponents of two differing theoretical and mathematical positions in economics that starte ...
.
* Finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of f ...
theory, in which he is known for the efficient-market hypothesis.
* Public finance theory, in which he is particularly known for his work on determining the optimal allocation of resources in the presence of both public goods and private goods.
* International economics, where he influenced the development of two important international trade models: the Balassa–Samuelson effect
The Balassa–Samuelson effect, also known as Harrod–Balassa–Samuelson effect (Kravis and Lipsey 1983), the Ricardo–Viner–Harrod–Balassa–Samuelson–Penn–Bhagwati effect (Samuelson 1994, p. 201), or productivity biased purchasi ...
, and the Heckscher–Ohlin model
The Heckscher–Ohlin model (, H–O model) is a general equilibrium mathematical model of international trade, developed by Eli Heckscher and Bertil Ohlin at the Stockholm School of Economics. It builds on David Ricardo's theory of comparative a ...
(with the Stolper–Samuelson theorem
The Stolper–Samuelson theorem is a basic theorem in Heckscher–Ohlin trade theory. It describes the relationship between relative prices of output and relative factor rewards—specifically, real wages and real returns to capital.
The the ...
).
* Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
For example, using interest rates, taxes, and ...
, where he popularized the overlapping generations model
The overlapping generations (OLG) model is one of the dominating frameworks of analysis in the study of macroeconomic dynamics and economic growth. In contrast, to the Ramsey–Cass–Koopmans neoclassical growth model in which individuals are ...
as a way to analyze economic agents' behavior across multiple periods of time (''Collected Scientific Papers'', v. 1, ch. 21) and contributed to formation of the neoclassical synthesis
The neoclassical synthesis (NCS), neoclassical–Keynesian synthesis, or just neo-Keynesianism was a neoclassical economics academic movement and paradigm in economics that worked towards reconciling the macroeconomic thought of John Maynard Key ...
.
* Market economics: Samuelson believed unregulated markets have drawbacks, he stated, "free markets do not stabilise themselves. Zero regulating is vastly suboptimal to rational regulating. Libertarianism is its own worst enemy!" Samuelson strongly criticised Friedman and Friedrich Hayek
Friedrich August von Hayek ( , ; 8 May 189923 March 1992), often referred to by his initials F. A. Hayek, was an Austrian–British economist, legal theorist and philosopher who is best known for his defense of classical liberalism. Hayek ...
, arguing their opposition to state intervention "tells us something about them rather than something about Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
or Franklin Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
. It is paranoid to warn against inevitable slippery slopes ... once individual commercial freedoms are in any way infringed upon."
Impact
Samuelson is considered one of the founders of neo-Keynesian economics and a seminal figure in the development ofneoclassical economics
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good ...
. In awarding him the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences
The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, officially the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel ( sv, Sveriges riksbanks pris i ekonomisk vetenskap till Alfred Nobels minne), is an economics award administered ...
the committee stated:
He was also essential in creating the neoclassical synthesis
The neoclassical synthesis (NCS), neoclassical–Keynesian synthesis, or just neo-Keynesianism was a neoclassical economics academic movement and paradigm in economics that worked towards reconciling the macroeconomic thought of John Maynard Key ...
, which ostensibly incorporated Keynesian and neoclassical principles and still dominates current mainstream economics
Mainstream economics is the body of knowledge, theories, and models of economics, as taught by universities worldwide, that are generally accepted by economists as a basis for discussion. Also known as orthodox economics, it can be contrasted to ...
. In 2003, Samuelson was one of the ten Nobel Prize–winning economists signing the Economists' statement opposing the Bush tax cuts.
Aphorisms and quotations
Stanislaw Ulam
Stanisław Marcin Ulam (; 13 April 1909 – 13 May 1984) was a Polish-American scientist in the fields of mathematics and nuclear physics. He participated in the Manhattan Project, originated the Teller–Ulam design of thermonuclear weapon ...
once challenged Samuelson to name one theory in all of the social sciences that is both true and nontrivial. Several years later, Samuelson responded with David Ricardo
David Ricardo (18 April 1772 – 11 September 1823) was a British political economist. He was one of the most influential of the classical economists along with Thomas Malthus, Adam Smith and James Mill. Ricardo was also a politician, and a ...
's theory of comparative advantage
In an economic model, agents have a comparative advantage over others in producing a particular good if they can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. C ...
: "That it is logically true need not be argued before a mathematician; that is not trivial is attested by the thousands of important and intelligent men who have never been able to grasp the doctrine
Doctrine (from la, doctrina, meaning "teaching, instruction") is a codification of beliefs or a body of teachings or instructions, taught principles or positions, as the essence of teachings in a given branch of knowledge or in a belief syste ...
for themselves or to believe it after it was explained to them."
For many years, Samuelson wrote a column for ''Newsweek
''Newsweek'' is an American weekly online news magazine co-owned 50 percent each by Dev Pragad, its president and CEO, and Johnathan Davis (businessman), Johnathan Davis, who has no operational role at ''Newsweek''. Founded as a weekly print m ...
''. One article included Samuelson's most quoted remark and a favorite economics joke:
To prove that Wall Street is an early omen of movements still to come in GNP, commentators quote economic studies alleging that market downturns predicted four out of the last five recessions. That is an understatement. Wall Street indexes predicted nine out of the last five recessions! And its mistakes were beauties.In the early editions of his famous, bestselling economics textbook Paul Samuelson joked that GDP falls when a man "marries his maid".
Publications

''Foundations of Economic Analysis''
Paul Samuelson's book '' Foundations of Economic Analysis'' (1946) is considered his magnum opus. It is derived from his doctoral dissertation, and was inspired by the classical thermodynamic methods.Liossatos, Panagis, S. (2004)"Statistical Entropy in General Equilibrium Theory"
(p. 3). Department of Economics, Florida International University. The book proposes to: * examine underlying analogies between central features in theoretical and applied economics and * study how '' operationally meaningful theorems'' can be derived with a small number of ''analogous methods'' (p. 3), in order to derive "a general theory of economic theories" (Samuelson, 1983, p. xxvi). The book showed how these goals could be parsimoniously and fruitfully achieved, using the language of the mathematics applied to diverse subfields of economics. The book proposes two general hypotheses as sufficient for its purposes: * ''maximizing behavior'' of ''agents'' (including ''consumers'' as to utility and ''business firms'' as to profit) and * economic ''systems'' (including a market and an economy) in ''stable equilibrium''. In the first tenet, his views presented the idea that all actors, whether firms or consumers, are striving to maximize something. They could be attempting to maximize profits, utility, or wealth, but it did not matter because their efforts to improve their well-being would provide a basic model for all actors in an economic system. His second tenet was focused on providing insight on the workings of equilibrium in an economy. Generally in a market, supply would equal demand. However, he urged that this might not be the case and that the important thing to look at was a system's natural resting point. ''Foundations'' presents the question of how an equilibrium would react when it is moved from its optimal point. Samuelson was also influential in providing explanations on how the changes in certain factors can affect an economic system. For example, he could explain the economic effect of changes in taxes or new technologies. In the course of analysis, '' comparative statics'', (the analysis of changes in equilibrium of the system that result from a parameter change of the system) is formalized and clearly stated. The chapter on welfare economics "attempt(s) to give a brief but fairly complete survey of the whole field of welfare economics" (Samuelson, 1947, p. 252). It also exposits on and develops what became commonly called the
Bergson
Henri-Louis Bergson (; 18 October 1859 – 4 January 1941) was a French philosopherHenri Bergson. 2014. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 13 August 2014, from https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/61856/Henri-Bergson
–Samuelson social welfare function. It shows how to represent (in the maximization calculus) all real-valued economic measures of any belief system that is required to rank consistently different feasible social configurations in an ethical sense as "better than", "worse than", or "indifferent to" each other (p. 221).
''Economics''
Samuelson is also author (and since 1985 co-author) of an influential principles textbook, ''Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics anal ...
'', first published in 1948 (19th ed. as of 2010; multiple reprints). The book sold more than 300,000 copies of each edition from 1961 through 1976 and was translated in the forty-one languages. As of 2018, it has sold over four million copies. William Nordhaus
William Dawbney Nordhaus (born May 31, 1941) is an American economist, a Sterling Professor of Economics at Yale University, best known for his work in economic modeling and climate change, and one of the 2 recipients of the 2018 Nobel Memoria ...
joined as co-author on the 12th edition (1985). Sometime before 1988, it had become the best-selling economics textbook of all time.
Samuelson was once quoted as saying, "Let those who will write the nation's laws if I can write its textbooks." Written in the shadow of the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
and the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, it helped to popularize the insights of John Maynard Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes, ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originally trained in ...
. A main focus was how to avoid, or at least mitigate, the recurring slumps in economic activity.
Samuelson wrote: "It is not too much to say that the widespread creation of dictatorships and the resulting World War II stemmed in no small measure from the world's failure to meet this basic economic problem he Great Depressionadequately." This reflected the concern of Keynes himself with the economic causes of war and the importance of economic policy in promoting peace.
Samuelson's book was the second to introduce Keynesian economics to a wide audience, and was by far the most successful. Canadian economist Lorie Tarshis, who had been a student attending Keynes's lectures at Harvard in the 1930s, published in 1947 an introductory textbook that incorporated his lecture notes, titled Elements of Economics
'.
Other publications
There are 388 papers in Samuelson's ''Collected Scientific Papers''.Stanley Fischer
Stanley Fischer ( he, סטנלי פישר; born October 15, 1943) is an Israeli American economist who served as the 20th Vice Chair of the Federal Reserve from 2014 to 2017. Fisher previously served as the 8th governor of the Bank of Israel fr ...
(1987, p. 234) writes that taken together they are "unique in their verve, breadth of economic and general knowledge, mastery of setting, and generosity of allusions to predecessors".
Samuelson was co-editor, along with William A. Barnett, of ''Inside the Economist's Mind: Conversations with Eminent Economists'' (Blackwell Publishing, 2007), a collection of interviews with notable economists of the 20th century.
Criticisms
Textbook influences in higher education
Samuelson's textbook was a watershed in introducing a serious study of business cycles in the economics curriculum. It was particularly timely because it followed the Great Depression, which had only ended because of the fiscal stimulus of World War II. The study of business cycles along with the introduction of the Keynesian approach of aggregate demand set the stage for the macroeconomic revolution in America, which then diffused throughout the world through translations into every major language. Generations of students, who then became teachers, learned their first and most influential lessons from Samuelson's ''Economics.'' It attracted many imitators, who became successful in different niches of the college market. The text was not without criticism. While it praised the "mixed economy" of market and government, some found that too radical and attacked it as socialist. As a precursor to criticisms of Samuelson's ''Economics'' textbook, Lorie Tarshis's textbook was attacked by trustees of, and donors to, American colleges and universities as preaching a "socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the ...
heresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important relig ...
". Piling on, William F. Buckley, Jr., in his 1951 book, '' God and Man at Yale,'' devoted an entire chapter, attacking both Samuelson's and Tarshis' textbooks. For Samuelson's book, Buckley drew from the ''Educational Examiner'' and credited it as an "excellent review of Samuelson's text." ("Note to Chapter Two." p. 234) For Tarshis' book, Buckley drew from Merwin K. Hart's organization : "I am also grateful to the National Economic Council for its telling analysis of the Tarshis." ("Note to Chapter Two." p. 234) Buckley essentially characterized both as – in the words of Paul Davidson – "communist inspired". Buckley, for the rest of his life, defended the criticisms set forth in his book.
Economic growth of USSR
One criticism – of a concept that Samuelson added to his ''Economics'' textbook – was the comparison of USA growth rates with those of theUSSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
, which, according to the criticism, was inconsistent with historical GNP differences. The textbook's 1967 edition (7th ed.) extrapolates (projects) the possibility of USSR/US real GNP parity between 1977 and 1995. Each subsequent edition extrapolates a date range further in the future until those graphs were dropped from the 1985 edition (12th ed.).
Phillips Curve
Samuelson, together withRobert Solow
Robert Merton Solow, GCIH (; born August 23, 1924) is an American economist whose work on the theory of economic growth culminated in the exogenous growth model named after him. He is currently Emeritus Institute Professor of Economics at th ...
, helped develop and popularize the mathematics of the Phillips Curve. The curve suggested that unemployment and inflation were inversely related; with the advent of stagflation in the 1970s some economists including Milton Friedman
Milton Friedman (; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and the ...
and Friedrich Hayek
Friedrich August von Hayek ( , ; 8 May 189923 March 1992), often referred to by his initials F. A. Hayek, was an Austrian–British economist, legal theorist and philosopher who is best known for his defense of classical liberalism. Hayek ...
attacked the economics based on the Phillips Curve as questionable or mistaken.
Memberships
* Member of theAmerican Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, a ...
, the American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and communit ...
, the United States National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nat ...
, fellow of Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
of London
* Fellow of the American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and communit ...
and the British Academy
The British Academy is the United Kingdom's national academy for the humanities and the social sciences.
It was established in 1902 and received its royal charter in the same year. It is now a fellowship of more than 1,000 leading scholars s ...
;
* President (1965–68) of the International Economic Association
* Member and past president (1961) of the American Economic Association
The American Economic Association (AEA) is a learned society in the field of economics. It publishes several peer-reviewed journals acknowledged in business and academia. There are some 23,000 members.
History and Constitution
The AEA was esta ...
* Member of the editorial board and past-president (1951) of the Econometric Society
The Econometric Society is an international society of academic economists interested in applying statistical tools to their field. It is an independent organization with no connections to societies of professional mathematicians or statisticians. ...
*Fellow, council member and past vice-president of the Royal Economic Society.
*Member of Phi Beta Kappa
The Phi Beta Kappa Society () is the oldest academic honor society in the United States, and the most prestigious, due in part to its long history and academic selectivity. Phi Beta Kappa aims to promote and advocate excellence in the liberal ...
.
List of publications
* Samuelson, Paul A. (1947), Enlarged ed. 1983. '' Foundations of Economic Analysis'', Harvard University Press. * Samuelson, Paul A. (1948), '' Economics: An Introductory Analysis'', ; withWilliam D. Nordhaus
William Dawbney Nordhaus (born May 31, 1941) is an American economist, a Sterling Professor of Economics at Yale University, best known for his work in economic modeling and climate change, and one of the 2 recipients of the 2018 Nobel Memori ...
(since 1985), 2009, 19th ed., McGraw–Hill.
* Samuelson, Paul A. (1952), "Economic Theory and Mathematics – An Appraisal", ''American Economic Review'', 42(2), pp56–66
* * Samuelson, Paul A. (1958), ''Linear Programming and Economic Analysis'' with
Robert Dorfman
Robert Dorfman (27 October 1916 – 24 June 2002) was professor of political economy at Harvard University. Dorfman made great contributions to the fields of economics, statistics, group testing and in the process of coding theory.
His pape ...
and Robert M. Solow, McGraw–Hill. Chapter-previelinks.
* * * ''The Collected Scientific Papers of Paul A. Samuelson'', MIT Press. Preview links for vol. 1–3 below. Contents links for vol. 4–7. . :Samuelson, Paul A. (1966), Vol
1
→ via
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
, 1937–mid-1964.
:Samuelson, Paul A. (1966), Vol2
→ via
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
, 1937–mid-1964.
:Samuelson, Paul A. (1972), Vol3
→ via
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
, mid-1964–1970.
:Samuelson, Paul A. (1977), Vol4
→ via
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, ...
, 1971–76.
:Samuelson, Paul A. (1986), Vol5
→ via
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
, 1977–198Description
→ via :Samuelson, Paul A. (2011), Vol
6
1986–2009
Description
→ via
Wayback Machine
The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the World Wide Web founded by the Internet Archive, a nonprofit based in San Francisco, California. Created in 1996 and launched to the public in 2001, it allows the user to go "back in time" and see ...
:Samuelson, Paul A. (2011), Vol7
1986–2009.
Paul A. Samuelson Papers, 1933–2010
Rubenstein Library,
Duke University
Duke University is a private research university in Durham, North Carolina. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1892. In 1924, tobacco and electric power industrialist Jam ...
. .
* Samuelson, Paul A. (1983). "My Life Philosophy," ''The American Economist'', 27(2)pp. 5-12.
* Samuelson, Paul A. (2007), ''Inside the Economist's Mind: Conversations with Eminent Economists'' with William A. Barnett, Blackwell Publishing, * Samuelson, Paul A. (2002), ''Paul Samuelson and the Foundations of Modern Economics'', Transaction Publishers, *Samuelson, Paul A. (2004), Macroeconomics *Samuelson, Paul A. (2004), Microeconomics
See also
* Samuelson's inequality * Samuelson's Iceberg transport cost model *Keynesian economics
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output ...
* New Keynesian economics
* Neo-Keynesian economics
*Neoclassical economics
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good ...
* Paul Samuelson - Wikiquote
Bibliography
Annotations
References
Further reading
Description
arrow-scrollable preview
* * . * . * . * .
External links
* *by Professor Assar Lindbeck, Stockholm School of Economics, Award Ceremony, The Bank of Sweden Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel, 1970
''A History of Economic Thought'' biography
2004 *
Yale Honorands biography, May 2005
''MIT News'', December 13, 2009 * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Samuelson, Paul 1915 births 2009 deaths Nobel laureates in Economics American Nobel laureates 20th-century American writers 21st-century American non-fiction writers 20th-century American economists 21st-century American economists American people of Polish-Jewish descent Fellows of the Econometric Society Harvard University alumni Jewish American writers Jewish American social scientists Kennedy administration personnel MIT School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences faculty Members of the United States National Academy of Sciences National Medal of Science laureates Writers from Gary, Indiana Trade economists University of Chicago alumni Neo-Keynesian economists Presidents of the Econometric Society People from Belmont, Massachusetts Presidents of the American Economic Association Economists from Massachusetts Economists from Indiana Corresponding Fellows of the British Academy Hyde Park Academy High School alumni Burials at Mount Auburn Cemetery Members of the American Philosophical Society