Pancreas divisum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pancreatic divisum is a congenital anomaly in the anatomy of the ducts of the pancreas in which a single pancreatic duct is not formed, but rather remains as two distinct dorsal and ventral ducts. Most individuals with pancreas divisum remain without symptoms or complications. A minority of people with pancreatic divisum may develop episodes of abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting due to
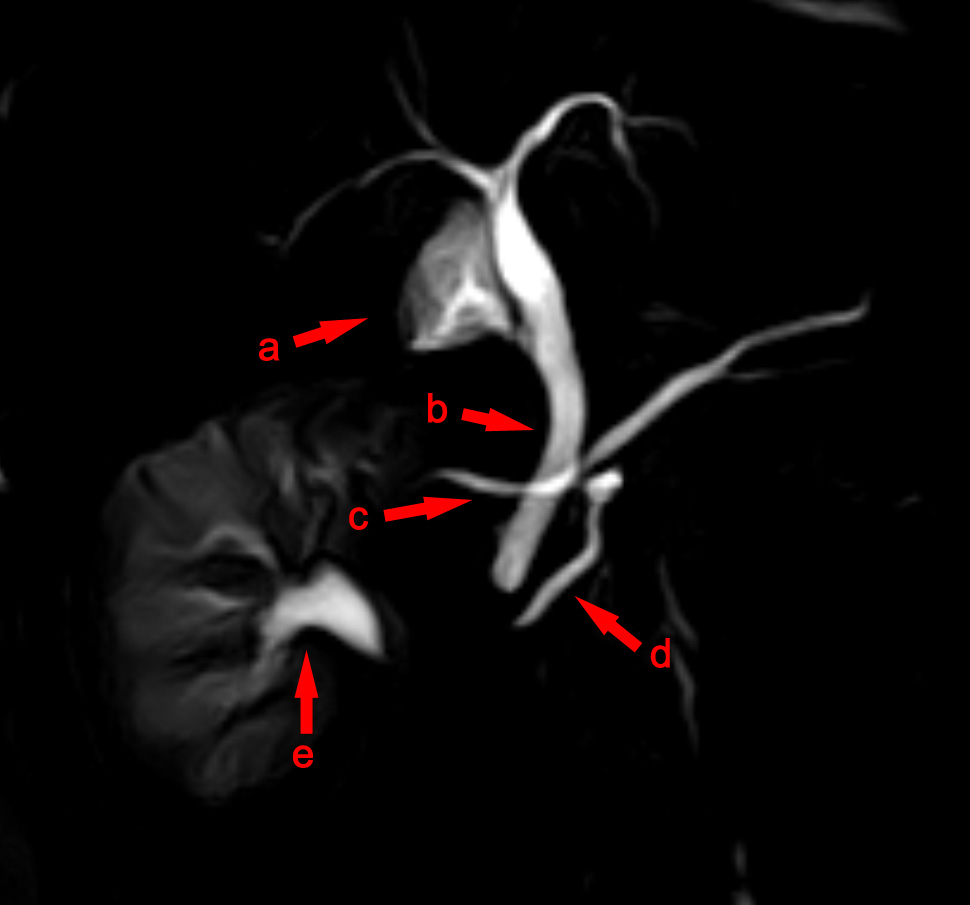 The most common and accurate way of diagnosing an individual with this anomaly is by MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography) or
The most common and accurate way of diagnosing an individual with this anomaly is by MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography) or
acute
Acute may refer to:
Science and technology
* Acute angle
** Acute triangle
** Acute, a leaf shape in the glossary of leaf morphology
* Acute (medicine), a disease that it is of short duration and of recent onset.
** Acute toxicity, the adverse eff ...
or chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters the organ's normal structure and functions. It can present as episodes of acute inflammation in a previously injured pancreas, or as chronic damage with persistent pa ...
. The presence of pancreas divisum is usually identified with cross sectional diagnostic imaging, such as MRI or computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
(CT) imaging. In some cases, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is performed, revealing the diagnosis of pancreas divisum. If no symptoms or complications are present, then treatment is not necessary. However, if there is recurrent pancreatitis, then a sphincterotomy of the minor papilla may be indicated.
Causes
The human embryo begins life with two ducts in the pancreas, the ventral duct and the dorsal duct. Normally, the two ducts will fuse together to form one main pancreatic duct; this occurs in more than 90% of embryos. In approximately 10% of embryos the ventral and dorsal ducts fail to fuse together, resulting in pancreas divisum. In utero, the majority of the pancreas is drained by the dorsal duct which opens up into theminor duodenal papilla
The minor duodenal papilla is the opening of the accessory pancreatic duct into the descending second section of the duodenum.
Structure
The minor duodenal papilla is contained within the second part of the duodenum. It is situated 2 cm proxi ...
. The ventral duct drains the minority of the pancreas and opens into the major duodenal papilla. In adults however, this situation is reversed whereby 70% of the pancreas is drained by the ventral duct. Therefore in pancreas divisum, where fusion of the ducts does not occur, the major drainage of the pancreas is done by the dorsal duct which opens up into the minor papilla.
Diagnosis
 The most common and accurate way of diagnosing an individual with this anomaly is by MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography) or
The most common and accurate way of diagnosing an individual with this anomaly is by MRCP (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography) or ERCP
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems. It is primarily performed by highly skille ...
(Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography). This test can demonstrate the presence of two separately draining ducts within the pancreas. Other tests can assist doctors with diagnosis, such as a CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
and an MRI.
Treatment
Pancreas divisum in individuals with no symptoms does not require treatment. For cases with mild and infrequent attacks, management may involve a low-fat diet, medications to reduce pain and gastrointestinal reactions, and pancreatic enzyme supplementation. A surgeon may attempt a sphincterotomy by cutting the minor papilla to enlarge the opening and allowpancreatic enzymes
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption into the cells of the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of anima ...
to flow normally. During surgery, a stent may be inserted into the duct to ensure that the duct will not close causing a blockage. This surgery can cause pancreatitis in patients, or in rare cases, kidney failure and death. Endoscopic approaches (ERCP
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems. It is primarily performed by highly skille ...
) are sometimes used for symptomatic pancreas divisum, which offers the benefit of a less invasive approach compared with surgery. No large-scale clinical studies comparing surgical and endoscopic approaches are available.
Occurrence
Studies involving autopsy and imaging series indicate that between 6% and 10% of the population have pancreas divisum, but it is asymptomatic in the majority (>95%) of cases. In those who develop symptoms, the symptoms seen in pancreas divisum and pancreatitis with typical anatomy are the same: abdominal pain is common, typically of sudden onset and located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen and often accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Pancreatic pain is characteristically described as a constant, severe, dull, epigastric pain that often radiates to the back and typically worsens after high-fat meals. However, many different pain patterns have been described, ranging from no pain to recurrent episodes of pain and pain free intervals, to constant pain with clusters of severe exacerbations.References
External links
* {{Congenital malformations and deformations of digestive system Congenital disorders of digestive system Pancreas disorders