Pacific Fur Company on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Pacific Fur Company (PFC) was an American
 John Jacob Astor was a merchant of
John Jacob Astor was a merchant of
 During the summer of 1810, Alexander McKay hired thirteen French-Canadians for the ''Tonquin''. The majority of the group remained in Montreal until late July, when they given directives to withdraw to New York City. A canoe provided transportation for the trip down the Richelieu River and
During the summer of 1810, Alexander McKay hired thirteen French-Canadians for the ''Tonquin''. The majority of the group remained in Montreal until late July, when they given directives to withdraw to New York City. A canoe provided transportation for the trip down the Richelieu River and
 Thirteen men signed contracts in Montreal to join Hunt on the journey to the Pacific coast by land. Notably only one had previously operated under a contract lasting longer than a year. The generous cash advancements were taken advantage by three men who deserted before Hunt and the remaining group left the city for
Thirteen men signed contracts in Montreal to join Hunt on the journey to the Pacific coast by land. Notably only one had previously operated under a contract lasting longer than a year. The generous cash advancements were taken advantage by three men who deserted before Hunt and the remaining group left the city for
 Under the command of Jonathan Thorn the ''Tonquin'' left New York on September 8, 1810. PFC employees numbered thirty-three men in total on board. The vessel landed at the
Under the command of Jonathan Thorn the ''Tonquin'' left New York on September 8, 1810. PFC employees numbered thirty-three men in total on board. The vessel landed at the
 Diplomatic relationships with the Chinookan villages near the Columbia were critical for the viability of Fort Astoria. Scholars have affirmed that the American company and its "economic success depended on mutually beneficial economic exchanges with Indian groups... who controlled trade." Many of the settlements near the station were under the influence of headman Comcomly.
Diplomatic relationships with the Chinookan villages near the Columbia were critical for the viability of Fort Astoria. Scholars have affirmed that the American company and its "economic success depended on mutually beneficial economic exchanges with Indian groups... who controlled trade." Many of the settlements near the station were under the influence of headman Comcomly.
 Hunt's expedition broke the Nodaway winter camp on April 21. The Astorians reached a major
Hunt's expedition broke the Nodaway winter camp on April 21. The Astorians reached a major
 While at the Arikara village, Hunt met and employed several American trappers that had previously worked for the MFC in modern
While at the Arikara village, Hunt met and employed several American trappers that had previously worked for the MFC in modern
 The expedition reached Fort Henry on 8 September, made by MFC employee Andrew Henry the previous year, near present-day St. Anthony and made a camp there. The post was and was later abandoned. While at the location work began creating enough canoes necessary to take the party down Henry's Fork and later the
The expedition reached Fort Henry on 8 September, made by MFC employee Andrew Henry the previous year, near present-day St. Anthony and made a camp there. The post was and was later abandoned. While at the location work began creating enough canoes necessary to take the party down Henry's Fork and later the
 Donald Stuart and his party of Robert McClellan, John Reed, Étienne Lucier and seven other men continued to march ahead of the two main PFC groups. While traversing the lands of the Niimíipu, a stranded employee of the PFC,
Donald Stuart and his party of Robert McClellan, John Reed, Étienne Lucier and seven other men continued to march ahead of the two main PFC groups. While traversing the lands of the Niimíipu, a stranded employee of the PFC,
 The ''Beaver'' was the second supply ship sent by Astor to the Pacific Coast, with Cornelius Sowle as its captain. It sailed from New York City in October 1811 and reached Fort Astoria on 9 May 1812. While stopping at the Kingdom of Hawaii, more men were recruited as Kanakas for the company. After unloading necessary supplies to the Fort, the ''Beaver'' sailed to Russian America. Hunt joined the crew to negotiate with RAC governor Alexander Andreyevich Baranov at New Archangel. The cargo was purchased by the Russians amounted to ₽124,000 in value, with payment in seal skins located on Saint Paul Island. Orders from Astor dictated that the ship to return to the Columbia, but the ''Beaver'' was in poor repair and sailed for the Kingdom of Hawaii instead. Hunt was left there as the ''Beaver'' went west to Guangzhou. News of the
The ''Beaver'' was the second supply ship sent by Astor to the Pacific Coast, with Cornelius Sowle as its captain. It sailed from New York City in October 1811 and reached Fort Astoria on 9 May 1812. While stopping at the Kingdom of Hawaii, more men were recruited as Kanakas for the company. After unloading necessary supplies to the Fort, the ''Beaver'' sailed to Russian America. Hunt joined the crew to negotiate with RAC governor Alexander Andreyevich Baranov at New Archangel. The cargo was purchased by the Russians amounted to ₽124,000 in value, with payment in seal skins located on Saint Paul Island. Orders from Astor dictated that the ship to return to the Columbia, but the ''Beaver'' was in poor repair and sailed for the Kingdom of Hawaii instead. Hunt was left there as the ''Beaver'' went west to Guangzhou. News of the
fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
venture wholly owned and funded by John Jacob Astor that functioned from 1810 to 1813. It was based in the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
, an area contested over the decades between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Grea ...
, the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
, the United States of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territo ...
and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
.
Management, clerks and fur trappers were sent both by land and by sea to the Pacific Coast in the Autumn of 1810. The base of operations was constructed at the mouth of the Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia ...
in 1811, Fort Astoria (present-day Astoria, Oregon
Astoria is a port city and the seat of Clatsop County, Oregon, United States. Founded in 1811, Astoria is the oldest city in the state and was the first permanent American settlement west of the Rocky Mountains. The county is the northwest corne ...
). The destruction of the company vessel the '' Tonquin'' later that year off the shore of Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
took with it the majority of the annual trading goods. Commercial competition with the British-Canadian North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great weal ...
began soon after the foundation of Fort Astoria. The Canadian competitors maintained several stations in the interior, primarily Spokane House
Spokane House was a fur-trading post founded in 1810 by the British-Canadian North West Company, located on a peninsula where the Spokane River and Little Spokane River meet. When established, it was the North West Company's farthest outpost in ...
, Kootanae House and Saleesh House Saleesh House, also known as Flathead Post, was a North West Company fur trading post built near present-day Thompson Falls, Montana in 1809 by David Thompson and James McMillan of the North West Company. It became a Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) ...
. Fort Okanogan
Fort Okanogan (also spelled Fort Okanagan) was founded in 1811 on the confluence of the Okanogan and Columbia Rivers as a fur trade outpost. Originally built for John Jacob Astor’s Pacific Fur Company, it was the first American-owned settle ...
was also opened in 1811, the first of several PFC posts created to counter these locations. The Overland Expedition faced military hostilities from several Indigenous cultures
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
and later had an acute provision crisis leading to starvation. Despite losing men crossing the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, a ...
and later at the Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake ...
, they arrived in groups throughout January and February 1812 at Fort Astoria.
A beneficial agreement with the Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty (russian: Под высочайшим Его Императорского Величества покровительством Российская-Американс� ...
was also planned through the regular supply of provisions for posts in Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
. This was planned in part to prevent the rival Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
based North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great weal ...
(NWC) to gain a presence along the Pacific Coast, a prospect neither Russian colonial authorities nor Astor favored.
The lack of military protection during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
forced the sale of PFC assets to the NWC. While the transactions were not finalized until 1814, due to the distance from Fort Astoria to Montreal and New York City, the company was functionally defunct by 1813. A party of Astorians returning overland to St. Louis in 1813 made the important discovery of the South Pass through the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
. This geographic feature would later be used by hundreds of thousands of settlers traveling over the Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, and Mormon
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into se ...
routes, collectively called the Westward Expansion Trails
In the history of the American frontier, overland trails were built by pioneers throughout the 19th century and especially between 1829 and 1870 as an alternative to sea and railroad transport. These immigrants began to settle much of North Ameri ...
. The emporium envisioned by Astor was a failure for a number of reasons, including the loss of two supply ships, the material difficulties of crossing the North American continent and competition from the North West Company. Historian Arthur S. Morton concluded that "The misfortunes which befell the Pacific Fur Company were great, but such as might be expected at the initiation of an enterprise in a distant land whose difficulties and whose problems lay beyond the experience of the traders."
Formation
 John Jacob Astor was a merchant of
John Jacob Astor was a merchant of New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
and founder of the American Fur Company
The American Fur Company (AFC) was founded in 1808, by John Jacob Astor, a German immigrant to the United States. During the 18th century, furs had become a major commodity in Europe, and North America became a major supplier. Several British ...
. To create a chain of trading stations spread across the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
to the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
, he incorporated an AFC subsidiary, the Pacific Fur Company. The commercial venture was originally designed to last for twenty years. Unlike its major competitor the Canadian owned NWC, the Pacific Fur Company was not a Joint-stock company
A joint-stock company is a business entity in which shares of the company's stock can be bought and sold by shareholders. Each shareholder owns company stock in proportion, evidenced by their shares (certificates of ownership). Shareholders a ...
. Capital for the PFC amounted to $200,000 divided into 100 shares individually valued at $2,000 and was funded entirely by Astor. The American Fur Company held half of the stock and the other half divided among prospective management and clerks. The chief representative of Astor in the daily operations was Wilson Price Hunt, a St. Louis businessman with no outback experience who received five shares. Each working partner was assigned four shares with the remaining shares held in reserve for hired clerks. Fellow partners in the venture were recruited from the NWC, the members being Alexander McKay, David Stuart, Duncan McDougall, and Donald Mackenzie. Astor and the partners met in New York on 23 June 1810 to sign the Pacific Fur Company's provisional agreement.
To establish the fledgling PFC trade posts in the distant Oregon Country, Astor's plan called for an extensive movement of large groups of employees overland following the route of the Lewis and Clark Expedition
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gr ...
and navally by sailing around Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramí ...
. The venture was planned on methods used in the AFC for the collection of fur pelts. Complements of employees (later called "Astorians") would operate in various parts of the region to complete trapping excursions. Outposts maintained by the PFC would be freighted necessary foodstuffs and supplies by annual cargo ships from New York City. Trade goods such as beads, blankets, and copper would be exchanged with the local Native Americans for fur pelts.
Ongoing supply issues faced by the Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty (russian: Под высочайшим Его Императорского Величества покровительством Российская-Американс� ...
were seen as a means to gain more furs. Cargo ships en route from the Columbia were planned to then sail north for Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
to bring much needed provisions. By cooperating with Russian colonial authorities to strengthen their material presence in Russian America, it was hoped by Astor to stop the NWC or any other British presence to be established upon the Pacific Coast. A tentative agreement for merchant vessels owned by Astor to ship furs gathered in Russian America into the Qing Empire was signed in 1812. Company ships then were directed to sail to the port of Guangzhou, where furs were then sold for impressive profits. Chinese products like porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
, nankeens and tea were to be purchased; with the ships then to cross the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
and head for European and American markets to sell the Chinese wares.
Labor recruitment
The PFC required a sizable number of laborers, fur trappers and in particularVoyageurs
The voyageurs (; ) were 18th and 19th century French Canadians who engaged in the transporting of furs via canoe during the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places (New France, including th ...
to staff company locations. Recruiting for the company's two expeditions were led by Wilson Hunt and Donald Mackenzie for the overland party and Alexander McKay for the naval bound group. All three men were based out of Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple- ...
throughout May to July 1810. Hunt was designated to lead the Overland Expedition, despite his inexperience in dealing with Indigenous cultures, or residing in the wilderness. It was suggested that Hunt instead trade positions with McKay and travel on the ''Tonquin''. However, it was determined to keep Hunt in charge of the land party.
The customary time for free agents to be sent into the interior from Montreal was in May, leaving few men left in the city available for hire. The recruitment effort stalled in part from the bitter treatment by the NWC and Hunt's lack of prior experience as a fur merchant, the source of many issues later on. PFC contracts were atypically favorable for hired men when compared to its Montreal competitors. Terms included a forty percent larger annual salary, double the cash advanced prior to departure and a length of service lasting five years, rather than the more common two or three year employment.
McKay's efforts
 During the summer of 1810, Alexander McKay hired thirteen French-Canadians for the ''Tonquin''. The majority of the group remained in Montreal until late July, when they given directives to withdraw to New York City. A canoe provided transportation for the trip down the Richelieu River and
During the summer of 1810, Alexander McKay hired thirteen French-Canadians for the ''Tonquin''. The majority of the group remained in Montreal until late July, when they given directives to withdraw to New York City. A canoe provided transportation for the trip down the Richelieu River and Lake Champlain
, native_name_lang =
, image = Champlainmap.svg
, caption = Lake Champlain-River Richelieu watershed
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = New York/ Vermont in the United States; and Quebec in Canada
, coords =
, type ...
. At Whitehall
Whitehall is a road and area in the City of Westminster, Central London. The road forms the first part of the A3212 road from Trafalgar Square to Chelsea. It is the main thoroughfare running south from Trafalgar Square towards Parliament Sq ...
additional men that were employed by McKay joined the southbound party, among them Ovide de Montigny
Ovide de Montigny was a French-Canadian fur trapper active in the Pacific Northwest from 1811 to 1822.
Pacific Fur Company
de Montigny was hired by Alexander MacKay (fur trader), Alexander MacKay at Montreal in July 1810. McKay and W. Price Hunt ...
. On 3 August they reached New York City, with the group's "hats decorated with parti-colored ribands and feathers..." causing some Americans to believe them to Natives. The following day lodgings at Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United States and the 18 ...
were reached and the scene was described by clerk Gabriel Franchère:"We sang as we rowed; which, joined to the unusual sight of a birch bark canoe impelled by nine stout Canadians, dark as Indians, and as gayly adorned, attracted a crowd upon the wharves to gaze at us as we glided along."While waiting to depart for the Pacific, McKay met with British diplomatic official Francis James Jackson. The official assured McKay that in the event of war between the United States and
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, all PFC employees that were British employees would be treated as such.
Hunt's efforts
 Thirteen men signed contracts in Montreal to join Hunt on the journey to the Pacific coast by land. Notably only one had previously operated under a contract lasting longer than a year. The generous cash advancements were taken advantage by three men who deserted before Hunt and the remaining group left the city for
Thirteen men signed contracts in Montreal to join Hunt on the journey to the Pacific coast by land. Notably only one had previously operated under a contract lasting longer than a year. The generous cash advancements were taken advantage by three men who deserted before Hunt and the remaining group left the city for Michilimackinac
Michilimackinac ( ) is derived from an Ottawa Ojibwe name for present-day Mackinac Island and the region around the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.. Early settlers of North America applied the term to the entire region ...
in July. The party reached Mackinac Island
Mackinac Island ( ; french: Île Mackinac; oj, Mishimikinaak ᒥᔑᒥᑭᓈᒃ; otw, Michilimackinac) is an island and resort area, covering in land area, in the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the island in Odawa is Michilimackinac ...
on 28 July 1810. Acting as a major depot for the regional Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
fur trade, the island was where Hunt focused on hiring more men for the company. The veteran fur merchant Ramsay Crooks was convinced to join the company and assisted in recruiting additional men. Over the sixteen days spent there, a total seventeen men were recruited to the concern with sixteen being French-Canadian
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fre ...
. This group of men, unlike those hired in Montreal, had extensive experience working in the fur trade as voyageurs
The voyageurs (; ) were 18th and 19th century French Canadians who engaged in the transporting of furs via canoe during the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places (New France, including th ...
and other roles. Likely suggested by Crooks, interested men already hired by other companies would have their contracts purchased from their employers.
After the men were finally gathered in early August, Hunt and the party departed for St. Louis and arrived there on 3 September. The hired voyageurs and fur trappers completed many transactions with various merchants in St. Louis and in the nearby French-Canadian settlement of Ste. Genevieve throughout September and October. These were recorded on the company ledger and particular purchases been argued as the men collecting goods to trade with various Indigenous nations they would visit. In particular, these negotiations by the French-Canadians have been thought to be steps towards later establishing themselves as independent traders in relatively unexploited fur regions. Most of the men in the Overland Party were engaged as hunters, interpreters, guides and voyageurs.
Oceanic component
The advanced party was sent to create the initial base of operations at themouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
of the Columbia River. Necessary trade goods for deals with Indigenous and needed supplies to establish the station were shipped on the same vessel In addition to beginning the company headquarters, this party would block any attempts by the NWC to create a station in the area. The ship '' Tonquin'' was purchased by Astor in 1810 to start commercial operations on the Pacific Ocean. The majority of the company partners. Duncan McDougall, David and Robert Stuart, and Alexander McKay would head this detachment. In addition, clerks Gabriel Franchère and Alexander Ross would join them on the planned voyage.
The ''Tonquin''
 Under the command of Jonathan Thorn the ''Tonquin'' left New York on September 8, 1810. PFC employees numbered thirty-three men in total on board. The vessel landed at the
Under the command of Jonathan Thorn the ''Tonquin'' left New York on September 8, 1810. PFC employees numbered thirty-three men in total on board. The vessel landed at the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouze ...
on 4 December to make repairs and take on water supplies at Port Egmont. Captain Thorn attempted to abandon eight of the crew still on shore, among them clerks Gabriel Franchère and Alexander Ross. The stranded men were taken on board after Robert Stuart threatened to kill Thorn. Communication between company workers was no longer held in English to keep the captain excluded from discussions. Company partners held talks in their ancestral Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
and the laborers used Canadian French
Canadian French (french: français canadien) is the French language as it is spoken in Canada. It includes multiple varieties, the most prominent of which is Québécois (Quebec French). Formerly ''Canadian French'' referred solely to Quebec ...
. On December 25 the ''Tonquin'' rounded Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramí ...
and sailed north into the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
.
The ship anchored at the Kingdom of Hawaii
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi ( Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawaiʻi Pae ʻĀina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent islan ...
in February 1811. Due to the possibility of men abandoning their posts to live in the tropical islands, Thorn assembled all of the crew and PFC employees to harass them to remain on the ship. Commercial transactions with Hawaiians saw the crew purchasing cabbage
Cabbage, comprising several cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'', is a leafy green, red (purple), or white (pale green) biennial plant grown as an annual vegetable crop for its dense-leaved heads. It is descended from the wild cabbage ( ''B.&n ...
, sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
, purple yams, taro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in Afri ...
, coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the f ...
s, watermelon, breadfruit
Breadfruit (''Artocarpus altilis'') is a species of flowering tree in the mulberry and jackfruit family ( Moraceae) believed to be a domesticated descendant of '' Artocarpus camansi'' originating in New Guinea, the Maluku Islands, and the Phil ...
, hogs, goats, two sheep, and poultry in return for "glass beads, iron rings, needles, cotton cloth". Upon entering Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the isla ...
, the crew was greeted by Isaac Davis and Francisco de Paula Marín
Don Francisco de Paula Marín (1774–1837) was a Spaniard who became influential in the early Kingdom of Hawaii. Often called Manini, Marini or other variations, he became a confidant of Hawaiian King Kamehameha I. Marín acted as a jack-of- ...
, the latter acting an interpreter in negotiations with Kamehameha I
Kamehameha I (; Kalani Paiea Wohi o Kaleikini Kealiikui Kamehameha o Iolani i Kaiwikapu kaui Ka Liholiho Kūnuiākea; – May 8 or 14, 1819), also known as Kamehameha the Great, was the conqueror and first ruler of the Kingdom of Hawaii. Th ...
and prominent government official Kalanimoku
William Pitt Kalanimoku or Kalaimoku ( – February 7, 1827) was a High Chief who functioned similarly to a prime minister of the Hawaiian Kingdom during the reigns of Kamehameha I, Kamehameha II and the beginning of the reign of Kamehameha III. ...
. 24 Native Hawaiian
Native Hawaiians (also known as Indigenous Hawaiians, Kānaka Maoli, Aboriginal Hawaiians, First Hawaiians, or simply Hawaiians) ( haw, kānaka, , , and ), are the indigenous ethnic group of Polynesian people of the Hawaiian Islands.
Hawa ...
Kanakas were hired with the approval of Kamehameha I, who appointed Naukane
Naukane (c. 1779 – February 2, 1850), also known as John Coxe, Edward Cox, and Coxe was a Native Hawaiian chief who traveled widely through North America in the early 19th century. He was either considered a member of the royal household of Kam ...
to oversee their interests.
The Columbia River was reached in March 1811. Despite stormy conditions, over several days Thorn ordered two boats dispatched to scout a safe route over the treacherous Columbia Bar
The Columbia Bar, also frequently called the Graveyard of the Pacific, is a system of bars and shoals at the mouth of the Columbia River spanning the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington. It is known as one of the most dangerous bar crossings in ...
. Both boats would capsize and eight men lost their lives. Finally on March 24, the ''Tonquin'' crossed the bar, passing into the Columbia’s estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
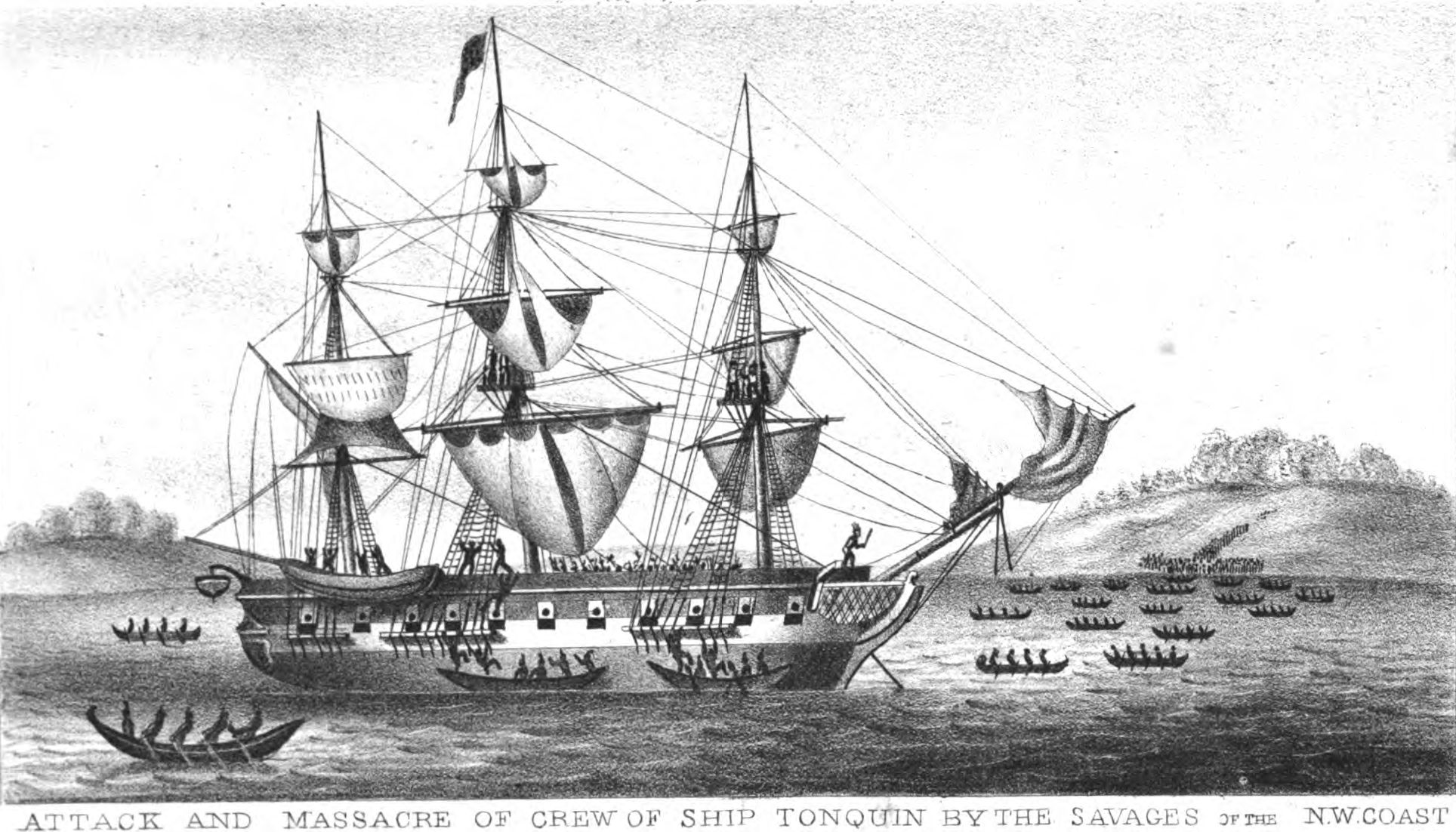
and laid anchor in Baker’s Bay. Captain Thorn stressed the urgency for the ''Tonquin'' to start trading further north along the Pacific Coast as instructed by Astor. After 65 days on the Columbia River, the ''Tonquin'' departed with a crew of 23 with McKay was aboard the ship as supercargo. At Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
she was boarded by the Tla-o-qui-aht people of Clayoquot Sound, where Thorn caused an uproar by hitting a Tla-o-qui-aht noble with a pelt. In the ensuing conflict all of men brought on the ''Tonquin'' were killed besides an interpreter from the Quinault nation and the ship was destroyed. This put the occupants of Fort Astoria in a tough position, having no access to seaborne transport until the following year.
Fort Astoria
Construction on Fort Astoria, an "emporium of the west", began in the middle of April 1811. It was built upon Point George, the location being about from the Lewis and Clark Expedition winter camp ofFort Clatsop
Fort Clatsop was the encampment of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in the Oregon Country near the mouth of the Columbia River during the winter of 1805–1806. Located along the Lewis and Clark River at the north end of the Clatsop Plains approxi ...
. The terrain and thick forests made clearing a foundation exceedingly difficult. Late in the month, McDougall reported that there was "little progress in clearing, the place being so full of half decayed trunks, large fallen timber & thick brush." No one among the party had previous experience in the logging industry and many hadn't used an axe before in general. Trees had a layer of hardened resin and were of a massive size. Four men worked as a team on platforms at least eight feet above the ground to effectively cut a tree, with it taking typically two days for a single tree to be felled. Medical issues quickly became another major issue for the party as there was not a single medical officer among the passengers brought on the ''Tonquin''. This left treatments rudimentary at best. During the initial months on the Columbia River at any time upwards of half of the expedition was unable to perform manual labor due to illness.
Fort Okanogan
Kaúxuma Núpika, aTwo-Spirit
Two-spirit (also two spirit, 2S or, occasionally, twospirited) is a modern, , umbrella term used by some Indigenous North Americans to describe Native people in their communities who fulfill a traditional third-gender (or other gender-varia ...
from the Ktunaxa people, and his wife arrived at Fort Astoria on 15 June 1811 with a letter from John Stuart. Kaúxuma offered accounts of the interior and recommended that the station be opened at the confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
of the Columbia and "the Okannaakken River" among the Syilx
The ''Syilx'' () people, also known as the Okanagan, Okanogan or Okinagan people, are a First Nations and Native American people whose traditional territory spans the Canada–US boundary in Washington state and British Columbia in the Okanagan ...
peoples. It was determined that David Stuart would take a party to with Kaúxuma to the Syilx. Before they left however the inhabitants of Astoria were surprised by the arrival of David Thompson on 15 July. Thompson later stated that his group "set off on a voyage down the Columbia River to explore this river in order to open out a passage for the interior trade with the Pacific Ocean." The competing fur traders were cordially received at Astoria.
A party of eight led by David Stuart departed on 22 July for the Syilx territories. The personnel assigned to join Stuart were eight men, including Alexander Ross, François Benjamin Pillet, Ovide de Montigny
Ovide de Montigny was a French-Canadian fur trapper active in the Pacific Northwest from 1811 to 1822.
Pacific Fur Company
de Montigny was hired by Alexander MacKay (fur trader), Alexander MacKay at Montreal in July 1810. McKay and W. Price Hunt ...
, and Naukane
Naukane (c. 1779 – February 2, 1850), also known as John Coxe, Edward Cox, and Coxe was a Native Hawaiian chief who traveled widely through North America in the early 19th century. He was either considered a member of the royal household of Kam ...
. The group joined David Thompson and his eight men in traveling up the Columbia, staying together until the Dalles. Upon entering Watlala Chinookan territory, Stuart failed establish favorable relations with them. Watlala men performed several military displays and stole a small amount of goods. Naukane agreed to join the NWC shortly after this episode and the two parties separated. Stuart was able to secure the protection of Wasco-Wishram leadership in early August. Groups of Chinookan laborers were used to cross the portages of the Columbia in their homeland.
Stuart's party soon began to travel through the Sahaptin
The Sahaptin are a number of Native American tribes who speak dialects of the Sahaptin language. The Sahaptin tribes inhabited territory along the Columbia River and its tributaries in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Sahaptin-s ...
nations and on the 12th of August an assembly of Walla Walla, Cayuse and Nez Perce welcomed the fur traders. Once the reception was complete, the PFC men continued up the Columbia and passed by the future site of Fort Nez Percés
Fort Nez Percés (or Fort Nez Percé, with or without the accent aigu), later known as (Old) Fort Walla Walla, was a fortified fur trading post on the Columbia River on the territory of modern-day Wallula, Washington. Despite being named after the ...
. Towards the end of August the party began to become troubled with Western Rattlesnake Western rattlesnake may refer to:
* ''Crotalus oreganus'', a venomous pitviper species found in North America in the western United States, parts of British Columbia and northwestern Mexico
* ''Crotalus viridis
''Crotalus viridis'' (Common name ...
populations and rapids, almost losing one canoe and the men aboard it to a section of swift currents. Stuart and his men were greeted by Wenatchi leadership at the Wenatchee River, who gave two horses to the fur traders as a gift in addition to several more being purchased. While passing through other Indigenous homelands the PFC continued financial dealings for food supplies. Members of the Chelan nation traded "some salmon, roots, and berries" and later Methows offered their "abundance of salmon" and "many horses" to the fur trappers for sale.
While at the junction of the Columbia and Okanogan River
The Okanogan River (known as the Okanagan River in Canada) is a tributary of the Columbia River, approximately 115 mi (185 km) long, in southern British Columbia and north central Washington. It drains a scenic plateau region called th ...
, a large encampment of Syilx
The ''Syilx'' () people, also known as the Okanagan, Okanogan or Okinagan people, are a First Nations and Native American people whose traditional territory spans the Canada–US boundary in Washington state and British Columbia in the Okanagan ...
were encountered. Prominent members of the nation entreated the fur traders to reside among their people, proclaiming "themselves to be always be our friends, to kill us plenty of beavers, to furnish us at all times with provisions, and to ensure our protection and safety." The cargo of the canoes were taken to land on 1 September and work soon began on Fort Okanogan. A residence crafted from driftwood acquired from the Okanogan River. While construction of the post was ongoing, four men that included Pillet were detailed to inform the progress of inland trade. The party arrived back at the company headquarters on 11 October and gave its favorable report.
Stuart led Montigny and two other men to follow the course of the Okanogan, leaving only Ross at the post. As promised, the Syilx provided security for the station, frequently alerting Ross when intruders from other nations came near. Despite planning on exploring the Okanogan watershed for a month, Stuart and his three men did not return until 22 March 1812. Upon reaching the Okanogan headwaters the party then went over to the Thompson River. Snows in mountain passes made it exceedingly difficult for the party to travel. Detained among the Secwepemc, Stuart developed cordial relations with them. Finding their areas rich in beaver populations, he promised to return later that year to create a trading post.
The Lower Chinookan peoples
 Diplomatic relationships with the Chinookan villages near the Columbia were critical for the viability of Fort Astoria. Scholars have affirmed that the American company and its "economic success depended on mutually beneficial economic exchanges with Indian groups... who controlled trade." Many of the settlements near the station were under the influence of headman Comcomly.
Diplomatic relationships with the Chinookan villages near the Columbia were critical for the viability of Fort Astoria. Scholars have affirmed that the American company and its "economic success depended on mutually beneficial economic exchanges with Indian groups... who controlled trade." Many of the settlements near the station were under the influence of headman Comcomly.
Assistance in exploration
Chinookans were highly important in company explorations of the Pacific Coast. In particular, they were instrumental in finding a suitable location for what became Fort Astoria. In early April 1811 McDougall and David Stuart visited Comcomly, who advised them not to return to the Columbia River as it was then quite tumultuous. The two men didn't listen and shortly afterward their canoe capsized in the river. The "timely succor" of Comcomly and his villagers ensured the partners were saved before they drowned. After recuperating there for three days, they returned to the PFC camp. Additional services tendered was the relaying information from more distant peoples to the Astorians. Reports were circulated by them in late April 1811 of a trade post maintained by white men in the interior. This was correctly conjectured by PFC employees to be their NWC rivals, later found to beSpokane House
Spokane House was a fur-trading post founded in 1810 by the British-Canadian North West Company, located on a peninsula where the Spokane River and Little Spokane River meet. When established, it was the North West Company's farthest outpost in ...
. Departing on 2 May, McKay led Robert Stuart, Franchère, Ovide de Montigny
Ovide de Montigny was a French-Canadian fur trapper active in the Pacific Northwest from 1811 to 1822.
Pacific Fur Company
de Montigny was hired by Alexander MacKay (fur trader), Alexander MacKay at Montreal in July 1810. McKay and W. Price Hunt ...
and a number of voyaguers up the Columbia, with Clatsop noble Coalpo
Coalpo was a Clatsop Chinookan peoples, Chinookan leader alive in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. He married a daughter of Comcomly, the most prominent Chinookan headman on the lower Columbia River.
Fort Astoria
In March 1811, the Pacifi ...
acting as guide and interpreter. The following day they explored the Cowlitz River and soon encountered a large canoe flotilla of Cowlitz Cowlitz may refer to:
People
* Cowlitz people, an indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest
** Cowlitz language, member of the Tsamosan branch of the Coast Salish family of Salishan languages
* Cowlitz Indian Tribe, a federally recognized tribe o ...
warriors. McKay was able to request a parlay, during which the Cowlitz stated they were armed for combat against the nearby Skilloot Chinookan village near the river mouth. Reaching the Dalles on 10 May, no trade station was found at the important fishery. Due to Coalpo's fear of reprisal from his enemies among the Wasco and Wishram, the party went back to Fort Astoria, returning on 14 May.
Despite not finding the NWC post, management at Fort Astoria soon became "anxious to acquire a knowledge of the country & the prospects of trade... within our reach". On 6 June 1811, Robert Stuart went north on a tour of western Olympic Peninsula
The Olympic Peninsula is a large arm of land in western Washington that lies across Puget Sound from Seattle, and contains Olympic National Park. It is bounded on the west by the Pacific Ocean, the north by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, a ...
with Calpo acting as a guide again. Returning on 24 June, Stuart reported that the Quinault and nearby Quileute nations would kill Sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the smal ...
s and trade their pelts for the valuable Dentalium shell
The word dentalium, as commonly used by Native American artists and anthropologists, refers to tooth shells or tusk shells used in indigenous jewelry, adornment, and commerce in western Canada and the United States. These tusk shells are a kind o ...
s sold by the Nuu-chah-nulth
The Nuu-chah-nulth (; Nuučaan̓uł: ), also formerly referred to as the Nootka, Nutka, Aht, Nuuchahnulth or Tahkaht, are one of the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast in Canada. The term Nuu-chah-nulth is used to describe fifte ...
on Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
. Stuart felt that a company trade post in Grays Harbor Grays Harbor is an estuarine bay located north of the mouth of the Columbia River, on the southwest Pacific coast of Washington state, in the United States of America. It is a ria, which formed at the end of the last ice age, when sea levels floo ...
offered the best location to secure these furs. Additionally he gave the opinion that Alutiiq in Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
should be recruited to hunt various fur bearing animals at the hypothetical factory
A factory, manufacturing plant or a production plant is an industrial facility, often a complex consisting of several buildings filled with machinery, where workers manufacture items or operate machines which process each item into another. ...
.
However, Chinookans were not always willing to help Astorians in visiting distant locations. This was a means of delaying the Astorians from making commercial connections with Indigenous peoples on the Upper Columbia. One particular incident has been described by historian Robert F. Jones as "an effort to keep Comcomly's Chinooks as middlemen between the natives of the upper Columbia and the Astorians." François Benjamin Pillet was ordered to make a trading trip along the Columbia. Accompanied by a Chinook headman, they left Fort Astoria in late June 1811. Small trade deals were completed with Skilloots near modern Oak Point. Afterwards, the headman cited the seasonal flooding as making the Columbia unsafe to travel further upriver. This forced Pillet to return to Astoria with what pelts he had purchased from the Skilloots.
Commercial ties
Consistently small stockpiles of foodstuffs at Fort Astoria created the need for frequent transactions with Chinookans for sustenance. Seasonal fish runs provided the major nutritional sources for the Columbian River-based Natives. After ceremonial rituals during each major fish run, trade for caught fish would begin in earnest with the Astorians. A constant task for Hawaiians would be to perform fisherman duties. Major fish populations active in the Columbia included the Candlefish smelt,White sturgeon
White sturgeon (''Acipenser transmontanus'') is a species of sturgeon in the family Acipenseridae of the order Acipenseriformes. They are an anadromous fish species ranging in the Eastern Pacific; from the Gulf of Alaska to Monterey, California. ...
, Sockeye salmon
The sockeye salmon (''Oncorhynchus nerka''), also called red salmon, kokanee salmon, blueback salmon, or simply sockeye, is an anadromous species of salmon found in the Northern Pacific Ocean and rivers discharging into it. This species is a ...
and Chinook salmon
The Chinook salmon (''Oncorhynchus tshawytscha'') is the largest and most valuable species of Pacific salmon in North America, as well as the largest in the genus '' Oncorhynchus''. Its common name is derived from the Chinookan peoples. Other ...
. This dependence on fish made it a primary food source for the Astorians, which caused some discontent among employees desiring a more familiar diet.
Terrestrial animals like members of the family Cervidae such as Roosevelt elk
The Roosevelt elk (''Cervus canadensis roosevelti)'', also known commonly as the Olympic elk and Roosevelt's wapiti, is the largest of the four surviving subspecies of elk (''Cervus canadensis'') in North America by body mass (although by antl ...
and black-tailed deer were not found in large numbers around Fort Astoria. This made them another important source of trade for the Chinookans when visiting the PFC station. Another frequent item sold when fish supplies were low in the winter was the Wapato root. Wapato provided a common source of calories for Chinookans and other nations. The Astorians described the tuber as "a good substitute for potatoes" Purchases of Wapato occurred in such volumes that a small cellar had to be created specifically to house the produce. Other typical purchases from Chinookans included manufactured goods. In particular woven hats were frequently bought for protection against the seasonal rains. These hats were tightly interwoven, making them essentially waterproof. Of benefit to the Astorians was that they were typically wide enough to cover the shoulders. Ross described the common artwork depicted them as "chequered" with various animal designs that were "not painted, but ingeniously interwoven."
Chinookans near Fort Astoria employed various means of retaining their valuable middle man position between various neighboring Indigenous peoples and the PFC. Additional tactics involved manipulating the perception neighboring Natives had of the American company. In August 1811, a small party of Chehalis visited Fort Astoria. In dialogue with them McDougall inquired why they would rarely directly trade with the PFC. The Chehalis merchants responded that Chinooks affiliated with Comcomly claimed that the Astorians were "very inveterate against their nation." McDougall concluded this story was used by Comcomly to continue his commercial hegemony over the area.
Fear of hostilities
It wasn't always that the Astorians, especially McDougall trusted Comcomly or Chinookans in general. His judgment of them, despite eventually marrying a daughter of Comcomly was that they were often ready to attack the fort. In particular Jones noted that he "seems to place implicit faith in any possible hostile actions by the natives." In June 1812, the number of men at Fort Astoria were reduced to 11 Hawaiians and 39 European descendants. Fear of attack by Chinookans was high and drills were directed by McDougall frequently. A delegation of Chinookans visited Fort Astoria on 2 July quickly left after witnessing these military demonstrations. This fear by the natives convinced the Astorians that "they are not friendly disposed towards us..." having "a desire to harm us." According to Jones, this "latent distrust" of Chinookans by Astorians from this incident was probably unfounded, as they entered the post "for an innocent purpose" and were frightened by the drills. Fears of attack didn't disappear and Astorians kept themselves guarded in dealing with natives. After the ''Beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
'' left for Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
rumors spread of a coming attack on Astoria in August 1812. There were large numbers of Chinookans and Chehalis near Comcomly's village at the time. This expedited construction on two bastion
A bastion or bulwark is a structure projecting outward from the curtain wall of a fortification, most commonly angular in shape and positioned at the corners of the fort. The fully developed bastion consists of two faces and two flanks, with fi ...
s and the fort was "put in readiness for an attack." Jones has pointed out that these movements of Indigenous was very likely a part of seasonal fishing, rather than a supposed hostile gathering.
Overland Expedition
As the leader of the expedition Hunt would make a number of decisions which were disastrous. The movement of Hunt's group has been described as "a company of traders forging westward in haphazard fashion." He ordered the expedition to leave St. Louis just before the winter to reduce company expenses of supporting employees. The group departed on October 21, 1810 forFort Osage
Fort Osage (also known as Fort Clark or Fort Sibley) was an early 19th-century factory trading post run by the United States Government in western Missouri on the American frontier; it was located in present-day Sibley, Missouri. The Treaty o ...
. The expedition traveled up the Missouri River before setting up winter camp on Nodaway Island
Nodaway is an unincorporated community in Andrew County, in the U.S. state of Missouri.
History
Nodaway was founded in 1868, and named after the nearby Nodaway River
The Nodaway River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Datase ...
, at the mouth of Nodaway River in Andrew County, Missouri, just north of St. Joseph. French-Canadian employees made frequent purchases from the company store during the idle season, especially those hired at Michilimackinac. Small items like blue beads, vermilion
Vermilion (sometimes vermillion) is a color, color family, and pigment most often made, since antiquity until the 19th century, from the powdered mineral cinnabar (a form of mercury sulfide, which is toxic) and its corresponding color. It i ...
, brass rings, tobacco "carrots", small axes among others were used in transactions with Missouria neighboring the camp.
On January 1811, Hunt sailed down the Missouri River to complete several pending transactions at St. Louis. It was during this time he recruited Pierre Dorion Jr., as he was the only qualified speaker of the Sioux language
Sioux is a Siouan language spoken by over 30,000 Sioux in the United States and Canada, making it the fifth most spoken indigenous language in the United States or Canada, behind Navajo, Cree, Inuit languages, and Ojibwe.
Regional variation
S ...
s in St. Louis at the time. Notably he was in debt to Manuel Lisa and the Missouri Fur Company (MFC), something that would lead to tensions between the fur companies later in the year. In the end Hunt was able to secure Dorion, on the condition that Marie and his two children be brought along as well. Once finalized, he took British naturalists John Bradbury and Thomas Nuttall
Thomas Nuttall (5 January 1786 – 10 September 1859) was an English botanist and zoologist who lived and worked in America from 1808 until 1841.
Nuttall was born in the village of Long Preston, near Settle in the West Riding of Yorkshire and ...
with him to the Nodaway camp, as previously agreed upon. The party left St. Louis on 12 March and reached Fort Osage on the 8th of April. Early into the travel Dorion physically abused his wife and caused her to flee for a day. At the station Ramsay Crooks was waiting for them and the group recuperated for two days. The group left Fort Osage on the 10th of April and during the day Dorion "severely beat his squaw" as Marie desired to stay with newly made Osage acquaintances rather than continue with the expedition. The group reached the winter camp on the 17th. The overland group at this point amounted to almost sixty men, forty being French-Canadian voyageurs.
Following the Missouri
 Hunt's expedition broke the Nodaway winter camp on April 21. The Astorians reached a major
Hunt's expedition broke the Nodaway winter camp on April 21. The Astorians reached a major Omaha
Omaha ( ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Nebraska and the county seat of Douglas County. Omaha is in the Midwestern United States on the Missouri River, about north of the mouth of the Platte River. The nation's 39th-largest c ...
village in early May. Active commercial transactions were completed there, with Omaha merchants offering "jerked buffalo meat, tallow, corn, and marrow" for vermilion, beads and tobacco carrots. Bradbury detailed that the Omaha village had plots of nicotiana rustica, melons, beans, squashes, and corn under cultivation. While at the Omaha settlement, Hunt received information from several visiting Yankton Sioux that a group of Sioux
The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin (; Dakota: /otʃʰeːtʰi ʃakoːwĩ/) are groups of Native American tribes and First Nations peoples in North America. The modern Sioux consist of two major divisions based on language divisions: the Dakota and ...
was gathering further up the river to stop the expedition from traveling further.
Proceeding further the Missouri River, the Sioux party was encountered on 31 May. The Sioux bands were a conglomeration of Yankton and Lakota and had around six hundred armed men. Tensions quickly arose between the two disparate groups and both took up positions by the Missouri River. The two company howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like ot ...
s and single Swivel gun
The term swivel gun (or simply swivel) usually refers to a small cannon, mounted on a swiveling stand or fork which allows a very wide arc of movement. Another type of firearm referred to as a swivel gun was an early flintlock combination gun wi ...
were loaded with powder and fired to intimidate the Sioux bands. The artillery were then loaded with live ammunition, but the Sioux across the river began to "spread their buffalo robes before them, and moved them side to side." Dorion stopped the firing of the armaments a second time, as he understood this action by the Sioux meant they desired a parley. Peace talks were held and the Sioux explained that they had formed to prevent the PFC from trading with the neighboring nations they were at war with, the Arikara
Arikara (), also known as Sahnish,
''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
, ''Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation.'' (Retrieved Sep 29, 2011)
Mandan
The Mandan are a Native American tribe of the Great Plains who have lived for centuries primarily in what is now North Dakota. They are enrolled in the Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation. About half of the Mandan still re ...
and the Gros Ventre. Hunt explained that the expedition intended to travel to the Pacific Ocean and they had no interest in the neighboring Indigenous groups. This was found to be acceptable by the Sioux leaders, and the PFC was allowed to depart further north.
On 3 June, employees of the Missouri Fur Company under the command of Manuel Lisa were encountered on the Missouri River. Lisa reminded Dorion of his pending debt to the company, and a duel between the two men was narrowly averted by Bradbury and Henry Marie Brackenridge intervening. After this incident the rival fur companies refrained from interacting and camped on opposite sides of the Missouri River. Despite this, Lisa and Hunt led their parties north towards an Arikara village and reached it on 12 June. In a council with local leadership Lisa declared that if any of Hunt's party were harmed he'd take it as an offense against him as well. In setting the standard rate for purchasing horses, "carbines, powder, ball, tomahawks knives" were in high demand as the Arikara were planning an attack upon the Sioux. Lisa and Hunt made a deal allowing for Hunt's boats to be exchanged for additional horses, kept at Fort Lisa further up the Missouri River. Crooks was sent with a small group to fetch the horses and while they reached Fort Lisa on the 23rd, they had to wait until the 25th for Lisa to arrive to finalize the transaction. The party left the following day and returned south to Hunt's camp.
The Rocky Mountains
 While at the Arikara village, Hunt met and employed several American trappers that had previously worked for the MFC in modern
While at the Arikara village, Hunt met and employed several American trappers that had previously worked for the MFC in modern Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Monta ...
. The men advised strongly against going into the Piikáni homelands of modern Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
. The Piikáni and other Niitsitapi nations at the time were typically unreceptive to trespass from European descendants and made a showing of military force against the Lewis and Clark Expedition. This changed Hunt's plans, who according determined it best to avoid the Niitsitapi peoples.
The expedition left their Arikara hosts in late July for the nearby Grand River. After following the Little Missouri River, the party to rest for several days while transactions were made with a band of Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enr ...
. In total 36 horses were purchased from the Cheyenne. The expedition broke camp on 6 August and Hunt ordered six men to hunt Bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North A ...
. Hunt's party continued southwest through the modern state of Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to t ...
and the hunting party rejoined on the 18th of August, having killed 8 Bison. While at the base of Cloud Peak on 30 August, a scouting party of Apsáalooke visited the camp. The following day a delegation of Apsáalooke on horseback invited them to visit their nearby village. Hunt recalled the importance of mercantile deals with the Apsáalooke stating that:"We spent the first day of September buying some robes and belts and trading our tired, maimed horses for fresh ones... thereby augmenting the number of our horses to about 121, most of which were well-trained and able to cross the mountains."Continuing westward towards the Continental Divide of the Americas, the PFC party followed the course of the Wind River, crossed the Divide and followed the
Gros Ventre River
The Gros Ventre River (''pronounced GROW-VAUNT'') is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed May 4, 2011 tributary of the Snake River in the state of Wyoming, USA. During i ...
.
Snake River
 The expedition reached Fort Henry on 8 September, made by MFC employee Andrew Henry the previous year, near present-day St. Anthony and made a camp there. The post was and was later abandoned. While at the location work began creating enough canoes necessary to take the party down Henry's Fork and later the
The expedition reached Fort Henry on 8 September, made by MFC employee Andrew Henry the previous year, near present-day St. Anthony and made a camp there. The post was and was later abandoned. While at the location work began creating enough canoes necessary to take the party down Henry's Fork and later the Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake ...
or so called "Mad River" to the Columbia. This was done as it felt no longer necessary to travel with pack horses, a decision that would soon cause more issues for the party. On the 10th, four men and two Natives under the command of Joseph Miller departed to begin trapping in the area. The horses that remained in the possession of the PFC, amounting to seventy-seven, were left in the care of "two young Snakes
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
". The party departed from Fort Henry on 19 September on the newly made canoes.
Traveling down the Snake River proved highly difficult due to the many rapids such as Caldron Linn. The party was forced to perform multiple portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ...
s due to these fierce currents. Over course of the remainder of September through early November, four incidents of canoes capsizing killed one man meant major losses in trade goods and food supplies. In addition to the hardships caused from attempting to follow the course of the Snake more problems arose due to dwindling food stockpiles. By 31 October there was enough provisions to last for five days. In early November there were not many animals in the area to gather for food, the few that were caught by the hunting parties were beaver. The traveling partners agreed to end travel by canoe, finding the mode of transportation too difficult continue using. Hunt ordered several groups go in various directions to contact neighboring Indigenous for material support. In the meantime the PFC expedition began to deposit its trade goods in small caches to lighten the workload of the men.
At the suggestion of Ramsay Crooks, the expedition was divided into two parties of nineteen men each, with each member receiving 5 pounds of dried meat. A third small group was led by Donald MacKenzie to reach Fort Astoria ahead of the main contingent. All that remained in the company stores was "forty pounds of corn, twenty of fat, and nearly five pounds of bouillon tablets." On 9 November the two groups began traveling on either side of the Snake. Soon the cliffs became too steep to allow an easy descent to the river banks for water. Sources of hydration became very limited and despite intercourse with several groups of Indigenous the situation didn't improve. Water was collected on 20 November after it rained the previous night. Up to that point "several Canadians had begun to drink their urine" in desperation.
Crooks reunited with Hunt's party in early December alone. Crooks was so weakened from starvation that his pace would have slowed the expedition immensely. Hunt left two men to tend to Crooks while the main group pushed forward. Several villages of Northern Shoshone
Northern Shoshone are Shoshone of the Snake River Plain of southern Idaho and the northeast of the Great Basin where Idaho, Wyoming and Utah meet. They are culturally affiliated with the Bannock people and are in the Great Basin classification ...
were visited and vitally needed food sources such as horses along with "some dried fish, a few roots, and some pounded dried cherries" were purchased. A Shoshone was convinced to act as a scout to guide the PFC group to the Umatilla River. On 23 December, thirteen men assigned to Crooks party were met who gave the unfortunate news that they hadn't seen him since he left Hunt's group.
Reaching the Columbia
 Donald Stuart and his party of Robert McClellan, John Reed, Étienne Lucier and seven other men continued to march ahead of the two main PFC groups. While traversing the lands of the Niimíipu, a stranded employee of the PFC,
Donald Stuart and his party of Robert McClellan, John Reed, Étienne Lucier and seven other men continued to march ahead of the two main PFC groups. While traversing the lands of the Niimíipu, a stranded employee of the PFC, Archibald Pelton
The Pacific Fur Company (PFC) was an American fur trade venture wholly owned and funded by John Jacob Astor that functioned from 1810 to 1813. It was based in the Pacific Northwest, an area contested over the decades between the United Kingdom of ...
, was found and brought along with the party. They finally arrived at Fort Astoria on 18 January 1812. The party was described as clothed in "nothing but fluttering rags." While waiting for the main contingent under Hunt to arrive, the men informed the personnel of the overland journey's progress from St. Louis.
Hunt's group found a band of Liksiyu on 8 January, whom hosted the downtrodden expedition for a week. Meals of dried Mule deer
The mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') is a deer indigenous to western North America; it is named for its ears, which are large like those of the mule. Two subspecies of mule deer are grouped into the black-tailed deer.
Unlike the related whi ...
meat and loafs of pounded Camas bulbs were provided during their stay. While exploring the area, Hunt found out from particular Liksiyu that there was an active white fur trader in the area. This would turn out to be Jacques Raphaël Finlay, located at the NWC Spokane House
Spokane House was a fur-trading post founded in 1810 by the British-Canadian North West Company, located on a peninsula where the Spokane River and Little Spokane River meet. When established, it was the North West Company's farthest outpost in ...
. On 21 January, the expedition finally reached the banks of the Columbia River. Hunt soon entered discussions with the Wasco-Wishram when entering their villages. It was here he learned the destruction of the ''Tonquin'' the previous year. The remaining three horses of the party were used to purchase two canoes from Wasco merchants. Several portages were required on the Columbia, especially at the Cascade Rapids
The Cascades Rapids (sometimes called Cascade Falls or Cascades of the Columbia) were an area of rapids along North America's Columbia River, between the U.S. states of Washington (state), Washington and Oregon. Through a stretch approximately ...
. The main body of the expedition reached Fort Astoria on 15 February to much fanfare. Besides Hunt there was thirty men, along with Marie Aioe Dorion and her two children on six canoes. McDougall was apprehensive about feeding all these additional people, a sentiment Franchère shared, as the post had recently faced issues with provisions. Due to seasonal salmon runs harvested by various Chinookans however, there was a sizable food supply at Fort Astoria.
Activities in 1812
Attempted expedition to interior
In late March, three clerks in command of fourteen men were ordered to depart for the hinterlands. Robert Stuart was take needed trade goods to Fort Okanogan. John Reed was to take food supplies to the stranded Crooks and Day, in addition to later taking dispatches for Astor to St. Louis. Russel Farnham was to retrieve the caches left by Hunt near Fort Henry. To complete several of the necessary portages at the Dalles, Wascos were hired to help freight the trade goods. Two bales of trade goods and later some personal items were however stolen. Stuart ordered his men to complete the portages during the night. A skirmish arose at sunrise between arriving Wascos and Reed, who was defending several bales of goods with one man. After being grievously injured, Reed lost the box containing the dispatches. Additional PFC arrived at the scene and two natives were reportedly killed in the struggle. The Chinookans returned in larger numbers and armed several hours later. To avoid more bloodshed Stuart was able to negotiate a settlement with the aggrieved families. In return for a reported six blankets and tobacco, the Astorians were able to continue their journey up the Columbia. The conflict raised security concerns of crossing into further Indigenous nations, forcing the three parties to all travel to Fort Okanogan. Arriving there on the 24th of April, the clerks, voyageurs and trappers departed for Fort Astoria on the 29th, leaving Alexander Ross and two men at the station. Stockpiles of pelts accumulated there amounted to an estimated 2,500 were taken as well. Near the mouth of the Umatilla River the party was surprised to loudly hear English shouted among an assembled group of Indigenous, perhaps Umatilla. Ramsay Crooks and John Day were there them, exhausted from several months of tribulations. Wandering over a large area, the two men at one point received the help of an Umatilla noble, Yeck-a-tap-am, who "in particular treated us like a father." After being robbed by another band of Natives, Crooks and Day were able to find the Umatilla once more. Taking two worn men with them, the party reached Fort Astoria on 11 May.The ''Beaver''
 The ''Beaver'' was the second supply ship sent by Astor to the Pacific Coast, with Cornelius Sowle as its captain. It sailed from New York City in October 1811 and reached Fort Astoria on 9 May 1812. While stopping at the Kingdom of Hawaii, more men were recruited as Kanakas for the company. After unloading necessary supplies to the Fort, the ''Beaver'' sailed to Russian America. Hunt joined the crew to negotiate with RAC governor Alexander Andreyevich Baranov at New Archangel. The cargo was purchased by the Russians amounted to ₽124,000 in value, with payment in seal skins located on Saint Paul Island. Orders from Astor dictated that the ship to return to the Columbia, but the ''Beaver'' was in poor repair and sailed for the Kingdom of Hawaii instead. Hunt was left there as the ''Beaver'' went west to Guangzhou. News of the
The ''Beaver'' was the second supply ship sent by Astor to the Pacific Coast, with Cornelius Sowle as its captain. It sailed from New York City in October 1811 and reached Fort Astoria on 9 May 1812. While stopping at the Kingdom of Hawaii, more men were recruited as Kanakas for the company. After unloading necessary supplies to the Fort, the ''Beaver'' sailed to Russian America. Hunt joined the crew to negotiate with RAC governor Alexander Andreyevich Baranov at New Archangel. The cargo was purchased by the Russians amounted to ₽124,000 in value, with payment in seal skins located on Saint Paul Island. Orders from Astor dictated that the ship to return to the Columbia, but the ''Beaver'' was in poor repair and sailed for the Kingdom of Hawaii instead. Hunt was left there as the ''Beaver'' went west to Guangzhou. News of the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
kept the ship at the port for the remainder of the conflict. The ''Beaver'' then proceeded to New York City and entered the city harbor in 1816.
Second interior expedition
Failure to accomplish many of the tasks set for work the hinterland earlier in 1812 did not discourage the Astorians. The supplies and reinforcements brought aboard the ''Beaver'' made management consider "grander schemes" for the summer. New establishments would be created to challenge the NWC across the region in addition to pursuing trading expeditions among various Indigenous nations. A total of almost 60 men were directed to locations from theWillamette Valley
The Willamette Valley ( ) is a long valley in Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. The Willamette River flows the entire length of the valley and is surrounded by mountains on three sides: the Cascade Range to the eas ...
of Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
to the Bitterroot Valley
The Bitterroot Valley is located in southwestern Montana, along the Bitterroot River between the Bitterroot Range and Sapphire Mountains, in the Northwestern United States.
Geography
The valley extends approximately from Lost Trail Pass in Ida ...
of Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
and the vicinity of modern Kamloops
Kamloops ( ) is a city in south-central British Columbia, Canada, at the confluence of the South flowing North Thompson River and the West flowing Thompson River, east of Kamloops Lake. It is located in the Thompson-Nicola Regional District, w ...
in British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, for ...
. The movement of workers to their assigned locales began in late June. Robert Stuart led a party bound for St. Louis to send information to Astor as Reed had attempted earlier in the year. His group was composed two French-Canadians and four Americans. John Day became afflicted by mental instability and Stuart paid several Multnomah men of Cathlapotle village to transport him back to Fort Astoria. The group would make the important discovery of the South Pass, critical for the later westward movement of tens of thousands of American migrants.
Liquidation
Funds provided by Astor established several major trading stations across the Pacific Northwest. While intended to gain control of the regional fur trade, the Pacific Fur Company would ultimately flounder. This came from a variety of issues, many caused by the tumultuous diplomatic relationship between the United Kingdom and the United States. The destruction of the ''Tonquin'' left Fort Astoria under supplied and heavily reliant upon neighboring Chinookans for sustenance. Competition from the interior based North West Company threatened to the loss of major fur producing Oregon Country regions. The Overland Expedition would arrive many months later than planned by Astor. Wilson Hunt's inexperience in the outback in along with dwindling supplies would leave the majority of the expedition facing starvation. While the arrival of the ''Beaver'' brought much needed trading goods, foodstuffs and additional employees, events would soon see the ending of the PFC. News of theWar of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
was relayed to the Astorians at Fort Spokane, information that Donald McKenzie brought to Fort Astoria in January 1813. As Franchere recalled, a council of clerks and management noted that the Astorians were "almost to a man British subjects", forcing them to agree to "abandon the establishment" of Fort Astoria and its secondary stations. A British warship was learned from NWC clerks to be en route to capture the station. The PFC management agreed to sell its assets across the Oregon Country, formalized on 23 October 1813 with the raising of the Union Jack
The Union Jack, or Union Flag, is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. Although no law has been passed making the Union Flag the official national flag of the United Kingdom, it has effectively become such through precedent. ...
. On 30 November arrived at the Columbia River and in honor of George III of the United Kingdom
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
Fort Astoria was renamed Fort George. On board the ''Racoon'' was John MacDonald who oversaw the formal takeover of PFC properties. Later in March 1814, the NWC's ship arrived on the Columbia, delivering much-needed supplies to Fort George. She then sailed on to China, and England. She carried some PFC personnel, many of whom were former employees of the NWC, back to England, from where they returned to Montreal.
Legacy
During a NWC shareholder meeting in July 1814, the partners declared that the sale "greatly facilitated the getting out of the acificCountry our competitors the American Fur Company. They also concluded that the sale of Astoria and other PFC properties gave "considerable" advancements for their company. Plans were considered to use the stations much in the same manner Astor meant, for trade with China. The Columbia also offered a less costly means of supplying the interior NWC posts in the region. TheTreaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 betw ...
established a "joint occupancy" of the Pacific Northwest between the United States and the United Kingdom was confirmed, each nation agreeing not to inhibit the activities of each other's citizens. During 1821, the British Government ordered the NWC to be merged in their long time rivals, the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
. In a short time the HBC controlled the majority of the fur trade across the Pacific Northwest. This was done in a manner that "the Americans were forced to acknowledge that Astor's dream" of a multi-continent economic web "had been realized... by his enterprising and far-sighted competitors." The PFC held additional influence on the region in some particular and subtle ways. The book Astoria was written by Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and " The Legen ...
in 1836, after interviewing some men connected to the venture and consulting documents held by Astor. Two surviving members of the Astorians, Étienne Lucier and Joseph Gervais
Joseph Gervais (October 21, 1777 – July 14, 1861) was a French-Canadian, later American, pioneer settler and trapper in the Pacific Northwest. He is the namesake for the town of Gervais, Oregon.
Early life
Joseph Gervais was born in Maskinong� ...
, would later become farmers on the French Prairie and participate in the Champoeg Meetings.
See also
*Maritime Fur Trade
The maritime fur trade was a ship-based fur trade system that focused on acquiring furs of sea otters and other animals from the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast and natives of Alaska. The furs were mostly sold in China in exc ...
* North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great weal ...
References
Citations
Primary sources
* * * * * * * * * *Secondary sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control Astor family Astoria, Oregon Botanical expeditions Expeditions from the United States Fur trade American Fur Company Oregon Country Pre-Confederation British Columbia Pre-statehood history of Oregon Pre-statehood history of Idaho Pre-statehood history of Montana Pre-statehood history of Washington (state) Clothing companies established in 1810 American companies established in 1810