Pulp Stone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
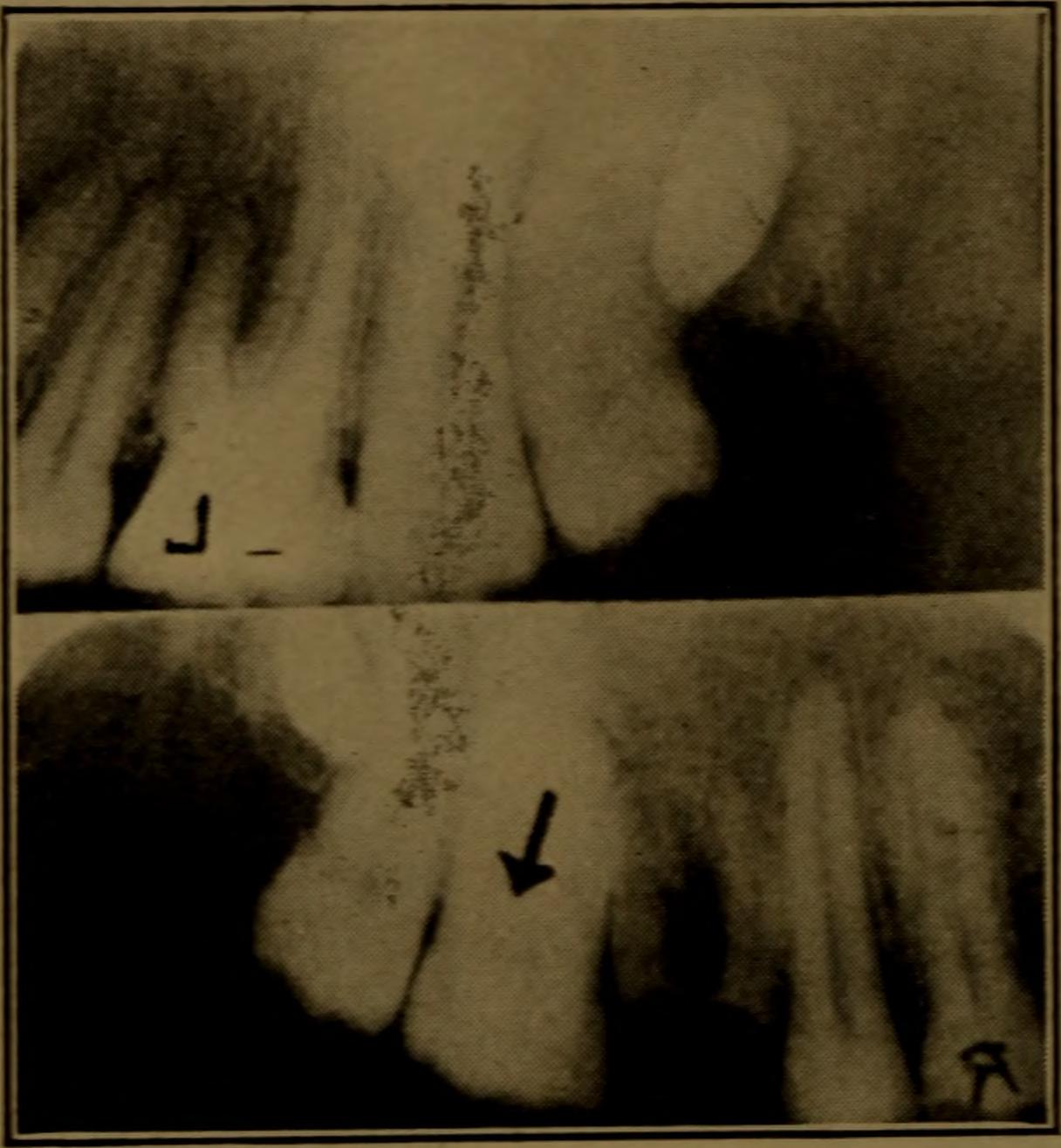 Pulp stones (also denticles or endoliths) are nodular,
Pulp stones (also denticles or endoliths) are nodular,
 Pulp stones (also denticles or endoliths) are nodular,
Pulp stones (also denticles or endoliths) are nodular, calcified
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Mat ...
masses appearing in either or both the coronal and root portion of the pulp
Pulp may refer to:
* Pulp (fruit), the inner flesh of fruit
Engineering
* Dissolving pulp, highly purified cellulose used in fibre and film manufacture
* Pulp (paper), the fibrous material used to make paper
* Molded pulp, a packaging material
...
organ in teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
. Pulp stones are not painful unless they impinge on nerves.
They are classified:
:A) On the basis of structure
::1) True pulp stones: formed of dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by ena ...
by odontoblast
In vertebrates, an odontoblast is a cell of neural crest origin that is part of the outer surface of the dental pulp, and whose biological function is dentinogenesis, which is the formation of dentin, the substance beneath the tooth enamel on t ...
s
::2) False pulp stones: formed by mineralization of degenerating pulp cells, often in a concentric pattern
:B) On the basis of location
::1) Free: entirely surrounded by pulp tissue
::2) Adherent: partly fused with dentin
::3) Embedded: entirely surrounded by dentin
Introduction
Pulp stones are discrete calcifications found in the pulp chamber of the tooth which may undergo changes to become diffuse pulp calcifications such as dystrophic calcification. They are usually noticed by radiographic examination and appeared as round or ovoid radiopaque lesions. Clinically, a tooth with a pulp stone has normal appearance like any other tooth. The number of pulp stones in a single tooth may vary from 1 to 12 or more, with varying sizes from minute particles to large masses which tend to occlude the pulpal space. It is reported that pulp stones are more commonly found in the coronal region of pulp, albeit also found in the radicular pulp. It is believed that pulp stones develop around a central nidus of pulp tissue, for instance collagen fibril, ground substance and necrotic cell remnants. Initial calcification occurs around the central nidus and extends outward with regular calcified material in a concentric or radial manner.Etiology
The pulp calcifications can arise due to: * pulp degeneration * increasing age * circulatory disturbances within the pulp * long standing local irritants such asdental caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
, pulp-capping procedures, healed tooth fractures, tooth injury restorations and periodontal disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main caus ...
s
* orthodontic
Orthodontics is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, management, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, and misaligned bite patterns. It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial ...
tooth movements
* transplantation of teeth
* trauma
It is shown that pulp stone occurring in adolescents is significantly associated with carious and/or restored teeth, which suggests a causative relationship of chronic pulp irritation to pulp stone formation. A defence reaction in the pulpodentinal complex may be triggered by caries and microleakage around restorations which lead to pulp calcifications. The formation of pulp stone may have a similar mechanism as the tertiary dentine formation near the irritated odontoblast
In vertebrates, an odontoblast is a cell of neural crest origin that is part of the outer surface of the dental pulp, and whose biological function is dentinogenesis, which is the formation of dentin, the substance beneath the tooth enamel on t ...
s. Apart from that, with aging, the pulp decreases in size due to the deposition of secondary or tertiary dentine. This subsequently results in favourable conditions for the formation of pulpal calcifications.
The other reported etiologic factors also include:
* idiopathic factors
* consumption of fluoride supplements
* hypervitaminosis D
* a possible genetic predisposition such as dentinogenesis imperfecta
Dentinogenesis imperfecta (DI) is a genetic disorder of tooth development. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, as a result of mutations on chromosome 4q21, in the dentine sialophosphoprotein gene (DSPP). It is one of the most frequen ...
and dentinal dysplasia
Types/classification
Pulp stones can be classified based on different location and structure. Based on location, they can classified into free, embedded and adherent pulp stones. Free pulp stones are found within the pulp tissue and is the most common encounter. The size vary from 50μm in diameter to several millimetres and may occlude the entire pulp chamber. Embedded pulp stone is fully embedded in dentine and most commonly found in the apical portion of the root. Adherent pulp stones are attached to the wall of pulp space but not fully enclosed by dentine. Structurally, pulp stones can be classified as true and false pulp stones. True pulp stones are made up of dentine that is lined by odontoblast. True pulp stones are quite rare. On the other hand, false pulp stones are made up of concentric layers of mineralised tissue around blood thrombi, collagen fibres, or dying and dead cells.Histopathology
Histologically, there are two types of stones: (1) stones with regular calcifications (2) stones with irregular calcifications. For regular calcification, the pulp stones are smooth, round or ovoid with concentric laminations. It is commonly found in the coronal pulp. As for irregular calcifications without laminations, pulp stones may have the shape of rods or leaves and the surface is rough. It is more common in the radicular pulp. Pulp stones with regular calcification grow in size by addition of collagen fibrils to their surface, whereas the irregular type of pulp stones are formed by calcification of pre-existing collagen fibres. Pulp stones may also form around epithelial cells such as remnants of Hertwig's epithelial root sheath. It is presumed that epithelial remnants are able to induce adjacent mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into odontoblasts.Associations
A pilot study was done with patients withcardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
(CVD) and it shows increased incidence of pulp stones in teeth with patients with CVD compared to healthy patients without CVD. There are also researchers which suggest the link between pulpal calcification and carotid artery Carotid artery may refer to:
* Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery
* External carotid artery, an artery on each side of t ...
calcification, despite not having a strong proof on this correlation. Besides cardiovascular disease, other disease such as end stage renal disease
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can b ...
, Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints a ...
, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Calcinosis universalis, tumoral calcinosis
Tumoral calcinosis is a rare condition in which there is calcium deposition in the soft tissue in periarticular location, around joints, outside the joint capsule. They are frequently (0.5–3%) seen in patients undergoing renal dialysis. Clinica ...
are also discovered to be in association with pulpal calcifications.
Several genetic diseases such as dentin dysplasia and dentinogenesis imperfecta
Dentinogenesis imperfecta (DI) is a genetic disorder of tooth development. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, as a result of mutations on chromosome 4q21, in the dentine sialophosphoprotein gene (DSPP). It is one of the most frequen ...
are also accompanied by pulpal calcifications and hence, Marfan syndrome was suspected to be in association with pulp stones due to abnormal dentin formation, leading to the increased frequency of pulpal calcifications in these individuals. Another theory suggests that individuals with Marfan syndrome have connective tissue dysplasia or vascular defects which in the case of tooth pulp, endothelial rupture of the pulp arterioles will lead to hemorrhagic
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagi ...
areas in the pulp. It was proposed that these hemorrhagic areas in the pulp will induce mineralization within the pulp.
Prevalence
Pulpal calcifications can be developed throughout the life and prevalence rates from 8–9% in worldwide population had been reported in studies. It was also found that pulpal stones occurred most frequently over the fourth decade, in advancing age. Generally, pulp stones are more frequent to be found in maxillary teeth compared to mandibular teeth. A study in Australia resulted higher occurrences of pulp stones in molars as opposed to premolars, and first molars as opposed to second molars. First molars which were restored and/or with caries showed a higher incidence of pulp stones as compared to intact, unrestored first molars.Clinical implications
Pulp stones generally do not have significant clinical implications as they are usually not a source of pain, discomfort or any form ofpulpitis
Pulpitis is inflammation of dental pulp tissue. The pulp contains the blood vessels, the nerves, and connective tissue inside a tooth and provides the tooth’s blood and nutrients. Pulpitis is mainly caused by bacterial infection which itself is ...
. However, when the tooth concerned will undergo endodontic
Endodontics (from the Greek roots ''endo-'' "inside" and ''odont-'' "tooth") is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.
Overview
Endodontics encompasses the study (practice) of the basic and clinical ...
treatment such as root canal treatment
Root canal treatment (also known as endodontic therapy, endodontic treatment, or root canal therapy) is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of ...
, presence of large pulp stones will be clinically significant.
Large pulp stones in the pulp chamber
The pulp is the connective tissue, nerves, blood vessels, and odontoblasts that comprise the innermost layer of a tooth. The pulp's activity and signalling processes regulate its behaviour.
Anatomy
The pulp is the neurovascular bundle cent ...
might block the access to canal orifices and prevent the exploring dental instruments from passaging down the canal. In these cases, burs or even ultrasonic instrumentation can be used to remove the blocking pulp stones. During the removal process, sodium hypochlorite
Sodium hypochlorite (commonly known in a dilute solution as bleach) is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula, formula NaOCl (or NaClO), comprising a sodium cation () and a hypochlorite anion (or ). It may ...
which has dissolving action can also be used as a synergistic effect.
References
{{oral pathology __FORCETOC__ Acquired tooth pathology