pulmonary angiogram on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
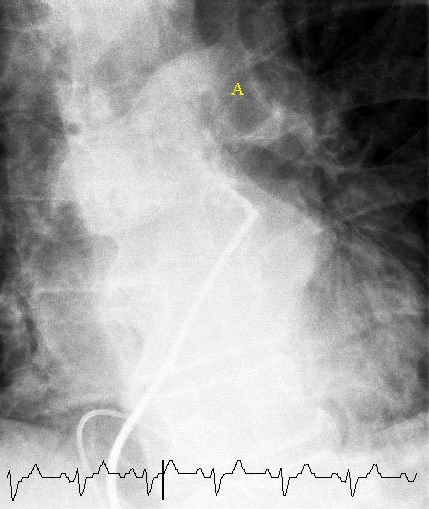 Pulmonary angiography (or pulmonary arteriography,conventional pulmonary angiography, selective pulmonary angiography) is a medical
Pulmonary angiography (or pulmonary arteriography,conventional pulmonary angiography, selective pulmonary angiography) is a medical
"Pulmonary angiography" @ MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
{{Medical imaging Cardiology Projectional radiography
fluoroscopic
Fluoroscopy () is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope () allows a physician to see the internal anatomy, structure and ...
procedure used to visualize the pulmonary arteries and much less frequently, the pulmonary veins. It is a minimally invasive procedure performed most frequently by an interventional radiologist
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs bo ...
or interventional cardiologist
Interventional cardiology is a branch of cardiology that deals specifically with the catheter based treatment of structural heart diseases. Andreas Gruentzig is considered the father of interventional cardiology after the development of angioplasty ...
to visualise the arteries of the lungs.
Uses
Pulmonary angiography is useful as the confirmation test where the non-invasive imaging such asCT pulmonary angiography
A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging i ...
is inconclusive on determining the presence of pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain p ...
. The accuracy of pulmonary angiography may be higher than clinical examination, arterial blood gas
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test, or arterial blood gas analysis (ABGA) measures the amounts of arterial gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. An ABG test requires that a small volume of blood be drawn from the radial artery with a syringe an ...
results, and ventilation/perfusion scan
A ventilation/perfusion lung scan, also called a V/Q lung scan, or ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy, is a type of medical imaging using scintigraphy and medical isotopes to evaluate the circulation of air and blood within a patient's lungs, in ...
. Pulmonary angiography is also used to confirm chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) is a long-term disease caused by a blockage in the blood vessels that deliver blood from the heart to the lungs ( the pulmonary arterial tree). These blockages cause increased resistance to flo ...
(CTEPH) and provides a platform for balloon pulmonary angioplasty to treat the disease.
CT pulmonary angiography
A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging i ...
has nearly entirely replaced conventional pulmonary angiography in common practice as it is less invasive, faster, safer, and provides most of the same diagnostic information with the added benefit of visualizing the lung tissue as well as other structures. Nevertheless, it is still used in cases where CT angiography is nondiagnostic.
Procedure
Types of catheters that can be used are pigtail catheters and balloon occlusion catheters. Tip of the catheter is advanced through theinferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
, right atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two atr ...
, right ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper ...
, right ventricular outflow tract, pulmonary trunk, and the tip is parked in the left pulmonary artery.
History
Conventional pulmonary angiography was first performed in 1931 by Portuguese angiography pioneers Lopo de Carvalho, Egas Moniz and colleagues. Robb and Steinberg described pulmonary angiography by infusion of peripheral radiocontrast.References
External links
"Pulmonary angiography" @ MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
{{Medical imaging Cardiology Projectional radiography