Pseudoviridae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Pseudoviridae'' is a family of
''Pseudoviridae'' is a family of
Penicillium camemberti virus - GP1
(species) * '' Phaseolus vulgaris Tpv2-6 virus''
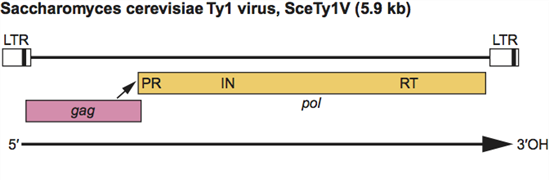 The
The
ICTV Report: ''Pseudoviridae''Pseudoviridae
(Darwin Zoology) {{Taxonbar, from=Q3772842 RNA reverse-transcribing viruses Virus families Ortervirales
 ''Pseudoviridae'' is a family of
''Pseudoviridae'' is a family of virus
A virus is a wikt:submicroscopic, submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and ...
es, which includes three genera.
Viruses of the family are actually LTR retrotransposons of the Ty1-copia family. They replicate via structures called virus-like particles (VLPs). VLPs are not infectious like normal virions, but they nevertheless make up an essential part of the pseudoviral lifecycle.
Taxonomy
''Pseudoviridae'' is unofficially classified under group VIRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
Reverse Transcribing Viruses and infect fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
and invertebrates
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
.
''Pseudoviridae'' comprises highly divergent members and most ''Pseudoviridae'' encode Gag and Pol on a single open reading frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a Prokaryote, prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the #Six-fra ...
.
''Pseudoviridae'' is included in the order ''Ortervirales'' along with families '' Belpaoviridae'', ''Metaviridae
''Metaviridae'' is a family of viruses which exist as Ty3-gypsy LTR retrotransposons in a eukaryotic host's genome. They are closely related to retroviruses: members of the family ''Metaviridae'' share many genomic elements with retroviruses, i ...
'', ''Retroviridae
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase e ...
'', and '' Caulimoviridae''.
The family includes the following genera:
* '' Hemivirus''
* '' Pseudovirus''
* '' Sirevirus''
Further ''Pseudoviridae'' species not classified into a genus are:
* ''Penicillium camemberti virus - GP1''NCBIPenicillium camemberti virus - GP1
(species) * '' Phaseolus vulgaris Tpv2-6 virus''
Genome
 The
The genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
of viruses from this family is unsegmented, -RT, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA and is 4200–9700 nucleotides
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules wi ...
long. The genome encodes structural proteins and non-structural proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respondi ...
which codes for an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
, replicase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to t ...
, and reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
for the reverse transcription
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes ...
step during replication
Replication may refer to:
Science
* Replication (scientific method), one of the main principles of the scientific method, a.k.a. reproducibility
** Replication (statistics), the repetition of a test or complete experiment
** Replication crisi ...
.
Virology
The viralcapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may ...
is unenveloped and looks roughly spherical. The capsid is round with icosahedral symmetry with triangulation number (T) = 3 and 4. It is also isometric
The term ''isometric'' comes from the Greek for "having equal measurement".
isometric may mean:
* Cubic crystal system, also called isometric crystal system
* Isometre, a rhythmic technique in music.
* "Isometric (Intro)", a song by Madeon from ...
to quasi-isometric and has a diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid fo ...
of 30-50 nm. LTR-retrotransposons
Retrotransposons (also called Class I transposable elements or transposons via RNA intermediates) are a type of genetic component that copy and paste themselves into different genomic locations ( transposon) by converting RNA back into DNA throug ...
are poorly characterized and lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids includ ...
have not reported.
The genome integrates into the host genome and gets transcribed by host cell enzymes such as eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
nuclear RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukary ...
. Genome replication takes place in the host cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
, or the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
* Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
and assembly can occur in the cytoplasm, or in the nucleus.
References
External links
ICTV Report: ''Pseudoviridae''
(Darwin Zoology) {{Taxonbar, from=Q3772842 RNA reverse-transcribing viruses Virus families Ortervirales