Prypeć - Newir (lubieszowski) 2019 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


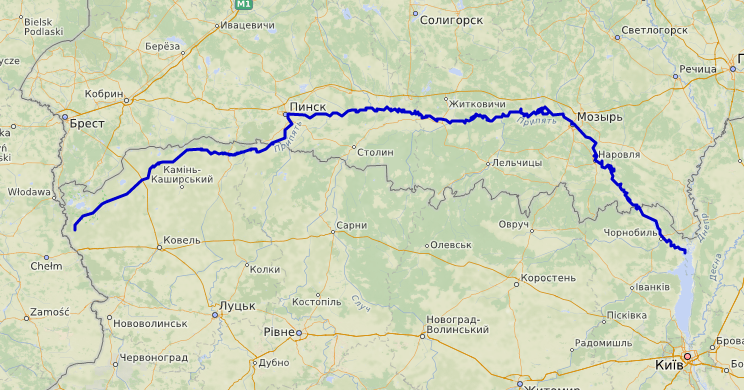 The Pripyat or Prypiat ( , uk, Прип'ять, ; be, Прыпяць, translit=Prypiać}, ; pl, Prypeć, ; russian: Припять, ) is a river in
The Pripyat or Prypiat ( , uk, Прип'ять, ; be, Прыпяць, translit=Prypiać}, ; pl, Prypeć, ; russian: Припять, ) is a river in
Припять
Pripyat: Radioactive pollution, 2003
{{Authority control Belarus–Ukraine border Chernobyl Exclusion Zone International rivers of Europe Rivers of Belarus] Rivers of Brest Region Rivers of Gomel Region Rivers of Ukraine

 The Pripyat or Prypiat ( , uk, Прип'ять, ; be, Прыпяць, translit=Prypiać}, ; pl, Prypeć, ; russian: Припять, ) is a river in
The Pripyat or Prypiat ( , uk, Прип'ять, ; be, Прыпяць, translit=Prypiać}, ; pl, Prypeć, ; russian: Припять, ) is a river in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
, approximately long. It flows east through Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
, and Ukraine again, draining into the Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and B ...
.
Overview
The Pripyat passes through the exclusion zone established around the site of theChernobyl nuclear disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR in the Sov ...
. The city of Pripyat, Ukraine
Pripyat ( ; russian: При́пять), also known as Prypiat ( uk, При́пʼять, , ), is an abandoned city in northern Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 19 ...
(population 45,000) was completely evacuated after the Chernobyl disaster.
Pripyat has a catchment area of , of which are in Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
. of the whole river length lies within Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
.
As of 2020, it is being dredged
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
to enable the E40 waterway.
Location
The Pripyat begins on the Volyn Hill, between the villages of Budnik and Horn Smolars of Lyubomlsky District in Ukraine. After 204 km downstream, it crosses the border ofBelarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
, where it travels 500 km through Polesia
Polesia, Polesie, or Polesye, uk, Полісся (Polissia), pl, Polesie, russian: Полесье (Polesye) is a natural and historical region that starts from the farthest edge of Central Europe and encompasses Eastern Europe, including East ...
, Europe's largest wilderness, within which lie the vast sandy wetlands known as the Pinsk marshes
__NOTOC__
The Pinsk Marshes ( be, Пінскія балоты, ''Pinskiya baloty''), also known as the Pripet Marshes ( be, Прыпяцкія балоты, ''Prypiackija baloty''), the Polesie Marshes, and the Rokitno Marshes, are a vast natural ...
, a dense network of swamps, bogs, rivers and rivulets within a forested basin. For the last 50 kilometers the Pripyat flows again in Ukraine and flows several kilometers south of Chernobyl into the Kyiv reservoir.
Geography
The length of the river is 775 kilometers. The area of the watershed is 114,300 km2. The Pripyat valley in the upper reaches is weak, in the lower reaches it is clearer. Thecave
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
is developed all along, allocating two super-floodplain terraces. The width of the floodplain in the upper course of 2–4 km and more, in some years, is flooded for several months. In the lower reaches, the width of the floodplain reaches 10–15 km. The channel in the upper canalized; below - winding, forms meanders, elders, many ducts (one of them is combined with the lake Nobel); there are sandy islands. The width of the river in the upper reaches is up to 40 m, on the average - 50–70 m, in the lower reaches 100 - predominantly 250 m, with the entrance to the Kyiv reservoir - 4–5 km. The bottom is sandy and sandy-spruce. The slope of the river is 0.08 m / km
Name etymology
Max Vasmer
Max Julius Friedrich Vasmer (; russian: Максимилиан Романович Фа́смер, translit=Maksimilian Romanovič Fásmer; 28 February 1886 – 30 November 1962) was a Russo-German linguist. He studied problems of etymology in In ...
in his etymological dictionary notes that the historical name of the river mentioned in the earliest East Slavic document, ''Primary Chronicle
The ''Tale of Bygone Years'' ( orv, Повѣсть времѧньныхъ лѣтъ, translit=Pověstĭ vremęnĭnyxŭ lětŭ; ; ; ; ), often known in English as the ''Rus' Primary Chronicle'', the ''Russian Primary Chronicle'', or simply the ...
'' is ''Pripet'See also
*Pripyat (city)
Pripyat ( ; russian: При́пять), also known as Prypiat ( uk, При́пʼять, , ), is an abandoned city in northern Ukraine, located near the border with Belarus. Named after the nearby river, Pripyat, it was founded on 4 February 19 ...
*Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nuc ...
*Chernobyl Exclusion Zone
The Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant Zone of Alienation, Belarusian: Хона адчужэння Чарнобыльскай АЭС, ''Zona adčužennia Čarnobyĺskaj AES'', russian: Зона отчуждения Чернобыльской АЭС ...
*Dnieper–Bug Canal
, image = Селішча._Дняпроўска-Бугскі_канал._Водападзел_(15).jpg
, image_caption =
, original_owner =
, engineer =
, other_engineer ...
Books
* (in Russian, English and Polish) Ye.N.Meshechko, A.A.Gorbatsky (2005) ''Belarusian Polesye: Tourist Transeuropean Water Mains'', Minsk,Four Quarters
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures.
In mathematics
Four is the smallest c ...
,
* (in Belorussian, Russian and English) T.A.Khvagina (2005) ''POLESYE from the Bug to the Ubort'', Minsk Vysheysha shkola
Vysheysha shkola ( be, Вышэйшая школа) is a state-owned publishing house in Minsk, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республи ...
, .
Notes
References
Припять
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; ) is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Bolshaya rossiyskaya e ...
* Pripyat // Dictionary of Contemporary Geographical Names / Rus. geogr. oh Moscow center; By common. Ed. acad. V. M. Kotlyakova. Institute of Geography, Russian Academy of Sciences. - Yekaterinburg: U-Factorium, 2006.
* Joint River Management Program. Final Report: River Pripyat Basin (February 2004)
External links
Pripyat: Radioactive pollution, 2003
{{Authority control Belarus–Ukraine border Chernobyl Exclusion Zone International rivers of Europe Rivers of Belarus] Rivers of Brest Region Rivers of Gomel Region Rivers of Ukraine