Provinces of Flanders on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province and nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration.
Most of the provinces take their name from earlier

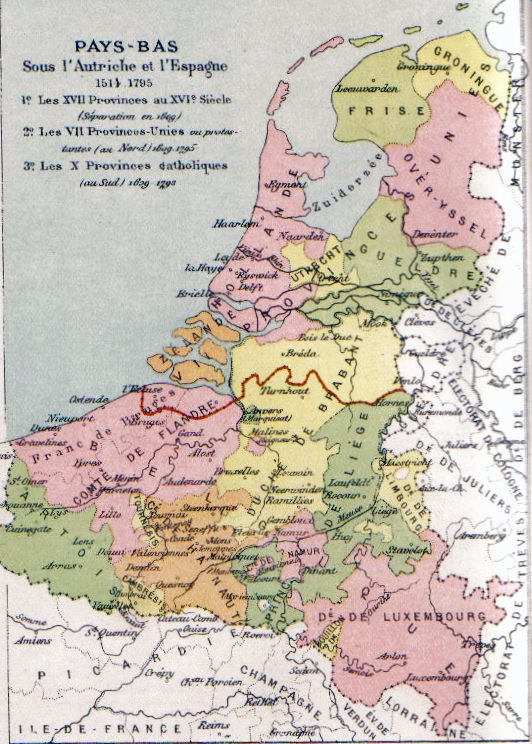 The medieval Low Countries, including present-day Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg, as well as parts of modern Germany and France, comprised a number of rival and independent feudal states of varying sizes. These each had their own identities and governments, though in the early modern period almost all the Belgian states became part of larger entities (the Seventeen Provinces (1549–1581) and the Southern Netherlands (after 1581)). Prominent early states in the area of modern Belgium included the Duchy of Brabant, the County of Flanders, the Prince-Bishopric of Liège and the
The medieval Low Countries, including present-day Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg, as well as parts of modern Germany and France, comprised a number of rival and independent feudal states of varying sizes. These each had their own identities and governments, though in the early modern period almost all the Belgian states became part of larger entities (the Seventeen Provinces (1549–1581) and the Southern Netherlands (after 1581)). Prominent early states in the area of modern Belgium included the Duchy of Brabant, the County of Flanders, the Prince-Bishopric of Liège and the  When these territories were annexed by France in 1795, they were reorganised into '' départments''; the borders were redrawn and the historical names were replaced by names of geographical features (generally the main river of the area).
When these territories were annexed by France in 1795, they were reorganised into '' départments''; the borders were redrawn and the historical names were replaced by names of geographical features (generally the main river of the area).
 At the end of French rule and the creation of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1815, the departmental territories were generally retained but were renamed into provinces and the historical names returned. At the time of the
At the end of French rule and the creation of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1815, the departmental territories were generally retained but were renamed into provinces and the historical names returned. At the time of the
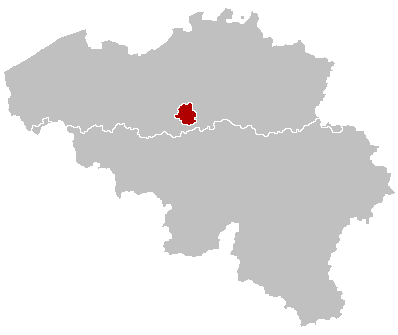 The Brussels Capital Region does not belong to any province, nor does it contain any. The extraprovincial status of Brussels has existed since 1995, when the former province of Brabant, which had Brussels as its capital, was divided into the Dutch-speaking province of
The Brussels Capital Region does not belong to any province, nor does it contain any. The extraprovincial status of Brussels has existed since 1995, when the former province of Brabant, which had Brussels as its capital, was divided into the Dutch-speaking province of
 Because the
Because the
The provinces
belgium.be
Vereniging van de Vlaamse Provincies
(Association of the Flemish Provinces)
Association des Provinces wallonnes
(Association of the Walloon Provinces) {{DEFAULTSORT:Provinces Of Belgium Subdivisions of Belgium Provinces Belgium 2 Provinces, Belgium Local government in Belgium cs:Belgie#Administrativní rozdělení de:Politische Gliederung Belgiens
duchies
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a medieval country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between " ...
and counties of similar location, while their territory is mostly based on the departments
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
installed during French annexation. At the time of the creation of Belgium in 1830, only nine provinces existed, including the province of Brabant, which held the City of Brussels
The City of Brussels (french: Ville de Bruxelles or alternatively ''Bruxelles-Ville'' ; nl, Stad Brussel or ''Brussel-Stad'') is the largest municipality and historical City centre, centre of the Brussels, Brussels-Capital Region, as well a ...
. In 1995, Brabant was split into three areas: Flemish Brabant
Flemish Brabant ( nl, Vlaams-Brabant ; french: Brabant flamand ) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Haina ...
, which became a part of the region of Flanders; Walloon Brabant, which became part of the region of Wallonia; and the Brussels-Capital Region, which became a third region. These divisions reflected political tensions between the French-speaking Walloons and the Dutch-speaking Flemish; the Brussels-Capital Region is officially bilingual.
The division into provinces is fixed by Article 5 of the Belgian Constitution. The provinces and Brussels are subdivided into 43 administrative arrondissements
An arrondissement (, , ) is any of various administrative divisions of France, Belgium, Haiti, certain other Francophone countries, as well as the Netherlands.
Europe
France
The 101 French departments are divided into 342 ''arrondissements'', ...
, and further into 581 municipalities.
List

History
 The medieval Low Countries, including present-day Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg, as well as parts of modern Germany and France, comprised a number of rival and independent feudal states of varying sizes. These each had their own identities and governments, though in the early modern period almost all the Belgian states became part of larger entities (the Seventeen Provinces (1549–1581) and the Southern Netherlands (after 1581)). Prominent early states in the area of modern Belgium included the Duchy of Brabant, the County of Flanders, the Prince-Bishopric of Liège and the
The medieval Low Countries, including present-day Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg, as well as parts of modern Germany and France, comprised a number of rival and independent feudal states of varying sizes. These each had their own identities and governments, though in the early modern period almost all the Belgian states became part of larger entities (the Seventeen Provinces (1549–1581) and the Southern Netherlands (after 1581)). Prominent early states in the area of modern Belgium included the Duchy of Brabant, the County of Flanders, the Prince-Bishopric of Liège and the Duchy of Luxembourg
The Duchy of Luxemburg ( nl, Luxemburg; french: Luxembourg; german: Luxemburg; lb, Lëtzebuerg) was a state of the Holy Roman Empire, the ancestral homeland of the noble House of Luxembourg. The House of Luxembourg, now Duke of Limburg, becam ...
; smaller ones included the County of Hainaut
The County of Hainaut (french: Comté de Hainaut; nl, Graafschap Henegouwen; la, comitatus hanoniensis), sometimes spelled Hainault, was a territorial lordship within the medieval Holy Roman Empire that straddled what is now the border of Belg ...
, the Duchy of Limburg and the County of Namur, though there were other small states as well.
 At the end of French rule and the creation of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1815, the departmental territories were generally retained but were renamed into provinces and the historical names returned. At the time of the
At the end of French rule and the creation of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1815, the departmental territories were generally retained but were renamed into provinces and the historical names returned. At the time of the independence of Belgium
The Belgian Revolution (, ) was the conflict which led to the secession of the southern provinces (mainly the former Southern Netherlands) from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands and the establishment of an independent Kingdom of Belgium.
Th ...
from the Netherlands in 1830, Belgium's territory simply consisted of the existing nine southern provinces. The first article of the Belgian Constitution said: "Belgium is divided into provinces. These provinces are Antwerp, Brabant, West Flanders, East Flanders, Hainaut, Liège, Limburg, Luxembourg, Namur, except for the relations of Luxembourg with the German Confederation." As such, each of the modern provinces of Belgium (with the exception of Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
) takes its name from one of the medieval predecessors, whereas the borders largely correspond to those of the French departments, which in most cases differ substantially from the historical entities.
In 1839, as part of the Treaty of London, half of the province of Limburg became part of the Netherlands, which consequently has its own province of Limburg.
In 1920, following the First World War, Belgium annexed the Eupen-Malmedy territory, which became part of Liège Province
Liège (; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is the easternmost province of the Wallonia region of Belgium.
Liège Province is the only Belgian province that has borders with three countries. It borders (clockwise from the north) the Du ...
.
During the second half of the 20th century, Belgium transitioned from a unitary state to a federal state with three Communities and three Regions. As part of the state reforms, the (bilingual) province of Brabant was split in 1995 three ways: into two (unilingual) provinces (Flemish Brabant and Walloon Brabant) and into the (bilingual) Brussels-Capital Region. (The Brussels-Capital Region does not belong to any province, is not a province, and does not contain any provinces.) The two new Brabant provinces became part of the Flemish Region and the Walloon Region respectively. The remaining eight provinces became part of these regions as well, so the Flemish Region and the Walloon Region each contain five provinces.
Schematic overview
The following table presents a simplified overview of the evolution of the Frenchdepartments
Department may refer to:
* Departmentalization, division of a larger organization into parts with specific responsibility
Government and military
*Department (administrative division), a geographical and administrative division within a country, ...
into the present-day Belgian provinces.
Provincial governments
The provincial government consists of three main branches: the ''Provincial Council'', which is the elected body, the ''Deputation'' or ''Provincial College'', which is the executive body, and the ''Governor'', who is appointed by the regional government (i.e. the Flemish or Walloon Government). The Provincial Councils ( nl, Provincieraad; french: Conseil provincial) are the representative bodies of the population of the provinces. This is the equivalent of theStates-Provincial
The provincial council (, PS), also known as the States Provincial, is the provincial parliament and legislative assembly in each of the provinces of the Netherlands. It is elected for each province simultaneously once every four years and has ...
in the Netherlands. The numbers of seats in the Provincial Councils are proportional to the population of the province; the numbers were reduced in both Flanders and Wallonia, starting 2013 (following the 2012 elections
The following elections occurred in the year 2012.
International
* 2012 United Nations Security Council election
Africa Egypt
* 2012 Egyptian presidential election
Mali
* 2012 Malian presidential election
* 2012 Malian parliamentary electio ...
). They are directly elected each six years, at the same time of the municipal elections. Before 1994, the provincial elections instead coincided with the national elections. Until then, the provincial councils also appointed Provincial Senators to the Belgian Senate. The last elections were held on 14 October 2018.
The executive branch was previously called the ''Permanent Deputation''. In the Flemish Region it is now simply called the Deputation ( nl, Deputatie) and it consists of the Governor and six Deputies elected by the Provincial Council from among its members. Following the next 2018 election, there will be one Deputy less, i.e. five Deputies. In the Walloon Region it is called the Provincial College (french: Collège provincial) which consists of the Governor and four to five Deputies (depending on the number of inhabitants of the province) elected by the Provincial Council from among its members.
In Flemish Brabant
Flemish Brabant ( nl, Vlaams-Brabant ; french: Brabant flamand ) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Haina ...
, there is also a Deputy Governor ( nl, Adjunct van de gouverneur). The Deputy Governor is appointed by the Flemish Government on the unanimous advice of the Federal Council of Ministers and must have a considerable knowledge of both the Dutch and the French language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Nor ...
. He is responsible for ensuring that the language legislation is observed in the municipalities in the Brussels Periphery.
Following the Fifth State Reform, the responsibility for the provincial institutions was devolved to the Regions. The Regions have the power to amend or replace the existing legislation on the provincial institutions, most notably the Provincial Law of 30 April 1836. In the Flemish Region, the Provincial Decree of 9 December 2005 applies. In the Walloon Region, the Code of Local Democracy and Decentralisation applies. The legal framework in these Regions is still very similar, but that could change in the future. Although the Regions are responsible for the provincial institutions, the Federal State has retained its responsibility over the provinces in certain cases. For instance, the Regions are responsible for the appointment of the Provincial Governors, but only after the unanimous advice of the Federal Council of Ministers. Legislation regarding the Governor and Vice-Governor of Brussels-Capital
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
, and the Deputy Governor of Flemish Brabant
Flemish Brabant ( nl, Vlaams-Brabant ; french: Brabant flamand ) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Haina ...
, has also remained a federal competency.
Absence of any province in the Brussels Capital Region
 The Brussels Capital Region does not belong to any province, nor does it contain any. The extraprovincial status of Brussels has existed since 1995, when the former province of Brabant, which had Brussels as its capital, was divided into the Dutch-speaking province of
The Brussels Capital Region does not belong to any province, nor does it contain any. The extraprovincial status of Brussels has existed since 1995, when the former province of Brabant, which had Brussels as its capital, was divided into the Dutch-speaking province of Flemish Brabant
Flemish Brabant ( nl, Vlaams-Brabant ; french: Brabant flamand ) is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on (clockwise from the North) the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Haina ...
and the French-speaking province of Walloon Brabant.
Within this mainly French speaking region, nearly all former provincial competencies are assumed by its regional institutions and by the French Community Commission
The ''Commission communautaire française'' (COCOF) or the French Community Commission is the local representative of the French-speaking authorities in the Brussels-Capital Region, one of the three regions of Belgium.
On 3 December 2001, the ''A ...
, the Flemish Community Commission or the Common Community Commission. However, the Arrondissement of Brussels-Capital
The Arrondissement of Brussels-Capital ( nl, Arrondissement Brussel-Hoofdstad; french: Arrondissement de Bruxelles-Capitale; german: Verwaltungsbezirk Brüssel-Hauptstadt) is the only administrative arrondissement in the Brussels Capital Region ...
has two commissioners of the Federal Government
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government (federalism). In a federation, the self-governin ...
who are called "Governor of the Brussels-Capital Region
The Governor of the Administrative Arrondissement of Brussels-Capital (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (French: ''Gouverneur de Bruxelles-Capitale'', Dutch: ''Gouverneur van Brussel-Hoofdstad'') ...
" and "Vice-Governor". The Governor exercises most of the few remaining powers elsewhere exercised by a provincial governor, particularly in the field of public order, as far as no (federal) law, (regional) decree, ordinance or decision states otherwise.
The Governor is appointed by the cabinet of the Brussels Capital Region on the unanimous advice of the Federal Council of Ministers. The regional government also appoints the Vice-Governor, who must have a considerable knowledge of both French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
and Dutch and who must ensure that the legislation regarding the use of the two languages is observed in Brussels.
Proposed additional province
 Because the
Because the German-speaking Community
The German-speaking Community (german: links=no, Deutschsprachige Gemeinschaft, or DG; french: links=no, Communauté germanophone; nl, links=no, Duitstalige Gemeenschap), since 2017 also known as East Belgium (german: links=no, Ostbelgien), is ...
is located entirely within Liège Province
Liège (; wa, Lîdje ; nl, Luik ; german: Lüttich ) is the easternmost province of the Wallonia region of Belgium.
Liège Province is the only Belgian province that has borders with three countries. It borders (clockwise from the north) the Du ...
, it has been proposed on multiple occasions to create an eleventh province, the Province of Eupen- Sankt Vith, which would comprise the nine municipalities of the German-speaking Community. Most of the functions carried out by provincial organs would then be exercised by the organs of the German-speaking Community.
The community is however small in area () and has only about 76,000 inhabitants, which would make it the smallest and by far the least populated province.
See also
*Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium
Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap.
The la ...
* List of Belgian provinces by GDP
This article lists Belgian provinces and regions (NUTS 2) by gross domestic product (GDP).
By GDP
This table reports the gross domestic product (nominal GDP), expressed in billions of euro, of the ten provinces and the Brussels capital region i ...
* List of Belgian provinces by Human Development Index
This is a list of Belgian provinces and the Region of Brussels by Human Development Index as of 2019.
See also
* List of Belgian provinces by GDP
References
{{Subnational entities by Human Development Index
Human Development Index
Bel ...
* State reform in Belgium
State reform, in the context of Belgium, is the ongoing process of seeking and finding constitutional and legal solutions to the problems and tensions in the different segments of the Belgian population, mostly between the Dutch-speakers of Flande ...
References
External links
The provinces
belgium.be
Vereniging van de Vlaamse Provincies
(Association of the Flemish Provinces)
Association des Provinces wallonnes
(Association of the Walloon Provinces) {{DEFAULTSORT:Provinces Of Belgium Subdivisions of Belgium Provinces Belgium 2 Provinces, Belgium Local government in Belgium cs:Belgie#Administrativní rozdělení de:Politische Gliederung Belgiens