Proto-Tupian Language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Proto-Tupian (PT) is the reconstructed common ancestor of all the
 Rodrigues (2007) considers the Proto-Tupian
Rodrigues (2007) considers the Proto-Tupian
A Computational-phylogenetic Classification of Tupí-Guaraní and its Geographical Spread
Language Variation and Change, October 20, Chicago. proposes that Proto-Tupi-Guarani was spoken in the region of the lower
Proto-Macro-Jê: um estudo reconstrutivo
'. Doctoral dissertation, University of Brasília. see the corresponding Portuguese article.
Tupian languages
The Tupi or Tupian language family comprises some 70 languages spoken in South America, of which the best known are Tupi language, Tupi proper and Guarani language, Guarani.
Homeland and ''urheimat''
Rodrigues (2007) considers the Proto-Tupian u ...
. It consists, therefore, of a hypothetical language, reconstructed by the comparative method
In linguistics, the comparative method is a technique for studying the development of languages by performing a feature-by-feature comparison of two or more languages with common descent from a shared ancestor and then extrapolating backwards t ...
from data of the descendant languages.
In Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, Tupian historical-comparative studies are being developed mainly by two scientific teams: one from the Laboratório de Línguas Indígenas (LALI) of the University of Brasília
The University of Brasília ( pt, Universidade de Brasília, UnB) is a federal public university in Brasília, the capital of Brazil. It was founded in 1960 and has since consistently been named among the top five Brazilian universities and the ...
, under the coordination of Aryon Rodrigues; and the other one from the Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi
The Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi (MPEG) is a Brazilian research institution and museum located in the city of Belém, state of Pará, Brazil. It was founded in 1866 by Domingos Soares Ferreira Penna as the Pará Museum of Natural History and Ethn ...
, located in Belém
Belém (; Portuguese for Bethlehem; initially called Nossa Senhora de Belém do Grão-Pará, in English Our Lady of Bethlehem of Great Pará) often called Belém of Pará, is a Brazilian city, capital and largest city of the state of Pará in t ...
, under the orientation of Denny Moore. These studies provide evidence about the Proto-Tupian economy and culture, suggesting, for example, that they had agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
.
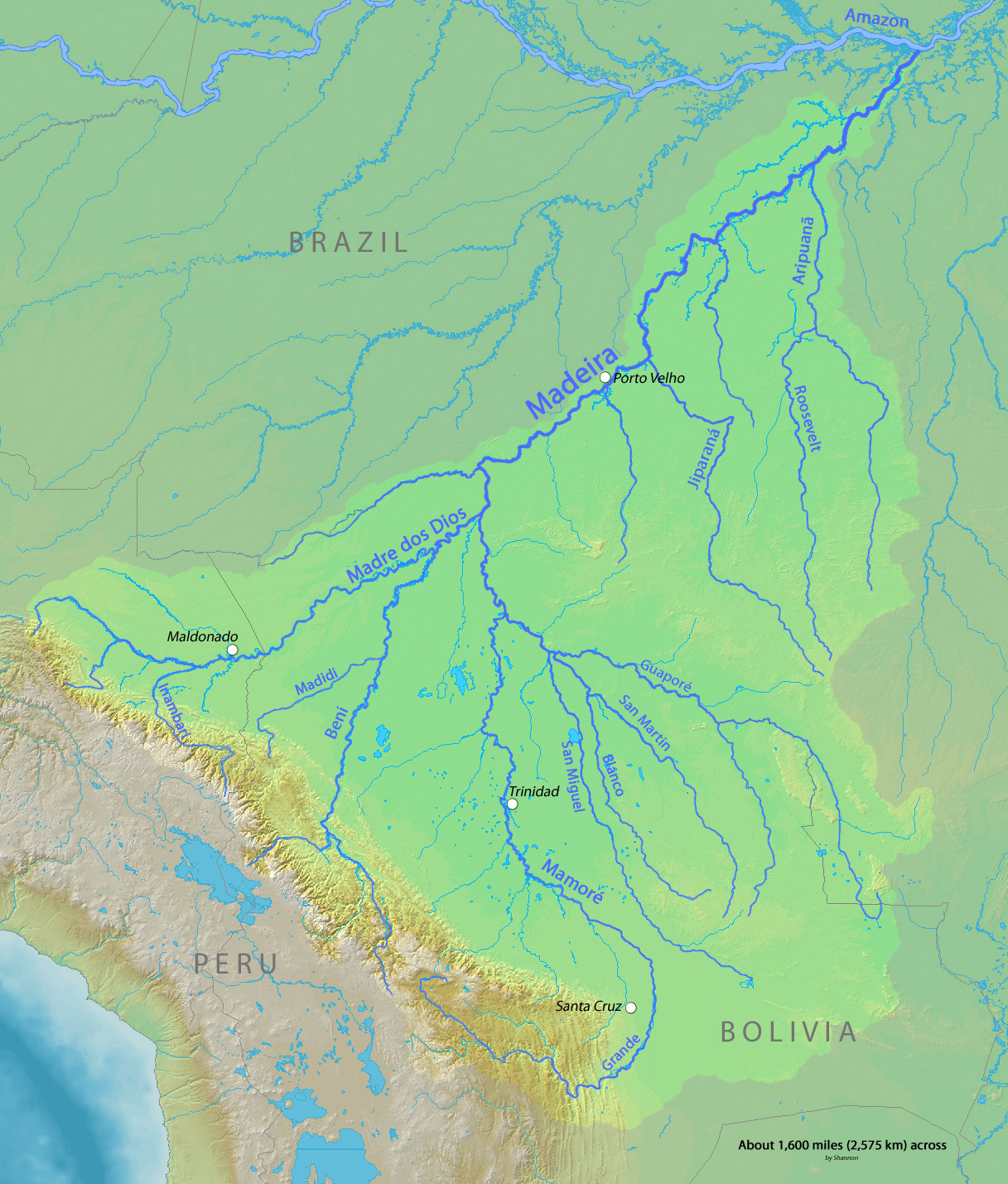
The most accepted theory is that the Tupian language family originated between the Guaporé and Aripuanã
Aripuanã is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil. It is located on the banks of the Aripuanã River
Aripuanã River ( pt, Rio Aripuanã) is a river in the Mato Grosso and Amazonas states in north-w ...
rivers, in the Madeira River
The Madeira River ( pt, Rio Madeira, link=no ) is a major waterway in South America. It is estimated to be in length, while the Madeira-Mamoré is estimated near or in length depending on the measuring party and their methods. The Madeira is ...
basin. There are currently 70 Tupian languages, including Tupi Tupi may refer to:
* Tupi people of Brazil
* Tupi or Tupian languages, spoken in South America
** Tupi language, an extinct Tupian language spoken by the Tupi people
* Tupi oil field off the coast of Brazil
* Tupi Paulista, a Brazilian municipalit ...
, Paraguayan Guarani, Awetï, Ayvu, etc.
Linguistic homeland
 Rodrigues (2007) considers the Proto-Tupian
Rodrigues (2007) considers the Proto-Tupian linguistic homeland
In historical linguistics, the homeland or ''Urheimat'' (, from German '' ur-'' "original" and ''Heimat'', home) of a proto-language is the region in which it was spoken before splitting into different daughter languages. A proto-language is the r ...
to be somewhere between the Guaporé and Aripuanã
Aripuanã is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil. It is located on the banks of the Aripuanã River
Aripuanã River ( pt, Rio Aripuanã) is a river in the Mato Grosso and Amazonas states in north-w ...
rivers, in the Madeira River
The Madeira River ( pt, Rio Madeira, link=no ) is a major waterway in South America. It is estimated to be in length, while the Madeira-Mamoré is estimated near or in length depending on the measuring party and their methods. The Madeira is ...
basin. Much of this area corresponds to the modern-day state of Rondônia
Rondônia () is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northern subdivision of the country (central-western part). To the west is a short border with the state of Acre, to the north is the state of Amazonas, in the east is Mato Grosso, ...
, Brazil. Five of the ten Tupian branches are found in this area, as well as some Tupi–Guarani languages
Tupi–Guarani () is the most widely distributed subfamily of the Tupian languages of South America. It consists of about fifty languages, including Guarani and Old Tupi.
The words ''petunia, jaguar, piranha, ipecac, tapioca, jacaranda, anhing ...
(especially Kagwahiva
Kawahíva (Kawahíb, Kagwahib) is a Tupi–Guarani dialect cluster of Brazil. The major variety is Tenharim.
The Tenharim (self-designation, Pyri 'near, together'), Parintintín, Jiahúi, Amondawa, Karipúna (not to be confused with neither th ...
), making it the probable linguistic homeland of these languages and maybe of its speaking peoples. Rodrigues believes that proto-Tupian dates back to around 5000 B.P.
O'Hagan (2014)O'Hagan, Zachary (with Keith Bartolomei, Natalia Chousou-Polydouri, Emily Clem, Erin Donnelly and Lev Michael). 2014A Computational-phylogenetic Classification of Tupí-Guaraní and its Geographical Spread
Language Variation and Change, October 20, Chicago. proposes that Proto-Tupi-Guarani was spoken in the region of the lower
Tocantins
Tocantins () is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is the newest state, formed in 1988 and encompassing what had formerly been the northern two-fifths of the state of Goiás. Tocantins covers and had an estimated population of 1,496,880 in 20 ...
and Xingu River
The Xingu River ( ; pt, Rio Xingu, ; Mẽbêngôkre: ''Byti'', ) is a river in north Brazil. It is a southeast tributary of the Amazon River and one of the largest clearwater rivers in the Amazon basin, accounting for about 5% of its water.
...
s. Proto-Omagua-Kokama then expanded up the Amazon River
The Amazon River (, ; es, Río Amazonas, pt, Rio Amazonas) in South America is the largest river by discharge volume of water in the world, and the disputed longest river system in the world in comparison to the Nile.
The headwaters of t ...
, Proto-Tupinamba expanded south along the Atlantic coast, and the Southern branch expanded up along the Tocantins/Araguaia River
The Araguaia River ( pt, Rio Araguaia , Karajá: ♂ ''Berohokỹ'' eɾohoˈkə̃ ♀ ''Bèrakuhukỹ'' ɛɾakuhuˈkə̃ is one of the major rivers of Brazil though it is almost equal in volume at its confluence with the Tocantins. It has a total ...
towards the Paraná River
The Paraná River ( es, Río Paraná, links=no , pt, Rio Paraná, gn, Ysyry Parana) is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some ."Parana River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Br ...
basin.
Lexicon
This section lists Proto-Tupían reconstructions from Rodrigues and Cabral (2012). Since the reconstructions are highly tentative, the Proto-Tupían forms are all marked by two asterisks. For a list of Proto-Tupian reconstructions by Nikulin (2020),Nikulin, Andrey. 2020.Proto-Macro-Jê: um estudo reconstrutivo
'. Doctoral dissertation, University of Brasília. see the corresponding Portuguese article.
Independent nouns
Proto-Tupian independent nouns: ;Human beings: * **apʷũ ‘person’/‘who’ * **aɨče ‘man’ * **pet ‘woman’ * **orʲe ‘we, I; he/they’ * **ru ‘fellow’ ;Animals: * **ɨčɨ ‘deer’ * **ameko ‘jaguar’ * **aʔɨ ‘sloth’ * **awuru/aworo ‘parrot’ * **arat ‘macaw’ * **moj ‘snake’ * **ɨp ‘fish’ * **enem ‘beetle’ * **ŋap ‘wasp’ ;Plants: * **mani ‘manioc
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated a ...
’
* **awa/awai ‘yams’
* **ɨčɨpo ‘vine’
* **kʔɨp ‘tree, wood’
* **kɨče ‘bamboo’
* **ɨʔa ‘calabash
Calabash (; ''Lagenaria siceraria''), also known as bottle gourd, white-flowered gourd, long melon, birdhouse gourd, New Guinea bean, Tasmania bean, and opo squash, is a vine grown for its fruit. It can be either harvested young to be consumed ...
’
* **wetʲɨk ‘sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the Convolvulus, bindweed or morning glory family (biology), family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a r ...
’
;Nature:
* **ŋʷat ‘sun’
* **watɨ ‘moon’
* **ɨpʷɨ ‘earth’
* **aman ‘rain’
* **ičʔɨ ‘river’
* **wita ‘stone’
* **ʔat ‘day’
Dependent nouns
Proto-Tupian dependent nouns: ;Kinship: * **amõj ‘grandfather’ * **up ‘father’ * **čɨ ‘mother’ * **aʔɨt ‘son of a man’ * **ɨket ‘older sister of a woman’ * **kɨpʷɨt ‘brother of a woman’ ;Parts of the body of animals: * **po ‘hand’ * **ʔa ‘head’ * **ap ‘hair’ * **apɨ ‘ear’ * **pepʔo ‘wing’ * **uwaj ‘tail’ * **kaŋ ‘bone’ ;Parts of plants: * **epʷ ‘leaf’ * **akã ‘branch’ * **potʔɨt ‘flower’ * **wu ‘thorn’ ;Artifacts: * **ekʷʔɨp ‘arrow’ * **wɨ ‘ax’ * **ɨrʲu ‘basket’ * **waʔẽ ‘pot’ * **čʔam ‘rope’ * **atʲa ‘fire’ * **ekʷ ‘house’ * **moʔɨt ‘necklace’ ;Sensations, feelings, and attributes * **ačɨ ‘ache’ * **akʲup ‘warm’ * **ečaraj ‘forgetful’ * **pocɨj ‘heavy’ * **acʔaŋ ‘thick’Verbs, affixes, and others
Proto-Tupian verbs, affixes, and other parts of speech: ;Positional verbs * **ʔam ‘to stand’ * **up ~ wup ‘to lie’ * **in ‘to sit’ * **eko ‘to be moving’ * **kup ‘to be.plural’ ;Motion /directional verb
The grammar of American Sign Language (ASL) is the best studied of any sign language, though research is still in its infancy, dating back only to William Stokoe in the 1960s.
Morphology
ASL morphology is to a large extent iconic. This shows ...
s
* **ka ‘to go’
* **co ‘to go’
* **ut ~ **wut ‘to come’
;Dicendi / faciendi verb
* **kʔe ‘to say/to do’
;Postpositions
* **pe ‘punctual locative/dative’
* **ka ‘allative’
* **wo ~ mo ‘diffuse locative’
* **ece ‘relative’/‘associative’
* **eɾi, **wi ‘ablative’
* **eɾʲo ~ **eɾʲe ‘associative’
* **coče ‘superessive’
* **na ‘translative’
;Derivational valence changing prefixes
* **mo- ‘causative prefix’
* **eɾʲo- ~ **eɾʲe- ‘causative-comitative prefix’
* **we- ‘reflexive prefix’
* **wo- ‘reciprocal prefix’
Cultural vocabulary
Proto-Tupían cultural vocabulary (Rodrigues and Cabral 2012): :See also
*Apapocuva
The Apapocúva (Apapokuva), also known as the Nandeva, are an agricultural Tupian tribe of the group of southern Brazil, living in the state of São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, a ...
* Indigenous languages of the Americas
Over a thousand indigenous languages are spoken by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. These languages cannot all be demonstrated to be related to each other and are classified into a hundred or so language families (including a large numbe ...
* Languages of Brazil
Portuguese is the official and national language of Brazil being widely spoken by most of the population. Brazil is the most populous Portuguese-speaking country in the world, being the only country colonized by the Portuguese in the Americas. ...
* Lingua Geral
Lingua (Latin, 'tongue') may refer to:
* ''Lingua'' (journal), a peer-reviewed academic journal of general linguistics
* ''Lingua'' (sculpture), by Jim Sanborn
* ''Lingua'' (play), a 17th-century play attributed to Thomas Tomkis
* Project Lingu ...
* List of Spanish words of Indigenous American Indian origin
This is a list of Spanish words that come from indigenous languages of the Americas. It is further divided into words that come from Arawakan, Aymara, Carib, Mayan, Nahuatl, Quechua, Taíno, Tarahumara, Tupi and uncertain (the word is known to b ...
References
Further reading
* * * *Rodrigues, Aryon Dall'Igna (2007). "As consoantes do Proto-Tupí". In Ana Suelly Arruda Câmara Cabral, Aryon Dall'Igna Rodrigues (eds). ''Linguas e culturas Tupi'', p. 167-203. Campinas: Curt Nimuendaju; Brasília: LALI. {{DEFAULTSORT:Proto-Tupian LanguagesTupian
The Tupi or Tupian language family comprises some 70 languages spoken in South America, of which the best known are Tupi proper and Guarani.
Homeland and ''urheimat''
Rodrigues (2007) considers the Proto-Tupian urheimat to be somewhere between ...