Projectile Use By Non-human Organisms on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Although projectiles are commonly used in human conflict, projectile use by
Although projectiles are commonly used in human conflict, projectile use by
 Some New World
Some New World
 Chameleons,
Chameleons,
Nature's Marksmen - a video showing projectile use by archerfish and velvet worms
Ballistics Ethology
 Although projectiles are commonly used in human conflict, projectile use by
Although projectiles are commonly used in human conflict, projectile use by organisms
In biology, an organism () is any life, living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy (biology), taxonomy into groups such as Multicellular o ...
other than humans is relatively rare.
Animals
Liquid projectiles
Most projectiles used by terrestrial animals are liquids. Among invertebrates there are a number of examples.Velvet worm
Onychophora (from grc, ονυχής, , "claws"; and , , "to carry"), commonly known as velvet worms (due to their velvety texture and somewhat wormlike appearance) or more ambiguously as peripatus (after the first described genus, '' Peripatus ...
s can squirt out an slimy adhesive fluid from glands on the sides of their head, and use it to trap their prey. The spitting spider
Spitting spiders (Scytodidae) is a family of Araneomorphae, araneomorph spiders first described by John Blackwall in 1864. It contains over 250 species in five genus, genera, of which ''Scytodes'' is the best-known.
Description
Like Sicariidae, ...
s ''Scytodes
''Scytodes'' is a genus of Scytodidae, spitting spiders that occur all around the world. The most widely distributed species is ''Scytodes thoracica'', which originally had a Palearctic realm, palearctic distribution, but has been introduced to ...
'' can spit a venomous sticky fluid that traps its victims and also poisons them. The bombardier beetle is unusual by using a violent exothermic chemical reaction to launch a boiling noxious chemical spray in a rapid burst of pulses from special glands in its abdomen, accompanied with a popping sound. The ''Anthia
''Anthia'' (common name saber-toothed ground beetles) is a genus of the ground beetle family (Carabidae). Species of ''Anthia'' can spray a jet of formic acid up to , which, if not treated, can cause blindness in animals that harass the beetles ...
'' (oogpister beetle) will fire formic acid at attackers, probably extracting the formic acid from the ants that it eats. The devil-rider stick insects ('' Anisomorpha'') can fire terpenes
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n > 1. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes ar ...
from glands on the metathorax
The metathorax is the posterior of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the third pair of legs. Its principal sclerites ( exoskeletal plates) are the metanotum (dorsal), the metasternum (ventral), and the metapleuron (lateral) ...
that can cause an intense burning irritation of the eyes and mouth of potential predators. Wood ants will spray acid at attackers. A type of planthopper of Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
is able to flick small balls of honeydew, this attracts day gecko
''Phelsuma'' is a large genus of geckos in the Family (biology), family Gekkonidae. Species in the genus ''Phelsuma'' are commonly referred to as day geckos.
Some day geckos are seriously endangered and some are common, but all ''Phelsuma'' spec ...
s that feed on the honeydew and whose presence may deter predators from approaching the sap-sucking insect. Termite
Termites are small insects that live in colonies and have distinct castes (eusocial) and feed on wood or other dead plant matter. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blatto ...
s of the North American
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Ca ...
subfamily Nasutitermitinae
The Nasutitermitinae are a subfamily of higher termites that includes more than 80 genera. They are most recognisable by the more highly derived soldier caste which exhibits vestigial mandibles and a protruding fontanellar process on the head ...
can project a sticky fluid from a nozzle on their heads. They can use this fontanellar gun
The fontanellar gun is a defense mechanism in the form of a horn-like frontal projection (''nasus'') on the head of the soldier caste which is capable of expelling chemical weaponry at a distance, a trait exclusive to the subfamily Nasutitermitina ...
accurately, over a range of many centimeters, even though the termite is blind, possibly using auditory or olfactory cues instead.
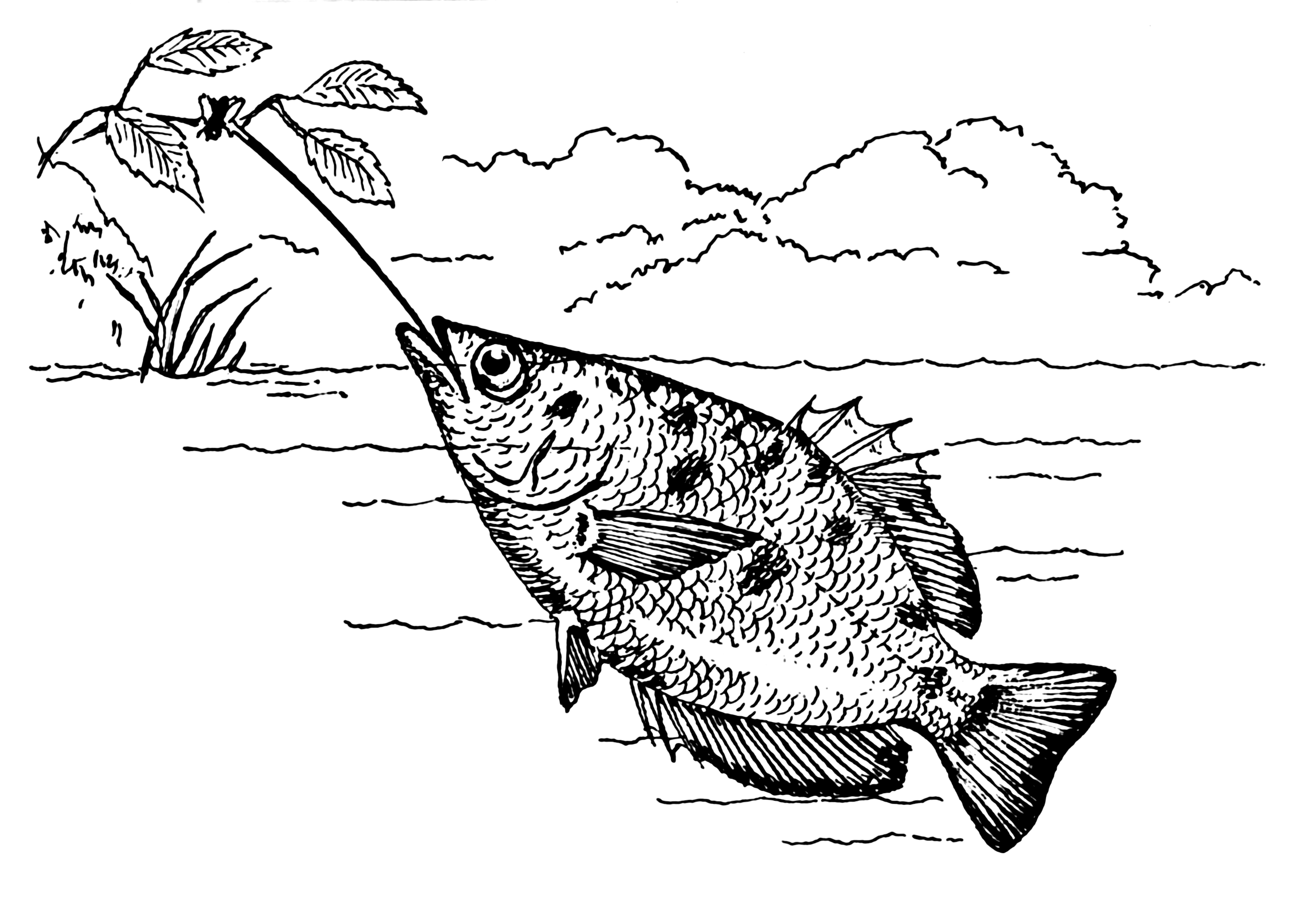
A number of vertebrates also use liquid projectiles. The archerfish
The archerfish (spinner fish or archer fish) form a monotypic family, Toxotidae, of fish known for their habit of preying on land-based insects and other small animals by shooting them down with water droplets from their specialized mouths. ...
will squirt water from its mouth to dislodge invertebrates from overhanging branches. Some diptodactyline geckos can fire a black or pale yellow sticky fluid out of glands in their tail for a distance of about a meter, and with good aim. This fluid has a musky unpleasant odour and although it is not toxic it may discourage predators, in particular the big arthropods that prey on these geckos. The spitting cobra
A spitting cobra is any of several species of cobras that can defensively spray a toxic secretion - functioning as both a venom (that can be injected via a wound) and a toxungen (that can be sprayed on the target surface) - from their fangs in ...
can squirt venom from forward-facing holes in its fangs. It aims for its victim's eyes, spitting up to 1.5 m. The venom may cause blindness. The Mangshan pitviper
''Protobothrops mangshanensis'', commonly known as the Mangshan pit viper, Mangshan pitviper, Mt. Mang pitviper, or Mang Mountain pitviper,Gumprecht A, Tillack F, Orlov NL, Captain A, Ryabov S. 2004. ''Asian Pitvipers''. Geitje Books. Berlin. 1 ...
is also reported to spit venom.
A bird that uses liquid projectiles in defense is the southern giant petrel which produces a stomach oil made up of wax esters and triglycerides that are stored in the proventriculus and can be projectile vomited on predators. Other petrel
Petrels are tube-nosed seabirds in the bird order Procellariiformes.
Description
The common name does not indicate relationship beyond that point, as "petrels" occur in three of the four families within that group (all except the albatross f ...
s such as the fulmar
The fulmars are tubenosed seabirds of the family Procellariidae. The family consists of two extant species and two extinct fossil species from the Miocene.
Fulmars superficially resemble gulls, but are readily distinguished by their flight on ...
can also squirt oils from their mouths as a defense. They can squirt oils with accuracy up to a distance of 1 to 2 meters. The oil mats the feathers of birds together and destroys their waterproofing abilities, so oiled birds may die from chilling or drowning, although fulmars seem able to remove the oil from themselves by preening. Birds ranging from gulls to sea-eagles have died after being squirted by fulmars. Some species of penguin expel liquid feces in a projectile manner, to a distance of up to about 50 cm. They are believed to do this because during the brooding season, when penguins are sitting on their nests, they avoid leaving their nests and thereby leaving their eggs open to predation and thus to maintain a clean nest they evolved the ability to project their feces.
Among mammals, skunks can eject a noxious fluid from glands near their anus. It is not only foul smelling, but can cause skin irritation and, if it gets in the eyes, temporary blindness. When it feels threatened a camel will bring up their stomach contents, along with saliva, and project it out towards the threat to distract, surprise, or bother the threat.
Solid projectiles
tarantulas
Tarantulas comprise a group of large and often hairy spiders of the family Theraphosidae. , 1,040 species have been identified, with 156 genera. The term "tarantula" is usually used to describe members of the family Theraphosidae, although ...
have a dense covering of hairs called urticating hair
Urticating hairs or urticating bristles are one of the primary defense mechanisms used by numerous plants, almost all New World tarantulas, and various lepidopteran caterpillars. ''Urtica'' is Latin for "nettle" (stinging nettles are in the genu ...
s on the abdomen that they sometimes use as protection against enemies.Cooke, J.A.L., Roth, V.D., Miller, F.H. (1972). The urticating hairs of theraphosid spiders. ''American Museum Novitates'' 2498. Species with urticating hairs can kick these hairs off; they are flicked into the air at a target using their back pairs of legs. These fine hairs are barbed and designed to irritate and can be lethal to small animals such as rodents. The symptoms range from a burning itch to a minor rash, from being lethal to simply being a deterrent. With humans, they can cause irritation to the eyes, nose, and skin, and more dangerously, the lungs and airways, if inhaled. In some cases, tarantula hairs have caused permanent damage to human eyes. Urticating hairs do not grow back, but are replaced with each moult.
Another invertebrate, the antlion, also makes use of solid projectiles. The antlion lies at the bottom of a sloping pit that it digs in the sand. Small prey slip into the pit on the loose substrate. If the prey crawls up the slopes of the pit, the antlion throws sand at the prey, which may dislodge it and send it back down the pit.
In gastropods, cone snails
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines co ...
have modified radula tooth which is stored in the radular sac and at the end of proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elong ...
, acting like a harpoon. Their "harpoon" is venomous, which assists cone snail to paralyze or kill the prey before eating it.
A number of vertebrate species also make use of solid projectiles. Among birds the hornbill uses projectile motion to eat food. The hornbill's beak typically only contacts at the tip, and it has a short tongue. To swallow food the hornbill instead throws the food from the tip of its long bill backwards into the throat. One example of solid projectile use among mammals is the California ground squirrel, which is known to distract predators such as the rattlesnake and gopher snake
''Pituophis'' is a genus of non venomous colubrid snakes, commonly referred to as gopher snakes, pine snakes, and bullsnakes, which are endemic to North America.
Geographic range
Species and subspecies within the genus ''Pituophis'' are found t ...
from locating their nest burrows by kicking sand into their eyes. A wild female African elephant has also been observed to throw various materials at an interfering rhino. Orca
The orca or killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is the only extant species in the genus '' Orcinus'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white ...
s have been observed to throw seal prey using their tail flukes in apparent play behavior. Some primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s, including human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s, can throw
Throwing is an action which consists in accelerating a projectile and then releasing it so that it follows a ballistic trajectory, usually with the aim of impacting a remote target. This action is best characterized for animals with prehensil ...
objects such as rocks, sticks, and feces as projectiles. Primates that are known to throw are humans, bonobos, chimpanzees, gorilla
Gorillas are herbivorous, predominantly ground-dwelling great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or fi ...
s, orangutan
Orangutans are great apes native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia. They are now found only in parts of Borneo and Sumatra, but during the Pleistocene they ranged throughout Southeast Asia and South China. Classified in the genu ...
s, capuchins, certain gibbons and perhaps some baboon
Baboons are primates comprising the genus ''Papio'', one of the 23 genera of Old World monkeys. There are six species of baboon: the hamadryas baboon, the Guinea baboon, the olive baboon, the yellow baboon, the Kinda baboon and the chacma ...
s and Japanese macaque
The Japanese macaque (''Macaca fuscata''), also known as the snow monkey, is a terrestrial Old World monkey species that is native to Japan. Colloquially, they are referred to as "snow monkeys" because some live in areas where snow covers the gr ...
s (although not rhesus macaques
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally ...
). A chimpanzee named Santino in a Swedish zoo was observed to stockpile stones to be used as missiles against visitors.
Tethered projectiles
 Chameleons,
Chameleons, frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is ...
s and some lungless salamander
Plethodontidae, or lungless salamanders, are a family of salamanders. Most species are native to the Western Hemisphere, from British Columbia to Brazil, although a few species are found in Sardinia, Europe south of the Alps, and South Korea. In ...
s have tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ...
s that act like a tethered projectile. In frogs, the tongue is attached at the front of the mouth and rotates about this attachment as it flips out (thus the top of the tongue at rest becomes the bottom when extended). In chameleons, the tongue contracts against a tapered hyoid
The hyoid bone (lingual bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. ...
bone, eventually slipping off and projecting forward at very high speed. Lungless salamanders use a similar method, however, both the tongue and underlying hyoid bone project (in contrast to chameleons, whose hyoid remains fixed while the fleshy portion of the tongue projects). In both salamanders and chameleons, the movement is too fast and requires too much mechanical power for muscle alone to provide – instead, muscles slowly pre-load elastic elements such as connective tissue, which can then recoil and release the stored energy at a much higher rate. In order to retract their tongues over such great distances, the tongue muscles of chameleons have perforated Z-disk
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called musc ...
s, allowing each sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called mus ...
to shorten far greater distances than those of other vertebrates.
Bubbles
Thepistol shrimp
Alpheidae is a family of caridean snapping shrimp, characterized by having asymmetrical claws, the larger of which is typically capable of producing a loud snapping sound. Other common names for animals in the group are pistol shrimp or alpheid s ...
claw has a pistol-like feature made of two parts. A joint allows the "hammer" part to move backward into a right-angled position. When released, it snaps into the other part of the claw, emitting an enormously powerful wave of bubbles capable of stunning larger fish and breaking glass.
Plants and fungi
Theseed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiospe ...
pods of the orange jewelweed have projectile seeds that, if ripe, explode out of the pods when they are lightly touched. The seed pods of the scotch broom
''Cytisus scoparius'' ( syn. ''Sarothamnus scoparius''), the common broom or Scotch broom, is a deciduous leguminous shrub native to western and central Europe. In Britain and Ireland, the standard name is broom; this name is also used for other ...
also burst open, often with an audible crack, projecting the seeds from the parent plant. Similarly, the fruit of the sandbox tree
''Hura crepitans'', the sandbox tree, also known as possumwood and jabillo, is an evergreen tree of the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae), native to tropical regions of North and South America including the Amazon rainforest. It is also present in p ...
burst open to disperse seeds, but the reaction is so violent that it can injure nearby people or livestock. Some plants such as the dogwood bunchberry and white mulberry will also fling pollen from their flowers. Peat moss
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store wa ...
es are known to explosively launch their spores.
Hat-throwing fungi fire their spore capsules up to 2 m, and the cannonball fungi of the genus '' Sphaerobolus'', such as ''S. stellatus'', the artillery fungus can throw sticky spore sacs up to 6 m horizontally. This species is phototropic, and propels spores towards the nearest source of direct or reflected light, like the sides of brightly colored houses.
References
{{Reflist, 2External links
Nature's Marksmen - a video showing projectile use by archerfish and velvet worms
Ballistics Ethology