Product planning on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Product Planning, or product discovery, is the ongoing

 Product planning must also include managing the product through various stages of its
Product planning must also include managing the product through various stages of its
process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic.
Things called a process include:
Business and management
*Business process, activities that produce a specific se ...
of identifying and articulating market requirements that define a product's feature set. It serves as the basis for decision-making about price, distribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
* Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a vari ...
and promotion. Product planning is also the means by which companies and businesses can respond to long-term challenges within the business environment, often achieved by managing the product throughout its life cycle using various marketing strategies, including product extensions or improvements, increased distribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
* Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a vari ...
, price
A price is the (usually not negative) quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services. In some situations, the price of production has a different name. If the product is a "good" in the c ...
changes and promotions. It involves understanding the needs and wants of core customer groups so products can target key customer desires and allows a firm to predict how a product will be received within a market upon launch.
The product planning process

Developing the product concept
In theproduct concept
A product concept is a description of a product or service, at an early stage in the product lifecycle. It is generated before any detailed design work is undertaken and takes into consideration market analysis, customer experience, product feature ...
phase, managers generate ideas for new products by identifying certain problems that consumers face or various customers needs. For example, a small computer retailer may see the need to create a computer repair division for the products it sells. After idea conception, managers may plan the dimensions
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coordina ...
and features of the product and develop a trial product
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
Mathematics
* Produ ...
.
Studying the market
The next step is engaging in acompetitor
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indivi ...
analysis. Secondary research usually provides details on key competitors
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indivi ...
and their market share
Market share is the percentage of the total revenue or sales in a market that a company's business makes up. For example, if there are 50,000 units sold per year in a given industry, a company whose sales were 5,000 of those units would have a ...
, which is the percent of total sales that they hold in the marketplace. The business can then determine places in which it has an advantage over the competition to identify areas of opportunity.
Market research
Market research is one stage of product planning and is regarded as the way to accomplish the activity though designing questions, preparing the samples, collecting data and analysing them. It provides significant insight into customers wants, needs, buying habits and behaviours and is a key tool used in the product planning process. For example, customer satisfaction information can be obtained through surveys and market research. The process consists of 4 components:definition
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions (which try to give the sense of a term), and extensional definitio ...
, collection, analysis
Analysis ( : analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (38 ...
and interpretation.Zikmund, W., D’Alessandro, S., Winzar, H., Lowe, B., & Babin, B. (2017). ''Marketing research : Asia-Pacific edition'' (4th edition.). Cengage Learning.
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Both qualitative andquantitative marketing research
Quantitative marketing research is the application of quantitative research techniques to the field of marketing research. It has roots in both the positivist view of the world, and the modern marketing viewpoint that marketing is an interactive ...
techniques can be used within marketing research. The aim of qualitative research
Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This ...
is to gather an in-depth understanding of human behavior
Human behavior is the potential and expressed capacity ( mentally, physically, and socially) of human individuals or groups to respond to internal and external stimuli throughout their life. Kagan, Jerome, Marc H. Bornstein, and Richard M. L ...
and the reasons
In the most general terms, a reason is a consideration which justifies or explains an action, a belief, an attitude, or a fact.
''Normative reasons'' are what people appeal to when making arguments about what people should do or believe. For exa ...
that govern such behaviour. The qualitative method investigates the why and how of decision making, not just what, where, when. Hence, smaller but focused samples are more often used than large samples. Quantitative research refers to the systematic empirical investigation of social phenomena via statistical
Statistics (from German: ''Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industria ...
, mathematical
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
or numerical data or computational techniques. The objective of quantitative research
Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philosop ...
is to develop and employ mathematical
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
models
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure.
Models c ...
, theories
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be s ...
and/or hypotheses
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous obser ...
pertaining to phenomena.
Market researchers use quantitative
Quantitative may refer to:
* Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties
* Quantitative analysis (disambiguation)
* Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry
* Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis ...
and qualitative research to gain better and more complete perspectives about a market segment
In marketing, market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market, normally consisting of existing and potential customers, into sub-groups of consumers (known as ''segments'') based on some type of shared charact ...
or hypothesis. Qualitative research involves consideration and analysis that are non-numerical in nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physics, physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomenon, phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. ...
, which includes questions of "how" and "what". Qualitative research is suited to solve the problem areas of basic market exploratory studies, product development and diagnostic studies. In market exploratory studies, the research findings can be used to define consumer segmentations in relation to a product brand
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create an ...
or understand the dimensions which differentiate between brands. In new product development, product, packaging, positioning and advertising information can be collected through researching to confirm a new product proposition. In diagnostic studies, qualitative research is used to determine how the brand image
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's good or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create a ...
has changed since the start of an advertising campaign
An advertising campaign is a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme which make up an integrated marketing communication (IMC). An IMC is a platform in which a group of people can group their ideas, beliefs, and conc ...
.
Research Methods
The methods of qualitative research can be departed into observation andfocus groups
A focus group is a group interview involving a small number of demographically similar people or participants who have other common traits/experiences. Their reactions to specific researcher/evaluator-posed questions are studied. Focus groups are ...
. Recently, observation is used in observation-based researches, in which people may not articulate correctly and clearly of their thoughts. A particular example is the application in in-store shopping surveys, which regularly allow customers to try the products and gather feedback. Focus group is a tool on the basis of psychotherapy where it has found that if people are divided into small groups and asked to share their opinions suggestions, and open up. Because there will generate a brainstorming effect in the groups so that a comment from one person can stimulate another one's ideas. In general, there are always need four groups to cover a single respondent type. The outcomes of group discussions rely on the group leaders’ abilities of structuring
Structuring, also known as smurfing in banking jargon, is the practice of executing financial transactions such as making bank deposits in a specific pattern, calculated to avoid triggering financial institutions to file reports required by law ...
the discussion, conducting the meeting and analysing and understanding the results.
Quantitative research
Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philosop ...
is about understanding aspects of a market or what kinds of customers make up the market. It can be split into soft and hard parts. Soft parts refer to phenomena like customer attitudes and hard part is market size, brand shares and so on. Quantitative researchers are different from qualitative researchers, they pay more attention to asking 'What' questions. Quantitative research often provides three aims: description
Description is the pattern of narrative development that aims to make vivid a place, object, character, or group. Description is one of four rhetorical modes (also known as ''modes of discourse''), along with exposition, argumentation, and narr ...
, forecasting
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared (resolved) against what happens. For example, a company might estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the actual ...
and decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
. Quantitative market research means getting relevant information or measures from each single customer or shopper who are carrying out a census in the market. It is based on the strict sampling methods so that its data or results have levels of accuracy and can be taken to represent and stand for the population or to projecting.
If the survey results prove favorable, the company may decide to sell the new product on a small scale or regional
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
basis. During this time, the company will distribute the products in one or more cities. The company will run advertisements
Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a product or service. Advertising aims to put a product or service in the spotlight in hopes of drawing it attention from consumers. It is typically used to promote a ...
and sales promotions for the product, tracking sales results to determine the products potential success.
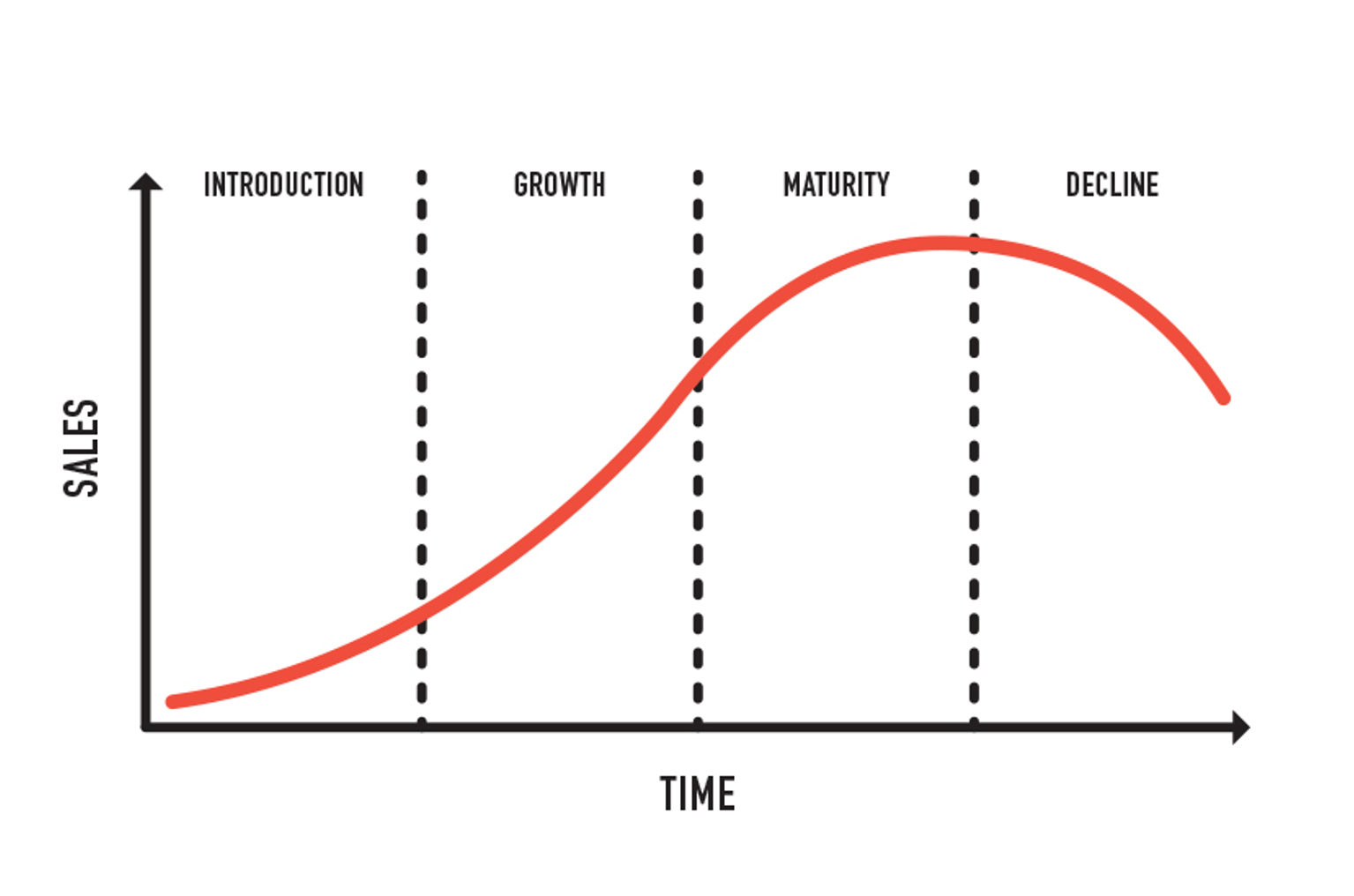
Product life cycle
 Product planning must also include managing the product through various stages of its
Product planning must also include managing the product through various stages of its product life cycle
In industry, Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM ...
. These stages include the introduction
Introduction, The Introduction, Intro, or The Intro may refer to:
General use
* Introduction (music), an opening section of a piece of music
* Introduction (writing), a beginning section to a book, article or essay which states its purpose and g ...
, growth, maturity and decline stages. Sales are usually strong during the growth phase, while competition is low. However, continued success of the product will pique the interest of competitors, which will develop products of their own. The introduction of these competitive products may force a small company to lower its price. This low pricing strategy may help prevent the small company from losing market share. The company may also decide to better differentiate its product to keep its prices steady. For example, a small cell phone company may develop new, useful features on its cell phones that competitors do not have. Product life cycle
In industry, Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. PLM ...
can be viewed as an important source of investment decision for the company.
If a company or brand wants to make sure that its products are successful, it needs to study the product life cycle to analyze market attractiveness and supplement the conclusion before it launches a new product or enters a new market. Product life cycle plays an important role in marketing. The first reason is that the managers will follow the four stages to make product plans for pushing out new products. Secondly, the level and growth of sales will change a lot during the four stages so the managers need to adjust the product plan appropriately and timely. The last one is that the prices and costs will decrease markedly in the early stages of the product life cycle. Marketing Science, 2004
Introduction
The first stage is the introduction (or market development), when a product is first brought to market. The goal in this stage is to attract customers’ attention as much as possible and confirm the products’ initialdistribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
* Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a vari ...
. In this stage will be the first communication
Communication (from la, communicare, meaning "to share" or "to be in relation with") is usually defined as the transmission of information. The term may also refer to the message communicated through such transmissions or the field of inquir ...
between marketers and customers relating to this product and will be the first time the consumer is aware of the product. In addition, the cost of the things will be high like research, testing and development and the sales are low as the customer base is small.
Growth
The second stage is growth. In this stage, the new products have been accepted in the market and their sales and profits has begun to increase, the competition has happened so that the company will promote their quality to stay competitive. The products also have basic consumers’ attention and can develop their loyal customers. There will have second communication as marketers can start to receive customers’ feedback and then make improvements.Maturity
The third stage is maturity where the sales and profit have grown slowly and will reach their peak. The firm will face fierce competition in terms of providing high quality products.Decline
The last stage is decline which means the product is going to end and be discontinued. The sales of product will decrease until it is no longer in demand as it has become saturated, all the customers who want to buy this product has already got that. Then the company or brand will cut down the old products and pays attention to designing and developing the new products to gain back the customer base, stay in the markets and make profits.References
{{reflist Product management