Privileged Transit Traffic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Privileged transit traffic or corridor traffic is traffic of one country across the territory of another country without usual customs and passport checks. The corresponding line of communication (usually a railway) is called the (privileged) traffic corridor and a train used in this kind of transit is called a corridor train (german: Korridorzug, it, Treno-corridoio). The reason for such arrangements is usually border changes or border creation which cut through an existing transport corridor.
Privileged transit traffic or corridor traffic is traffic of one country across the territory of another country without usual customs and passport checks. The corresponding line of communication (usually a railway) is called the (privileged) traffic corridor and a train used in this kind of transit is called a corridor train (german: Korridorzug, it, Treno-corridoio). The reason for such arrangements is usually border changes or border creation which cut through an existing transport corridor.

 *A historical case of privileged transit was the arrival of
*A historical case of privileged transit was the arrival of
 Privileged transit traffic or corridor traffic is traffic of one country across the territory of another country without usual customs and passport checks. The corresponding line of communication (usually a railway) is called the (privileged) traffic corridor and a train used in this kind of transit is called a corridor train (german: Korridorzug, it, Treno-corridoio). The reason for such arrangements is usually border changes or border creation which cut through an existing transport corridor.
Privileged transit traffic or corridor traffic is traffic of one country across the territory of another country without usual customs and passport checks. The corresponding line of communication (usually a railway) is called the (privileged) traffic corridor and a train used in this kind of transit is called a corridor train (german: Korridorzug, it, Treno-corridoio). The reason for such arrangements is usually border changes or border creation which cut through an existing transport corridor.
Examples
Belgium
*Vennbahn
The (, "Fen Railway") is a former railway line that was built partly across what was then German territory by the Prussian state railways. It is now entirely in Belgium, because the trackbed of the line, as well as the stations and other instal ...
was a railway built 1885 at the time fully in Germany. In 1919 some areas were transferred to Belgium. The railway did as a result cross the new border several times. To handle this, the railway embankment with tracks were also made Belgian territory if inside Germany, without having border controls at the road-rail crossings. The railway was dismantled in 2008, although the embankment still belongs to Belgium.
Estonia
*The road fromVärska
Värska ( seto, Verska) is a Populated places in Estonia, small borough () in Setomaa Parish, Võru County in southeastern Estonia. At the 2011 Estonia Census, 2011 Census, the settlement's population was 443.
History
Värska was first historica ...
to Ulitina
Ulitina is a village in Setomaa Parish, Võru County in southeastern Estonia. (retrieved 28 July 2021)
Ulitina and its neighbouring villages ( Kundruse, Litvina, Pattina, Perdaku, Saabolda, Saatse, Samarina and Sesniki) are notable as p ...
in Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
, the only road to the Ulitina area, goes through Russian territory for one kilometre (0.6 mi) of its length, an area called Saatse Boot
Saatse ( seto, Satserina) is a village in Setomaa Parish, Võru County in southeastern Estonia. It has a population of 89 (as of 2007).
Saatse and its neighbouring villages ( Kundruse, Litvina, Pattina, Perdaku, Saabolda, Samarina, Sesniki ...
. This road has no border control, but there is no connection to any other road in Russia. It is not permitted to stop or walk along the road. This area is a part of Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
but is also a de facto part of the Schengen area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
. This arrangement started in 1991 and remains to the present.
Finland
* Finlandleases
A lease is a contractual arrangement calling for the user (referred to as the ''lessee'') to pay the owner (referred to as the ''lessor'') for the use of an asset. Property, buildings and vehicles are common assets that are leased. Industrial ...
the -long Russian part of the Saimaa Canal
The Saimaa Canal ( fi, Saimaan kanava; sv, Saima kanal; russian: Сайменский канал) is a transportation canal that connects lake Saimaa with the Gulf of Finland near Vyborg, Russia. The canal was built from 1845 to 1856 and opened ...
from Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and is granted extraterritoriality
In international law, extraterritoriality is the state of being exempted from the jurisdiction of local law, usually as the result of diplomatic negotiations.
Historically, this primarily applied to individuals, as jurisdiction was usually cla ...
rights. Russian visas are not required just to pass through the canal, but a passport is needed, and it is checked at the border.
Poland
*A 1931 agreement betweenPoland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
for railway traffic between parts of Poland across Romania, between Zaleszczyki
Zalishchyky ( ; uk, Залiщики, Zalishchyky; pl, Zaleszczyki), also spelled Zalischyky, is a small city located on the Dniester river in Chortkiv Raion of Ternopil Oblast (province), in western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Za ...
and Jasienów Polny (now Yaseniv-Pil'nyi). Since 1945, both places have been in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
.
*During the years between the world wars German trains could travel to and from East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
across the Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (Pomeranian Voivodeship, eastern ...
with legally sealed doors, thereby relieving the passengers of the need to obtain Polish visas.
Russia
*Railway connection between mainlandRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and its Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast (russian: Калинингра́дская о́бласть, translit=Kaliningradskaya oblast') is the westernmost federal subject of Russia. It is a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic Sea. The largest city and administr ...
exclave across Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
. This was not privileged between 2007 and 2020 since normal passport and visa rules apply (since Lithuania entered the Schengen area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
in 2007).
Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
in 2020, the train has become privileged transit traffic again due to border closure by Lithuania, and now trains run non-stop through the territory of Lithuania.
Slovenia
*The road to the Brda region of Slovenia, betweenSolkan
Solkan ( or ; it, Salcano, german: link=no, Sollingen or ''Salcano'') is a settlement in the Municipality of Nova Gorica in the Gorizia region of western Slovenia, at the border with Italy. Although it forms a single urban area with the city of N ...
and Podsabotin
Podsabotin (, it, Poggio San Valentino) is a village in the Municipality of Brda in the Littoral region of Slovenia, right on the border with Italy.
The parish church in the settlement is dedicated to Saint Nicholas and belongs to the Koper Dioc ...
settlements, crosses Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
territory. That stretch is long and surrounded by fence (). Cars are not allowed to stop there and taking photos is not allowed either. The road was built in 1975, as part of the Treaty of Osimo
The Treaty of Osimo was signed on 10 November 1975 by Italy and Yugoslavia in Osimo, Italy, to definitively divide the Free Territory of Trieste between the two states: the port city of Trieste with a narrow coastal strip to the north-west (Zone ...
agreements between Italy and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
. The road remains surrounded by fence, even though both countries are now part of the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
.
Germany
 *A historical case of privileged transit was the arrival of
*A historical case of privileged transit was the arrival of Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
in a "sealed train car" through Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
from Switzerland to Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
(through Sweden as a normal passenger) in April 1917, amidst World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and Russian revolutionary activity.
*Communication between East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
and mainland Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
across the Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (Pomeranian Voivodeship, eastern ...
during the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the World War I, First World War to the beginning of the World War II, Second World War. The in ...
.
*From 1948, it became possible to travel from Zittau
Zittau ( hsb, Žitawa, dsb, Žytawa, pl, Żytawa, cs, Žitava, :de:Oberlausitzer Mundart, Upper Lusatian Dialect: ''Sitte''; from Slavic languages, Slavic "''rye''" (Upper Sorbian and Czech: ''žito'', Lower Sorbian: ''žyto'', Polish: ''żyto' ...
to Görlitz
Görlitz (; pl, Zgorzelec, hsb, Zhorjelc, cz, Zhořelec, :de:Ostlausitzer Mundart, East Lusatian dialect: ''Gerlz'', ''Gerltz'', ''Gerltsch'') is a town in the Germany, German state of Saxony. It is located on the Lusatian Neisse River, and ...
through Poland via Ostdeutsche Eisenbahn
Ostdeutsche Eisenbahn GmbH (''ODEG''; literally "East German Railway") is a joint venture, founded in June 2002, of the Prignitzer Eisenbahn (part of the Netinera Group) and BeNEX, with each company owning 50% of the joint venture. It operates pas ...
. The train has a station in Poland, Krzewina Zgorzelecka, located 100 metres from the border of the German city of Ostritz
Ostritz (, hsb, Wostrowc) is a town in the district Görlitz, in Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the border with Poland, on the left bank of the Lusatian Neisse, 16 km south of Görlitz.
It was the scene of a small battle in the Seven ...
. Passengers could walk between the train and East Germany without border control under surveillance by Polish guards. This route is still in operation , but since 2007 the inclusion of Poland in the Schengen area ended all passport checks at the German–Polish border.
* From 1949 to 1961, trains between East Berlin
East Berlin was the ''de facto'' capital city of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. Formally, it was the Allied occupation zones in Germany, Soviet sector of Berlin, established in 1945. The American, British, and French sectors were known as ...
and parts of East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
went through West Berlin
West Berlin (german: Berlin (West) or , ) was a political enclave which comprised the western part of Berlin during the years of the Cold War. Although West Berlin was de jure not part of West Germany, lacked any sovereignty, and was under mi ...
because no other railways existed. It was easy to deboard the trains when they stopped in West Berlin. This was a major way of fleeing East Germany. Subsequently the Berlin outer ring
The Berlin outer ring (german: Berliner Außenring, BAR) is a long double track electrified railway, originally built by the German Democratic Republic to bypass West Berlin in preparation for the building of the Berlin Wall during the division o ...
was built and when in operation from 1961 to 1990, West Berlin was sealed off and the Berlin Wall
The Berlin Wall (german: Berliner Mauer, ) was a guarded concrete barrier that encircled West Berlin from 1961 to 1989, separating it from East Berlin and East Germany (GDR). Construction of the Berlin Wall was commenced by the government ...
built.
*In the Cold War era from 1961 to 1990, Berlin U-Bahn
The Berlin U-Bahn (; short for , "underground railway") is a rapid transit system in Berlin, the capital and largest city of Germany, and a major part of the city's public transport system. Together with the S-Bahn, a network of suburban train li ...
and Berlin S-Bahn
The Berlin S-Bahn () is a rapid transit railway system in and around Berlin, the capital city of Germany. It has been in operation under this name since December 1930, having been previously called the special tariff area ''Berliner Stadt-, Ring ...
trains passed along sealed tunnels through East Berlin
East Berlin was the ''de facto'' capital city of East Germany from 1949 to 1990. Formally, it was the Allied occupation zones in Germany, Soviet sector of Berlin, established in 1945. The American, British, and French sectors were known as ...
, without any checks or stops. The sealed stations were called ghost station
A ghost station is a disused train station through which revenue-service passenger trains (especially rapid transit trains) pass but at which they do not stop. The term is also sometimes used for any unused underground station or any unused s ...
s.
*Büsingen am Hochrhein
Büsingen am Hochrhein (, "Büsingen on the Upper Rhine"; Alemannic: ''Büesinge am Hochrhi''), commonly known as Büsingen, is a German municipality () in the south of Baden-Württemberg and an enclave entirely surrounded by the Swiss cantons ...
is politically part of Germany but is surrounded by Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
and as such economically it forms part of the Swiss customs area, as does the independent principality of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarchy ...
. As such there have been no border controls between Switzerland and Büsingen am Hochrhein since 4 October 1967. Unofficially, the Italian village of Campione d'Italia
Campione d'Italia ( Comasco: , ) is a ''comune'' of the Province of Como in the Lombardy region of Italy and an enclave surrounded by the Swiss canton of Ticino (it is also an exclave). At its closest, the enclave is less than from the rest of ...
was also part of the Swiss customs area until the end of 2019.
Austria
*Trains betweenSalzburg
Salzburg (, ; literally "Salt-Castle"; bar, Soizbuag, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian) is the List of cities and towns in Austria, fourth-largest city in Austria. In 2020, it had a population of 156,872.
The town is on the site of the ...
and Kufstein
Kufstein (; Central Bavarian: ''Kufstoa'') is a town in the Austrian state of Tyrol, the administrative seat of Kufstein District. With a population of about 19,600 it is the second largest Tyrolean town after the state capital Innsbruck. The great ...
operated (via Germany) as privileged transit until 1997 when the Schengen area removed passport checks at this border. Border checks were reintroduced for them in 2015-2016 because of the European migrant crisis
The 2015 European migrant crisis, also known internationally as the Syrian refugee crisis, was a period of significantly increased movement of refugees and migrants into Europe in 2015, when 1.3 million people came to the continent to reques ...
. The route has been called Deutsches Eck (German corner).
* After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
a 'corridor-train' service was established between Lienz
Lienz (; Southern Bavarian: ''Lianz'') is a Town privileges, medieval town in the Austrian state of Tyrol (state), Tyrol. It is the administrative centre of the Lienz (district), Lienz district, which covers all of East Tyrol. The municipality a ...
and Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-largest city in Austria. On the Inn (river), River Inn, at its junction with the ...
using the Puster Valley Railway
The Puster Valley Railway (German: ''Pustertalbahn''; Italian: ''Ferrovia della Val Pusteria'') is a standard gauge, single-track railway line in the Puster Valley between Franzensfeste (Italian: Fortezza) and Innichen (San Candido), South Tyrol ...
(via Italy); this service lost importance after the Schengen Agreement
The Schengen Agreement ( , ) is a treaty which led to the creation of Europe's Schengen Area, in which internal border checks have largely been abolished. It was signed on 14 June 1985, near the town of Schengen, Luxembourg, by five of the t ...
was implemented and was discontinued after 2013.
*From the end of the Second World War in 1945 to near the end of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
in c. 1990, trains with locked doors (to prevent people from boarding or disembarking the train in then- Communist Hungary without permission) were allowed to go from Loipersdorf-Schattendorf
Schattendorf ( hr, Šundrof, hu, Somfalva) is a town in the district of Mattersburg in the Austrian state of Burgenland.
The Rosalia-Kogelberg nature preserve lies within the district.
History
This district was a part of the pre-Christian Ce ...
in northern Burgenland
Burgenland (; hu, Őrvidék; hr, Gradišće; Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland;'' Slovene: ''Gradiščanska'') is the easternmost and least populous state of Austria. It consists of two statutory cities and seven rural districts, with a total of ...
to Deutschkreutz
Deutschkreutz ( hu, Sopronkeresztúr until 1899, ''Németkeresztúr'' yi, צעלעם, translit=Zelem hr, Kerestur) is an Austrian market town in the district of Oberpullendorf in the state of Burgenland.
Geography
Deutschkreutz lies in Middle ...
in southern Burgenland via the Hungarian city of Sopron
Sopron (; german: Ödenburg, ; sl, Šopron) is a city in Hungary on the Austrian border, near Lake Neusiedl/Lake Fertő.
History
Ancient times-13th century
When the area that is today Western Hungary was a province of the Roman Empire, a ...
. The 44 minute train ride on a three-car diesel train crossed about 16 km of Hungarian territory up to five times a day traversing between Loipersdorf and Deutschkreutz. Nowadays, after the fall of Communism in Hungary and the accession of Hungary to the European Union, trains from Vienna call at Sopron before continuing on to Deutschkreutz. Austrian fares apply for the whole line.
Czech Republic
* After World War II, in 1945, a section of the railway lineVarnsdorf
Varnsdorf (; german: Warnsdorf, hsb, Warnoćicy) is a town in the Ústí nad Labem Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 15,000 inhabitants. It lies on the border with Germany.
Administrative parts
Villages of Studánka and Světliny 1.díl ...
(CS) – Zittau
Zittau ( hsb, Žitawa, dsb, Žytawa, pl, Żytawa, cs, Žitava, :de:Oberlausitzer Mundart, Upper Lusatian Dialect: ''Sitte''; from Slavic languages, Slavic "''rye''" (Upper Sorbian and Czech: ''žito'', Lower Sorbian: ''žyto'', Polish: ''żyto' ...
(DE) – Liberec
Liberec (; german: Reichenberg ) is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 103,000 inhabitants and it is the fifth-largest city in the country. It lies on the Lusatian Neisse, in a basin surrounded by mountains. The city centre is well preser ...
(CS) through Porajów became part of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
, and international traffic was stopped. In 1951, the Czechoslovak Railways restored the Varnsdorf – Liberec connection based on an agreement with East Germany (GDR) and Poland; ČSD trains had no stop in Polish or German territory. In 1964, a new treatment was signed. From 1972, GDR and Czechoslovakia restored standard international transport on this line. After the expansion of the Schengen area, Varnsdorf – Liberec trains also stop in Germany, but traffic through the Polish section is still based on the transit agreement. The Polish side gets a charge from the Czech side but neglects the Polish section and refuses proposals of Czech or German participation in the maintenance.
Switzerland
* Basel tram Line 10 (BLT) operates from Switzerland to Switzerland, passing viaLeymen
Leymen (; german: Leimen) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France. The commune is served by Leymen station, on line 10 of the Basel tramway between Rodersdorf and Flüh, and until December 2017 was the onl ...
in France. Transit passengers are not subject to customs rules and checks, but those boarding or alighting in Leymen are subject to customs regulations.
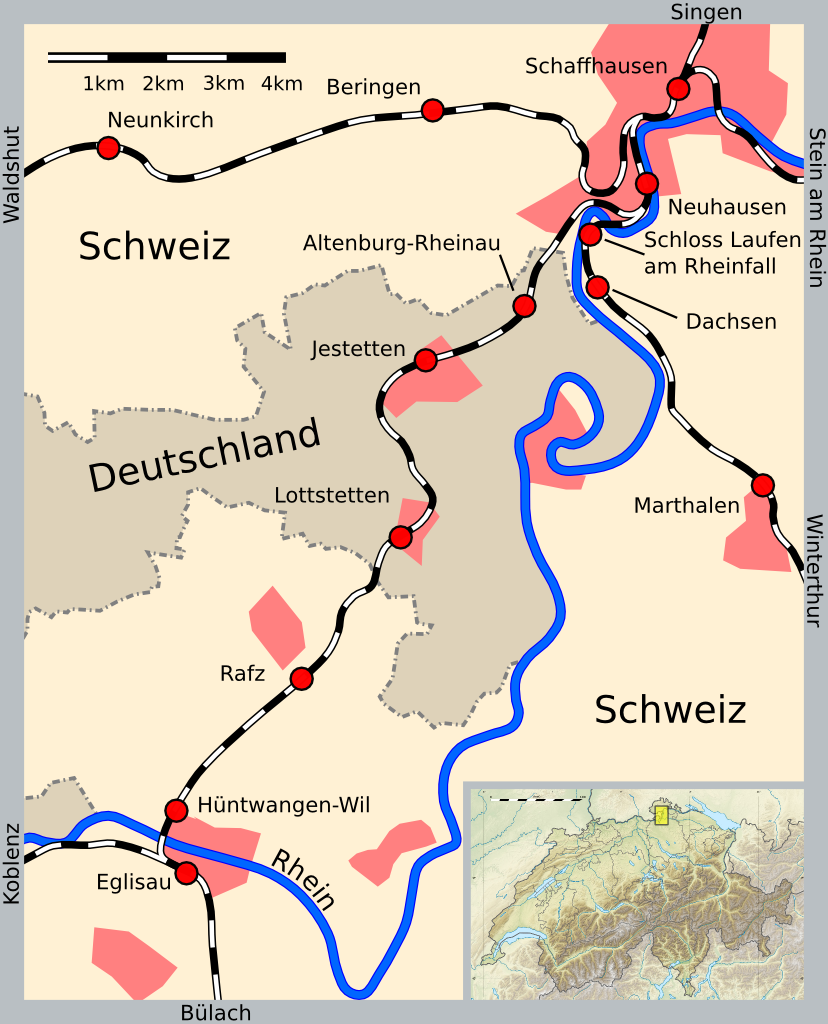
*The Eglisau–Neuhausen railway line is a cross-border railway line in Germany and Switzerland. The line links Eglisau
Eglisau is a municipality in the district of Bülach in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland.
History
Eglisau is first mentioned in 892 as several independent farm houses known as ''Ouwa''. In 1238 it was mentioned as ''Owe'', in 1304 as ''ze S ...
in the Swiss canton of Zurich
Canton may refer to:
Administrative division terminology
* Canton (administrative division), territorial/administrative division in some countries, notably Switzerland
* Township (Canada), known as ''canton'' in Canadian French
Arts and ent ...
with the city of Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the ...
in the Swiss canton of Schaffhausen
The canton of Schaffhausen, also canton of Schaffouse (german: Kanton Schaffhausen; rm, Chantun Schaffusa; french: Canton de Schaffhouse; it, Canton Sciaffusa) is the northernmost canton of Switzerland. The principal city and capital of the c ...
, crossing some of the German state of Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg (; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a ...
in between. It thus crosses the Germany–Switzerland border
The border between the modern states of Germany and Switzerland extends to , mostly following the High Rhine between Lake Constance and Basel.
Much of the border is within the sphere of the Zurich metropolitan area and there is substantial tr ...
twice. Trains which pass through German territory without stopping at any of the stations on the line in Germany, are not subject to any customs formalities or restrictions of either country, despite the train and its passengers technically leaving the Swiss Customs Area
Swiss may refer to:
* the adjectival form of Switzerland
*Swiss people
Places
*Swiss, Missouri
* Swiss, North Carolina
*Swiss, West Virginia
*Swiss, Wisconsin
Other uses
*Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports
*Swiss International ...
, entering the European Union customs area and entering Swiss customs territory again. An agreement in this respect was entered into by the two countries and became law in 1936.
* The Basel Badischer station is located in Switzerland, but operated by German Railways, and with border control done in the building. It was possible to travel from e.g. Freiburg
Freiburg im Breisgau (; abbreviated as Freiburg i. Br. or Freiburg i. B.; Low Alemannic: ''Friburg im Brisgau''), commonly referred to as Freiburg, is an independent city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. With a population of about 230,000 (as o ...
on the Rhine Valley Railway
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
to e.g. Rheinfelden on the High Rhine Railway
The High Rhine Railway (german: Hochrheinbahn) is the Deutsche Bahn railway line from Basel to Singen. It is also part of the tri-national S-Bahn Basel and referenced as . It was built by the Grand Duchy of Baden State Railways as part of the Bad ...
or to Lörrach
Lörrach () is a town in southwest Germany, in the valley of the Wiese, close to the French and the Swiss borders. It is the capital of the district of Lörrach in Baden-Württemberg. It is the home of a number of large employers, including the ...
on the Wiese Valley Railway
The Wiese Valley Railway (german: Wiesentalbahn) is a 27.2 km long, electrified main line in German Baden-Württemberg in the tri-national area of Germany, Switzerland and France near the Swiss city of Basel. It is part of the Basel trinationa ...
with a train change at Basel Badischer without border and customs control. After Swiss introduction into the Schengen Area, border controls are abolished but customs rules still apply.
* A 1.7 km customs road links Ferney-Voltaire
Ferney-Voltaire () is a commune in the Ain department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of eastern France. It lies between the Jura Mountains and the Swiss border; it forms part of the metropolitan area of Geneva.
History
Ferney was first n ...
with the French section of Geneva Airport
Geneva Airport ,, german: Flughafen Genf, it, Aeroporto di Ginevra, rm, Eroport de Genevra formerly and still unofficially known as Cointrin Airport, is the international airport of Geneva, the second most populous city in Switzerland. It i ...
, which is located entirely within Swiss territory.
* A 2.5 km customs road links Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
with the Swiss section of EuroAirport
EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg IATA airport 3-letter codes for the French area, the Swiss area, and the metropolitan area, french: Aéroport de Bâle-Mulhouse-Fribourg, it, Aeroporto di Basilea-Mulhouse-Friburgo, rm, Eroport da Basilea-Mu ...
, which is located entirely within French territory.
Belgium
* TheVennbahn
The (, "Fen Railway") is a former railway line that was built partly across what was then German territory by the Prussian state railways. It is now entirely in Belgium, because the trackbed of the line, as well as the stations and other instal ...
railway passed through German territory on parts of its route until the situation was corrected in 1919 when the land became part of Belgium and six German exclaves surrounded by Belgian territory were created as well as one counter-enclave. Five enclaves remain today. The sixth enclave and the sole counter-enclave no longer exist.
Ireland
* The N54 road betweenCavan
Cavan ( ; ) is the county town of County Cavan in Ireland. The town lies in Ulster, near the border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. The town is bypassed by the main N3 road that links Dublin (to the south) with Enniskillen, Bally ...
and Clones
Clone or Clones or Cloning or Cloned or The Clone may refer to:
Places
* Clones, County Fermanagh
* Clones, County Monaghan, a town in Ireland
Biology
* Clone (B-cell), a lymphocyte clone, the massive presence of which may indicate a pathologi ...
in the Republic of Ireland passes twice through Northern Ireland, where it is designated A3. Similarly, the N53 road between Dundalk
Dundalk ( ; ga, Dún Dealgan ), meaning "the fort of Dealgan", is the county town (the administrative centre) of County Louth, Ireland. The town is on the Castletown River, which flows into Dundalk Bay on the east coast of Ireland. It is h ...
and Castleblaney
Castleblayney (; ) is a town in County Monaghan, Ireland. The town had a population of 3,607 as of the 2016 census. Castleblayney is near the border with County Armagh in Northern Ireland, and lies on the N2 road from Dublin to Derry and Lett ...
includes a 5.5km stretch passing through Cullaville
Cullaville or Culloville ( or McCulloch's ville or town is a small village and townland near Crossmaglen in County Armagh, Northern Ireland. It is the southernmost settlement in the county and one of the southernmost in Northern Ireland, straddlin ...
north of the border, where it is designated A37. As with the rest of the Irish border, there are no permanent customs posts or checkpoints on these roads.
The Netherlands
* Provincial road 274 (also known as N274) is a Dutch main road that runs fromRoermond
Roermond (; li, Remunj or ) is a city, municipality, and diocese in the Limburg province of the Netherlands. Roermond is a historically important town on the lower Roer on the east bank of the river Meuse. It received town rights in 1231. Roer ...
to Brunssum
Brunssum (; li, Broensem) is a municipality and a town in the province of Limburg in the Netherlands. The municipality of Brunssum has residents as of .
Brunssum was a center of coal mining until 1973.
Population centres
Topography
Histor ...
, crossing in and out of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
for about 7 km through the German municipality Selfkant
Selfkant (; nl, Selfkant or ''Zelfkant'' ; Limburgish: ) is a municipality in the Heinsberg district, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the most westerly municipality in Germany.
Geography
Isenbruch in Selfkant is the most westerly po ...
. The road was built in a time when some German municipalities (including Selfkant) were under Dutch control after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Until 2002 the German section was maintained by the Dutch Rijkswaterstaat
Rijkswaterstaat, founded in 1798 as the ''Bureau voor den Waterstaat'' and formerly translated to Directorate General for Public Works and Water Management, is a Directorate-General of the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management of the Net ...
, the road had no level intersections, and it was not possible to leave or join the road from German territory. On February 25, 2002, the corridor was handed over to Germany, giving it the name Landesstraße 410 (L410). The road was further integrated into the German network, making it possible to leave and join from German territory. In contrast to other German roads, freight trucks are allowed to drive here on Sundays and national holidays, while in the rest of Germany this is prohibited.
Air traffic
Air traffic has in general a number of privileged transit traffic rights, making it suitable to reach enclaves or isolated countries. * First freedom of the air: The right to fly over another country. * Second freedom of the air: The right to make technical stops (such as refuelling) in another country without customs and passport check. * Airside transit: The right for passengers to change aircraft at airports, without going through passport control.See also
* Enclave and exclave#Unusual cross-border transport channelsReferences
{{reflist Rail infrastructure Road infrastructure Transportation planning Urban studies and planning terminology International relations