Prime Minister Justin Trudeau on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Justin Pierre James Trudeau ( , ; born December 25, 1971) is a Canadian politician who is the 23rd and current
 His father had intended Trudeau to begin his formal education at a French-language lycée, but Trudeau's mother convinced his father of the importance of sending their sons to a public school. In the end, Trudeau was enrolled in 1976 in the French immersion program at
His father had intended Trudeau to begin his formal education at a French-language lycée, but Trudeau's mother convinced his father of the importance of sending their sons to a public school. In the end, Trudeau was enrolled in 1976 in the French immersion program at
 Trudeau and his family started the Kokanee Glacier Alpine Campaign for winter sports safety in 2000, two years after his brother Michel died in an avalanche during a ski trip. In 2002, Trudeau criticized the Government of British Columbia's decision to stop its funding for a public avalanche warning system.
From 2002 to 2006, Trudeau chaired the Katimavik youth program, a project started by longtime family friend Jacques Hébert.
In 2002–03, Trudeau was a panelist on
Trudeau and his family started the Kokanee Glacier Alpine Campaign for winter sports safety in 2000, two years after his brother Michel died in an avalanche during a ski trip. In 2002, Trudeau criticized the Government of British Columbia's decision to stop its funding for a public avalanche warning system.
From 2002 to 2006, Trudeau chaired the Katimavik youth program, a project started by longtime family friend Jacques Hébert.
In 2002–03, Trudeau was a panelist on
 Following his father's death, Trudeau became more involved with the Liberal Party throughout the 2000s. Along with Olympian Charmaine Crooks, he co-hosted a tribute to outgoing prime minister Jean Chrétien at the party's 2003 leadership convention, and was appointed to chair a task force on youth renewal after the party's defeat in the 2006 federal election.
In October 2006, Trudeau criticized Quebec nationalism by describing political nationalism generally as an "old idea from the 19th century", "based on a smallness of thought" and not relevant to modern Quebec. This comment was seen as a criticism of
Following his father's death, Trudeau became more involved with the Liberal Party throughout the 2000s. Along with Olympian Charmaine Crooks, he co-hosted a tribute to outgoing prime minister Jean Chrétien at the party's 2003 leadership convention, and was appointed to chair a task force on youth renewal after the party's defeat in the 2006 federal election.
In October 2006, Trudeau criticized Quebec nationalism by describing political nationalism generally as an "old idea from the 19th century", "based on a smallness of thought" and not relevant to modern Quebec. This comment was seen as a criticism of
 The Conservative Party won a minority government in the 2008 election, and Trudeau entered parliament as a member of the Official Opposition. Trudeau's first legislative act was a motion that called for the creation of a "national voluntary service policy for young people". He later co-chaired the Liberal Party's April 2009 national convention in
The Conservative Party won a minority government in the 2008 election, and Trudeau entered parliament as a member of the Official Opposition. Trudeau's first legislative act was a motion that called for the creation of a "national voluntary service policy for young people". He later co-chaired the Liberal Party's April 2009 national convention in
 In the days following his victory in the leadership race, snapshot polls recorded a surge in support for the Liberal party.
In 2013, Trudeau chose to give up his seat at the
In the days following his victory in the leadership race, snapshot polls recorded a surge in support for the Liberal party.
In 2013, Trudeau chose to give up his seat at the
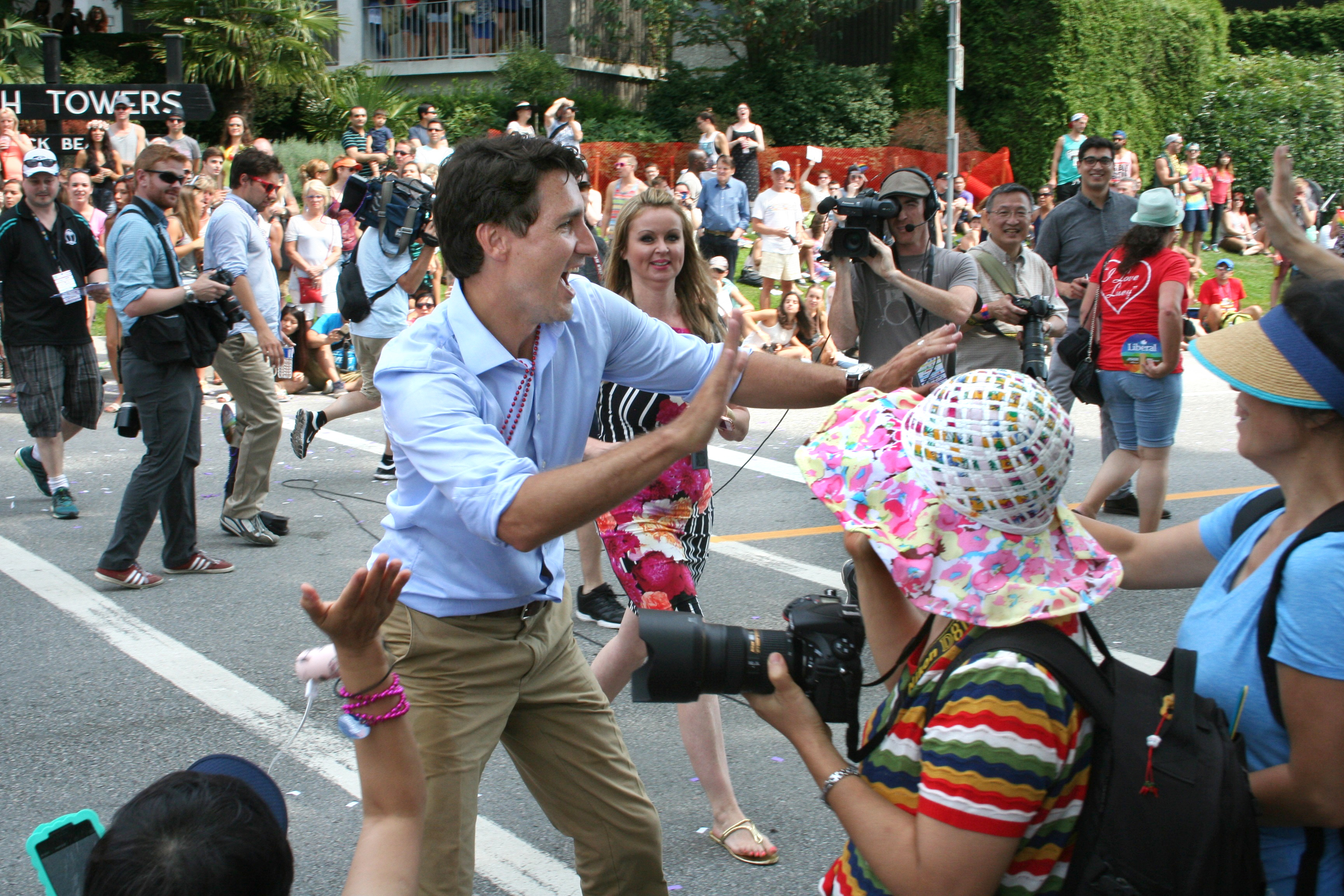 On October 19, 2015, after the longest official campaign in over a century, Trudeau led the Liberals to a decisive victory in the federal election. The Liberals won 184 of the 338 seats, with 39.5% of the popular vote, for a strong majority government; a gain of 150 seats compared to the 2011 federal election.
This was the second-best performance in the party's history. The Liberals won mostly on the strength of a solid performance in the eastern half of the country. In addition to taking all of Atlantic Canada and Toronto, they won 40 seats in Quebec—the most that the Liberals had won in that province since Trudeau's father led them to a near-sweep of the province in 1980, and also the first time since then that the Liberals won a majority of Quebec's seats in an election. The 150-seat gain was the biggest numerical increase for a single party since Confederation and marked the first time that a party had rebounded from third place in the Commons to a majority government.
In addition to the appeal of his party's platform, Trudeau's success has been credited to his performance both on the campaign trail and televised
On October 19, 2015, after the longest official campaign in over a century, Trudeau led the Liberals to a decisive victory in the federal election. The Liberals won 184 of the 338 seats, with 39.5% of the popular vote, for a strong majority government; a gain of 150 seats compared to the 2011 federal election.
This was the second-best performance in the party's history. The Liberals won mostly on the strength of a solid performance in the eastern half of the country. In addition to taking all of Atlantic Canada and Toronto, they won 40 seats in Quebec—the most that the Liberals had won in that province since Trudeau's father led them to a near-sweep of the province in 1980, and also the first time since then that the Liberals won a majority of Quebec's seats in an election. The 150-seat gain was the biggest numerical increase for a single party since Confederation and marked the first time that a party had rebounded from third place in the Commons to a majority government.
In addition to the appeal of his party's platform, Trudeau's success has been credited to his performance both on the campaign trail and televised  Trudeau declared victory shortly after
Trudeau declared victory shortly after
 Trudeau and the rest of the
Trudeau and the rest of the  In January 2017, the
In January 2017, the
 On September 11, 2019, Trudeau visited Governor General
On September 11, 2019, Trudeau visited Governor General
 While Trudeau's Liberal Party lost 20 seats in the House of Commons (lowering its total from 177 to 157) from the time of dissolution, they still won the most seats of any party—enough seats to allow Trudeau to form a minority government. For the first time since 1979, the party that garnered the largest share of the national popular vote did not win the most seats; the Liberals under Trudeau had 33.1 per cent of the popular vote, while the Conservatives under
While Trudeau's Liberal Party lost 20 seats in the House of Commons (lowering its total from 177 to 157) from the time of dissolution, they still won the most seats of any party—enough seats to allow Trudeau to form a minority government. For the first time since 1979, the party that garnered the largest share of the national popular vote did not win the most seats; the Liberals under Trudeau had 33.1 per cent of the popular vote, while the Conservatives under
 In 2015, Trudeau told the New York Times Magazine that Canada could be the “first
In 2015, Trudeau told the New York Times Magazine that Canada could be the “first
The full list of 229 US products targeted by Canada's retaliatory tariffs
''Quartz'' (June 29, 2018). Canada's relationship with
Canada's relationship with
 Trudeau first met
Trudeau first met
 ;Honorary degrees
;Honorary degrees
Liberal Party of Canada profile
*
House of Commons profile
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Trudeau, Justin 1971 births 21st-century Canadian politicians Anglophone Quebec people Canadian feminists Canadian people of Anglo-Irish descent Canadian people of English descent Canadian people of French descent Canadian people of Scottish descent Canadian Roman Catholics Canadian schoolteachers Catholic feminists Children of prime ministers of Canada Franco-Ontarian people French Quebecers Leaders of the Liberal Party of Canada Liberal Party of Canada leadership candidates Liberal Party of Canada MPs Living people Male feminists McGill University alumni Members of the 29th Canadian Ministry Members of the House of Commons of Canada from Quebec Members of the King's Privy Council for Canada Pierre Trudeau Politicians from Montreal Politicians from Ottawa Prime Ministers of Canada
prime minister of Canada
The prime minister of Canada (french: premier ministre du Canada, link=no) is the head of government of Canada. Under the Westminster system, the prime minister governs with the confidence of a majority the elected House of Commons; as su ...
. He has served as the prime minister of Canada since 2015 and as the leader of the Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world. The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left.
__TOC__ Active liberal parties
This is a li ...
since 2013. Trudeau is the second-youngest prime minister in Canadian history after Joe Clark
Charles Joseph Clark (born June 5, 1939) is a Canadian statesman, businessman, writer, and politician who served as the 16th prime minister of Canada from 1979 to 1980.
Despite his relative inexperience, Clark rose quickly in federal polit ...
; he is also the first to be the child or other relative of a previous holder of the post, as the eldest son of Pierre Trudeau.
Trudeau was born in Ottawa and attended Collège Jean-de-Brébeuf. He graduated from McGill University
McGill University (french: link=no, Université McGill) is an English-language public research university located in Montreal, Quebec
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous ...
in 1994 with a Bachelor of Arts degree in literature, then in 1998 acquired a Bachelor of Education degree from the University of British Columbia
The University of British Columbia (UBC) is a public research university with campuses near Vancouver and in Kelowna, British Columbia. Established in 1908, it is British Columbia's oldest university. The university ranks among the top thre ...
. After graduating he taught at the secondary school level in Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the ...
, before relocating back to Montreal in 2002 to further his studies. He was chair for the youth charity Katimavik and director of the not-for-profit Canadian Avalanche Association. In 2006, he was appointed as chair of the Liberal Party's Task Force on Youth Renewal.
In the 2008 federal election, he was elected to represent the riding of Papineau in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. T ...
. He was the Liberal Party's Official Opposition critic for youth and multiculturalism in 2009, and the following year he became critic for citizenship and immigration. In 2011, he was appointed as a critic for secondary education and sport. Trudeau won the leadership of the Liberal Party in April 2013 and led his party to victory in the 2015 federal election, moving the third-placed Liberals from 36 seats to 184 seats, the largest-ever numerical increase by a party in a Canadian federal election.
Major government initiatives he undertook during his first term as prime minister included legalizing recreational marijuana through the '' Cannabis Act''; attempting Senate appointment reform by establishing the Independent Advisory Board for Senate Appointments and establishing the federal carbon tax. In foreign policy, Trudeau's government negotiated trade deals such as the Canada-United States-Mexico Agreement (CUSMA) and the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership, and signed the Paris Agreement on climate change. He was sanctioned by Canada's ethics commissioner for violating conflict of interest rules regarding the Aga Khan affair
The Aga Khan affair was a political scandal in Canada involving Prime Minister Justin Trudeau. In 2017, Trudeau was found guilty of violating sections 5,11,12, and 21 of the Federal Conflict of Interest Act by accepting private-island vacati ...
, and later again with the SNC-Lavalin affair.
Trudeau led the Liberals to consecutive minority governments in the 2019
File:2019 collage v1.png, From top left, clockwise: Hong Kong protests turn to widespread riots and civil disobedience; House of Representatives votes to adopt articles of impeachment against Donald Trump; CRISPR gene editing first used to experim ...
and 2021
File:2021 collage V2.png, From top left, clockwise: the James Webb Space Telescope was launched in 2021; Protesters in Yangon, Myanmar following the coup d'état; A civil demonstration against the October 2021 coup in Sudan; Crowd shortly after t ...
federal elections, during which his government has responded to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
. During his second term he announced an "assault-style" weapons ban in response to the 2020 Nova Scotia attacks
On April 18 and 19, 2020, Gabriel Wortman committed multiple shootings and set fires at 16 locations in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, killing 22 people and injuring three others before he was shot and killed by the Royal Canadian Mou ...
. He was investigated for a third time by the ethics commissioner for his part in the WE Charity scandal, but was cleared of wrongdoing. In 2022, he invoked the '' Emergencies Act'' in response to the Freedom Convoy protests, the first time the act was brought into force since it was enacted in 1988.
Early life
Ancestry and birth
On June 23, 1971, the Prime Minister's Office (PMO) announced that Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau's wife of four months, the former Margaret Sinclair, was pregnant and due in December. Justin Trudeau was born on December 25, 1971, at 9:27 pm EST at theOttawa Civic Hospital
The Ottawa Civic Hospital is one of three main campuses of The Ottawa Hospital – along with the General and Riverside campuses. With 549 beds (including the Heart Institute), the Civic Campus has the region's only adult-care trauma centre, servin ...
. He is the second child in Canadian history to be born to a prime minister in office; the first was John A. Macdonald
Sir John Alexander Macdonald (January 10 or 11, 1815 – June 6, 1891) was the first prime minister of Canada, serving from 1867 to 1873 and from 1878 to 1891. The dominant figure of Canadian Confederation, he had a political career that sp ...
's daughter Margaret Mary Theodora Macdonald (February 8, 1869 – January 28, 1933). Trudeau's younger brothers Alexandre Alexandre may refer to:
* Alexandre (given name)
* Alexandre (surname)
* Alexandre (film)
See also
* Alexander
* Xano (disambiguation) Xano is the name of:
* Xano, a Portuguese hypocoristic of the name "Alexandre (disambiguation) Alexandre may re ...
(Sacha) (born December 25, 1973) and Michel (October 2, 1975 – November 13, 1998) were the third and fourth.
Trudeau is predominantly of Scottish and French Canadian descent. His grandfathers were businessman Charles-Émile Trudeau and Scottish-born James Sinclair, who was minister of fisheries in the cabinet of Prime Minister Louis St. Laurent. Trudeau's maternal great-grandfather Thomas Bernard was born in Makassar, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and immigrated to Penticton, British Columbia, in 1906 at age 15 with his family. Through the Bernard family, kinsmen of the Earls of Bandon
Earl of Bandon was a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created in 1800 for Francis Bernard, 1st Viscount Bandon. He had already been created Baron Bandon, of Bandon Bridge in the County of Cork, in 1793, Viscount Bandon, of Bandon Bridge ...
, Trudeau is the fifth great-grandson of Major-General William Farquhar
William Farquhar ( ; 26 February 1774 – 11 May 1839) was a Scottish colonial administrator employed by the East India Company, who served as the sixth Resident of Malacca between 1813 and 1818, and the first Resident of Singapore between ...
, a leader in the founding of modern Singapore; Trudeau also has remote ethnic Malaccan and Nias ancestry.
Trudeau was baptized with his father's niece Anne Rouleau-Danis as godmother and his mother's brother-in-law Thomas Walker as godfather, at Ottawa's Notre Dame Basilica on the afternoon of January 16, 1972, which marked his first public appearance. and given the names "Justin Pierre James". On April 14, 1972, Trudeau's father and mother hosted a gala at the National Arts Centre
The National Arts Centre (NAC) (french: Centre national des Arts) is a performing arts organisation in Ottawa, Ontario, along the Rideau Canal. It is based in the eponymous National Arts Centre building.
History
The NAC was one of a number of ...
, at which visiting U.S. president Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon (January 9, 1913April 22, 1994) was the 37th president of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served as a representative and senator from California and was ...
said, "I'd like to toast the future prime minister of Canada, to Justin Pierre Trudeau" to which Pierre Trudeau responded that should his son ever assume the role, he hoped he would have "the grace and skill of the president". Earlier that same day U.S. first lady Pat Nixon
Thelma Catherine "Pat" Nixon (''née'' Ryan; March 16, 1912 – June 22, 1993) was First Lady of the United States from 1969 to 1974 as the wife of President Richard Nixon. She also served as Second Lady of the United States from 1953 to 1961 wh ...
had come to see him in his nursery to deliver a gift, a stuffed toy
A stuffed toy is a toy doll with an outer fabric sewn from a textile and stuffed with flexible material. They are known by many names, such as plush toys, plushies, stuffed animals, and stuffies; in Britain and Australia, they may also be ...
Snoopy
Snoopy is an anthropomorphic beagle in the comic strip ''Peanuts'' by Charles M. Schulz. He can also be found in all of the ''Peanuts'' films and television specials. Since his debut on October 4, 1950, Snoopy has become one of the most recog ...
. Nixon's White House audio tapes later revealed Nixon referred to that visit as "wasting three days up there. That trip we needed like a hole in the head."
Childhood
Trudeau's parents announced their separation on May 27, 1977, when he was five years old; his father was given primary custody. There had been repeated rumours of a reconciliation for many years afterwards. However, his mother's attorney Michael Levine filed inToronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
to the Supreme Court of Ontario
The Supreme Court of Ontario was a superior court of the Canadian province of Ontario. Created in 1881 pursuant to the Ontario Judicature Act (1881), the Supreme Court of Ontario had two branches: the High Court of Justice Division and the Appell ...
for a no-fault divorce on November 16, 1983, which was finalized on April 2, 1984; his father had announced his intention to retire as prime minister on February 29 of that year. Eventually his parents came to an amicable joint-custody arrangement and learned to get along quite well. Interviewed in October 1979, his nanny
A nanny is a person who provides child care. Typically, this care is given within the children's family setting. Throughout history, nannies were usually servants in large households and reported directly to the lady of the house. Today, modern ...
Dianne Lavergne was quoted, "Justin is a mommy's boy, so it's not easy, but children's hurts mend very quickly. And they're lucky kids, anyway." Of his mother and father's marriage, Trudeau said in 2009, "They loved each other incredibly, passionately, completely. But there was 30 years between them, and my mom never was an equal partner in what encompassed my father's life, his duty, his country." Trudeau has three half-siblings, Kyle and Alicia, from his mother's remarriage to Fried Kemper, and Sarah, from his father's relationship with Deborah Coyne.
Trudeau lived at 24 Sussex Drive, Ottawa, the official residence of Canada's prime minister, from his birth until his father's government was defeated in the federal election on May 22, 1979. The Trudeaus were expected to move into Stornoway, the residence of the leader of the Official Opposition, but because of flooding in the basement, Prime Minister Joe Clark
Charles Joseph Clark (born June 5, 1939) is a Canadian statesman, businessman, writer, and politician who served as the 16th prime minister of Canada from 1979 to 1980.
Despite his relative inexperience, Clark rose quickly in federal polit ...
offered them Harrington Lake, the prime minister's official country retreat in Gatineau Park
Gatineau Park (french: Parc de la Gatineau) is a federal park located in the Outaouais, Outaouais region of Quebec, Canada. Administered by the National Capital Commission as part of the National Capital Region (Canada), National Capital Region, ...
, with the expectation they would move into Stornoway at the start of July. However, the repairs were not complete, so Pierre Trudeau took a prolonged vacation with his sons to the Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
summer home of his friend, Member of Parliament Don Johnston, and later sent his sons to stay with their maternal grandparents in North Vancouver for the rest of the summer while he slept at his friend's Ottawa apartment. Justin and his brothers returned to Ottawa for the start of the school year but lived only on the top floor of Stornoway while repairs continued on the bottom floor. His mother purchased and moved into a new home nearby at 95 Victoria Street in Ottawa's New Edinburgh neighbourhood in September 1979. Pierre Trudeau and his sons returned to the prime minister's official residence after the February 1980 election that returned him to the Prime Minister's Office.
 His father had intended Trudeau to begin his formal education at a French-language lycée, but Trudeau's mother convinced his father of the importance of sending their sons to a public school. In the end, Trudeau was enrolled in 1976 in the French immersion program at
His father had intended Trudeau to begin his formal education at a French-language lycée, but Trudeau's mother convinced his father of the importance of sending their sons to a public school. In the end, Trudeau was enrolled in 1976 in the French immersion program at Rockcliffe Park Public School
Rockcliffe Park Public School (RPPS) is a public elementary school in the Rockcliffe Park neighbourhood of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
History
The school was founded in 1922. The school is located in the centre of Ottawa's wealthiest neighbourhood. ...
, the same school his mother had attended for two years while her father was a member of Parliament. He could have been dropped off by limousine, but his parents elected he take the school bus albeit with a Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal police, federal and national police service of ...
(RCMP) car following. This was followed by one year at the private Lycée Claudel d'Ottawa
The Lycée Claudel d'Ottawa is a French-language private school in Ottawa built in the early 1960s. It was renovated by Edward J. Cuhaci to provide an infill between two existing school buildings comprising classrooms and a 600-seat auditorium.< ...
.
After his father's retirement in June 1984, his mother remained at her New Edinburgh home while the rest of the family moved into his father's home at 1418 Pine Avenue, Montreal known as Cormier House, where the following autumn he began attending the private Collège Jean-de-Brébeuf, his father's alma mater. The school had begun as a Jesuit school but was non-denominational by the time Justin matriculated. In 2008, Trudeau said that of all his early family outings he enjoyed camping with his father the most, because "that was where our father got to be just our father – a dad in the woods". During the summers his father would send him and his brothers to Camp Ahmek, on Canoe Lake in Algonquin Provincial Park
Algonquin Provincial Park is a provincial park located between Georgian Bay and the Ottawa River in Ontario, Canada, mostly within the Unorganized South Part of Nipissing District. Established in 1893, it is the oldest provincial park in Can ...
, where he would later work in his first paid job as a camp counsellor.
Trudeau and his brothers were given shares in a numbered company by their father, from which they received regular dividends, up to $20,000 per year. As of August 2011, Trudeau's company had assets of $1.2 million.
University and early career
Trudeau has a bachelor of arts degree in literature fromMcGill University
McGill University (french: link=no, Université McGill) is an English-language public research university located in Montreal, Quebec
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous ...
and a bachelor of education degree from the University of British Columbia
The University of British Columbia (UBC) is a public research university with campuses near Vancouver and in Kelowna, British Columbia. Established in 1908, it is British Columbia's oldest university. The university ranks among the top thre ...
. In his first year at McGill, Trudeau became acquainted with his future principal secretary, Gerald Butts, through their mutual friend, Jonathan Ablett. Butts invited Trudeau to join the McGill Debating Union. They bonded while driving back to Montreal after a debate tournament at Princeton University
Princeton University is a private research university in Princeton, New Jersey. Founded in 1746 in Elizabeth as the College of New Jersey, Princeton is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and one of the ...
, in which the Princeton team included Ted Cruz
Rafael Edward "Ted" Cruz (; born December 22, 1970) is an American politician and attorney serving as the junior United States Senator from Texas since 2013. A member of the Republican Party, Cruz served as Solicitor General of Texas from ...
, who would go on to be elected a U.S. senator for Texas in 2013 and be candidate for the U.S. Republican Party's presidential nomination in 2016. After graduation, Trudeau stayed in Vancouver where he became a substitute teacher at local schools such as Killarney Secondary and worked permanently as a French and math teacher at the private West Point Grey Academy. He became a roommate at the Douglas Lodge with fellow West Point Grey Academy faculty member and friend Christopher Ingvaldson
Christopher Charles Ingvaldson (born November 1, 1969) is a Canadian teacher and former international field hockey player. He was the head of the Social Studies department at St. George's School (Vancouver) until he was fired June 4, 2010 after b ...
. From 2002 to 2004, he studied engineering at the École Polytechnique de Montréal, affiliated with Université de Montréal
The Université de Montréal (UdeM; ; translates to University of Montreal) is a French-language public research university in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The university's main campus is located in the Côte-des-Neiges neighborhood of Côte- ...
, but did not graduate. He started a master's degree in environmental geography at McGill but withdrew from the program to seek public office.
In August 2000, Justin Trudeau attended the Kokanee Summit in Creston, British Columbia, to raise funds in honour of his brother Michel Trudeau and other avalanche victims. After the event, an unsigned editorial in the ''Creston Valley Advance'' (a local newspaper) accused Trudeau of having groped an unnamed female reporter while at the music festival. The editorial stated Trudeau provided a "day-late" apology to the reporter, saying, "If I had known you were reporting for a national paper, I never would have been so forward". In 2018, Trudeau was questioned about the groping incident but said he did not remember any negative incidents from that time. His apology and later statement about the event have been described as hypocritical, while responses to the story have been described as a witch hunt
A witch-hunt, or a witch purge, is a search for people who have been labeled witches or a search for evidence of witchcraft. The classical period of witch-hunts in Early Modern Europe and Colonial America took place in the Early Modern perio ...
or non-story.
In October 2000, Trudeau, then 28, emerged as a prominent figure after delivering a eulogy at his father's state funeral. The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation
The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (french: Société Radio-Canada), branded as CBC/Radio-Canada, is a Canadian public broadcaster for both radio and television. It is a federal Crown corporation that receives funding from the government. ...
(CBC) received numerous calls to rebroadcast the speech after its initial transmission, and leading Quebec politician Claude Ryan
Claude Ryan, (January 26, 1925 – February 9, 2004) was a Canadian journalist and politician. He was the director of the newspaper ''Le Devoir'' from 1964 to 1978, leader of the Quebec Liberal Party from 1978 to 1982, National Assembly of Q ...
described it as "perhaps ... the first manifestation of a dynasty". A book issued by the CBC in 2003 included the speech in its list of significant Canadian events from the past fifty years.
In 2007, Trudeau starred in the two-part CBC Television miniseries ''The Great War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
'', which gave an account of Canada's participation in the First World War. He portrayed his fifth cousin, twice removed, Major Talbot Mercer Papineau, who was killed on October 30, 1917, during the Battle of Passchendaele. Trudeau is one of several children of former prime ministers who have become Canadian media personalities. The others are Ben Mulroney
Ben is frequently used as a shortened version of the given names Benjamin, Benedict, Bennett or Benson, and is also a given name in its own right.
Ben (in he, בֶּן, ''son of'') forms part of Hebrew surnames, e.g. Abraham ben Abraham ( he ...
(son of Brian Mulroney), Catherine Clark (daughter of Joe Clark), and Trudeau's younger brother, Alexandre. Ben Mulroney was a guest at Trudeau's wedding.
Advocacy
 Trudeau and his family started the Kokanee Glacier Alpine Campaign for winter sports safety in 2000, two years after his brother Michel died in an avalanche during a ski trip. In 2002, Trudeau criticized the Government of British Columbia's decision to stop its funding for a public avalanche warning system.
From 2002 to 2006, Trudeau chaired the Katimavik youth program, a project started by longtime family friend Jacques Hébert.
In 2002–03, Trudeau was a panelist on
Trudeau and his family started the Kokanee Glacier Alpine Campaign for winter sports safety in 2000, two years after his brother Michel died in an avalanche during a ski trip. In 2002, Trudeau criticized the Government of British Columbia's decision to stop its funding for a public avalanche warning system.
From 2002 to 2006, Trudeau chaired the Katimavik youth program, a project started by longtime family friend Jacques Hébert.
In 2002–03, Trudeau was a panelist on CBC Radio
CBC Radio is the English-language radio operations of the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. The CBC operates a number of radio networks serving different audiences and programming niches, all of which (regardless of language) are outlined below ...
's ''Canada Reads
''Canada Reads'' is an annual "battle of the books" competition organized and broadcast by Canada's public broadcaster, the CBC. The program has aired in two distinct editions, the English-language ''Canada Reads'' on CBC Radio One, and the Frenc ...
'' series, where he championed '' The Colony of Unrequited Dreams'' by Wayne Johnston. Trudeau and his brother Alexandre inaugurated the Trudeau Centre for Peace and Conflict Studies at the University of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public university, public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park (Toronto), Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 ...
in April 2004; the centre later became a part of the Munk School of Global Affairs
The Munk School of Global Affairs and Public Policy at the University of Toronto is an interdisciplinary academic centre with various research and educational programs committed to the field of globalization. Located in Toronto, Ontario, it offers ...
. In 2006, he hosted the presentation ceremony for the Giller Prize for literature.
In 2005, Trudeau fought against a proposed $100-million zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
mine that he argued would poison the Nahanni River, a United Nations World Heritage Site located in the Northwest Territories. He was quoted as saying, "The river is an absolutely magnificent, magical place. I'm not saying mining is wrong ... but that is not the place for it. It's just the wrong thing to be doing."
On September 17, 2006, Trudeau was the master of ceremonies at a Toronto rally organized by Roméo Dallaire
Roméo Antonius Dallaire (born June 25, 1946) is a Canadian humanitarian, author, retired senator and Canadian Forces lieutenant-general. Dallaire served as force commander of UNAMIR, the ill-fated United Nations peacekeeping force for Rwanda ...
that called for Canadian participation in resolving the Darfur crisis
The War in Darfur, also nicknamed the Land Cruiser War, is a major armed conflict in the Darfur region of Sudan that began in February 2003 when the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM) and the Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) rebel groups bega ...
.
Political beginnings
Trudeau supported the Liberal Party from a young age, offering his support to party leaderJohn Turner
John Napier Wyndham Turner (June 7, 1929September 19, 2020) was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 17th prime minister of Canada from June to September 1984. He served as leader of the Liberal Party of Canada and leader of t ...
in the 1988 federal election. Two years later, he defended Canadian federalism
Canadian federalism () involves the current nature and historical development of the federal system in Canada.
Canada is a federation with eleven components: the national Government of Canada and ten provincial governments. All eleven ...
at a student event at the Collège Jean-de-Brébeuf, which he attended.
 Following his father's death, Trudeau became more involved with the Liberal Party throughout the 2000s. Along with Olympian Charmaine Crooks, he co-hosted a tribute to outgoing prime minister Jean Chrétien at the party's 2003 leadership convention, and was appointed to chair a task force on youth renewal after the party's defeat in the 2006 federal election.
In October 2006, Trudeau criticized Quebec nationalism by describing political nationalism generally as an "old idea from the 19th century", "based on a smallness of thought" and not relevant to modern Quebec. This comment was seen as a criticism of
Following his father's death, Trudeau became more involved with the Liberal Party throughout the 2000s. Along with Olympian Charmaine Crooks, he co-hosted a tribute to outgoing prime minister Jean Chrétien at the party's 2003 leadership convention, and was appointed to chair a task force on youth renewal after the party's defeat in the 2006 federal election.
In October 2006, Trudeau criticized Quebec nationalism by describing political nationalism generally as an "old idea from the 19th century", "based on a smallness of thought" and not relevant to modern Quebec. This comment was seen as a criticism of Michael Ignatieff
Michael Grant Ignatieff (; born May 12, 1947) is a Canadian author, academic and former politician who served as the leader of the Liberal Party of Canada and Leader of the Official Opposition from 2008 until 2011. Known for his work as a histo ...
, then a candidate in the 2006 Liberal Party leadership election, who was promoting recognition of Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
as a nation. Trudeau later wrote a public letter on the subject, describing the idea of Quebec nationhood as "against everything my father ever believed".
Trudeau announced his support for leadership candidate Gerard Kennedy
Gerard Michael Kennedy (born July 24, 1960) is a Canadian politician in Ontario, Canada. He served as Ontario's minister of Education from 2003 to 2006, when he resigned to make an unsuccessful bid for the leadership of the Liberal Party of Ca ...
shortly before the 2006 convention and introduced Kennedy during the candidates' final speeches. When Kennedy dropped off after the second ballot, Trudeau joined him in supporting the ultimate winner, Stéphane Dion
Stéphane Maurice Dion (born 28 September 1955) is a Canadian diplomat, academic and former politician who has been the Canadian ambassador to France and Monaco since 2022 and special envoy to the European Union since 2017. Dion was Leader of ...
.
Rumours circulated in early 2007 that Trudeau would run in an upcoming by-election in the Montreal riding of Outremont
Outremont is an affluent residential borough (''arrondissement'') of the city of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It consists entirely of the former city on the Island of Montreal in southwestern Quebec. The neighbourhood is inhabited largely by fran ...
. The Montreal newspaper '' La Presse'' reported despite Trudeau's keenness, Liberal leader Stéphane Dion wanted Outremont for a star candidate who could help rebuild the Liberal Party. Instead, Trudeau announced that he would seek the Liberal nomination in the nearby riding of Papineau for the next general election. The riding, which had been held for 26 years by André Ouellet, a senior minister under his father, had been in Liberal hands for 53 years before falling to the Bloc Québécois in 2006.
On April 29, 2007, Trudeau won the Liberal party's nomination, picking up 690 votes to 350 for Deros and 220 for Giordano against Mary Deros, a Montreal city councillor and Basilio Giordano
Basilio Giordano (born February 3, 1952) is an Italian people, Italian and Canadians, Canadian politician and journalist. He was a city councillor in the Montreal, Montreal, Quebec borough of Saint-Leonard, Quebec, Saint-Leonard from 1982 to 199 ...
, the publisher of a local Italian-language newspaper.
Opposition, 2008–2015
Prime Minister Stephen Harper called an election for October 14, 2008, by which time Trudeau had been campaigning for a year in Papineau. On election day, Trudeau narrowly defeated Bloc Québécois incumbent Vivian Barbot. Following his election win, Edward Greenspon, editor-in-chief of ''The Globe and Mail
''The Globe and Mail'' is a Canadian newspaper printed in five cities in western and central Canada. With a weekly readership of approximately 2 million in 2015, it is Canada's most widely read newspaper on weekdays and Saturdays, although it ...
'', noted that Trudeau would "be viewed as few other rookie MPs are—as a potential future Prime Minister—and scrutinized through that lens".
 The Conservative Party won a minority government in the 2008 election, and Trudeau entered parliament as a member of the Official Opposition. Trudeau's first legislative act was a motion that called for the creation of a "national voluntary service policy for young people". He later co-chaired the Liberal Party's April 2009 national convention in
The Conservative Party won a minority government in the 2008 election, and Trudeau entered parliament as a member of the Official Opposition. Trudeau's first legislative act was a motion that called for the creation of a "national voluntary service policy for young people". He later co-chaired the Liberal Party's April 2009 national convention in Vancouver
Vancouver ( ) is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the ...
, and in October of the same year he was appointed as the party's critic for multiculturalism and youth.
In September 2010, he was reassigned as critic for youth, citizenship, and immigration. During that time, he criticized the government's legislation targeting human smuggling, which he argued would penalize the victims of smuggling.
Trudeau sparked controversy when it was revealed that he earned $1.3 million in public speaking fees from charities and school boards across Canada, $277,000 of which Trudeau received after becoming an MP.
He encouraged an increase of Canada's relief efforts after the 2010 Haiti earthquake
A catastrophic magnitude 7.0 Mw earthquake struck Haiti at 16:53 local time (21:53 UTC) on Tuesday, 12 January 2010. The epicenter was near the town of Léogâne, Ouest department, approximately west of Port-au-Prince, Haiti's c ...
, and sought more accessible immigration procedures for Haitians moving to Canada in the time of crisis. His own riding includes a significant Haitian community.
Trudeau was re-elected in Papineau in the 2011 federal election, as the Liberal Party fell to third-party standing in the House of Commons with only thirty-four seats. Ignatieff resigned as party leader immediately after the election, and rumours again circulated that Trudeau could run to become his successor. On this occasion, Trudeau said, "I don't feel I should be closing off any options ... because of the history packaged into my name, a lot of people are turning to me in a way that ... to be blunt, concerns me." Weeks after the election, Toronto MP Bob Rae was selected as the interim leader until the party's leadership convention, which was later decided to be held in April 2013. Rae appointed Trudeau as the party's critic for post-secondary education, youth and amateur sport. After his re-election, he travelled the country hosting fundraisers for charities and the Liberal Party.
Trudeau wanted to take part in a charity boxing match on behalf of the cancer research fundraising event Fight for the Cure, but was having difficulty finding a Conservative opponent until Conservative senator Patrick Brazeau agreed when asked on Trudeau's behalf by their mutual hairdresser Stefania Capovilla. The fight on March 31, 2012, in Ottawa at the Hampton Inn was broadcast live on Sun News with commentary by Ezra Levant
Ezra Isaac Levant (born February 20, 1972) is a Canadian conservative media personality, political activist, writer, broadcaster, and former lawyer. Levant is the founder and former publisher of the conservative magazine, The'' Western Standard''. ...
and Brian Lilley
Brian Lilley is a columnist, author, television show host, and was the senior correspondent for the now defunct Sun News Network in Ottawa, covering Parliament Hill. He has worked in radio, television and print across Canada. A former radio show ...
and Trudeau won in the third round, the result considered an upset.
Leader of the Liberal Party
Earlier speculation
After Dion's resignation as Liberal leader in 2008, Trudeau's name was mentioned as a potential candidate with polls showing him as a favourite among Canadians for the position. However, Trudeau did not enter the race and Ignatieff was named leader in December 2008. After the party's poor showing in the 2011 election, Ignatieff resigned from the leadership and Trudeau was again seen as a potential candidate to lead the party. Following the election, Trudeau said he was undecided about seeking the leadership; months later on October 12 atWilfrid Laurier University
Wilfrid Laurier University (commonly referred to as WLU or simply Laurier) is a public university in Ontario, Canada, with campuses in Waterloo, Brantford and Milton. The newer Brantford and Milton campuses are not considered satellite campuses ...
, he announced he would not seek the post because he had a young family. When interim leader Bob Rae, who was also seen as a frontrunner, announced he would not be entering the race in June 2012, Trudeau was hit with a "tsunami" of calls from supporters to reconsider his earlier decision to not seek the leadership.
Opinion polling conducted by several pollsters showed that if Trudeau were to become leader the Liberal Party would surge in support, from a distant third place to either being competitive with the Conservative Party or leading them. In July 2012, Trudeau stated that he would reconsider his earlier decision to not seek the leadership and would announce his final decision at the end of the summer.
2013 leadership election
On September 26, 2012, multiple media outlets started reporting that Trudeau would launch his leadership bid the following week. While Trudeau was seen as a frontrunner for the leadership of the Liberal Party, he was criticized for his perceived lack of substance. During his time as a member of Parliament, he spoke little on policy matters and it was not known where he stood on many issues such as the economy and foreign affairs. Some strategists and pundits believed the leadership would be the time for Trudeau to be tested on these issues; however, there was also fear within the party that his celebrity status and large lead might deter other strong candidates from entering the leadership race. On October 2, 2012, Trudeau held a rally in Montreal to launch his bid for the leadership of the Liberal Party. The core people on his campaign team were considered longtime friends, and all in their 30s and 40s. His senior advisor was Gerald Butts, the former president ofWWF-Canada
World Wildlife Fund Canada (WWF-Canada) is one of Canada's largest conservation organizations and is a member of the World Wide Fund for Nature, WWF global network, actively contributing to the Environmentalism, protection, management, and Resto ...
who had previously been principal secretary to former Ontario premier Dalton McGuinty
Dalton James Patrick McGuinty Jr. (born July 19, 1955) is a former Canadian politician who served as the 24th premier of Ontario from 2003 to 2013. He was the first Liberal leader to win two majority governments since Mitchell Hepburn nearl ...
. Other senior aides included campaign manager Katie Telford
Katie Telford (born 1978) is a Canadian political strategist who is the Chief of Staff to Prime Minister Justin Trudeau. She served as Trudeau's chief campaign advisor during his successful campaign in the 2015 election. Following the resignati ...
, and policy advisors Mike McNeir and Robert Asselin, who had all worked for recent Liberal Party leaders. His brother Alexandre also took a break from his documentary work to be a senior advisor on Trudeau's campaign.
During the leadership campaign three by-elections were held on November 26, 2012. The riding Calgary Centre
Calgary Centre (french: Calgary-Centre; formerly known as Calgary South Centre) is a federal electoral district in Alberta, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1968. The riding consists of many young adul ...
was expected to be a three-way race between the Conservatives, Liberals and Green Party. A week before by-election day Sun Media
Sun Media Corporation was the owner of several tabloid and broadsheet newspapers in Canada and the 49 percent owner of the now defunct Sun News Network. It was a subsidiary of Quebecor Media.
On October 6, 2014, Quebecor Media announced the sal ...
reported on comments Trudeau had made in a 2010 interview with Télé-Québec
The Société de télédiffusion du Québec (; en, Quebec Television Broadcasting Corporation), branded as Télé-Québec (), is a Canadian French-language public educational television network in the province of Quebec. It is a provincial Crown ...
, in which he said, "Canada isn't doing well right now because it's Albertans who control our community and socio-democratic agenda." Trudeau's campaign advisor said that the comments were being brought up now because of the close race in Calgary Centre. The following day, Trudeau apologized, saying he was wrong to use "Alberta" as "shorthand
Shorthand is an abbreviated symbolic writing method that increases speed and brevity of writing as compared to longhand, a more common method of writing a language. The process of writing in shorthand is called stenography, from the Greek ''ste ...
" in referring to Stephen Harper's government. The Conservatives held onto Calgary Centre in the by-election by less than 1,200 votes. Liberal candidate Harvey Locke
Harvey Locke is a Canadian conservationist, writer, and photographer. He is a recognized global leader in the field of parks, wilderness, wildlife and large landscape conservation. He is a founder of the Yellowstone to Yukon Conservation Initia ...
said he lost the by-election on his own and that comments made by Trudeau did not influence the outcome.
Fellow leadership candidate Marc Garneau
Joseph Jean-Pierre Marc Garneau (born February 23, 1949) is a Canadian politician, retired Royal Canadian Navy officer and former astronaut who served as a Cabinet minister from 2015 to 2021. A member of the Liberal Party of Canada, Liberal Par ...
, seen as Trudeau's main challenger in the race, criticized Trudeau for not releasing enough substantial policy positions. Garneau called on him to release more detailed policies before members and supporters begin to vote. Garneau later challenged Trudeau to a one-on-one debate, and said that if Trudeau could not defend his ideas in a debate against him, he wouldn't be able to do so against Prime Minister Harper. Trudeau clashed in debates with challenger Joyce Murray
Joyce Murray (born July 11, 1954) is a Canadian politician, businesswoman and environmental advocate. A member of the Liberal Party of Canada, she has represented the riding of Vancouver Quadra in the House of Commons since 2008. She was re-e ...
, who was the only Liberal leadership candidate to speak out strongly in favour of electing the House of Commons with a system of proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
. She challenged Trudeau over his support for a preferential ballot
The term ranked voting (also known as preferential voting or ranked choice voting) refers to any voting system in which voters rank their candidates (or options) in a sequence of first or second (or third, etc.) on their respective ballots. Ran ...
voting system.
On March 13, 2013, Garneau dropped out of the leadership race, saying that polling conducted by his campaign showed he would be unable to defeat Trudeau.
With Joyce Murray, the last challenger, receiving significant press time, more Liberal politicians and public figures declared themselves for Trudeau. Trudeau was declared the winner of the leadership election on April 14, 2013, garnering 80.1 per cent of 30,800 votes. Joyce Murray finished in second place with 10.2 per cent points, ahead of Martha Hall Findlay's 5.7 per cent. Trudeau had lost only five ridings, all to Murray and all in BC.
=Leadership, 2013–2015
= In the days following his victory in the leadership race, snapshot polls recorded a surge in support for the Liberal party.
In 2013, Trudeau chose to give up his seat at the
In the days following his victory in the leadership race, snapshot polls recorded a surge in support for the Liberal party.
In 2013, Trudeau chose to give up his seat at the funeral of Nelson Mandela
A funeral is a ceremony connected with the final disposition of a corpse, such as a burial or cremation, with the attendant observances. Funerary customs comprise the complex of beliefs and practices used by a culture to remember and respect th ...
, in deference to Irwin Cotler
Irwin Cotler, PC, OC, OQ (born May 8, 1940) is a retired Canadian politician who was Member of Parliament for Mount Royal from 1999 to 2015. He served as the Minister of Justice and Attorney General of Canada from 2003 until the Liberal gov ...
as representative of the Liberal Party of Canada
The Liberal Party of Canada (french: Parti libéral du Canada, region=CA) is a federal political party in Canada. The party espouses the principles of liberalism,McCall, Christina; Stephen Clarkson"Liberal Party". ''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' ...
, because of Cotler's work for and with Nelson Mandela
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela (; ; 18 July 1918 – 5 December 2013) was a South African Internal resistance to apartheid, anti-apartheid activist who served as the President of South Africa, first president of South Africa from 1994 to 1 ...
in fighting apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
.
During the leadership campaign Trudeau pledged to park all his assets, exclusive of real estate holdings, into a blind trust
A blind trust is a trust in which the trust beneficiaries have no knowledge of the holdings of the trust, and no right to intervene in their handling. In a blind trust, the trustees (fiduciaries, or those who have been given power of attorney) h ...
which is atypical for opposition MPs, including leaders. According to documents obtained by the ''Ottawa Citizen
The ''Ottawa Citizen'' is an English-language daily newspaper owned by Postmedia Network in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
History
Established as ''The Bytown Packet'' in 1845 by William Harris (journalist), William Harris, it was renamed the '' ...
'', he fulfilled the pledge in July 2013 when the blind trust was set up by BMO Private Banking.
On January 27, 2014, Trudeau and MP Carolyn Bennett
Carolyn Ann Bennett (born December 20, 1950) is a Canadian physician and politician who has served as minister of mental health and addictions, and associate minister of health since October 26, 2021. A member of the Liberal Party, she has repre ...
escorted Chrystia Freeland
Christina Alexandra Freeland (born August 2, 1968) is a Canadian politician serving as the tenth and current deputy prime minister of Canada since 2019 and the Minister of Finance (Canada), minister of finance since 2020. A member of the Libe ...
into the House of Commons, as is traditional for by-election victors. Trudeau launched an internet video the week before the 2014 Liberal party convention titled "An economy that benefits us all" in which he narrates his economic platform. He said that Canada's debt to GDP ratios have come down in recent years and now it's time for Ottawa to "step up".
2015 federal election
 On October 19, 2015, after the longest official campaign in over a century, Trudeau led the Liberals to a decisive victory in the federal election. The Liberals won 184 of the 338 seats, with 39.5% of the popular vote, for a strong majority government; a gain of 150 seats compared to the 2011 federal election.
This was the second-best performance in the party's history. The Liberals won mostly on the strength of a solid performance in the eastern half of the country. In addition to taking all of Atlantic Canada and Toronto, they won 40 seats in Quebec—the most that the Liberals had won in that province since Trudeau's father led them to a near-sweep of the province in 1980, and also the first time since then that the Liberals won a majority of Quebec's seats in an election. The 150-seat gain was the biggest numerical increase for a single party since Confederation and marked the first time that a party had rebounded from third place in the Commons to a majority government.
In addition to the appeal of his party's platform, Trudeau's success has been credited to his performance both on the campaign trail and televised
On October 19, 2015, after the longest official campaign in over a century, Trudeau led the Liberals to a decisive victory in the federal election. The Liberals won 184 of the 338 seats, with 39.5% of the popular vote, for a strong majority government; a gain of 150 seats compared to the 2011 federal election.
This was the second-best performance in the party's history. The Liberals won mostly on the strength of a solid performance in the eastern half of the country. In addition to taking all of Atlantic Canada and Toronto, they won 40 seats in Quebec—the most that the Liberals had won in that province since Trudeau's father led them to a near-sweep of the province in 1980, and also the first time since then that the Liberals won a majority of Quebec's seats in an election. The 150-seat gain was the biggest numerical increase for a single party since Confederation and marked the first time that a party had rebounded from third place in the Commons to a majority government.
In addition to the appeal of his party's platform, Trudeau's success has been credited to his performance both on the campaign trail and televised leaders' debates
A leaders' debate or presidential debate is a public debate held during a general election campaign, where the candidates expose their political opinions and public policy proposals, and criticism of them, to potential voters. They are normally b ...
exceeding the lowered expectations created by Conservative advertisements and conservative media outlets.
 Trudeau declared victory shortly after
Trudeau declared victory shortly after CBC News
CBC News is a division of the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation responsible for the news gathering and production of news programs on the corporation's English-language operations, namely CBC Television, CBC Radio, CBC News Network, and CBC.ca. ...
projected that he had won a majority government. He began his speech with a reference to former Liberal prime minister Wilfrid Laurier
Sir Henri Charles Wilfrid Laurier, ( ; ; November 20, 1841 – February 17, 1919) was a Canadian lawyer, statesman, and politician who served as the seventh prime minister of Canada from 1896 to 1911. The first French Canadian prime minis ...
's "sunny ways" (french: link=no, voies ensoleillées) approach to bringing Canadians together despite their differences. According to Trudeau, Laurier "knew that politics can be a positive force, and that's the message Canadians have sent today". Harper announced his resignation as the leader of the Conservative Party that night.
Prime Minister of Canada (2015–present)
 Trudeau and the rest of the
Trudeau and the rest of the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
were sworn in by Governor General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy t ...
David Johnston
David Lloyd Johnston (born June 28, 1941) is a Canadian academic, author, and statesman who served from 2010 to 2017 as Governor General of Canada, the 28th since Canadian Confederation. He is the commissioner of the Leaders' Debates Commis ...
on November 4, 2015. He said that his first legislative priority was to lower taxes for middle-income Canadians and raise taxes for the top one per cent of income earners after parliament was reconvened on December 3, 2015. Trudeau also issued a statement promising to rebuild relations with Indigenous peoples in Canada
In Canada, Indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although ''Indian'' is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors ''Indian'' and ''Eskimo'' have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider them ...
and run an open, ethical and transparent government. On November 5, 2015, during the first Liberal caucus meeting since forming a majority government, the party announced that it would reinstate the mandatory long-form census that had been scrapped in 2010, effective with the 2016 census.
Trudeau was criticized by opposition members in November 2016 for his fundraising tactics which they saw as "cash for access" schemes. Trudeau attended fundraisers where attendees paid an upward of $1500 for access to him and other cabinet members. In some instances, the events were attended by foreign businessmen who needed government approval for their businesses. Trudeau defended his fundraising tactics, saying that they were not in breach of any ethics rules. He also stated that he was lobbied at the fundraisers but not influenced. In 2017, Trudeau introduced legislation that would eliminate such exclusive events by requiring increased transparency for political fundraisers.
 In January 2017, the
In January 2017, the ethics commissioner
The Conflict of Interest and Ethics Commissioner of Canada is an entity of the Parliament of Canada. The commissioner is an independent officer of Parliament, who administers the ''Conflict of Interest Act'' and the ''Conflict of Interest Code ...
, Mary Dawson, began an investigation into Trudeau for a vacation he and his family took to Aga Khan IV
Shāh Karim al-Husayni (born 13 December 1936), known by the religious title Mawlānā Hazar Imam by his Ismaili followers and elsewhere as Aga Khan IV, is the 49th and current Imam of Nizari Ismailis, a denomination within Shia Islam. He ha ...
's private island in the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to ...
. The ethics commissioner's report, released in December 2017, found that Trudeau had violated four provisions of the ''Conflict of Interest Act''. He became the first sitting prime minister to break federal conflict of interest rules. In 2022, it was reported that the Royal Canadian Mounted Police
The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP; french: Gendarmerie royale du Canada; french: GRC, label=none), commonly known in English as the Mounties (and colloquially in French as ) is the federal police, federal and national police service of ...
had considered bringing criminal charges against Trudeau over the affair.
In February 2018, Trudeau was criticized when his government invited Khalistani nationalist Jaspal Atwal to the Canadian High Commission's dinner party in Delhi. Atwal had previously been convicted for the shooting and attempted murder of Indian Cabinet minister Malkiat Singh Sidhu
Malkiat Singh Sidhu (died 27 April 1991) was the former Planning Minister of Punjab, India. He was a member of the Akali Dal political party. In 1986, he was named Minister of State.
On 25 May 1986, he was ambushed by four Sikhs who learned h ...
in 1986, as well as the assault on former BC premier Ujjal Dosanjh
Ujjal Dev Dosanjh ( pa, ਉੱਜਲ ਦੇਵ ਦੁਸਾਂਝ) (), (born September 9, 1947) is a Canadian lawyer and politician. He served as the 33rd premier of British Columbia from 2000 to 2001 and as a Liberal Party of Canada member of ...
in 1985. Following the dinner, the PMO rescinded the invitation, and apologized for the incident.
During his time as Prime Minister, Justin Trudeau has been the target of multiple death threats and assassination plots.
Assessment of campaign promises
In July 2019, a group of 20 independent academics published an assessment on Trudeau's first term as Prime Minister, called ''Assessing Justin Trudeau's Liberal Government: 353 Promises and a Mandate for Change''. The assessment found that Trudeau's Liberal government kept 92 per cent of pledges, including complete and partial pledges. When calculating completed and realized pledges, they found Trudeau's government kept 53.5 per cent of their campaign promises. Trudeau's government, along with the "last Harper government had the highest rates of follow-through on their campaign promises of any Canadian government over the last 35 years," according to the assessment.SNC-Lavalin affair
On February 8, 2019, ''The Globe and Mail'' reported that sources close to the government said that the Prime Minister's Office had allegedly attempted to influenceAttorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general.
In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have exec ...
Jody Wilson-Raybould
Jody Wilson-Raybould (born March 23, 1971), also known by her initials JWR and by her Kwak’wala name Puglaas, is a Canadian lawyer and former politician who served as the member of Parliament (MP) for the British Columbia (BC) riding of Van ...
concerning an ongoing prosecution of SNC-Lavalin
SNC-Lavalin Group Inc. is a Canadian company based in Montreal that provides engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) services to various industries, including mining and metallurgy, oil and gas, environment and water, infrastructure, a ...
. When asked about the allegations, Trudeau said that the story in the ''Globe'' was false and that he had never "directed" Wilson-Raybould concerning the case. Wilson-Raybould did not comment on the matter, citing solicitor-client privilege
In common law jurisdictions, legal professional privilege protects all communications between a professional legal adviser (a solicitor, barrister or attorney) and his or her clients from being disclosed without the permission of the client. ...
. Soon after, Trudeau voluntarily waived privilege and cabinet confidences, permitting her to speak. On February 11, the ethics commissioner announced the opening of an investigation into the allegations. Trudeau said he "welcomed the investigation". The Justice Committee of the House of Commons has conducted a series of hearings on the alleged interference. The investigation heard from several witnesses, including Jody Wilson-Raybould, who submitted as evidence a telephone call she secretly recorded between herself and Privy Council Clerk Michael Wernick
Michael Wernick (born September 1957) is a Canadian retired public servant who served as the 23rd clerk of the Privy Council for Canada from 2016 to 2019. Following his tenure as clerk, Wernick joined the University of Ottawa, where he was name ...
, which was subsequently released to the public. On the recording, Wernick is heard asking to understand why the "DPA route" is not being used, stating that people were "talking past each other", and suggesting Trudeau obtain independent legal advice from former Supreme Court chief justice Beverly McLachlin
Beverley Marian McLachlin (born September 7, 1943) is a Canadian jurist and author who served as the 17th chief justice of Canada from 2000 to 2017. She is the longest-serving chief justice in Canadian history and the first woman to hold the p ...
. Wilson-Raybould is heard suggesting that Trudeau would be "breaching a constitutional principle of prosecutorial independence". On March 19, 2019, the Liberal committee members voted as a bloc to shut down the Justice Committee's investigation.
Trudeau was the subject of an investigation by the ethics commissioner
The Conflict of Interest and Ethics Commissioner of Canada is an entity of the Parliament of Canada. The commissioner is an independent officer of Parliament, who administers the ''Conflict of Interest Act'' and the ''Conflict of Interest Code ...
, pursuant to the ''Conflict of Interest Act'', in regards to criminal charges
A criminal charge is a formal accusation made by a governmental authority (usually a public prosecutor or the police) asserting that somebody has committed a crime. A charging document, which contains one or more criminal charges or counts, can ...
against SNC-Lavalin
SNC-Lavalin Group Inc. is a Canadian company based in Montreal that provides engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) services to various industries, including mining and metallurgy, oil and gas, environment and water, infrastructure, a ...
in the SNC-Lavalin affair. The commission's final report, issued August 14, 2019, concluded "Mr. Trudeau contravened section 9 of the Act".
2019 federal election
 On September 11, 2019, Trudeau visited Governor General
On September 11, 2019, Trudeau visited Governor General Julie Payette
Julie Payette (; born October 20, 1963) is a Canadian engineer, scientist and former astronaut who served from 2017 to 2021 as Governor General of Canada, the 29th since Canadian Confederation.
Payette holds engineering degrees from McGill ...
, to request the dissolution of Parliament, and formally triggering an election. Prior to the formal start of the campaign, Trudeau announced his intention to only participate in the three leaders' debates
A leaders' debate or presidential debate is a public debate held during a general election campaign, where the candidates expose their political opinions and public policy proposals, and criticism of them, to potential voters. They are normally b ...
, two organized by the Leaders' Debates Commission
The Leaders' Debates Commission is the independent Canadian government agency which was charged with organizing two debates, one in English and one in French, between the leaders of eligible political parties during the 2019 Canadian federal ele ...
, and one organized by TVA
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) is a Federal government of the United States, federally owned electric utility corporation in the United States. TVA's service area covers all of Tennessee, portions of Alabama, Mississippi, and Kentucky, an ...
. Other leader's debates were either cancelled or took place with an empty podium left on stage for Trudeau.
In September 2019, controversial pictures and video were published showing Trudeau in brownface
Brownface is a social phenomenon in which a white or light-skinned person attempts to portray themselves as a "brown" person of color, but less overtly and with a lighter complexion than traditional blackface. This may include mimicry of Midd ...
and blackface
Blackface is a form of theatrical makeup used predominantly by non-Black people to portray a caricature of a Black person.
In the United States, the practice became common during the 19th century and contributed to the spread of racial stereo ...
. On September 18, 2019, ''Time'' magazine published a photograph of Trudeau wearing brownface makeup in the spring of 2001, at an ''Arabian Nights
''One Thousand and One Nights'' ( ar, أَلْفُ لَيْلَةٍ وَلَيْلَةٌ, italic=yes, ) is a collection of Middle Eastern folk tales compiled in Arabic during the Islamic Golden Age. It is often known in English as the ''Arabian ...
''-themed gala, while Trudeau was a teacher at West Point Grey Academy. Trudeau publicly apologized, agreeing the photo was racist and saying: "I shouldn't have done that. I should have known better and I didn't. I'm really sorry." He further went on to say "It was something that I didn't think was racist at the time, but now I recognize it was something racist to do". Trudeau also admitted to wearing blackface makeup in high school while singing " Day-O" at a talent show that was subsequently published by Global News
Global News is the news and current affairs division of the Canadian Global Television Network. The network is owned by Corus Entertainment, which oversees all of the network's national news programming as well as local news on its 21 owned-and ...
. A third instance, a video, of Trudeau in racist dress was also published. After this video was published, Trudeau admitted he could not remember how often he had worn blackface makeup. In the days following the scandal, pollsters
An opinion poll, often simply referred to as a survey or a poll (although strictly a poll is an actual election) is a human research survey of public opinion from a particular sample. Opinion polls are usually designed to represent the opinions ...
pointed out that many Canadians either were not bothered by the scandal or had accepted Trudeau's apology. Additionally, some minority community groups, racialized commentators and some of Trudeau's opponents came to his defence. Others were more critical, including members of his own party.
2019 election results
Andrew Scheer
Andrew James Scheer (born May 20, 1979) is a Canadian politician who has served as the member of Parliament (MP) for Regina—Qu'Appelle since 2004. Scheer served as the 35th speaker of the House of Commons from 2011 to 2015, and was the lead ...
had 34.4 per cent. It was also the first time a government took power with less than 35 per cent of the national popular vote since the Conservatives of John A. Macdonald
Sir John Alexander Macdonald (January 10 or 11, 1815 – June 6, 1891) was the first prime minister of Canada, serving from 1867 to 1873 and from 1878 to 1891. The dominant figure of Canadian Confederation, he had a political career that sp ...
, in 1867, who had 34.8 per cent of the votes. In Alberta and Saskatchewan, the Liberal party won 14 per cent and 10 per cent of the popular vote, respectively. In Ontario, Liberals won all 25 Toronto seats and 24 of 29 seats in the surrounding suburbs of the Greater Toronto Area
The Greater Toronto Area, commonly referred to as the GTA, includes the City of Toronto and the regional municipalities of Durham, Halton, Peel, and York. In total, the region contains 25 urban, suburban, and rural municipalities. The Greater T ...
—reportedly due in part to the unpopularity of the Progressive Conservative party government of Premier Doug Ford
Douglas Robert Ford Jr. (born November 20, 1964) is a Canadian politician and businessman who has served as the 26th and current premier of Ontario since June 2018 and leader of the Progressive Conservative (PC) Party since March 2018. He ...
.
COVID-19 pandemic
Justin Trudeau was Prime Minister during the worldwideCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
. His government's response to the pandemic included funds for provinces and territories to adapt to the new situation, funds for coronavirus research, travel restrictions, screening of international flights, self-isolation orders under the ''Quarantine Act'', an industrial strategy, and a public health awareness campaign. Initially, Canada faced a shortage of personal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is protective clothing, helmets, goggles, or other garments or equipment designed to protect the wearer's body from injury or infection. The hazards addressed by protective equipment include physical, elec ...
, as the Trudeau government had cut PPE stockpile funding in the previous years.
To deal with the economic impact of the pandemic in 2020, Trudeau waived student loan payments, increased the Canada Child Benefit
The Canada Child Benefit (CCB), previously the Canada Child Tax Benefit (CCTB), is an income-tested income support program for Canadian families. It is delivered as a tax-free monthly payment available to eligible Canadian families to help with the ...
, doubled the annual Goods and Services Tax payment, and introduced the Canada Emergency Response Benefit
The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial CA$82-billion aid package was announced on March 18, 2020 by Jus ...
(CERB) as part of a first package in March. In April 2020, Trudeau introduced the Canada Emergency Wage Subsidy
The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial CA$82-billion aid package was announced on March 18, 2020 by Jus ...
, the Canada Emergency Business Account
The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial CA$82-billion aid package was announced on March 18, 2020 by Jus ...
, and the Canada Emergency Student Benefit
The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial CA$82-billion aid package was announced on March 18, 2020 by Jus ...
. Trudeau also deployed the Canadian Forces
}
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; french: Forces armées canadiennes, ''FAC'') are the unified military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air elements referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army, and Royal Canadian Air Force.
...
in long-term care homes in Quebec and Ontario as part of Operation LASER
Operation Laser is a domestic operation of the Canadian Armed Forces for contingency planning and response in the event of a pandemic. Its three goals are: protecting CAF personnel and capability, assessing CAF capabilities to respond to a pandemi ...
.
Throughout the pandemic, the federal government was also responsible for the procurement of COVID-19 vaccine
A COVID19 vaccine is a vaccine intended to provide acquired immunity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 ( COVID19).
Prior to the COVID19 pandemic, an e ...
s. On May 12, 2020, the Trudeau government announced it had reached an exclusive deal with CanSino Biologics
CanSino Biologics (), often abbreviated as CanSinoBIO, is a Chinese vaccine company.
History
CanSino Biologics was founded in 2009 in Tianjin by Yu Xuefeng, Zhu Tao, Qiu Dongxu and Helen Mao Huihua.
In July 2018, it filed an application to l ...
. However, due to deteriorating Canadian-Chinese relations, the Cansino
The Cansino family is a prominent Sephardic Jewish family originally from Oran, Algeria.
The family progenitor Jacob Cansino served as an interpreter at Oran, a Spanish colony in northwestern Africa, under Charles V, until 1556, when he was s ...
deal fell through. On August 5, 2020, the Trudeau government created a plan to secure doses of the Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer ...
and Moderna vaccines. Starting in December 2020, Justin Trudeau oversaw the implementation of Canada's mass-vaccination program.
The spread of COVID-19 in Canada continued beyond the initial outbreak, with a strong second wave in the fall of 2020 and an even more serious third wave in the spring of 2021. Throughout the crisis, Trudeau periodically extended the scope and duration of the federal aid programs. The 2021 Canadian federal budget planned to phase them out by the end of September 2021, and projected a $354.2-billion deficit in the 2020-21 fiscal year. While CERB was indeed phased out on September 26, the Canada Recovery Benefit
The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial Canadian dollar, CA$82-billion aid package was announced on Marc ...
(CBR) continued to provide support until October 23. The Canada Worker Lockdown Benefit
The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial CA$82-billion aid package was announced on March 18, 2020 by Jus ...
was introduced that month to replace the CBR, and expanded during the spread of the Omicron variant
Omicron (B.1.1.529) is a variant of SARS-CoV-2 first reported to the World Health Organization (WHO) by the Network for Genomics Surveillance in South Africa on 24 November 2021. It was first detected in Botswana and has spread to become the ...
in December 2021.
WE Charity ethics investigation
Following complaints by opposition parties that the Trudeau family had ties toWE Charity
WE Charity (french: Organisme UNIS), formerly known as Free the Children (French: ''Enfants Entraide''), is an international development charity and youth empowerment movement founded in 1995 by human rights advocates Marc and Craig Kielburger. ...
, the ethics commissioner on July 3, 2020, announced an investigation into Trudeau's and the government's decision to have the charity administer a summer, student-grant program which could assist students financially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Trudeau responded by saying WE was the charity that had the capability to administer such a program. WE and the federal government decided to "part ways" leaving administration of the grant program to the federal government.
We Charity was criticized for its close ties to the Trudeau family; the investigation came after revelations that Trudeau's mother, brother, and wife were paid nearly $300,000 in total to speak at WE Charity events.
On July 16, 2020, the ethics commissioner also announced the investigation was being expanded to include Finance Minister Bill Morneau
William Francis Morneau Jr. (born October 7, 1962) is a Canadian businessman and former Liberal Party politician who served as minister of finance and member of Parliament (MP) for Toronto Centre from 2015 to 2020.
Morneau was executive chai ...
. Trudeau was ultimately cleared of any wrongdoing by the ethics commissioner though Morneau was found to have broken the conflict of interest law.
2021 federal election
On August 15, 2021, Trudeau advised Governor GeneralMary Simon
Mary Jeannie May Simon (in Inuktitut syllabics: ᒥᐊᓕ ᓴᐃᒪᓐ, iu, script=Latn, Ningiukudluk; born August 21, 1947) is a Canadian civil servant, diplomat, and former broadcaster who has served as the 30th governor general of Canada ...
to dissolve parliament, scheduling an election for September 20. The election was called on the same day as the Fall of Kabul. In the first two weeks of the campaign, Trudeau received criticism for not acting fast enough in the face of the 2021 Taliban offensive
A military offensive by the Taliban insurgent group and other allied militants led to the fall of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan based in Kabul and marked the end of the nearly 20-year-old War in Afghanistan, that had begun following the ...
to evacuate Canadian citizens and Afghans who supported Canada’s military and diplomatic efforts during the War in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC – 327 BC)
*Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637–709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see als ...
.
In the 2021 federal election, Trudeau secured a third mandate and his second minority government after winning 160 seats. However, the Liberals came in second in the national popular vote, behind the Conservatives. They received 32.6 percent of the popular vote, the lowest percentage of the national popular vote for a governing party in Canadian history.
2022 convoy protest
The Canada convoy protest, called the Freedom Convoy, was aprotest
A protest (also called a demonstration, remonstration or remonstrance) is a public expression of objection, disapproval or dissent towards an idea or action, typically a political one.
Protests can be thought of as acts of coopera ...
in Canada against COVID-19 vaccine requirements for truckers to re-enter the country by land introduced by the Government of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown ...
on January 15, 2022. Originally composed of several routes traversing all of the Canadian provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outsi ...
, the truck convoys converged on Ottawa.
On January 29, the first day of protest at Parliament Hill
Parliament Hill (french: Colline du Parlement, colloquially known as The Hill, is an area of Crown land on the southern banks of the Ottawa River in downtown Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Its Gothic revival suite of buildings, and their architectu ...
, Prime Minister Trudeau moved to an undisclosed location.
According to ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
'', the demonstration developed to express a number of "antigovernment grievances", particularly against Trudeau.
On January 31, Trudeau called the protests an "insult to truth". On February 3, he said that a military response was "not in the cards right now".
On February 11, ''Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters Corporation. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency was estab ...
'' reported that Trudeau promised the US "quick action" regarding protesters who have forcefully blocked the Ambassador Bridge on the US-Canada border, the continent's busiest land border crossing." Trudeau subsequently indicated that there would be "robust police intervention" and called for all protesters to "go home."
Trudeau invoked the '' Emergencies Act'' on February 14, for the first time since it was enacted in 1988, as a result of the public order emergency caused by the demonstrations in Ottawa. On February 23, Trudeau announced that the federal government would revoke the emergency declaration. Later that day, the governor general signed a proclamation revoking it.
Policies
Domestic policy
The Trudeau government'seconomic policy
The economy of governments covers the systems for setting levels of taxation, government budgets, the money supply and interest rates as well as the labour market, national ownership, and many other areas of government interventions into the e ...
initially relied on increased tax revenues to pay for increased government spending. While the government did not balance the budget in its first term, it reduced Canada's debt-to-GDP ratio
In economics, the debt-to-GDP ratio is the ratio between a country's government debt (measured in units of currency) and its gross domestic product (GDP) (measured in units of currency per year). While it is a "ratio", it is technically measured i ...
every year until 2020, when the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
hit. Trudeau's progressive social policy
Social policy is a plan or action of government or institutional agencies which aim to improve or reform society.
Some professionals and universities consider social policy a subset of public policy, while other practitioners characterize soci ...
has included strong advocacy for feminism and abortion rights. His government introduced the bill that made conversion therapies
Conversion therapy is the pseudoscientific practice of attempting to change an individual's sexual orientation, gender identity, or gender expression to align with heterosexual and cisgender norms. In contrast to evidence-based medicine and cl ...
illegal in Canada.
In his first term, Canada set targets to welcome an increased number of immigrants and refugees. Canada introduced the right to medically-assisted dying in 2016 and legalized cannabis for recreational use in 2018. In 2021, Trudeau announced the creation of a national child care
Child care, otherwise known as day care, is the care and supervision of a child or multiple children at a time, whose ages range from two weeks of age to 18 years. Although most parents spend a significant amount of time caring for their child(r ...
plan with the intention of reducing day care
Child care, otherwise known as day care, is the care and supervision of a child or multiple children at a time, whose ages range from two weeks of age to 18 years. Although most parents spend a significant amount of time caring for their child(r ...
fees for parents down to $10 a day per child within five years.
His environmental policy included introducing new commitments to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 30% before 2030, and to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. His main tool for reaching this target is a federal carbon pricing
Carbon pricing (or pricing), also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS), is a method for nations to reduce global warming. The cost is applied to greenhouse gas emissions in order to encourage polluters to reduce the co ...
policy. Trudeau's parliament also adopted legislation for marine conservation, banning six common single-use plastic
A disposable (also called disposable product) is a product designed for a single use after which it is recycled or is disposed as solid waste. The term is also sometimes used for products that may last several months (e.g. disposable air filte ...
products, and strengthening environmental impact assessments. Trudeau pledged to ban single use plastic in 2019. In the year 2022 his government announced a ban on producing and importing single use plastic from December 2022. The sale of those items will be banned from December 2023 and the export from 2025. However, Trudeau is in favour of oil and gas pipelines to bring Canadian fossil fuel resources to foreign markets.
Foreign policy
 In 2015, Trudeau told the New York Times Magazine that Canada could be the “first
In 2015, Trudeau told the New York Times Magazine that Canada could be the “first postnational
Postnationalism or non-nationalism is the process or trend by which nation states and national identities lose their importance relative to cross-nation and self-organized or supranational and global entities as well as local entities. Although p ...
state".
Trudeau enjoyed good relations with the "like-minded" United States president
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United State ...
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
, despite Trudeau's support for the Keystone Pipeline
The Keystone Pipeline System is an oil pipeline system in Canada and the United States, commissioned in 2010 and owned by TC Energy and as of 31 March 2020 the Government of Alberta. It runs from the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin in Albert ...
which was rejected by the Democratic president. Trudeau's first foreign policy challenges included follow-through on his campaign promise to withdraw Canadian air support from the Syrian civil war and to welcome 25,000 Syrian war refugees.
When Donald Trump became president, Canada-US relations deteriorated. The Trump administration forced the renegotiation of NAFTA
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA ; es, Tratado de Libre Comercio de América del Norte, TLCAN; french: Accord de libre-échange nord-américain, ALÉNA) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that crea ...
to create the CUSMA, in which Canada made significant concessions in allowing increased imports of American milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Immune factors and immune ...
, weakening Canada's dairy supply management system. Donald Trump also implemented Tariffs on Canadian steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
and aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
, to which Trudeau retaliated by imposing Tariffs on American steel, aluminium and a variety of other American products.Daniel WolfeThe full list of 229 US products targeted by Canada's retaliatory tariffs
''Quartz'' (June 29, 2018).
 Canada's relationship with
Canada's relationship with China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
also deteriorated during Justin Trudeau's time as Prime Minister. The turmoil led to the arrest of Meng Wanzhou at the Vancouver International Airport
Vancouver International Airport is an international airport located on Sea Island in Richmond, British Columbia, serving the city of Vancouver and the Lower Mainland region. It is located from Downtown Vancouver. It is the second busiest ...
in December 2018 at the behest of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, and the arrest of Michael Spavor and Michael Kovrig in China 12 days later. As these three individuals were released at the exact same time in September 2021, many observers speculated they were exchanged as part of a deal between the United States and China.
In a similar fashion, Canada's relationship with Saudi Arabia was also put under strain, as human rights groups called on Trudeau to stop selling military equipment to that country under a deal struck by the Harper government. In 2018, Saudi Arabia recalled its Canadian ambassador and froze trade with the country in response to Canada's call for the Saudis to release opposition blogger Raif Badawi
Raif bin Muhammad Badawi ( ar, رائف بن محمد بدوي, also transcribed Raef bin Mohammed Badawi; born 13 January 1984) is a Saudi writer, dissident and activist, as well as the creator of the website ''Free Saudi Liberals''.
Badawi wa ...
. However, in 2019, Canada doubled its weapons sales to Saudi Arabia, despite a "moratorium on export permits following the killing of the Saudi journalist Jamal Khashoggi and mounting civilian deaths from the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen Saudi may refer to:
* Saudi Arabia
* Saudis, people from Saudi Arabia
* Saudi culture, the culture of Saudi Arabia
* House of Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is c ...
."
In 2020, Canada lost its bid to join the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the Organs of the United Nations, six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international security, international peace and security, recommending the admi ...
. This was the second time Canada had failed an attempt to join the Security Council, the first time being in 2009 under Prime Minister Stephen Harper.
Personal life
Family
 Trudeau first met
Trudeau first met Sophie Grégoire
Sophie is a version of the female given name Sophia, meaning "wise".
People with the name Born in the Middle Ages
* Sophie, Countess of Bar (c. 1004 or 1018–1093), sovereign Countess of Bar and lady of Mousson
* Sophie of Thuringia, Duchess o ...
when they were both children growing up in Montreal; Grégoire was a classmate and childhood friend of Trudeau's youngest brother, Michel. They reconnected as adults in June 2003, when Grégoire, by then a Quebec television personality, was assigned as Trudeau's co-host for a charity ball; they began dating several months later. Trudeau and Grégoire became engaged in October 2004 and married on May 28, 2005, in a ceremony at Montreal's Sainte-Madeleine d'Outremont Church. They have three children: a boy Xavier born in 2007, a girl Ella-Grace born in 2009, and a boy Hadrien born in 2014.
In June 2013, two months after Trudeau became the leader of the Liberal Party, the couple sold their home in the Côte-des-Neiges
Côte-des-Neiges (, ) is a neighbourhood of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is located at the geographic centre of the Island of Montreal on the western slope of Mount Royal and is part of the borough of Côte-des-Neiges–Notre-Dame-de-Grâce.
Côt ...
neighbourhood of Montreal. They began living in a rented home in Ottawa's Rockcliffe Park, the neighbourhood near where Trudeau resided as a child during his father's time as prime minister.
On August 18, 2014, an intruder broke into the house while Grégoire and the couple's three children were sleeping and left a threatening note; however, nothing was stolen and there was no damage to the property. Following the incident, Trudeau, who was in Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749,6 ...
at the time of the break-in, stated his intention to inquire with the Royal Canadian Mounted Police about his home security. After his 2015 electoral victory, Trudeau opted to live at Rideau Cottage
Rideau Cottage is a historic residential building located on the grounds of Rideau Hall in Ottawa, Ontario. The two-level, 22-room Georgian Revival home is owned by the Canadian Crown and has traditionally been inhabited by people associated wi ...
, on the grounds of Rideau Hall
Rideau Hall (officially Government House) is the official residence in Ottawa of both the Canadian monarch and their representative, the governor general of Canada. It stands in Canada's capital on a estate at 1 Sussex Drive, with the main b ...
.
On March 12, 2020, the Trudeau family self-isolated at Rideau Cottage after Sophie began exhibiting flu-like symptoms and later tested positive for COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
. By March 28, she had recovered.
On January 31, 2022, Trudeau announced on Twitter that he tested positive for COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
.
On June 13, 2022, Trudeau tested positive for COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, identified in Wuhan, China, in December ...
for the second time.
Religion
Trudeau's father was a devoutCatholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and his mother converted from Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
to Catholicism just before their wedding. Trudeau himself became a lapsed Catholic
A lapsed Catholic is a Catholic who is non-practicing. Such a person may still identify as a Catholic, and remains one according to canon law. Excommunication or an act of defection only separate a person from the sacraments. Nothing can terminate ...
at age 18, as he felt that much of his day-to-day life was not addressed by the formality and structure of the church. Trudeau described his faith during this period as "like so many Catholics across this country, I said, 'OK, I'm Catholic, I'm of faith, but I'm just not really going to go to church. Maybe on Easter, maybe midnight Mass
In many Western Christian traditions Midnight Mass is the first liturgy of Christmastide that is celebrated on the night of Christmas Eve, traditionally beginning at midnight when Christmas Eve gives way to Christmas Day. This popular Christmas c ...
at Christmas. After the death of his brother Michel in 1998, Trudeau was persuaded by a friend to participate in an Alpha course, during which he regained his faith. In 2011, Trudeau stated, "My own personal faith is an extremely important part of who I am and the values that I try to lead with."
Honours


Electoral record
Published works
* Trudeau, Justin (October 20, 2014). '' Common Ground''. HarperCollins Canada. . .Footnotes
References
External links
*Liberal Party of Canada profile
*
House of Commons profile
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Trudeau, Justin 1971 births 21st-century Canadian politicians Anglophone Quebec people Canadian feminists Canadian people of Anglo-Irish descent Canadian people of English descent Canadian people of French descent Canadian people of Scottish descent Canadian Roman Catholics Canadian schoolteachers Catholic feminists Children of prime ministers of Canada Franco-Ontarian people French Quebecers Leaders of the Liberal Party of Canada Liberal Party of Canada leadership candidates Liberal Party of Canada MPs Living people Male feminists McGill University alumni Members of the 29th Canadian Ministry Members of the House of Commons of Canada from Quebec Members of the King's Privy Council for Canada Pierre Trudeau Politicians from Montreal Politicians from Ottawa Prime Ministers of Canada
Justin
Justin may refer to: People
* Justin (name), including a list of persons with the given name Justin
* Justin (historian), a Latin historian who lived under the Roman Empire
* Justin I (c. 450–527), or ''Flavius Iustinius Augustus'', Eastern Rom ...
University of British Columbia Faculty of Education alumni