Precambrian Africa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of
 Evidence of the details of plate motions and other
Evidence of the details of plate motions and other




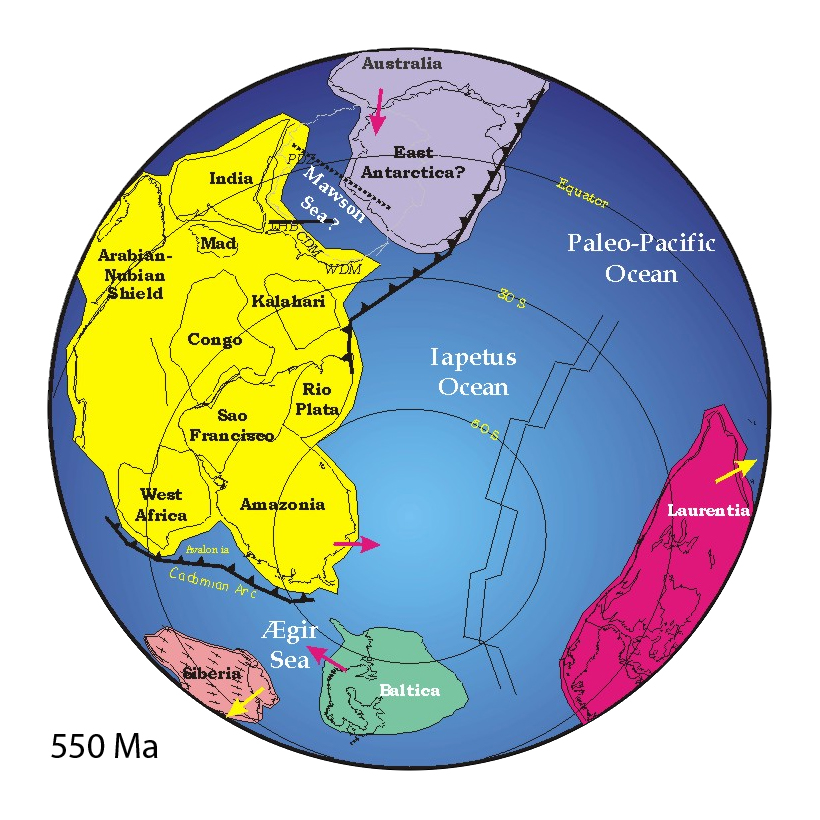 The movement of Earth's plates has caused the formation and break-up of continents over time, including occasional formation of a
The movement of Earth's plates has caused the formation and break-up of continents over time, including occasional formation of a
Wgeology.wisc.edu
– ''Evidence from detrital zircons for the existence of continental crust and oceans on the Earth 4.4 Gyr ago'' Accessed Jan. 10, 2006 * *
from the Paleomap Project {{Authority control
Earth's history
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geologic ...
, set before the current Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic Eon is the current geologic eon in the geologic time scale, and the one during which abundant animal and plant life has existed. It covers 538.8 million years to the present, and it began with the Cambrian Period, when anima ...
Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
, the first period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
of the Phanerozoic Eon, which is named after Cambria
Cambria is a name for Wales, being the Latinised form of the Welsh name for the country, . The term was not in use during the Roman period (when Wales had not come into existence as a distinct entity). It emerged later, in the medieval period, a ...
, the Latinised name for Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
, where rocks from this age were first studied. The Precambrian accounts for 88% of the Earth's geologic time.
The Precambrian is an informal unit of geologic time, subdivided into three eons (Hadean
The Hadean ( ) is a Eon (geology), geologic eon of History of Earth, Earth history preceding the Archean. On Earth, the Hadean began with the Formation of the Earth, planet's formation about 4.54 billion years ago (although the start of the H ...
, Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
, Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
) of the geologic time scale
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochrono ...
. It spans from the formation of Earth about 4.6 billion years ago ( Ga) to the beginning of the Cambrian Period, about million years ago ( Ma), when hard-shelled creatures first appeared in abundance.
Overview
Relatively little is known about the Precambrian, despite it making up roughly seven-eighths of theEarth's history
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geologic ...
, and what is known has largely been discovered from the 1960s onwards. The Precambrian fossil record is poorer than that of the succeeding Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic Eon is the current geologic eon in the geologic time scale, and the one during which abundant animal and plant life has existed. It covers 538.8 million years to the present, and it began with the Cambrian Period, when anima ...
, and fossils from the Precambrian (e.g. stromatolites
Stromatolites () or stromatoliths () are layered sedimentary formations (microbialite) that are created mainly by photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria, sulfate-reducing bacteria, and Pseudomonadota (formerly proteobacteria). The ...
) are of limited biostratigraphic
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Bio ...
use. This is because many Precambrian rocks have been heavily metamorphosed
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causin ...
, obscuring their origins, while others have been destroyed by erosion, or remain deeply buried beneath Phanerozoic strata.
It is thought that the Earth coalesced from material in orbit around the Sun at roughly 4,543 Ma, and may have been struck by another planet called Theia
In Greek mythology, Theia (; grc, Θεία, Theía, divine, also rendered Thea or Thia), also called Euryphaessa ( grc, Εὐρυφάεσσα) "wide-shining", is one of the twelve Titans, the children of the earth goddess Gaia and the sky god ...
shortly after it formed, splitting off material that formed the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
(see Giant impact hypothesis
The giant-impact hypothesis, sometimes called the Big Splash, or the Theia Impact, suggests that the Moon formed from the ejecta of a collision between the proto-Earth and a Mars-sized planet, approximately 4.5 billion years ago, in the Hadean ...
). A stable crust was apparently in place by 4,433 Ma, since zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the r ...
crystals from Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
have been dated
Date or dates may refer to:
*Date (fruit), the fruit of the date palm (''Phoenix dactylifera'')
Social activity
*Dating, a form of courtship involving social activity, with the aim of assessing a potential partner
**Group dating
*Play date, an ...
at 4,404 ± 8 Ma.
The term "Precambrian" is used by geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, althou ...
s and paleontologists
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
for general discussions not requiring a more specific eon name. However, both the United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
and the International Commission on Stratigraphy
The International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), sometimes referred to unofficially as the "International Stratigraphic Commission", is a daughter or major subcommittee grade scientific daughter organization that concerns itself with stratigra ...
regard the term as informal. Because the span of time falling under the Precambrian consists of three eons (the Hadean
The Hadean ( ) is a Eon (geology), geologic eon of History of Earth, Earth history preceding the Archean. On Earth, the Hadean began with the Formation of the Earth, planet's formation about 4.54 billion years ago (although the start of the H ...
, the Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
, and the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
), it is sometimes described as a ''supereon'', but this is also an informal term, not defined by the ICS in its chronostratigraphic guide.
' (from “earliest”) was a synonym for ''pre-Cambrian'', or more specifically ''Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
''.
Life forms
A specific date for the origin of life has not been determined.Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with o ...
found in 3.8 billion-year-old rocks (Archean Eon) from islands off western Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
may be of organic origin. Well-preserved microscopic fossils of bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
older than 3.46 billion years have been found in Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to th ...
. Probable fossils 100 million years older have been found in the same area. However, there is evidence that life could have evolved over 4.280 billion years ago. There is a fairly solid record of bacterial life throughout the remainder (Proterozoic Eon) of the Precambrian.
Complex multicellular organisms may have appeared as early as 2100 Ma. However, the interpretation of ancient fossils is problematic, and "... some definitions of multicellularity encompass everything from simple bacterial colonies to badgers." Other possible early complex multicellular organisms include a possible 2450 Ma red alga from the Kola Peninsula, 1650 Ma carbonaceous biosignatures in north China, the 1600 Ma ''Rafatazmia
''Rafatazmia chitrakootensis'' the sole member of the genus ''Rafatazmia'' is a fossil species of filamentous alga described from dolomite obtained from the Vindhya ranges of central India. It is among the oldest known eukaryotic
Eukaryot ...
'', and a possible 1047 Ma '' Bangiomorpha'' red alga from the Canadian Arctic. The earliest fossils widely accepted as complex multicellular organisms date from the Ediacaran Period. A very diverse collection of soft-bodied forms is found in a variety of locations worldwide and date to between 635 and 542 Ma. These are referred to as Ediacaran or Vendian biota. Hard-shelled creatures appeared toward the end of that time span, marking the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon. By the middle of the following Cambrian Period, a very diverse fauna is recorded in the Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest foss ...
, including some which may represent stem groups of modern taxa. The increase in diversity of lifeforms during the early Cambrian is called the Cambrian explosion
The Cambrian explosion, Cambrian radiation, Cambrian diversification, or the Biological Big Bang refers to an interval of time approximately in the Cambrian Period when practically all major animal phyla started appearing in the fossil recor ...
of life.
While land seems to have been devoid of plants and animals, cyanobacteria and other microbes formed prokaryotic mats that covered terrestrial areas.
Tracks from an animal with leg-like appendages have been found in what was mud 551 million years ago.
Planetary environment and the oxygen catastrophe
 Evidence of the details of plate motions and other
Evidence of the details of plate motions and other tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents k ...
activity in the Precambrian has been poorly preserved. It is generally believed that small proto-continents existed before 4280 Ma, and that most of the Earth's landmasses collected into a single supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
around 1130 Ma. The supercontinent, known as Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago.
were probably ...
, broke up around 750 Ma. A number of glacial periods
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betwe ...
have been identified going as far back as the Huronian
The Huronian glaciation (or Makganyene glaciation) was a period where several Ice age, ice ages occurred during the deposition of the Huronian Supergroup, rather than a single continuous event as it is commonly misrepresented to be. The depositi ...
epoch, roughly 2400–2100 Ma. One of the best studied is the Sturtian-Varangian
The Cryogenian (from grc, κρύος, krýos, meaning "cold" and , romanized: , meaning "birth") is a geologic period that lasted from . It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by ...
glaciation, around 850–635 Ma, which may have brought glacial conditions all the way to the equator, resulting in a "Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth hypothesis proposes that, during one or more of Earth's Greenhouse and icehouse Earth, icehouse Climate, climates, the Earth's surface, planet's surface became entirely or nearly entirely Freezing, frozen. It is believed that ...
".
The atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
of the early Earth is not well understood. Most geologists believe it was composed primarily of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and other relatively inert gases, and was lacking in free oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
. There is, however, evidence that an oxygen-rich atmosphere existed since the early Archean.
At present, it is still believed that molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
was not a significant fraction of Earth's atmosphere until after photosynthetic
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in c ...
life forms evolved and began to produce it in large quantities as a byproduct of their metabolism. This radical shift from a chemically inert to an oxidizing atmosphere caused an ecological crisis
An ecological or environmental crises occurs when changes to the environment of a species or population destabilizes its continued survival. Some of the important causes include:
* Degradation of an abiotic ecological factor (for example, increa ...
, sometimes called the oxygen catastrophe
The Great Oxidation Event (GOE), also called the Great Oxygenation Event, the Oxygen Catastrophe, the Oxygen Revolution, the Oxygen Crisis, or the Oxygen Holocaust, was a time interval during the Paleoproterozoic era when the Earth's atmosphere ...
. At first, oxygen would have quickly combined with other elements in Earth's crust, primarily iron, removing it from the atmosphere. After the supply of oxidizable surfaces ran out, oxygen would have begun to accumulate in the atmosphere, and the modern high-oxygen atmosphere would have developed. Evidence for this lies in older rocks that contain massive banded iron formation
Banded iron formations (also known as banded ironstone formations or BIFs) are distinctive units of sedimentary rock consisting of alternating layers of iron oxides and iron-poor chert. They can be up to several hundred meters in thickness a ...
s that were laid down as iron oxides.
Subdivisions
A terminology has evolved covering the early years of the Earth's existence, asradiometric dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares t ...
has allowed absolute dates to be assigned to specific formations and features. The Precambrian is divided into three eons: the Hadean
The Hadean ( ) is a Eon (geology), geologic eon of History of Earth, Earth history preceding the Archean. On Earth, the Hadean began with the Formation of the Earth, planet's formation about 4.54 billion years ago (although the start of the H ...
(– Ma), Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
(- Ma) and Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
(- Ma). See Timetable of the Precambrian
This timeline of natural history summarizes significant geological and biological events from the formation of the Earth to the arrival of modern humans. Times are listed in millions of years, or megaanni ( Ma).
Dating of the geologic record ...
.
* Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
: this eon refers to the time from the lower Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
boundary, Ma, back through Ma. As originally used, it was a synonym for "Precambrian" and hence included everything prior to the Cambrian boundary. The Proterozoic Eon is divided into three eras: the Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is ...
, Mesoproterozoic
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic), ...
and Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions (eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's ...
.
** Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is ...
: The youngest geologic era
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronol ...
of the Proterozoic Eon, from the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
Period lower boundary ( Ma) back to Ma. The Neoproterozoic corresponds to Precambrian Z rocks of older North American stratigraphy.
*** Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and th ...
: The youngest geologic period
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronol ...
within the Neoproterozoic Era. The "2012 Geologic Time Scale" dates it from to Ma. In this period the Ediacaran biota
The Ediacaran (; formerly Vendian) biota is a Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic period classification that consists of all life forms that were present on Earth during the Ediacaran Period (). These were composed of enigmatic tubular and frond-sh ...
appeared.
*** Cryogenian
The Cryogenian (from grc, κρύος, krýos, meaning "cold" and , romanized: , meaning "birth") is a geologic period that lasted from . It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by ...
: The middle period in the Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is ...
Era: - Ma.
*** Tonian
The Tonian (from grc, τόνος, tónos, meaning "stretch") is the first geologic period of the Neoproterozoic era (geology), Era. It lasted from to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined by t ...
: the earliest period of the Neoproterozoic Era: - Ma.
** Mesoproterozoic
The Mesoproterozoic Era is a geologic era that occurred from . The Mesoproterozoic was the first era of Earth's history for which a fairly definitive geological record survives. Continents existed during the preceding era (the Paleoproterozoic), ...
: the middle era of the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
Eon, - Ma. Corresponds to "Precambrian Y" rocks of older North American stratigraphy.
** Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (;, also spelled Palaeoproterozoic), spanning the time period from (2.5–1.6 Ga), is the first of the three sub-divisions (eras) of the Proterozoic Eon. The Paleoproterozoic is also the longest era of the Earth's ...
: oldest era of the Proterozoic Eon, - Ma. Corresponds to "Precambrian X" rocks of older North American stratigraphy.
* Archean
The Archean Eon ( , also spelled Archaean or Archæan) is the second of four geologic eons of Earth's history, representing the time from . The Archean was preceded by the Hadean Eon and followed by the Proterozoic.
The Earth
Earth ...
Eon: - Ma.
* Hadean
The Hadean ( ) is a Eon (geology), geologic eon of History of Earth, Earth history preceding the Archean. On Earth, the Hadean began with the Formation of the Earth, planet's formation about 4.54 billion years ago (although the start of the H ...
Eon: – Ma. This term was intended originally to cover the time before any preserved rocks were deposited, although some zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the r ...
crystals from about 4400 Ma demonstrate the existence of crust in the Hadean Eon. Other records from Hadean time come from the moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
and meteorite
A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from an object, such as a comet, asteroid, or meteoroid, that originates in outer space and survives its passage through the atmosphere to reach the surface of a planet or Natural satellite, moon. When the ...
s.
It has been proposed that the Precambrian should be divided into eons and eras that reflect stages of planetary evolution, rather than the current scheme based upon numerical ages. Such a system could rely on events in the stratigraphic record and be demarcated by GSSPs. The Precambrian could be divided into five "natural" eons, characterized as follows:
# Accretion and differentiation: a period of planetary formation until giant Moon-forming impact event.
# Hadean: dominated by heavy bombardment from about 4.51 Ga (possibly including a Cool Early Earth
The Hadean ( ) is a geologic eon of Earth history preceding the Archean. On Earth, the Hadean began with the planet's formation about 4.54 billion years ago (although the start of the Hadean is defined as the age of the oldest solid material ...
period) to the end of the Late Heavy Bombardment
The Late Heavy Bombardment (LHB), or lunar cataclysm, is a hypothesized event thought to have occurred approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years (Ga) ago, at a time corresponding to the Neohadean and Eoarchean eras on Earth. According to the hypoth ...
period.
# Archean: a period defined by the first crustal formations (the Isua greenstone belt) until the deposition of banded iron formation
Banded iron formations (also known as banded ironstone formations or BIFs) are distinctive units of sedimentary rock consisting of alternating layers of iron oxides and iron-poor chert. They can be up to several hundred meters in thickness a ...
s due to increasing atmospheric oxygen content.
# Transition: a period of continued iron banded formation until the first continental red beds
Red beds (or redbeds) are sedimentary rocks, typically consisting of sandstone, siltstone, and shale, that are predominantly red in color due to the presence of ferric oxides. Frequently, these red-colored sedimentary strata locally contain ...
.
# Proterozoic: a period of modern plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
until the first animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
s.
Precambrian supercontinents



 The movement of Earth's plates has caused the formation and break-up of continents over time, including occasional formation of a
The movement of Earth's plates has caused the formation and break-up of continents over time, including occasional formation of a supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
containing most or all of the landmass. The earliest known supercontinent was Vaalbara
Vaalbara was an Archean supercontinent consisting of the Kaapvaal Craton (now in eastern South Africa) and the Pilbara Craton (now in north-western Western Australia). E. S. Cheney derived the name from the last four letters of each craton's name ...
. It formed from proto-continents and was a supercontinent 3.636 billion years ago. Vaalbara
Vaalbara was an Archean supercontinent consisting of the Kaapvaal Craton (now in eastern South Africa) and the Pilbara Craton (now in north-western Western Australia). E. S. Cheney derived the name from the last four letters of each craton's name ...
broke up c. 2.845–2.803 Ga ago. The supercontinent Kenorland
Kenorland was one of the earliest known supercontinents on Earth. It is thought to have formed during the Neoarchaean Era c. 2.72 billion years ago (2.72 Ga) by the accretion of Neoarchaean cratons and the formation of new continental crust. I ...
was formed c. 2.72 Ga ago and then broke sometime after 2.45–2.1 Ga into the proto-continent craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
s called Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, although ...
, Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, is mo ...
, Yilgarn craton
The Yilgarn Craton is a large craton that constitutes the bulk of the Western Australian land mass. It is bounded by a mixture of sedimentary basins and Proterozoic fold and thrust belts. Zircon grains in the Jack Hills, Narryer Terrane have be ...
and Kalahari
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal de ...
. The supercontinent Columbia, or Nuna, formed 2.1–1.8 billion years ago and broke up about 1.3–1.2 billion years ago. The supercontinent Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago.
were probably ...
is thought to have formed about 1300-900 Ma, to have embodied most or all of Earth's continents and to have broken up into eight continents around 750–600 million years ago.
See also
* ** ** **References
Further reading
* Valley, John W., William H. Peck, Elizabeth M. King (1999) ''Zircons Are Forever'', The Outcrop for 1999, University of Wisconsin-MadisoWgeology.wisc.edu
– ''Evidence from detrital zircons for the existence of continental crust and oceans on the Earth 4.4 Gyr ago'' Accessed Jan. 10, 2006 * *
External links
from the Paleomap Project {{Authority control