Power Generator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Electricity generation is the process of generating
Electricity generation is the process of generating
 The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered in the 1820s and early 1830s by British scientist Michael Faraday. His method, still used today, is for electricity to be generated by the movement of a loop of wire, or Faraday disc, between the poles of a magnet. Central power stations became economically practical with the development of alternating current (AC) power transmission, using power transformers to transmit power at high voltage and with low loss.
Commercial electricity production started with the coupling of the dynamo to the hydraulic turbine. The mechanical production of electric power began the Second Industrial Revolution and made possible several inventions using electricity, with the major contributors being Thomas Alva Edison and Nikola Tesla. Previously the only way to produce electricity was by chemical reactions or using battery cells, and the only practical use of electricity was for the telegraph.
Electricity generation at central power stations started in 1882, when a
The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered in the 1820s and early 1830s by British scientist Michael Faraday. His method, still used today, is for electricity to be generated by the movement of a loop of wire, or Faraday disc, between the poles of a magnet. Central power stations became economically practical with the development of alternating current (AC) power transmission, using power transformers to transmit power at high voltage and with low loss.
Commercial electricity production started with the coupling of the dynamo to the hydraulic turbine. The mechanical production of electric power began the Second Industrial Revolution and made possible several inventions using electricity, with the major contributors being Thomas Alva Edison and Nikola Tesla. Previously the only way to produce electricity was by chemical reactions or using battery cells, and the only practical use of electricity was for the telegraph.
Electricity generation at central power stations started in 1882, when a
 Electrochemistry is the direct transformation of
Electrochemistry is the direct transformation of
 Electric generators were known in simple forms from the discovery of
Electric generators were known in simple forms from the discovery of
 Almost all commercial electrical power on Earth is generated with a turbine, driven by wind, water, steam or burning gas. The turbine drives a generator, thus transforming its mechanical energy into electrical energy by electromagnetic induction. There are many different methods of developing mechanical energy, including heat engines, hydro, wind and tidal power. Most electric generation is driven by heat engines. The combustion of
Almost all commercial electrical power on Earth is generated with a turbine, driven by wind, water, steam or burning gas. The turbine drives a generator, thus transforming its mechanical energy into electrical energy by electromagnetic induction. There are many different methods of developing mechanical energy, including heat engines, hydro, wind and tidal power. Most electric generation is driven by heat engines. The combustion of
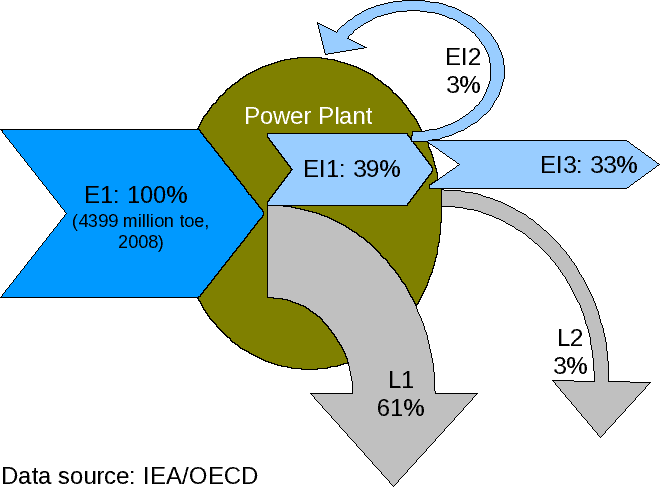

 Electricity generation is the process of generating
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Standard prefixes apply to watts as with other SI units: thousands, millions and billions o ...
from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery (transmission
Transmission may refer to:
Medicine, science and technology
* Power transmission
** Electric power transmission
** Propulsion transmission, technology allowing controlled application of power
*** Automatic transmission
*** Manual transmission
*** ...
, distribution Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
* Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a vari ...
, etc.) to end users or its storage
Storage may refer to:
Goods Containers
* Dry cask storage, for storing high-level radioactive waste
* Food storage
* Intermodal container, cargo shipping
* Storage tank
Facilities
* Garage (residential), a storage space normally used to store car ...
(using, for example, the pumped-storage method).
Electricity is not freely available in nature, so it must be "produced" (that is, transforming other forms of energy to electricity). Production is carried out in power stations (also called "power plants"). Electricity is most often generated at a power plant by electromechanical generators, primarily driven by heat engines fueled by combustion or nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
but also by other means such as the kinetic energy of flowing water and wind. Other energy sources include solar photovoltaics and geothermal power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 2 ...
. There are also exotic and speculative methods to recover energy, such as proposed fusion reactor designs which aim to directly extract energy from intense magnetic fields generated by fast-moving charged particles generated by the fusion reaction (see magnetohydrodynamics).
Phasing out coal-fired power stations and eventually gas-fired power stations, or capturing their greenhouse gas emissions, is an important part of the energy transformation
Energy transformation, also known as energy conversion, is the process of changing energy from one form to another. In physics, energy is a quantity that provides the capacity to perform work or moving, (e.g. Lifting an object) or provides heat. ...
required to limit climate change. Vastly more solar power and wind power is forecast to be required, with electricity demand
World energy supply and consumption is global production and preparation of fuel, generation of electricity, energy transport, and energy consumption. It is a basic part of economic activity. It includes heat, but not energy from food.
This a ...
increasing strongly with further electrification of transport, homes and industry.
History
 The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered in the 1820s and early 1830s by British scientist Michael Faraday. His method, still used today, is for electricity to be generated by the movement of a loop of wire, or Faraday disc, between the poles of a magnet. Central power stations became economically practical with the development of alternating current (AC) power transmission, using power transformers to transmit power at high voltage and with low loss.
Commercial electricity production started with the coupling of the dynamo to the hydraulic turbine. The mechanical production of electric power began the Second Industrial Revolution and made possible several inventions using electricity, with the major contributors being Thomas Alva Edison and Nikola Tesla. Previously the only way to produce electricity was by chemical reactions or using battery cells, and the only practical use of electricity was for the telegraph.
Electricity generation at central power stations started in 1882, when a
The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered in the 1820s and early 1830s by British scientist Michael Faraday. His method, still used today, is for electricity to be generated by the movement of a loop of wire, or Faraday disc, between the poles of a magnet. Central power stations became economically practical with the development of alternating current (AC) power transmission, using power transformers to transmit power at high voltage and with low loss.
Commercial electricity production started with the coupling of the dynamo to the hydraulic turbine. The mechanical production of electric power began the Second Industrial Revolution and made possible several inventions using electricity, with the major contributors being Thomas Alva Edison and Nikola Tesla. Previously the only way to produce electricity was by chemical reactions or using battery cells, and the only practical use of electricity was for the telegraph.
Electricity generation at central power stations started in 1882, when a steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
driving a dynamo at Pearl Street Station produced a DC current that powered public lighting on Pearl Street, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
. The new technology was quickly adopted by many cities around the world, which adapted their gas-fueled street lights to electric power. Soon after electric lights would be used in public buildings, in businesses, and to power public transport, such as trams and trains.
The first power plants used water power or coal. Today a variety of energy sources are used, such as coal, nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
*Nuclear space
* Nuclear ...
, natural gas, hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
, wind, and oil, as well as solar energy
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy (including solar water heating), and solar architecture. It is an essenti ...
, tidal power, and geothermal sources.
In the 1880s the popularity of electricity grew massively with the introduction of the Incandescent light bulb. Although there are 22 recognised inventors of the light bulb prior to Joseph Swan and Thomas Edison, Edison and Swan's invention became by far the most successful and popular of all. During the early years of the 19th century, massive jumps in electrical sciences were made. And by the later 19th century the advancement of electrical technology and engineering led to electricity being part of everyday life. With the introduction of many electrical inventions and their implementation into everyday life, the demand for electricity within homes grew dramatically. With this increase in demand, the potential for profit was seen by many entrepreneurs who began investing into electrical systems to eventually create the first electricity public utilities. This process in history is often described as electrification.
The earliest distribution of electricity came from companies operating independently of one another. A consumer would purchase electricity from a producer, and the producer would distribute it through their own power grid. As technology improved so did the productivity and efficiency of its generation. Inventions such as the steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
had a massive impact on the efficiency of electrical generation but also the economics of generation as well. This conversion ofheat energy into mechanical work was similar to that of steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
s, however at a significantly larger scale and far more productively. The improvements of these large-scale generation plants were critical to the process of centralised generation as they would become vital to the entire power system that we now use today.
Throughout the middle of the 20th century many utilities began merging their distribution networks due to economic and efficiency benefits. Along with the invention of long-distance power transmission, the coordination of power plants began to form. This system was then secured by regional system operators to ensure stability and reliability. The electrification of homes began in Northern Europe and in the Northern America in the 1920s in large cities and urban areas. It wasn't until the 1930s that rural areas saw the large-scale establishment of electrification.
Methods of generation
Several fundamental methods exist to convert other forms of energy into electrical energy. Utility-scale generation is achieved by rotating electric generators or byphotovoltaic
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
systems. A small proportion of electric power distributed by utilities is provided by batteries. Other forms of electricity generation used in niche applications include the triboelectric effect, the piezoelectric effect, the thermoelectric effect, and betavoltaics.
Generators

Electric generator
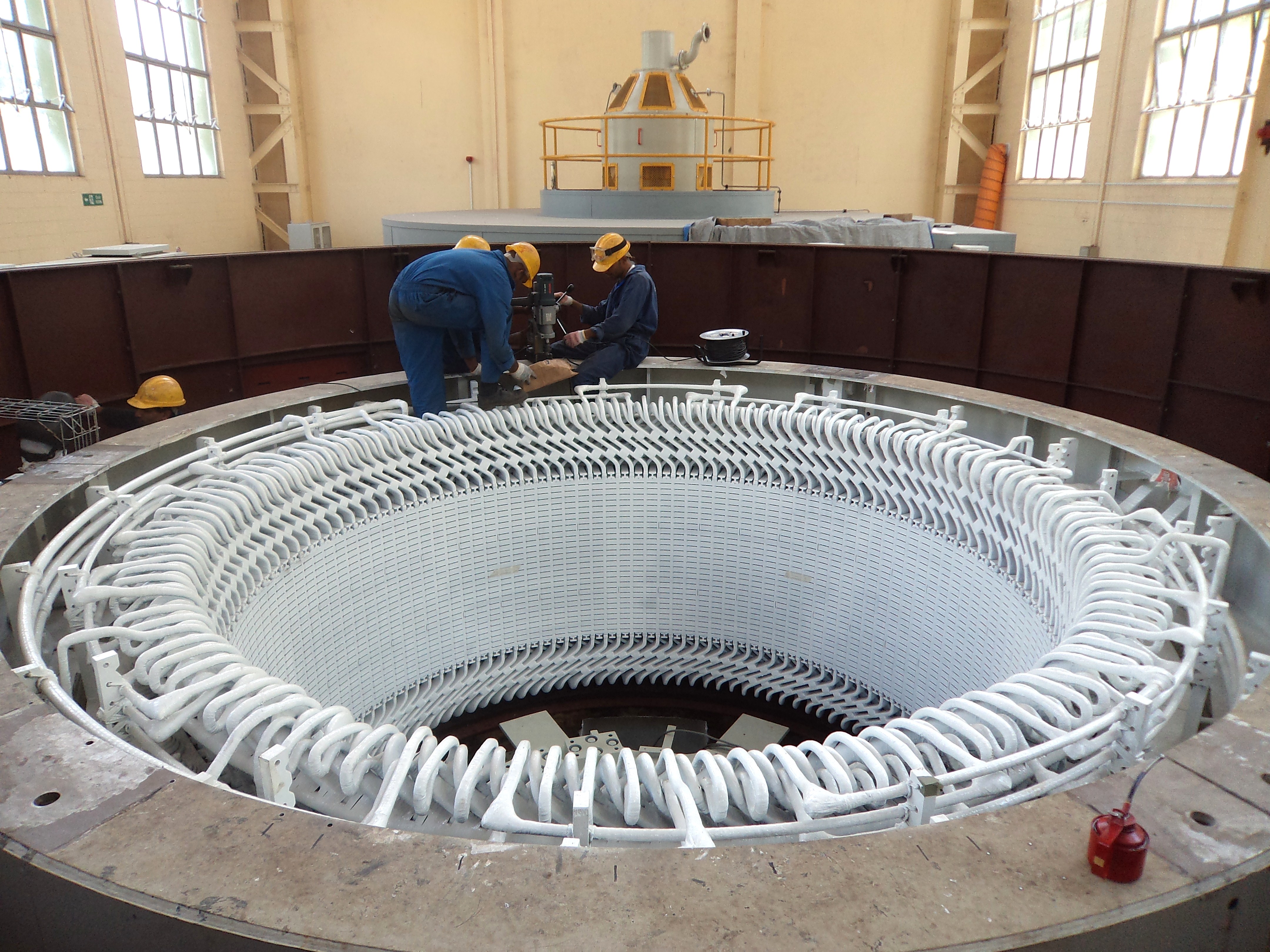
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy) or fuel-based power (chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas ...
s transform kinetic energy into electricity. This is the most used form for generating electricity and is based on Faraday's law. It can be seen experimentally by rotating a magnet within closed loops of conducting material (e.g. copper wire). Almost all commercial electrical generation is done using electromagnetic induction, in which mechanical energy forces a generator to rotate.
Electrochemistry
 Electrochemistry is the direct transformation of
Electrochemistry is the direct transformation of chemical energy
Chemical energy is the energy of chemical substances that is released when they undergo a chemical reaction and transform into other substances. Some examples of storage media of chemical energy include batteries, Schmidt-Rohr, K. (2018). "How ...
into electricity, as in a battery. Electrochemical electricity generation is important in portable and mobile applications. Currently, most electrochemical power comes from batteries. Primary cells, such as the common zinc–carbon batteries, act as power sources directly, but secondary cells (i.e. rechargeable batteries) are used for storage
Storage may refer to:
Goods Containers
* Dry cask storage, for storing high-level radioactive waste
* Food storage
* Intermodal container, cargo shipping
* Storage tank
Facilities
* Garage (residential), a storage space normally used to store car ...
systems rather than primary generation systems. Open electrochemical systems, known as fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most batteries in requ ...
s, can be used to extract power either from natural fuels or from synthesized fuels. Osmotic power is a possibility at places where salt and fresh water merge.
Photovoltaic effect
The photovoltaic effect is the transformation of light into electrical energy, as in solar cells. Photovoltaic panels convert sunlight directly to DC electricity. Power inverters can then convert that to AC electricity if needed. Although sunlight is free and abundant, solar power electricity is still usually more expensive to produce than large-scale mechanically generated power due to the cost of the panels. Low-efficiency silicon solar cells have been decreasing in cost and multijunction cells with close to 30% conversion efficiency are now commercially available. Over 40% efficiency has been demonstrated in experimental systems. Until recently, photovoltaics were most commonly used in remote sites where there is no access to a commercial power grid, or as a supplemental electricity source for individual homes and businesses. Recent advances in manufacturing efficiency and photovoltaic technology, combined with subsidies driven by environmental concerns, have dramatically accelerated the deployment of solar panels. Installed capacity is growing by around 20% per year led by increases in Germany, Japan, United States, China, and India.Economics
The selection of electricity production modes and their economic viability varies in accordance with demand and region. The economics vary considerably around the world, resulting in widespread residential selling prices. Hydroelectric plants,nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a electric generator, generato ...
s, thermal power plants and renewable sources have their own pros and cons, and selection is based upon the local power requirement and the fluctuations in demand. All power grids have varying loads on them but the daily minimum is the base load, often supplied by plants which run continuously. Nuclear, coal, oil, gas and some hydro plants can supply base load. If well construction costs for natural gas are below $10 per MWh, generating electricity from natural gas is cheaper than generating power by burning coal.
Nuclear power plants can produce a huge amount of power from a single unit. However, nuclear disasters have raised concerns over the safety of nuclear power, and the capital cost of nuclear plants is very high.
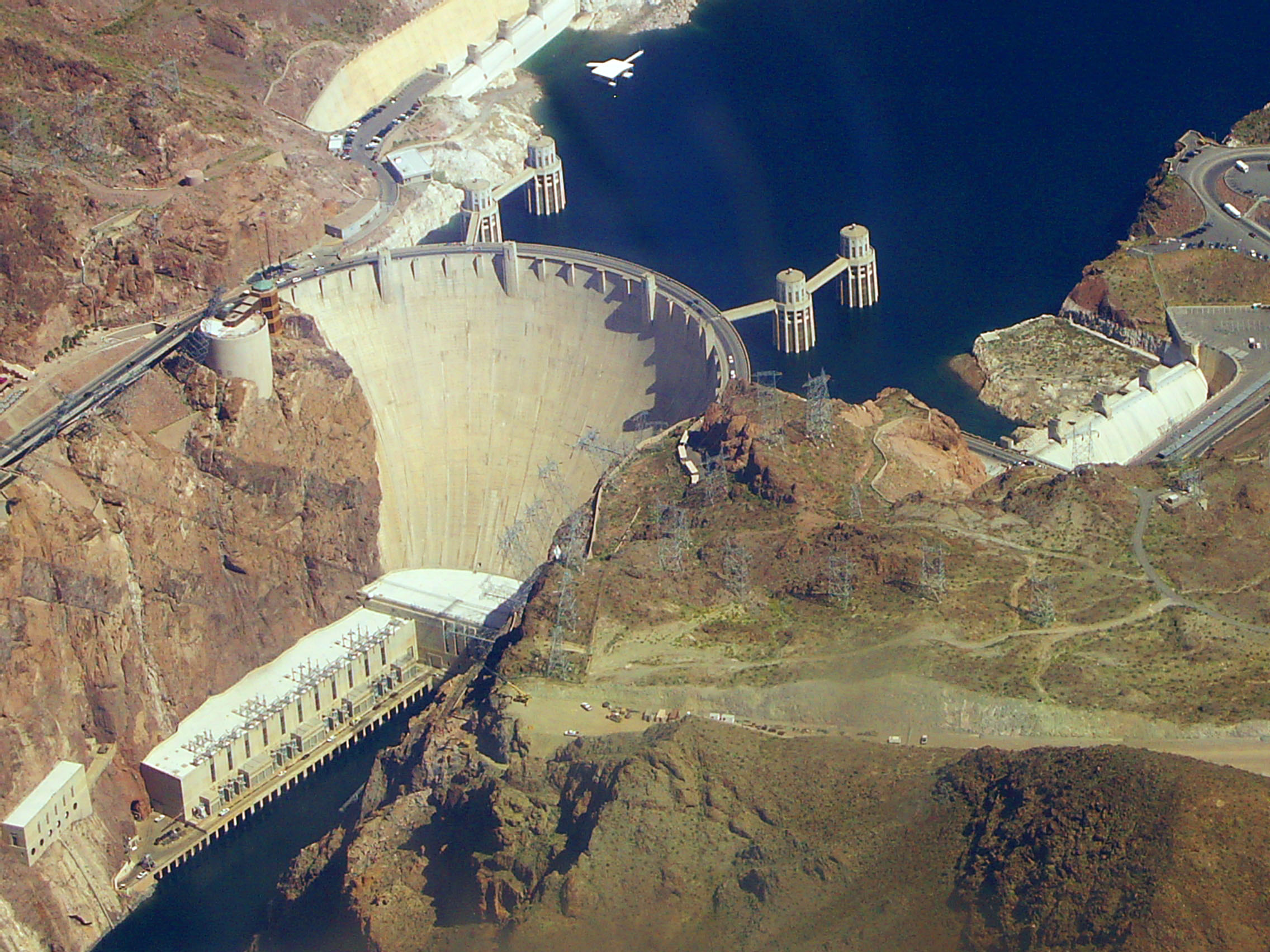
Hydroelectric power plants are located in areas where the potential energy from falling water can be harnessed for moving turbines and the generation of power. It may not be an economically viable single source of production where the ability to store the flow of water is limited and the load varies too much during the annual production cycle.
Generating equipment
electromagnetic induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831, and James Clerk ...
in the 1830s. In general, some form of prime mover such as an engine or the turbines described above, drives a rotating magnetic field past stationary coils of wire thereby turning mechanical energy into electricity. The only commercial scale electricity production that does not employ a generator is solar PV.
Turbines
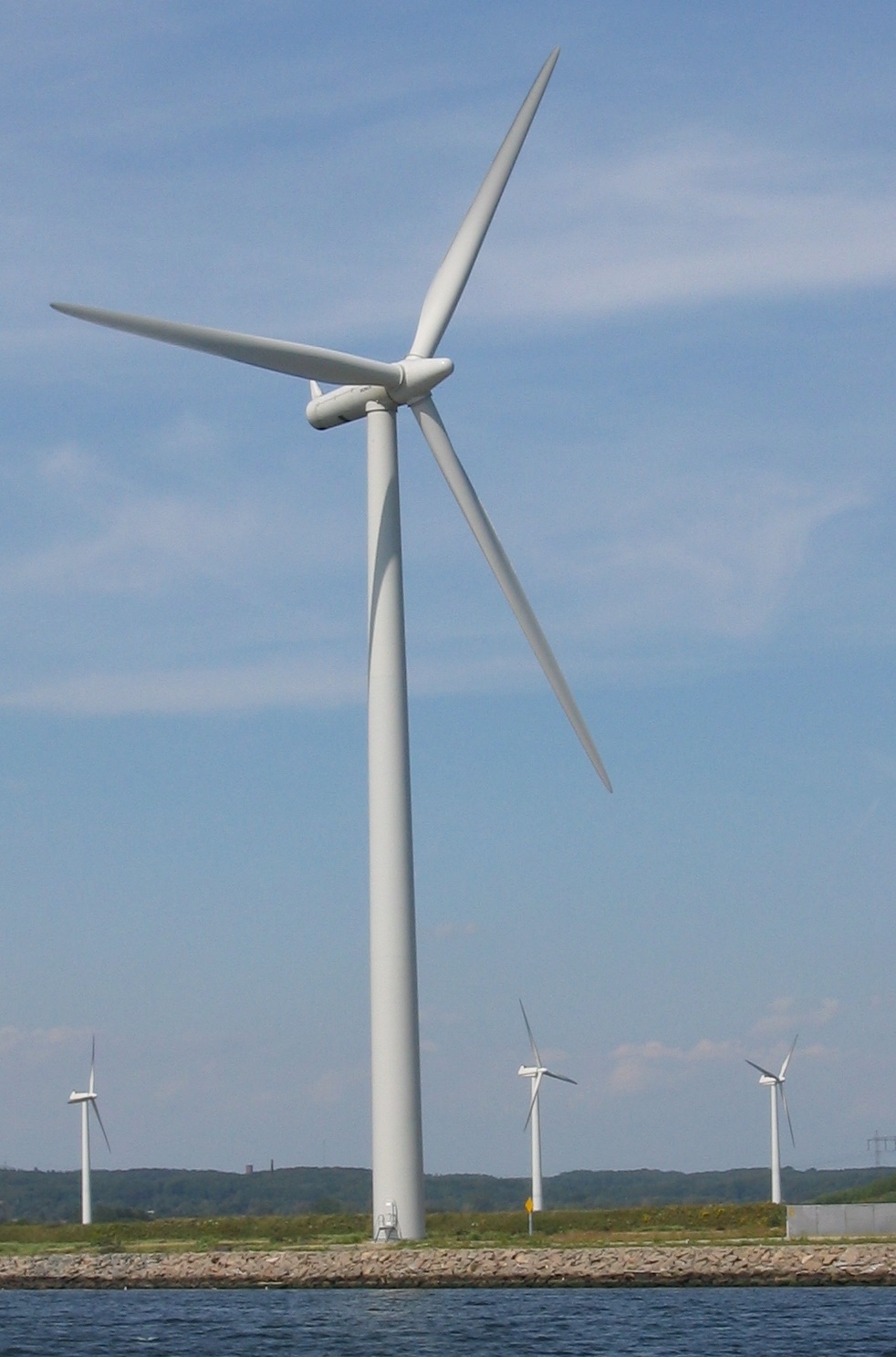
 Almost all commercial electrical power on Earth is generated with a turbine, driven by wind, water, steam or burning gas. The turbine drives a generator, thus transforming its mechanical energy into electrical energy by electromagnetic induction. There are many different methods of developing mechanical energy, including heat engines, hydro, wind and tidal power. Most electric generation is driven by heat engines. The combustion of
Almost all commercial electrical power on Earth is generated with a turbine, driven by wind, water, steam or burning gas. The turbine drives a generator, thus transforming its mechanical energy into electrical energy by electromagnetic induction. There are many different methods of developing mechanical energy, including heat engines, hydro, wind and tidal power. Most electric generation is driven by heat engines. The combustion of fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
s supplies most of the energy to these engines, with a significant fraction from nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
and some from renewable sources. The modern steam turbine
A steam turbine is a machine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884. Fabrication of a modern steam turbin ...
(invented by Sir Charles Parsons in 1884) currently generates about 80% of the electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Standard prefixes apply to watts as with other SI units: thousands, millions and billions o ...
in the world using a variety of heat sources. Turbine types include:
* Steam
** Water is boiled by coal burned in a thermal power plant. About 41% of all electricity is generated this way.
** Nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
heat created in a nuclear reactor creates steam. Less than 15% of electricity is generated this way.
** Renewable energy. The steam is generated by biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
, solar thermal energy, or geothermal power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 2 ...
.
* Natural gas: turbines are driven directly by gases produced by combustion. Combined cycle
A combined cycle power plant is an assembly of heat engines that work in tandem from the same source of heat, converting it into mechanical energy. On land, when used to make electricity the most common type is called a combined cycle gas turb ...
are driven by both steam and natural gas. They generate power by burning natural gas in a gas turbine and use residual heat to generate steam. At least 20% of the world's electricity is generated by natural gas.
*Water Energy is captured by a water turbine from the movement of water - from falling water, the rise and fall of tides or ocean thermal currents (see ocean thermal energy conversion). Currently, hydroelectric plants provide approximately 16% of the world's electricity.
*The windmill was a very early wind turbine. In 2018 around 5% of the world's electricity was produced from wind.
Although turbines are most common in commercial power generation, smaller generators can be powered by gasoline or diesel engines. These may used for backup generation or as a prime source of power within isolated villages.
Production
Total worldwide gross production of electricity in 2016 was 25 082 TWh. Sources of electricity were coal and peat 38.3%, natural gas 23.1%, hydroelectric 16.6%, nuclear power 10.4%, oil 3.7%, solar/wind/geothermal/tidal/other 5.6%, biomass and waste 2.3%. In 2021, Wind andsolar
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
generated electricity reached 10% of globally produced electricity. Clean sources (Solar and wind and other) generated 38% of the world's electricity.
:

Historical results of production of electricity
Production by country
The United States has long been the largest producer and consumer of electricity, with a global share in 2005 of at least 25%, followed byChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, Japan, Russia, and India. In 2011, China overtook the United States to become the largest producer of electricity.
Environmental concerns
Variations between countries generating electrical power affect concerns about the environment. In France only 10% of electricity is generated from fossil fuels, the US is higher at 70% and China is at 80%. The cleanliness of electricity depends on its source. Methane leaks (from natural gas to fuel gas-fired power plants) and carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel-based electricity generation account for a significant portion of world greenhouse gas emissions. In the United States, fossil fuel combustion for electric power generation is responsible for 65% of all emissions ofsulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
, the main component of acid rain. Electricity generation is the fourth highest combined source of NOx, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter
Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) – are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The ter ...
in the US.
According to the International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, with a recent focus on curbing carb ...
(IEA), low-carbon electricity generation needs to account for 85% of global electrical output by 2040 in order to ward off the worst effects of climate change. Like other organizations including the Energy Impact Center (EIC) and the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), the IEA has called for the expansion of nuclear and renewable energy to meet that objective. Some, like EIC founder Bret Kugelmass, believe that nuclear power is the primary method for decarbonizing electricity generation because it can also power direct air capture that removes existing carbon emissions from the atmosphere. Nuclear power plants can also create district heating and desalination
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in Soil salinity control, soil desalination, which is an issue f ...
projects, limiting carbon emissions and the need for expanded electrical output.
A fundamental issue regarding centralised generation and the current electrical generation methods in use today is the significant negative environmental effects that many of the generation processes have. Processes such as coal and gas not only release carbon dioxide as they combust, but their extraction from the ground also impacts the environment. Open pit coal mines use large areas of land to extract coal and limit the potential for productive land use after the excavation. Natural gas extraction releases large amounts of methane into the atmosphere when extracted from the ground greatly increase global greenhouse gases. Although nuclear power plants do not release carbon dioxide through electricity generation, there are significant risks associated with nuclear waste and safety concerns associated with the use of nuclear sources. This fear of nuclear power stems from large-scale nuclear catastrophes such as the Chernobyl Disaster and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. Both tragedies led to significant casualties and the radioactive contamination of large areas.
Per unit of electricity generated coal and gas-fired power life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions are almost always at least ten times that of other generation methods.
Centralised and distributed generation
Centralised generation is electricity generation by large-scale centralised facilities, sent through transmission lines to consumers. These facilities are usually located far away from consumers and distribute the electricity through high voltage transmission lines to a substation, where it is then distributed to consumers; the basic concept being that multi-megawatt or gigawatt scale large stations create electricity for a large number of people. The vast majority of electricity used is created from centralised generation. Most centralised power generation comes from large power plants run by fossil fuels such as coal or natural gas, though nuclear or large hydroelectricity plants are also commonly used. Centralised generation is fundamentally the opposite of distributed generation. Distributed generation is the small-scale generation of electricity to smaller groups of consumers. This can also include independently producing electricity by either solar or wind power. In recent years distributed generation as has seen a spark in popularity due to its propensity to userenewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
generation methods such as rooftop solar.
Technologies
Centralised energy sources are large power plants that produce huge amounts of electricity to a large number of consumers. Most power plants used in centralised generation are thermal power plants meaning that they use a fuel to heat steam to produce a pressurised gas which in turn spins a turbine and generates electricity. This is the traditional way of producing energy. This process relies on several forms of technology to produce widespread electricity, these being natural coal, gas and nuclear forms of thermal generation. More recently solar and wind have become large scale.Solar
Wind
Coal
Natural gas
Natural gas is ignited to create pressurised gas which is used to spin turbines to generate electricity. Natural gas plants use a gas turbine where natural gas is added along with oxygen which in turn combusts and expands through the turbine to force a generator to spin. Natural gas power plants are more efficient than coal power generation, they however contribute to climate change but not as highly as coal generation. Not only do they produce carbon dioxide from the ignition of natural gas, but also the extraction of gas when mined releases a significant amount of methane into the atmosphere.Nuclear
Nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a electric generator, generato ...
s create electricity through steam turbines where the heat input is from the process of nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
. Currently, nuclear power produces 11% of all electricity in the world. Most nuclear reactors use uranium as a source of fuel. In a process called nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
, energy, in the form of heat, is released when nuclear atoms are split. Electricity is created through the use of a nuclear reactor where heat produced by nuclear fission is used to produce steam which in turn spins turbines and powers the generators. Although there are several types of nuclear reactors, all fundamentally use this process.
Normal emissions due to nuclear power plants are primarily waste heat and radioactive spent fuel. In a reactor accident, significant amounts of radioisotopes can be released to the environment, posing a long term hazard to life. This hazard has been a continuing concern of environmentalists. Accidents such as the Three Mile Island accident, Chernobyl disaster
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nuc ...
and the Fukushima nuclear disaster illustrate this problem.
See also
* Cogeneration: the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. * Cost of electricity by source * Diesel generator *Electric generator
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motive power (mechanical energy) or fuel-based power (chemical energy) into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas ...
* Engine-generator
* Electric power transmission
Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a ''transmission network''. This is ...
* World energy consumption: the total energy used by all of human civilization.
* Electrification
* Nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
* Generation expansion planning
* Distributed generation
* Power station
References