Population of the Soviet Union on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
According to data from the 1989 Soviet census, the population of the
 Russia lost former territories of the
Russia lost former territories of the
 The following demographic statistics are from the 1990 edition of the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
The following demographic statistics are from the 1990 edition of the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.

File:USSR population density map 1982.jpg, Soviet Union urban and rural population density map 1982

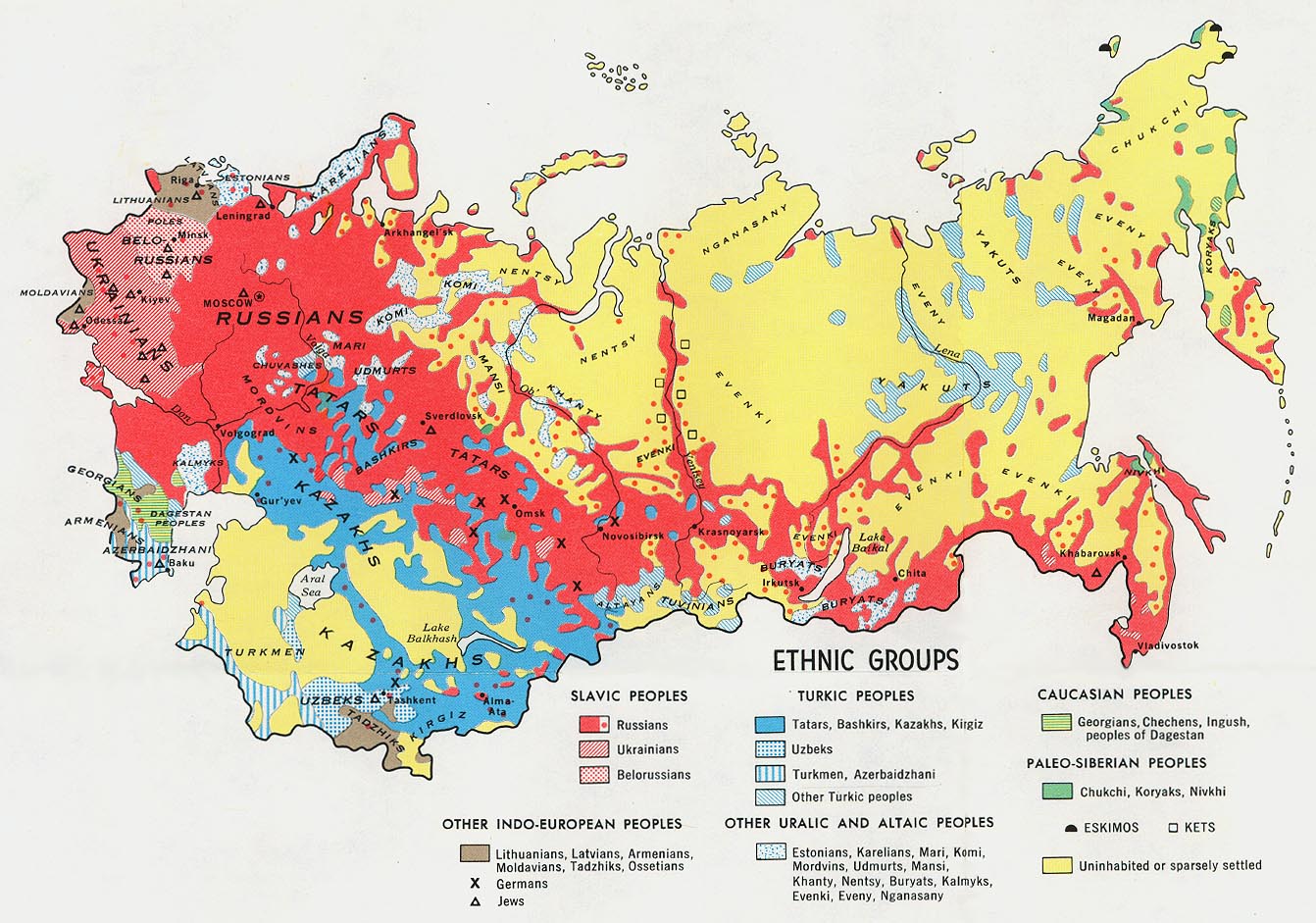 The Soviet Union was one of the world's most ethnically diverse countries, with more than 100 distinct national ethnicities living within its borders.
Other ethnic groups included Abkhaz, Adyghes,
The Soviet Union was one of the world's most ethnically diverse countries, with more than 100 distinct national ethnicities living within its borders.
Other ethnic groups included Abkhaz, Adyghes,
"ЗАКОН СССР ОТ 24.04.1990 О ЯЗЫКАХ НАРОДОВ СССР"
(The April 24, 1990 Soviet Union Law about the Languages of the Soviet Union) Until that time it was still necessary to have a language of common communication. The ''de facto'' result inevitably favored Russian, the native language of half Soviet citizens.Bernard Comrie, ''The Languages of the Soviet Union'', page 31, the Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, 1981. Overall Soviet citizens spoke more than 200 languages and dialects (at least 18 with more than 1 million speakers); Slavic group: 75%, other
USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
was 70% East Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert H ...
, 17% Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging t ...
, and all other ethnic groups below 2%. Alongside the atheist majority of 60% there were sizable minorities of Russian Orthodox
Russian Orthodoxy (russian: Русское православие) is the body of several churches within the larger communion of Eastern Orthodox Christianity, whose liturgy is or was traditionally conducted in Church Slavonic language. Most ...
Christians (approx. 20%) and Muslims (approx. 15%).
History
Revolution and Civil war, 1917 - 1923
Russia lost former territories of theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
with about 30 million inhabitants after the Russian Revolution of 1917 (Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
: 18 million; Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
: 3 million; Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
: 3 million; the Baltic states: 5 million and Kars to Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
: 400 thousand). At least 2 million citizens of the former Russian Empire died in the course of the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
of 1917–1923, and a further 1 to 2 million emigrated
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
.
Great Patriotic War, 1941 - 1945
During theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
on the Eastern Front, the Soviet Union lost an approximate 26.6 million people.
Rejuvenation of the population, 1946 - 1960s
After the Second World War, the population of the Soviet Union began to gradually recover itself to pre-war levels, by 1959 this had been surpassed with a registered 209,035,000 people over the 1941 population count of 196,716,000.Population dynamics in the 1970s - 1980s
Thecrude birth rate
The birth rate for a given period is the total number of live human births per 1,000 population divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registration system for births; populati ...
in the Soviet Union throughout its history had been decreasing - from 44.0 per thousand in 1926 to 18.0 in 1974, mostly due to urbanization and rising average age of marriages. The crude death rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of de ...
had been gradually decreasing as well - from 23.7 per thousand in 1926 to 8.7 in 1974. While death rates did not differ greatly across regions of the Soviet Union through much of Soviet history, birth rates in southern republics of Transcaucasia and Central Asia were much higher than those in the northern parts of the Soviet Union, and in some cases even increased in the post-World War II period. This was partly due to slower rates of urbanization and traditionally early marriages in southern republics.
As a result, mainly of differential birthrates, with most of the European nationalities moving toward sub-replacement fertility
Sub-replacement fertility is a total fertility rate (TFR) that (if sustained) leads to each new generation being less populous than the older, previous one in a given area. The United Nations Population Division defines sub-replacement fertilit ...
and the Central Asian and other nationalities of southern republics having well-above replacement-level fertility, the percentage who were Russians was gradually being reduced. According to some Western scenarios of the 1990s, if the Soviet Union had stayed together it is likely that Russians would have lost their majority status in the 2000s (decade). This differential could not be offset by assimilation of non-Russians by Russians, in part because the nationalities of southern republics maintained a distinct ethnic consciousness and were not easily assimilated.
The late 1960s and the 1970s witnessed a dramatic reversal of the path of declining mortality in the Soviet Union, and was especially notable among men in working ages, and also especially in Russia and other predominantly Slavic areas of the country. While not unique to the Soviet Union (Hungary in particular showed a pattern that was similar to Russia), this male mortality increase, accompanied by a noticeable increase in infant mortality rates in the early 1970s, drew the attention of Western demographer
Demography () is the statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups defined by criteria such as ed ...
s and Sovietologists at the time.
An analysis of the official data from the late 1980s showed that after worsening in the late 1970s and the early 1980s, the situation for adult mortality began to improve again. Referring to data for the two decades ending in 1989–1990, while noting some abatement in adult mortality rates in the Soviet republics in the 1980s, Ward Kingkade and Eduardo Arriaga characterized this situation as follows: "All of the former Soviet countries have followed the universal tendency for mortality to decline as infectious diseases are brought under control while death rates from degenerative diseases rise. What is exceptional in the former Soviet countries and some of their East European neighbors is that a subsequent increase in mortality from causes other than infectious disease has brought about overall rises in mortality from all causes combined. Another distinctive characteristic of the former Soviet case is the presence of unusually high levels of mortality from accidents and other external causes, which are typically associated with alcoholism."
The rising infant mortality rates in the Soviet Union in the 1970s became the subject of much discussion and debate among Western demographers. The infant mortality rate (IMR) had increased from 24.7 in 1970 to 27.9 in 1974. Some researchers regarded the rise in infant mortality as largely real, a consequence of worsening health conditions and services. Others regarded it as largely an artifact of improved reporting of infant deaths, and found the increases to be concentrated in the Central Asian republics where improvement in coverage and reporting of births and deaths might well have the greatest effect on increasing the published rates.
The rising reported adult mortality and infant mortality was not explained or defended by Soviet officials at the time. Instead, they simply stopped publishing all mortality statistics for ten years. Soviet demographers and health specialists remained silent about the mortality increases until the late 1980s when the publication of mortality data resumed and researchers could delve into the real and artificial aspects of the reported mortality increases. When these researchers began to report their findings, they accepted the increases in adult male mortality as real and focused their research on explaining its causes and finding solutions. In contrast, investigations of the rise in reported infant mortality concluded that while the reported increases in the IMR were largely an artifact of improved reporting of infant deaths in the Central Asian republics, the actual levels in this region were much higher than had yet been reported officially. In this sense the reported ''rise'' in infant mortality in the Soviet Union as a whole was an artifact of improved statistical reporting, but reflected the reality of a much higher actual infant mortality ''level'' than had previously been recognized in official statistics.
As the detailed data series that was ultimately published in the late 1980s showed, the reported IMR for the Soviet Union as a whole increased from 24.7 in 1970 to a peak of 31.4 in 1976. After that the IMR gradually decreased and by 1989 it had fallen to 22.7, which was lower than had been reported in any previous year (though close to the figure of 22.9 in 1971). In 1989, the IMR ranged from a low of 11.1 in the Latvian SSR to a high of 54.7 in the Turkmen SSR.
Research conducted subsequent to the dissolution of the Soviet Union revealed that the originally reported mortality rates very substantially underestimated the actual rates, especially for infant mortality. This has been shown for Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and Western Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Arme ...
n and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
n republics.
Population
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
with about 30 million inhabitants after the Russian Revolution of 1917 (Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
: 18 million; Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
: 3 million; Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
: 3 million; the Baltic states: 5 million and Kars to Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
: 400 thousand). At least 2 million citizens of the former Russian Empire died in the course of the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
of 1917–1923, and a further 1 to 2 million emigrated
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
. An estimated 800,000 to 1,200,000 people died during the purges of the 1930s.
According to the Russian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across ...
the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
suffered 26.6 million deaths (1941-1945) during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, including an increase in infant mortality of 1.3 million. Total war-loss figures include territories annexed by the Soviet Union in 1939–1945.
Although the population growth-rate decreased over time, it remained positive throughout the history of the Soviet Union in all republics
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
, and the population grew each year by more than 2 million except during periods of wartime, and famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompani ...
.
Life expectancy and infant mortality
A newborn Soviet child in 1926–27 had a life expectancy of 44.4 years, up from 32.3 years in the Russian Empire thirty years before. By 1958–59, the life expectancy for newborns had reached 68.6 years.The Seeming Paradox of Increasing Mortality in a Highly Industrialized Nation: the Example of the Soviet Union : 1985. author Dinkel, R. H. The life expectancy in the United States in 1958–59 was 66.2 for men and 72.9 for women. Life expectancy in the Soviet Union remained fairly stable during most years, although in the 1970s it decreased slightly.Demographic statistics
 The following demographic statistics are from the 1990 edition of the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
The following demographic statistics are from the 1990 edition of the CIA World Factbook, unless otherwise indicated.
Population
*Population: 290,644,721 (July 1992)Population growth rate
*0.4% (1992)Crude birth rate
*18 births/1,000 population (1990)Crude death rate
*10 deaths/1,000 population (1990)Net migration rate
*1 migrants/1,000 population (1990)Infant mortality rate
*24 deaths/1,000 live births (1990)Life expectancy at birth
*65 years male, 74 years female (1990)Total fertility rate
*2.4 children born/woman (1985) *2.528 children born/woman (1987) *2.26 children born/woman (1990)Nationality
*noun - Soviet(s); adjective - SovietLiteracy
*99.8% (1980)Labor force
Labor force: 152,300,000 civilians; 80% industry and other nonagricultural fields, 20% agriculture; shortage of skilled labor (1989) Organized labor: 98% of workers were union members; all trade unions are organized within theAll-Union Central Council of Trade Unions The All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions (ACCTU; russian: Всесоюзный центральный совет профессиональных союзов, VTsSPS) was the national trade union federation of the Soviet Union.
The federati ...
(AUCCTU) and conduct their work under guidance of the Communist party
A communist party is a political party that seeks to realize the socio-economic goals of communism. The term ''communist party'' was popularized by the title of ''The Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. ...
. There was a market relationship between the people and the state as the employer; people were free to choose their job and leave if they wished, although members of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union could be ordered to work in certain places, but seldom were.
Abortion
Ethnic groups
 The Soviet Union was one of the world's most ethnically diverse countries, with more than 100 distinct national ethnicities living within its borders.
Other ethnic groups included Abkhaz, Adyghes,
The Soviet Union was one of the world's most ethnically diverse countries, with more than 100 distinct national ethnicities living within its borders.
Other ethnic groups included Abkhaz, Adyghes, Aleut
The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the ...
s, Assyrians, Avars, Bashkirs
, native_name_lang = bak
, flag = File:Bashkirs of Baymak rayon.jpg
, flag_caption = Bashkirs of Baymak in traditional dress
, image =
, caption =
, population = approx. 2 million
, popplace ...
, Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely unders ...
, Buryats, Chechens
The Chechens (; ce, Нохчий, , Old Chechen: Нахчой, ''Naxçoy''), historically also known as ''Kisti'' and ''Durdzuks'', are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group of the Nakh peoples native to the North Caucasus in Eastern Europe. "Eu ...
, Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Chuvash, Cossacks, Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
, Evenks
The Evenks (also spelled Ewenki or Evenki based on their endonym )Autonym: (); russian: Эвенки (); (); formerly known as Tungus or Tunguz; mn, Хамниган () or Aiwenji () are a Tungusic people of North Asia. In Russia, the Eve ...
, Finns
Finns or Finnish people ( fi, suomalaiset, ) are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland.
Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these ...
, Gagauz, Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
, Ingushes
The Ingush (, inh, ГIалгIай, translit=Ghalghaj, pronounced ) per Oxford dictionary "a member of a people living mainly in Ingushetia in the central Caucasus." Ingushetia is a federal republic of Russian Federation. The Ingush are predomi ...
, Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Kalmyks, Karakalpaks
The Karakalpaks or Qaraqalpaqs (; kaa, Qaraqalpaqlar, Қарақалпақлар, قاراقلپقلر), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Karakalpakstan in Northwestern Uzbekistan. During the 18th century, they settled in the lower reach ...
, Karelians
Karelians ( krl, karjalaižet, karjalazet, karjalaiset, Finnish: , sv, kareler, karelare, russian: Карелы) are a Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russi ...
, Kets
Kets (russian: Кеты; Ket: Ostygan) are a tribe of Yeniseian speaking people in Siberia. During the Russian Empire, they were known as Ostyaks, without differentiating them from several other Siberian people. Later, they became known as ''Ye ...
, Koreans
Koreans ( South Korean: , , North Korean: , ; see names of Korea) are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula.
Koreans mainly live in the two Korean nation states: North Korea and South Korea (collectively and simply re ...
, Lezgins
Lezgins or Leks ( lez, Лезгияр, Лекьер. lezgijar) are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group native predominantly to southern Dagestan, a republic of Russia, and northeastern Azerbaijan. The Lezgin are predominantly Sunni Muslims and s ...
, Maris, Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
, Mordvins
The Mordvins (also Unified Mordvin people, Mordvinians, Mordovians; russian: мордва, Mordva, Mordvins (no equivalents in Moksha and Erzya)) is an obsolete but official term used in the Russian Federation to refer both to Erzyas and Mo ...
, Nenetses, Ossetians
The Ossetians or Ossetes (, ; os, ир, ирæттæ / дигорӕ, дигорӕнттӕ, translit= ir, irættæ / digoræ, digorænttæ, label=Ossetic) are an Iranian ethnic group who are indigenous to Ossetia, a region situated across the no ...
, Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in C ...
, Roma, Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
, Tats, Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Tuvans
The Tuvans ( tyv, Тывалар, Tıvalar) are a TurkicOtto Maenchen-Helfen, Journey to Tuva, p. 169 ethnic group indigenous to Siberia who live in Russia ( Tuva), Mongolia, and China. They speak Tuvan, a Siberian Turkic language. They are a ...
, Udmurts
The Udmurts ( udm, Удмуртъёс, ) are a Permian ( Finnic) ethnic group in Eastern Europe, who speak the Udmurt language. In the course of history, Russian-speakers have referred to them as ' (), Otyaks, Wotyaks or Votyaks.
Etymology
The ...
, and Yakuts
The Yakuts, or the Sakha ( sah, саха, ; , ), are a Turkic ethnic group who mainly live in the Republic of Sakha in the Russian Federation, with some extending to the Amur, Magadan, Sakhalin regions, and the Taymyr and Evenk Districts ...
. Dozens of these other ethnic groups were the titular nations of different Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republics
An Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (ASSR, russian: автономная советская социалистическая республика, АССР) was a type of administrative unit in the Soviet Union (USSR) created for certain nat ...
or Autonomous Oblasts within the union-level republics (ex. Tatars in Tatar ASSR
The Tatar Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (russian: Татарская Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Автономияле Совет Соци� ...
within the RSFSR, Abkhaz ASSR
The Abkhaz Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (russian: Абхазская Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика; ka, აფხაზეთის ავტონომიური ს� ...
within Georgia) or had been previously ( Volga German ASSR, Crimean ASSR
During the existence of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, different governments existed within the Crimean Peninsula. From 1921 to 1936, the government in the Crimean Peninsula was known as the Crimean Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic; ...
).
Religion
The Soviet Union promotedstate atheism
State atheism is the incorporation of positive atheism or non-theism into political regimes. It may also refer to large-scale secularization attempts by governments. It is a form of religion-state relationship that is usually ideologically l ...
from 1928 to 1941, in which religion was largely discouraged and heavily persecuted. The USSR remained a secular state from 1945 until its dissolution. However, according to various Soviet and Western sources, over one-third of the country's people professed religious beliefs: Russian Orthodox 20%, Muslim 15%, Protestant, Georgian Orthodox, Armenian Orthodox, and Roman Catholic 7%, Jewish less than 1%, atheist 60% (1990 est.). Some indigenous pagan belief systems existed in the Siberian and Russian Far East
The Russian Far East (russian: Дальний Восток России, r=Dal'niy Vostok Rossii, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in Northeast Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent; and is admin ...
ern lands in the local populations.
Language
Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
became the official language of the Soviet Union in 1990.(The April 24, 1990 Soviet Union Law about the Languages of the Soviet Union) Until that time it was still necessary to have a language of common communication. The ''de facto'' result inevitably favored Russian, the native language of half Soviet citizens.Bernard Comrie, ''The Languages of the Soviet Union'', page 31, the Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, 1981. Overall Soviet citizens spoke more than 200 languages and dialects (at least 18 with more than 1 million speakers); Slavic group: 75%, other
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
: 8%, Altaic
Altaic (; also called Transeurasian) is a controversial proposed language family that would include the Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic language families and possibly also the Japonic and Koreanic languages. Speakers of these languages are ...
: 12%, Uralic
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (w ...
: 3%, Caucasian
Caucasian may refer to:
Anthropology
*Anything from the Caucasus region
**
**
** ''Caucasian Exarchate'' (1917–1920), an ecclesiastical exarchate of the Russian Orthodox Church in the Caucasus region
*
*
*
Languages
* Northwest Caucasian l ...
: 2% (1990 est.)
See also
* Demographics of Central Asia *Religion in the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was established by the Bolsheviks in 1922, in place of the Russian Empire. At the time of the 1917 Revolution, the Russian Orthodox Church was deeply integrated into the autocratic state, enjoying official status. This was a si ...
* Family in the Soviet Union
The view of the Soviet family as the basic social unit in society evolved from revolutionary to conservative; the government of the Soviet Union first attempted to weaken the family and then to strengthen it.
According to the 1968 law "Principles ...
* List of Russian censuses
A Russian census is a census of the population of Russia. Such a census has occurred at various irregular points in the history of Russia.
Introduced in 1897 during the Russian Empire, the census took place decennially since 2010 according to the ...
References
General sources
# CIA World Factbook 1991 - most figures, unless attributed to another source. # ''J. A. Newth: The 1970 Soviet Census,Soviet Studies
''Europe-Asia Studies'' is an academic peer-reviewed journal published 10 times a year by Routledge on behalf of the Institute of Central and East European Studies, University of Glasgow, and continuing (since vol. 45, 1993) the journal ''Soviet St ...
vol. 24, issue 2 (October 1972) pp. 200–222.'' - Population figures from 1897 - 1970.
# ''The Russian State Archive of the Economy: Soviet Censuses of 1937 and 1939'' - Population figures for 1937 and 1939. https://web.archive.org/web/20020927142010/http://www.library.yale.edu/slavic/census3739.html
{{DEFAULTSORT:Demography Of The Soviet Union