Pope Marcellus Mass on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Missa Papae Marcelli'', or ''Pope Marcellus Mass'', is a
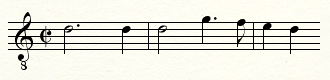 ''Missa Papae Marcelli'' does not (as far as is known) make use of any pre-existing theme. The motif of a rising
''Missa Papae Marcelli'' does not (as far as is known) make use of any pre-existing theme. The motif of a rising
"A New Look at Palestrina's ''Missa Papae Marcelli''"
''College Music Symposium'' 23 (1) (Spring, 1983), pp. 22–49. (subscription required) The
mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different eleme ...
''sine nomine
''Sine nomine'' (abbreviated s.n.) is a Latin expression, meaning "without a name". It is most commonly used in the contexts of publishing and bibliographical listings such as library catalogs, to signify that the publisher (or distributor, etc.) ...
'' by Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina
Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina ( – 2 February 1594) was an Italian composer of late Renaissance music. The central representative of the Roman School, with Orlande de Lassus and Tomás Luis de Victoria, Palestrina is considered the leading ...
. It is his best-known mass, and is regarded as an archetypal example of the complex polyphony championed by Palestrina. It was sung at the papal coronation Masses (the last being the coronation of Paul VI in 1963).
Style
The ''Missa Papae Marcelli'' consists, like mostRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
masses, of a Kyrie
Kyrie, a transliteration of Greek , vocative case of (''Kyrios''), is a common name of an important prayer of Christian liturgy, also called the Kyrie eleison ( ; ).
In the Bible
The prayer, "Kyrie, eleison," "Lord, have mercy" derives f ...
, Gloria, Credo
In Christian liturgy, the credo (; Latin for "I believe") is the Nicene-Constantinopolitan Creed – or its shorter version, the Apostles' Creed – in the Mass, either as a prayer, a spoken text, or sung as Gregorian chant or other musical sett ...
, Sanctus
The Sanctus ( la, Sanctus, "Holy") is a hymn in Christian liturgy. It may also be called the ''epinikios hymnos'' ( el, ἐπινίκιος ὕμνος, "Hymn of Victory") when referring to the Greek rendition.
In Western Christianity, th ...
/Benedictus
Benedictus may refer to:
Music
* Benedictus (Song of Zechariah), ''Benedictus'' (''Song of Zechariah''), the canticle sung at Lauds, also called the Canticle of Zachary
* The second part of the Sanctus, part of the Eucharistic prayer
* Benedictus ...
, and Agnus Dei
is the Latin name under which the " Lamb of God" is honoured within the Catholic Mass and other Christian liturgies descending from the Latin liturgical tradition. It is the name given to a specific prayer that occurs in these liturgies, and ...
, though the third part of the Agnus Dei is a separate movement (designated "Agnus II"). Taruskin, Richard. ''Music from the Earliest Notations to the Sixteenth Century''. The Oxford History of Western Music, Volume 1. New York: Oxford University Press, 2010. pp. 653–663 The mass is freely composed, not based upon a cantus firmus
In music, a ''cantus firmus'' ("fixed melody") is a pre-existing melody forming the basis of a polyphonic composition.
The plural of this Latin term is , although the corrupt form ''canti firmi'' (resulting from the grammatically incorrect tre ...
, paraphrase, or parody
A parody, also known as a spoof, a satire, a send-up, a take-off, a lampoon, a play on (something), or a caricature, is a creative work designed to imitate, comment on, and/or mock its subject by means of satiric or ironic imitation. Often its sub ...
. Perhaps because of this, the mass is not as thematically consistent as Palestrina's masses based on models. It is primarily a six-voice mass, but voice combinations are varied throughout the piece; Palestrina scores Agnus II for seven voices, and the use of the full forces is reserved for specific climactic portions in the text. It is set primarily in a homorhythm
In music, homorhythm (also homometer) is a texture having a "similarity of rhythm in all parts"Griffiths, Paul (2005). ''The Penguin Companion to Classical Music'', p.375. . or "very similar rhythm" as would be used in simple hymn
A hymn is ...
ic, declamatory style, with little overlapping of text and a general preference for block chord
A block chord is a chord or voicing built directly below the melody either on the strong beats or to create a four-part harmonized melody line in " locked-hands" rhythmic unison with the melody, as opposed to broken chords. This latter style, ...
s such that the text can clearly be heard in performance, unlike many polyphonic masses of the 16th century. As in much of Palestrina's contrapuntal
In music, counterpoint is the relationship between two or more musical lines (or voices) which are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. It has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradi ...
work, voices move primarily in stepwise motion, and the voice leading strictly follows the rules of the diatonic modes
Mode ( la, modus meaning "manner, tune, measure, due measure, rhythm, melody") may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* '' MO''D''E (magazine)'', a defunct U.S. women's fashion magazine
* ''Mode'' magazine, a fictional fashion magazine which is ...
codified by theorist Gioseffo Zarlino
Gioseffo Zarlino (31 January or 22 March 1517 – 4 February 1590) was an Italian music theorist and composer of the Renaissance. He made a large contribution to the theory of counterpoint as well as to musical tuning.
Life and career
Zarlin ...
.
History
The mass was composed in honor ofPope Marcellus II
Pope Marcellus II ( it, Marcello II; 6 May 1501 – 1 May 1555), born Marcello Cervini degli Spannocchi, was a Papalini Catholic prelate who served as head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 9 April 1555 until h ...
, who reigned for three weeks in 1555. Recent scholarship suggests the most likely date of composition is 1562, when it was copied into a manuscript at the Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore in Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
.
The third and closing sessions of the Council of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described a ...
were held in 1562–63, at which the use of polyphonic music in the Catholic Church was discussed. Concerns were raised over two problems: first, the use of music that was objectionable, such as secular songs provided with religious lyrics (contrafacta
In vocal music, contrafactum (or contrafact, pl. contrafacta) is "the substitution of one text for another without substantial change to the music". The earliest known examples of this procedure (sometimes referred to as ''adaptation''), date back ...
) or masses based on songs with lyrics about drinking or lovemaking; and second, whether imitation
Imitation (from Latin ''imitatio'', "a copying, imitation") is a behavior whereby an individual observes and replicates another's behavior. Imitation is also a form of that leads to the "development of traditions, and ultimately our culture. ...
in polyphonic music obscured the words of the mass, interfering with the listener's devotion. Some debate occurred over whether polyphony should be banned outright in worship, and some of the auxiliary publications by attendants of the Council caution against both of these problems. However, none of the official proclamations from the Council mentions polyphonic music, excepting one injunction against the use of music that is, in the words of the Council, "lascivious or impure".Monson, Craig. "The Council of Trent Revisited". ''Journal of the American Musicological Society'' 55 (2002), pp. 1–37.
Starting in the late 16th century, a legend began that the second of these points, the threat that polyphony might have been banned by the Council because of the unintelligibility of the words, was the impetus behind Palestrina's composition of this mass. It was believed that the simple, declamatory style of ''Missa Papae Marcelli'' convinced Cardinal Carlo Borromeo
Charles Borromeo ( it, Carlo Borromeo; la, Carolus Borromeus; 2 October 1538 – 3 November 1584) was the Archbishop of Milan from 1564 to 1584 and a cardinal of the Catholic Church. He was a leading figure of the Counter-Reformation combat ...
, on hearing, that polyphony could be intelligible, and that music such as Palestrina's was all too beautiful to ban from the Church. In 1607, the composer Agostino Agazzari
Agostino Agazzari (2 December 1578 – 10 April 1640) was an Italian composer and music theorist.
Life
Agazzari was born in Siena to an aristocratic family. After working in Rome, as a teacher at the Roman College, he returned to Siena in 1607, b ...
wrote:
Jesuit musicians of the 17th century maintained this rumor, and it made its way into music history books into the 19th century, when historian Giuseppe Baini, in his 1828 biography of Palestrina, couched him as the "savior of polyphony" from a council wishing to wipe it out entirely:
An entry in the papal chapel diaries confirms that a meeting such as the one described by Baini occurred, but no mention is made of whether the ''Missa Papae Marcelli'' was performed there or what the reaction of the audience was. This legend persisted into the 20th century; Hans Pfitzner
Hans Erich Pfitzner (5 May 1869 – 22 May 1949) was a German composer, conductor and polemicist who was a self-described anti-modernist. His best known work is the post-Romantic opera ''Palestrina'' (1917), loosely based on the life of the ...
's opera ''Palestrina
Palestrina (ancient ''Praeneste''; grc, Πραίνεστος, ''Prainestos'') is a modern Italian city and ''comune'' (municipality) with a population of about 22,000, in Lazio, about east of Rome. It is connected to the latter by the Via Pre ...
'' is based upon this understanding of the deliberations of the Tridentine officials. While Palestrina sympathized with many of the Council's decisions, and, like Vincenzo Ruffo, sought deliberately to compose in a simplified, easily understood style to please church officials, there is no evidence to support either the view that the Council sought to banish polyphony entirely or that Palestrina's mass was the deciding factor in changing their minds.
In the latter part of the 20th century, the ''Missa Papae Marcelli'' has been recorded frequently, and is often used as a model for the study of '' stile antico'' Renaissance polyphony in university courses on music.
Analysis
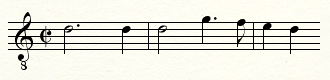 ''Missa Papae Marcelli'' does not (as far as is known) make use of any pre-existing theme. The motif of a rising
''Missa Papae Marcelli'' does not (as far as is known) make use of any pre-existing theme. The motif of a rising perfect fourth
A fourth is a musical interval encompassing four staff positions in the music notation of Western culture, and a perfect fourth () is the fourth spanning five semitones (half steps, or half tones). For example, the ascending interval from C to ...
and stepwise return (illustrated) is used extensively throughout this mass. It is similar in profile to the opening of the French secular song " L'homme armé", which provided the theme for many Renaissance masses. But this is probably a coincidence, as themes with this profile were common in the 16th century, and Palestrina himself used them in several other masses.Godt, Irving"A New Look at Palestrina's ''Missa Papae Marcelli''"
''College Music Symposium'' 23 (1) (Spring, 1983), pp. 22–49. (subscription required) The
Kyrie
Kyrie, a transliteration of Greek , vocative case of (''Kyrios''), is a common name of an important prayer of Christian liturgy, also called the Kyrie eleison ( ; ).
In the Bible
The prayer, "Kyrie, eleison," "Lord, have mercy" derives f ...
consists of imitative polyphony in Palestrina's earlier style, based on the main motif. It is in the middle movements that Palestrina applies the simpler style needed after the Council of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described a ...
. Richard Taruskin
Richard Filler Taruskin (April 2, 1945 – July 1, 2022) was an American musicologist and music critic who was among the leading and most prominent music historians of his generation. The breadth of his scrutiny into source material as well as ...
described the Credo as "a strategically planned series of cadential 'cells' ... each expressed through a fragment of text declaimed homorhythmically by a portion of the choir ... and rounded off by a beautifully crafted cadence". The words are clearly distinguishable, since melodic decoration is confined to the longest syllables. A different selection of voices is used for each such phrase.
The Sanctus begins with very short phrases cadencing on C. Longer phrases then cadence on F, D and G before the music returns to C with conclusive effect. This was a new technique, using "tonal planning" to replace imitation as the means to keep the music moving forward.
The Agnus Dei returns to the imitative polyphony of the Kyrie (the opening of Agnus Dei I repeats that of the Kyrie). As was frequently done in the 16th century, Palestrina adds an extra voice in Agnus Dei II, making seven for this movement, in which is embedded a three-part canon that begins with the head-motive.
References
Further reading
*External links
* {{italic titlePalestrina
Palestrina (ancient ''Praeneste''; grc, Πραίνεστος, ''Prainestos'') is a modern Italian city and ''comune'' (municipality) with a population of about 22,000, in Lazio, about east of Rome. It is connected to the latter by the Via Pre ...
Renaissance music
Compositions by Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina