Polynesian Navigator on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Polynesian navigation or Polynesian wayfinding was used for thousands of years to enable long voyages across thousands of kilometers of the open Pacific Ocean.
Polynesian navigation or Polynesian wayfinding was used for thousands of years to enable long voyages across thousands of kilometers of the open Pacific Ocean.
 Between about 3000 and 1000 BC speakers of
Between about 3000 and 1000 BC speakers of
 The positions of the stars helped guide Polynesian voyages. Stars, as opposed to planets, hold fixed celestial positions year-round, changing only their rising time with the seasons. Each star has a specific
The positions of the stars helped guide Polynesian voyages. Stars, as opposed to planets, hold fixed celestial positions year-round, changing only their rising time with the seasons. Each star has a specific
 On his first voyage of Pacific exploration, Captain James Cook had the services of a Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who drew a chart of the islands within a radius (to the north and west) of his home island of
On his first voyage of Pacific exploration, Captain James Cook had the services of a Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who drew a chart of the islands within a radius (to the north and west) of his home island of
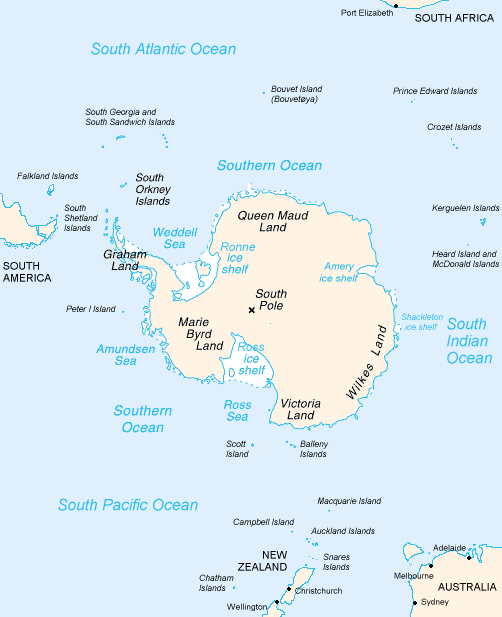 There is academic debate on the furthest southern extent of Polynesian expansion.
The islands of New Zealand, along with a series of outlying islands, have been labelled 'South Polynesia' by New Zealand archaeologist Atholl Anderson. These islands include the Kermadec Islands, the Chatham Islands, the Auckland Islands and
There is academic debate on the furthest southern extent of Polynesian expansion.
The islands of New Zealand, along with a series of outlying islands, have been labelled 'South Polynesia' by New Zealand archaeologist Atholl Anderson. These islands include the Kermadec Islands, the Chatham Islands, the Auckland Islands and
 Knowledge of the traditional Polynesian methods of navigation was widely lost after contact with and colonization by Europeans. This caused debates over the reasons for the presence of the Polynesians in such isolated and scattered parts of the Pacific. According to Andrew Sharp, the explorer Captain
Knowledge of the traditional Polynesian methods of navigation was widely lost after contact with and colonization by Europeans. This caused debates over the reasons for the presence of the Polynesians in such isolated and scattered parts of the Pacific. According to Andrew Sharp, the explorer Captain
 Anthropologist David Lewis sailed his catamaran from Tahiti to New Zealand, via Rarotonga using
Anthropologist David Lewis sailed his catamaran from Tahiti to New Zealand, via Rarotonga using

 Polynesian navigation or Polynesian wayfinding was used for thousands of years to enable long voyages across thousands of kilometers of the open Pacific Ocean.
Polynesian navigation or Polynesian wayfinding was used for thousands of years to enable long voyages across thousands of kilometers of the open Pacific Ocean. Polynesians
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Sou ...
made contact with nearly every island within the vast Polynesian Triangle
The Polynesian Triangle is a region of the Pacific Ocean with three island groups at its corners: Hawai‘i, Easter Island (''Rapa Nui'') and New Zealand (Aotearoa). It is often used as a simple way to define Polynesia.
Outside the triangle, th ...
, using outrigger canoes or double-hulled canoes. The double-hulled canoes were two large hulls, equal in length, and lashed side by side. The space between the paralleled canoes allowed for storage of food, hunting materials, and nets when embarking on long voyages. Polynesian navigators used wayfinding techniques such as the navigation by the stars, and observations of birds, ocean swells, and wind patterns, and relied on a large body of knowledge from oral tradition.
Navigators travelled to small inhabited islands using wayfinding techniques and knowledge passed by oral tradition from master to apprentice, often in the form of song. Generally, each island maintained a guild of navigators who had very high status; in times of famine or difficulty, they could trade for aid or evacuate people to neighbouring islands. As of 2014, these traditional navigation methods are still taught in the Polynesian outlier of Taumako
Taumako is the largest of the Duff Islands, in the Solomon Islands. This island has steep sides and rises to a height of above sea level. It is composed of basaltic lavas and pyroclastics like the other islands in the Duffs.
The inhabitants of ...
in the Solomons and by voyaging societies throughout the Pacific.
Both wayfinding techniques and outrigger canoe construction methods have been kept as guild secrets, but in the modern revival of these skills, they are being recorded and published.
History
 Between about 3000 and 1000 BC speakers of
Between about 3000 and 1000 BC speakers of Austronesian
Austronesian may refer to:
*The Austronesian languages
*The historical Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, M ...
languages spread through the islands of Southeast Asia – most likely starting out from Taiwan, as tribes whose natives were thought to have previously arrived from mainland South China about 8000 years ago – into the edges of western Micronesia and on into Melanesia, through the Philippines and Indonesia. In the archeogenetic record, there are well-defined traces of this expansion that allow the path it took to be followed and dated with a degree of certainty. In the mid-2nd millennium BC, a distinctive culture appeared suddenly in north-west Melanesia, in the Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
, the chain of islands forming a great arch from New Britain
New Britain ( tpi, Niu Briten) is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi the Dam ...
to the Admiralty Islands.
This culture, known as Lapita
The Lapita culture is the name given to a Neolithic Austronesian people and their material culture, who settled Island Melanesia via a seaborne migration at around 1600 to 500 BCE. They are believed to have originated from the northern Philipp ...
, stands out in the Melanesian archeological record, with its large permanent villages on beach terraces along the coasts. Particularly characteristic of the Lapita culture is the making of pottery, including a great many vessels of varied shapes, some distinguished by fine patterns and motifs pressed into the clay. Between about 1300 and 900 BC, the Lapita culture spread 6000 km farther to the east from the Bismarck Archipelago, until it reached as far as Tonga and Samoa. Lapita pottery persisted in places such as Samoa, Tonga, and Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
for many years after its introduction to Western Polynesia but eventually died out in most of Polynesia due to the scarcity of clay. Although the production of ceramics did not travel beyond Western Polynesia, some ceramic materials have been recovered through archeological excavations in the Central Polynesia but have been attributed to trade.
In accordance with Polynesian oral tradition, the geography of Polynesian navigation pathways is said to resemble the geometric qualities of an octopus with head centred on Ra'iātea (French Polynesia) and tentacles spread out across the Pacific. In oral tradition the octopus is known by various names such as Taumata-Fe'e-Fa'atupu-Hau (Grand Octopus of Prosperity), Tumu-Ra'i-Fenua (Beginning-of-Heaven-and-Earth) and Te Wheke-a-Muturangi (The Octopus of Muturangi In Māori mythology, Muturangi, also known as Ruamuturangi, was a renowned High Priest presiding over Taputapuatea marae at Rangiatea in French Polynesia.
The son of Ohomairangi, Muturangi was an accomplished navigator and it was he who started ...
).
Specific chronology of the discovery and settlement of specific island groups within Eastern and Central Polynesia is hotly debated among archeologists, but a generally accepted timeline puts the initial settlement of the Cook Islands before 1000 AD. From this point, navigation branched out in all directions with Eastern Polynesia (including the Society Islands and the Marquesas Islands) settled first followed by more remote regions such as Hawaii, Easter Island, and New Zealand peopled later. The pattern of settlement also extended to the north of Samoa to the Tuvaluan atolls, with Tuvalu providing a stepping stone to the founding of Polynesian Outlier communities in Melanesia and Micronesia. The natives of Easter Island likely originated from Mangareva. They discovered the island by using the flight path of the sooty tern. When the first European to visit the island, Jacob Roggeveen, landed on Easter Island, he found no evidence of navigation. Instead, he noticed that there were not enough trees to build seaworthy canoes and the rafts the natives were using were not seaworthy either.
The archeological record supports oral histories of the first peopling of region including both the timing and geographical origins of Polynesian society.
Navigational techniques
Navigation relies heavily on constant observation and memorization. Navigators have to memorize where they have sailed from in order to know where they are. The sun was the main guide for navigators because they could follow its exact points as it rose and set. Once the sun had set they would use the rising and setting points of the stars. When there were no stars because of a cloudy night or during daylight, a navigator would use the winds and swells as guides. Through constant observation, navigators were able to detect changes in the speed of their canoes, their heading, and the time of day or night. Polynesian navigators thus employed a wide range of techniques including the use of the stars, the movement of ocean currents and wave patterns, the patterns ofbioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some b ...
that indicated the direction in which islands were located, the air and sea interference patterns caused by islands and atolls, the flight of birds, the winds and the weather..
Bird observation
Certain seabirds such as the white tern and noddy tern fly out to sea in the morning to hunt fish, then return to land at night. Navigators seeking land sail opposite the birds' path in the morning and with them at night, especially relying on large groups of birds, and keeping in mind changes during nesting season. Harold Gatty suggested that long-distance Polynesian voyaging followed the seasonal paths ofbird migration
Bird migration is the regular seasonal movement, often north and south along a flyway, between breeding and wintering grounds. Many species of bird migrate. Migration carries high costs in predation and mortality, including from hunting by ...
s. In "The Raft Book", a survival guide he wrote for the U.S. military during World War II, Gatty outlined various Polynesian navigation techniques for shipwrecked sailors or aviators to find land. There are some references in their oral traditions to the flight of birds, and Gatty claimed that departing voyages used onshore range marks pointing to distant islands in line with their flight paths. A voyage from Tahiti, the Tuamotus or the Cook Islands to New Zealand might have followed the migration of the long-tailed cuckoo (''Eudynamys taitensis''), just as the voyage from Tahiti to Hawaii would coincide with the track of the Pacific golden plover (''Pluvialis fulva'') and the bristle-thighed curlew (''Numenius tahitiensis'').
It is also believed that Polynesians, like many seafaring peoples, kept shore-sighting birds. One theory is that voyagers took a frigatebird (''Fregata'') with them. This bird's feathers become drenched and useless if it lands on water, so voyagers would release it when they thought they were close to land, and would follow it if it did not return to the canoe.
Navigation by the stars
 The positions of the stars helped guide Polynesian voyages. Stars, as opposed to planets, hold fixed celestial positions year-round, changing only their rising time with the seasons. Each star has a specific
The positions of the stars helped guide Polynesian voyages. Stars, as opposed to planets, hold fixed celestial positions year-round, changing only their rising time with the seasons. Each star has a specific declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the ...
, and can give a bearing for navigation as it rises or sets. Polynesian voyagers would set a heading by a star near the horizon, switching to a new one once the first rose too high. A specific sequence of stars would be memorized for each route.
The Polynesians also took measurements of stellar elevation to determine their latitude. The latitudes of specific islands were also known, and the technique of "sailing down the latitude" was used. That is, Polynesians navigated by the stars through knowledge of when particular stars, as they rotated through the night sky, would pass over the island to which the voyagers were sailing. Also knowledge that the movement of stars over different islands followed a similar pattern, (that is all the islands had a similar relationship to the night sky) provided the navigators with a sense of latitude, so that they could sail with the prevailing wind, before turning east or west to reach the island that was their destination.
Some star compass systems specify as many as 150 stars with known bearings, though most systems have only a few dozen (illustration at right). The development of sidereal compasses has been studied and hypothesized
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous obser ...
to have developed from an ancient pelorus instrument.
For navigators near the equator, celestial navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space (or on the surface of ...
is simplified, given that the whole celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
is exposed. Any star that passes through the zenith (overhead) moves along the celestial equator, the basis of the equatorial coordinate system.
Swell
The Polynesians also used wave and swell formations to navigate. Many of the habitable areas of the Pacific Ocean are groups of islands (or atolls) in chains hundreds of kilometres long. Island chains have predictable effects on waves and currents. Navigators who lived within a group of islands would learn the effect various islands had on the swell shape, direction, and motion, and would have been able to correct their path accordingly. Even when they arrived in the vicinity of an unfamiliar chain of islands, they may have been able to detect signs similar to those of their home. Once they had arrived fairly close to a destination island, they would have been able to pinpoint its location by sightings of land-based birds, certain cloud formations, as well as the reflections of shallow water made on the undersides of clouds. It is thought that the Polynesian navigators may have measured sailing time between islands in "canoe-days". The energy transferred from the wind to the sea produces wind waves. The waves that are created when the energy travels down away from the source area (like ripples) are known as swell. When the winds are strong at the source area, the swell is larger. The longer the wind blows, the longer the swell lasts. Because the swells of the ocean can remain consistent for days, navigators relied on them to carry their canoe in a straight line from one house (or point) on the star compass to the opposite house of the same name. Navigators were not always able to see stars; because of this, they relied on the swells of the ocean. Swell patterns are a much more reliable method of navigation than waves, which are determined by the local winds. Swells move in a straight direction which makes it easier for the navigator to determine whether the canoe is heading in the correct direction.Clouds, reflections off clouds, and the colour of the sky
Polynesian navigators could identify the clouds that resulted from the white sand of coral atolls reflecting heat into the sky. Subtle differences in the colour of the sky also could be recognised as resulting from the presence of lagoons or shallow waters, as deep water was a poor reflector of light while the lighter colour of the water of lagoons and shallow waters could be identified in the reflection in the sky. In Eastern Polynesia, navigators sailing from Tahiti to the Tuamotus would sail directly east towards Anaa atoll, which has a shallow lagoon that reflects a faint green colour on to the clouds above the atoll. If the navigator drifted off their course, they could correct their course when they sighted the reflection of the lagoon in the clouds in the distance.Te lapa
Dr. David Lewis was one of the first academics, along with Marianne George, to document an unexplained light phenomenon.Te lapa
''Te lapa'' is a Polynesian term for an unexplained and scientifically unproven light phenomenon underneath, or on the surface of, the ocean. ''Te lapa'' has been loosely translated as "flashing light", "underwater lightning", "the flashing", o ...
is a burst of light in a straight line occurring on, or just below the water surface, and originates from islands. It is used by Polynesians to reorient themselves out at sea or to find new islands.
Navigational devices
There is currently no evidence of historic Polynesian navigators using navigational devices on board vessels. However, the Micronesian people of the Marshall Islands have a history of using a stick chart onshore, to serve as spatial representations of islands and the conditions around them. Micronesian navigators created charts using the rib of coconut leaves attached to a square frame, with the curvature and meeting-points of the coconut ribs indicating the wave motion that was the result of islands standing in the path of the prevailing wind and the run of the waves.Extent of voyaging
 On his first voyage of Pacific exploration, Captain James Cook had the services of a Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who drew a chart of the islands within a radius (to the north and west) of his home island of
On his first voyage of Pacific exploration, Captain James Cook had the services of a Polynesian navigator, Tupaia, who drew a chart of the islands within a radius (to the north and west) of his home island of Ra'iatea
Raiatea or Ra'iatea ( Tahitian: ''Ra‘iātea'') is the second largest of the Society Islands, after Tahiti, in French Polynesia. The island is widely regarded as the "centre" of the eastern islands in ancient Polynesia and it is likely that the ...
. Tupaia had knowledge of 130 islands and named 74 on his chart. Tupaia had navigated from Ra'iatea in short voyages to 13 islands. He had not visited western Polynesia, as since his grandfather's time the extent of voyaging by Raiateans had diminished to the islands of eastern Polynesia. His grandfather and father had passed to Tupaia the knowledge as to the location of the major islands of western Polynesia and the navigation information necessary to voyage to Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
, Samoa and Tonga. Tupaia was hired by Joseph Banks, the ship's naturalist, who wrote that Cook ignored Tupaia's chart and downplayed his skills as a navigator.
However, in February 1778, Cook recorded his impressions of the dispersal and settlement of Polynesian people across the Pacific ocean in favorable terms:
Subantarctic and Antarctica
 There is academic debate on the furthest southern extent of Polynesian expansion.
The islands of New Zealand, along with a series of outlying islands, have been labelled 'South Polynesia' by New Zealand archaeologist Atholl Anderson. These islands include the Kermadec Islands, the Chatham Islands, the Auckland Islands and
There is academic debate on the furthest southern extent of Polynesian expansion.
The islands of New Zealand, along with a series of outlying islands, have been labelled 'South Polynesia' by New Zealand archaeologist Atholl Anderson. These islands include the Kermadec Islands, the Chatham Islands, the Auckland Islands and Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island (, ; Norfuk: ''Norf'k Ailen'') is an external territory of Australia located in the Pacific Ocean between New Zealand and New Caledonia, directly east of Australia's Evans Head and about from Lord Howe Island. Together with ...
. In each of these islands there is radiocarbon dating evidence of visits from Polynesians by 1500. The material evidence of Polynesian visits to at least one of the subantarctic islands to the south of New Zealand consists of the remains of a settlement. This evidence from Enderby Island in the Auckland Islands has been radiocarbon dated back to the 13th Century.
Descriptions of a shard of early Polynesian pottery buried on the Antipodes Islands are unsubstantiated, and the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa
The Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa is New Zealand's national museum and is located in Wellington. ''Te Papa Tongarewa'' translates literally to "container of treasures" or in full "container of treasured things and people that spring fr ...
, where it was supposedly stored, has stated that "The Museum has not been able to locate such a shard in its collection, and the original reference to the object in the Museum's collection documentation indicates no reference to Polynesian influences."
Oral history describes Ui-te-Rangiora, around the year 650, leading a fleet of Waka Tīwai south until they reached, ''"a place of bitter cold where rock-like structures rose from a solid sea".'' The brief description might match the Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between hi ...
or possibly the Antarctic mainland, but may be a description of iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of freshwater ice more than 15 m long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open (salt) water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially-derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". The ...
s surrounded by sea ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oce ...
found in the Southern Ocean. The account also describes snow.
Pre-Columbian contact with the Americas
In the mid-20th century, Thor Heyerdahl proposed a new theory of Polynesian origins (one which did not win general acceptance), arguing that the Polynesians had migrated from South America on balsa-log boats.. Thepresence
Presence may refer to:
Technology
* Presence (sound recording), also known as room tone
* Presence (amplification), used in four band equalisation
* Presence (telepresence), the scientific and technological field
* Immersion (virtual reality ...
in the Cook Islands of sweet potatoes, a plant native to the Americas (called ''kūmara'' in Māori), which have been radiocarbon-dated to 1000 CE, has been cited as evidence that Native Americans could have traveled to Oceania. The current thinking is that sweet potato was brought to central Polynesia circa 700 CE and spread across Polynesia from there, possibly by Polynesians who had traveled to South America and back. An alternative explanation posits biological dispersal
Biological dispersal refers to both the movement of individuals (animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, etc.) from their birth site to their breeding site ('natal dispersal'), as well as the movement from one breeding site to another ('breeding dis ...
; plants and/or seeds could float across the Pacific without any human contact.
A 2007 study published in the '' Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences'' examined chicken bones at El Arenal El Arenal may refer to the following places:
Argentina
* El Arenal, Santiago del Estero, a municipality and village in Santiago del Estero
Mexico
*El Arenal, Hidalgo, a town and municipality in the state of Hidalgo
*El Arenal, Jalisco, a town and ...
, Chile near the Arauco Peninsula. The results suggested Oceania-to-America contact. The domestication of chickens originated in southern Asia, whereas the '' Araucana'' breed of Chile is thought to have been introduced to the Americas by Spaniards around 1500. The bones found in Chile were radiocarbon-dated to between 1304 and 1424, prior to the documented arrival of the Spanish. DNA sequences taken were exact matches to the sequences of chickens from the same period in American Samoa and Tonga, both over 5000 miles (8000 kilometers) away from Chile. The genetic sequences were also similar to those found in Hawaii and Easter Island, the closest Polynesian island, at only 2500 miles (4000 kilometers). The sequences did not match any breed of European chicken.
Although this initial report suggested a Polynesian pre-Columbian origin, a later report looking at the same specimens concluded:
However, in a later study, the original authors extended and elaborated their findings, concluding:
In 2005, a linguist and an archeologist proposed a theory of contact between Hawaiians and the Chumash people of Southern California between 400 and 800 CE. The sewn-plank canoes crafted by the Chumash and neighboring Tongva are unique among the indigenous peoples of North America, but similar in design to larger canoes used by Polynesians and Melanesians for deep-sea voyages. '' Tomolo'o'', the Chumash word for such a craft, may derive from ''tumula'au''/''kumula'au'', the Hawaiian term for the logs from which shipwrights carve planks to be sewn into canoes. The analogous Tongva term, ''tii'at'', is unrelated. If it occurred, this contact left no genetic legacy in California or Hawaii. This theory has attracted limited media attention within California, but most archaeologists of the Tongva and Chumash cultures reject it on the grounds that the independent development of the sewn-plank canoe over several centuries is well-represented in the material record.
Polynesian contact with the prehispanic Mapuche culture in central-south Chile has been suggested because of apparently similar cultural traits, including words like ''toki'' (stone axes and adzes), hand clubs similar to the Māori wahaika, the dalca –a sewn-plank canoe as used on Chiloe Archipelago, the curanto
Curanto (from arn, kurantu 'stony') is a traditional Chilote method of cooking food using heated rocks buried in a earth oven that is covered with pangue leaves and turf. The fundamental components are seafood, potatoes, along with other traditi ...
earth oven (Polynesian ''umu'') common in southern Chile, fishing techniques such as stone wall enclosures, palín –a hockey-like game– and other potential parallels. Some strong westerlies and El Niño wind blow directly from central-east Polynesia to the Mapuche region, between Concepción and Chiloe. A direct connection from New Zealand is possible, sailing with the Roaring Forties. In 1834, some escapees from Tasmania arrived at Chiloe Island after sailing for 43 days.
A Mangarevan legend tells of Anua Matua
Anua ( sm, Ānua) is a village on Tutuila Island, American Samoa. It is located close to the capital Pago Pago, on the coast of Pago Pago Harbor. The term Pago Pago is often used for several settlements on Pago Pago Bay, including Anua, Lepua, Ut ...
who sailed in south-west direction reaching southernmost South America.
Post-colonial research history
 Knowledge of the traditional Polynesian methods of navigation was widely lost after contact with and colonization by Europeans. This caused debates over the reasons for the presence of the Polynesians in such isolated and scattered parts of the Pacific. According to Andrew Sharp, the explorer Captain
Knowledge of the traditional Polynesian methods of navigation was widely lost after contact with and colonization by Europeans. This caused debates over the reasons for the presence of the Polynesians in such isolated and scattered parts of the Pacific. According to Andrew Sharp, the explorer Captain James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
, already familiar with Charles de Brosses's accounts of large groups of Pacific islanders who were driven off course in storms and ended up hundreds of miles away with no idea where they were, encountered in the course of one of his own voyages a castaway group of Tahitians who had become lost at sea in a gale and blown 1000 miles away to the island of Atiu. Cook wrote that this incident "will serve to explain, better than the thousand conjectures of speculative reasoners, how the detached parts of the earth, and, in particular, how the South Seas, may have been peopled"..
By the late 19th century to the early 20th century, a more generous view of Polynesian navigation had come into favor, creating a much romanticized view of their seamanship, canoes, and navigational expertise. Late 19th- and early 20th-century writers such as Abraham Fornander and Percy Smith told of heroic Polynesians migrating in great coordinated fleets from Asia far and wide into present-day Polynesia..
Another view was presented by Andrew Sharp, who challenged the "heroic vision" hypothesis, asserting instead that Polynesian maritime expertise was severely limited in the field of exploration, and that as a result, the settlement of Polynesia had been the result of luck, random island sightings, and drifting, rather than as organized voyages of colonization. Thereafter, the oral knowledge passed down for generations allowed for eventual mastery of traveling between known locations.. Sharp's reassessment caused a huge amount of controversy and led to a stalemate between the romantic and the skeptical views.
Re-creation of voyages
 Anthropologist David Lewis sailed his catamaran from Tahiti to New Zealand, via Rarotonga using
Anthropologist David Lewis sailed his catamaran from Tahiti to New Zealand, via Rarotonga using stellar navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space (or on the surface of ...
without instruments.. David Lewis also sought out navigators of the Caroline Islands, Santa Cruz Islands and Tonga to confirm that traditional navigation techniques had been retained by navigators from Polynesia, Micronesia and Melanesia. The voyages of David Lewis on his ketch ''Isbjorn'' included: Tevake navigating between the Santa Cruz Islands; and Hipour of Puluwat
Poluwat, also Polowat, formerly Puluwat, is a coral atoll and a municipality of Chuuk state, Federated States of Micronesia.
Geography
Polowat is located in the northwestern region ( Oksoritod), and there in the western area (Pattiw) of Chuuk ...
navigating in the Caroline Islands; and also conversations with Fe’iloakitau Kaho, Ve’ehala and Kaloni Kienga from Tonga; Temi Rewi of Beru and Iotiabata Ata of Tarawa in the Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
; and Yaleilei of Satawal in the Caroline Islands.
Anthropologist and historian Ben Finney built ''Nalehia'', a replica of a Hawaiian double canoe. Finney tested the canoe in a series of sailing and paddling experiments in Hawaiian waters. At the same time, ethnographic research in the Caroline Islands in Micronesia brought to light the fact that traditional stellar navigational methods were still very much in everyday use there. The building and testing of proa canoes ('' wa'') inspired by traditional designs, the harnessing of knowledge from skilled Micronesians
The Micronesians or Micronesian peoples are various closely related ethnic groups native to Micronesia, a region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They are a part of the Austronesian ethnolinguistic group, which has an Urheimat in Taiwan.
Ethno ...
, as well as voyages using stellar navigation, allowed practical conclusions about the seaworthiness and handling capabilities of traditional Polynesian canoes and allowed a better understanding of the navigational methods that were likely to have been used by the Polynesians and of how they, as people, were adapted to seafaring.. Recent re-creations of Polynesian voyaging have used methods based largely on Micronesian methods and the teachings of a Micronesian navigator, Mau Piailug.
In 1973, Ben Finney established the Polynesian Voyaging Society to test the contentious question of how Polynesians found their islands. The team claimed to be able to replicate ancient Hawaiian double-hulled canoes capable of sailing across the ocean using strictly traditional voyaging techniques. In 1980, a Hawaiian named Nainoa Thompson
Charles Nainoa Thompson (born March 11, 1953, in Oahu, Hawaii) is a Native Hawaiian navigator and the president of the Polynesian Voyaging Society. He is best known as the first Hawaiian to practice the ancient Polynesian art of navigation sinc ...
invented a new method of non-instrument navigation (called the "modern Hawaiian wayfinding system"), enabling him to complete the voyage from Hawaii to Tahiti and back. In 1987, a Māori named Matahi Whakataka-Brightwell and his mentor Francis Cowan sailed from Tahiti to New Zealand without instruments in the waka ''Hawaiki-nui''.
In 1978, the Hokulea was capsized en route to Tahiti. Eddie Aikau, a world champion surfer, and part of the crew, attempted to paddle his surfboard to the nearest island to find help. However, Aikau was never seen again. The crew was later rescued regardless of the fact that Aikau didn’t make it to the nearest island.
In New Zealand, a leading Māori navigator and ship builder was Hector Busby, who was also inspired and influenced by Nainoa Thompson and Hokulea's voyage there in 1985.
In 2008, an expedition starting in the Philippines sailed two modern Wharram-designed catamarans loosely based on a Polynesian catamaran found in Auckland Museum
The Auckland War Memorial Museum Tāmaki Paenga Hira (or simply the Auckland Museum) is one of New Zealand's most important museums and war memorials. Its collections concentrate on New Zealand history (and especially the history of the Auckla ...
. The boats were built in the Philippines by an experienced boat builder to Wharram designs using modern strip plank with epoxy resin glue built over plywood frames. The catamarans had modern Dacron sails, Terylene stays and sheets with modern roller blocks. Wharram says he used Polynesian navigation to sail along the coast of Northern New Guinea and then sailed 150 miles to an island for which he had modern charts, proving that it is possible to sail a modern catamaran along the path of the Lapita Pacific migration. Unlike many other modern Polynesian "replica" voyages, the Wharram catamarans were at no point towed or escorted by a modern vessel with modern GPS navigation system, nor were they fitted with a motor.
In 2010, O Tahiti Nui Freedom
''O Tahiti Nui Freedom'' is a single-hulled Polynesian outrigger canoe. Constructed in 2010 by Hiria Ottino, it in an voyaged from Tahiti to Shanghai an expedition in which she reversed the path of the Lapita culture and Polynesian expansion th ...
, an outrigger sailing canoe, retraced the path of the migration from Tahiti to China via Cooks, Tonga, Fiji, Vanuatu, Solomons, PNG, Palau, Philippines in 123 days.
In 2013, a modern, non-instrument voyage was launched called Mālama Honua. It traveled across the world leaving Hilo, Hawaii, initially. This was not a re-creation of a known historical voyage. The spirit of the voyage was to spread the message of conservation. In fact, "mālama honua" means, roughly, to care for Earth, in Hawaiian. The journey was made on two vessels: the Hōkūle'a and the Hikianalia. Nainoa Thompson was on the crew.
See also
*Fautasi
A fautasi ( ; also fa'utasis) is a Samoan boat, similar to a longboat. Fautasi boats are around 100 feet in length and can accommodate a rowing crew of 50. A coxwain uses a drum to beat a tempo to coordinate the rowing. Each fautasi also has a ca ...
* Hokulea
* Māori migration canoes
* Micronesian navigation
Notes
References
* * *. *. *. *. *. * . *. *. * Lusby, et al. (2009/2010) "Navigation and Discovery in the Polynesian Oceanic Empire" ''Hydrographic Journal'' Nos. 131, 132, 134. *. *. * .External links
* * * An interactive presentation with English and Hawaiian language options. {{Trade route 2