Polish 2nd Corps In Russia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Polish II Corps in Russia ( pl, II Korpus Polski w Rosji; russian: 2-й Польский корпус (Российская империя)) was a Polish military formation formed in revolutionary Russia in 1917.
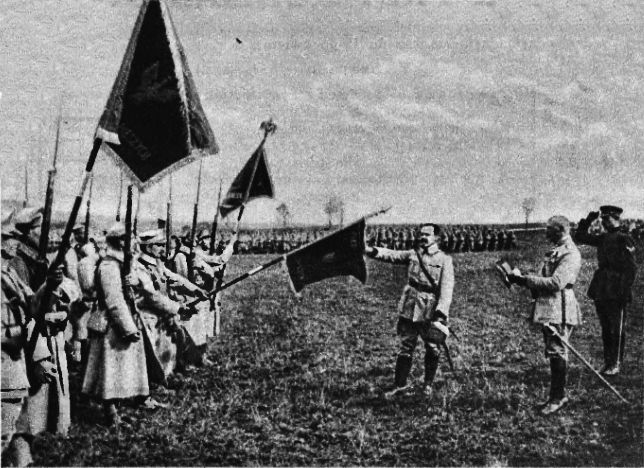 It was commanded initially by General Sylwester Stankiewicz (some sources also indicate it was briefly commanded by General
It was commanded initially by General Sylwester Stankiewicz (some sources also indicate it was briefly commanded by General
Google Print, p.332
/ref> The corps was disbanded afterwards, with most of its soldiers imprisoned by the Germans. General Haller avoided capture and made his way to
Korpusy Polskie
at
History
The Corps was formed at the initiative of the Chief Polish Military Committee (''Naczelny Polski Komitet Wojskowy''), a Polish faction in the revolutionary and split Russian Empire military. It was formed on 21 December 1917 inSoroca
Soroca (russian: link=no, Сороки, Soroki, uk, Сороки, Soroky, pl, Soroki, yi, סאָראָקע ''Soroke'') is a city and municipality in Moldova, situated on the Dniester River about north of Chișinău. It is the administrative ...
(now in Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The List of states ...
), then a Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Be ...
n region disputed by revolutionary Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
. The corps was formed primarily from Poles serving in the former Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian Ar ...
. It was a counterpart to the Polish I Corps in Russia
Polish I Corps in Russia ( pl, I Korpus Polski w Rosji; russian: 1-й Польский корпус) was a military formation formed on 24 July 1917 in Minsk from Polish and Lithuanian personnel serving in the Western and Northern Fronts of the ...
formed in the north, in Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
and the Polish III Corps in Russia
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
in central Ukraine.
 It was commanded initially by General Sylwester Stankiewicz (some sources also indicate it was briefly commanded by General
It was commanded initially by General Sylwester Stankiewicz (some sources also indicate it was briefly commanded by General Władysław Glass Władysław is a Polish given male name, cognate with Vladislav. The feminine form is Władysława, archaic forms are Włodzisław (male) and Włodzisława (female), and Wladislaw is a variation. These names may refer to:
Famous people Mononym
* W ...
). In February 1918 the corps merged with the Brigade II of the Polish Legions
Brigade II of the Polish Legions ( pl, II Brygada Legionów Polskich, de-AT, Brigade II der Polnischen Legion, hu, A Lengyel Légió II. Dandárja), also known as the Iron (''Żelazna'', ''Eisen'', ''Vas'') or Carpathian (''Karpacka'', ''Karp ...
and by late March Stankiewicz (and/or Glass) was replaced by the brigade commander, General Józef Haller
Józef Haller von Hallenburg (13 August 1873 – 4 June 1960) was a lieutenant general of the Polish Army, a legionary in the Polish Legions, harcmistrz (the highest Scouting instructor rank in Poland), the president of the Polish Scouti ...
.
The Corps avoided major engagements, and concentrated on protecting the Polish inhabitants of the region.
In March 1918 the corps had about 8,000 soldiers, and was equipped with weapons passed down from the Russian 29th Corps. At that time, the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace, separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russian SFSR, Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Germany, Austria-Hungary, Kingdom of ...
was signed between Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
and the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
. The Germans demanded that the Polish forces surrender.
Combat
The Poles refused to lay down their arms and General Haller took control of the forces which were then challenged by the Austrians at thebattle of Rarańcza
The Battle of Rarańcza was fought between Polish Legionnaires, and Austria-Hungary, from February 15 to 16, 1918, near Rarańcza in Bukovina, and ended with a Polish victory.
Background
The Brest-Litovsk Treaty, which was being negotiated ...
(15-16 February 1918). The Poles won the battle and broke through the frontlines to the Ukrainian side. Later, however, they were attacked by German forces. This time the engagement ended in defeat at the battle of Kaniów
Battle of Kaniv, or Battle of Kaniów took place during World War I on the night of 10–11 May 1918, near Kaniv, Ukraine ( uk, Канів, pl, Kaniów) between Polish and German army troops. The fighting pitted the Polish II Corps in Russia (in ...
(10-11 May).Spencer Tucker, Laura Matysek Wood, Justin D. Murphy, ''The European Powers in the First World War: An Encyclopedia'', Taylor & Francis, 1996, Google Print, p.332
/ref> The corps was disbanded afterwards, with most of its soldiers imprisoned by the Germans. General Haller avoided capture and made his way to
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. Some soldiers who also avoided capture (mostly from the 4th Rifle Division), moved toward Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
.
Organization
The corps was considered part of the Blue Army and was composed of two divisions: * 4th Rifle Division * 5th Rifle Division The corps also had supporting units (two cavalry regiments, artillery, engineer and others).See also
*Polish I Corps in Russia
Polish I Corps in Russia ( pl, I Korpus Polski w Rosji; russian: 1-й Польский корпус) was a military formation formed on 24 July 1917 in Minsk from Polish and Lithuanian personnel serving in the Western and Northern Fronts of the ...
References
Korpusy Polskie
at
WIEM Encyklopedia
WIEM Encyklopedia (full name in pl, Wielka Interaktywna Encyklopedia Multimedialna - "Great Interactive Multimedia Encyclopedia"; in Polish, ''wiem'' also means 'I know') is a Polish Internet encyclopedia.
The first printed edition was released i ...
{{Russian Empire Ground Forces
Military units and formations established in 1917
Military units and formations disestablished in 1918
Military history of Poland
Military of the Russian Empire
Poland in World War I
Military units and formations of Poland in World War I