pluripotent on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many things.
We can generate Induced Pluripotent cells by using the Induced pluripotency technique by triggering or expressing the genes or the transcription factors of the normal somatic cells. They are abbreviated as iPSC or IPS. We can forcefully express the transcription factors like 
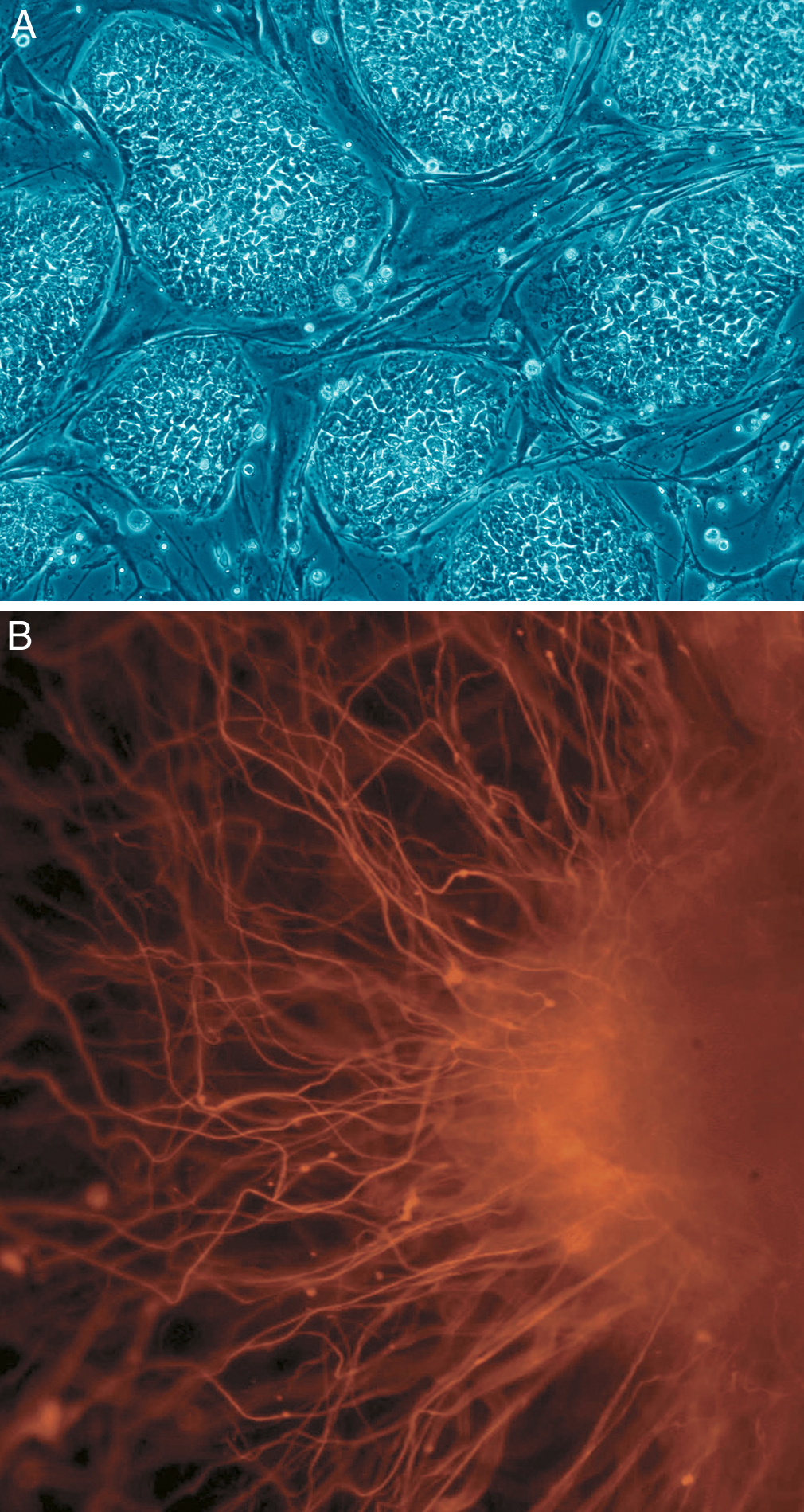 In cell biology, ''
In cell biology, ''
 Multipotency is when
Multipotency is when
Blog on treatment therapy using pluripotent stem cells and pluripotent stem cell derived exosomes
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cell Potency Developmental biology Cell biology Stem cells
Oct4
Oct-4 (octamer-binding transcription factor 4), also known as POU5F1 (POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''POU5F1'' gene. Oct-4 is a homeodomain transcription factor of the POU family. I ...
, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' (MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' (MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes refe ...
of a non-pluripotent cell and convert them into a stem cell. This procedure is first studied in a Mouse fibroblast cell in 2006 and followed the same instructions in developing a Human pluripotent cell from a Human epidermal fibroblast cell. The technique is called Regeneration.
Though the iPSC has similar properties to embryonic stem cells they were never approved for clinical stage research because they are highly Tumerogenic, having low replication rates and early senescence.
There are two distinctive phases called Naïve and Primed conditions of pluripotency in epiblasts. We call it pre and post-implementation. The pre-implemented epiblast is referred to as embryonic stem cells which can generate into an entire fetus.
On the other hand, the Post-implemented epiblasts show several marked differences from pre-implemented epiblasts like the difference in morphology (showing morphological differences like developing a cup-like shape called “egg cylinder” after implementation) and taking part in X-inactivation.
Cell potency is a cell's ability to differentiate into other cell types.
The more cell types a cell can differentiate into, the greater its potency. Potency is also described as the gene activation potential within a cell, which like a continuum, begins with totipotency Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
to designate a cell with the most differentiation potential, pluripotency Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
, multipotency Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
, oligopotency Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
, and finally unipotency Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
.

Totipotency
Totipotency Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
(Lat. ''totipotentia,'' "ability for all hings) is the ability of a single cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
to divide and produce all of the differentiated cells in an organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and ...
. Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, f ...
s and zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicellula ...
s are examples of totipotent cells.
In the spectrum of cell potency, totipotency represents the cell with the greatest differentiation potential, being able to differentiate into any embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
nic cell, as well as any extraembryonic cell. In contrast, pluripotent cells can only differentiate into embryonic cells.
A fully differentiated cell can return to a state of totipotency. The conversion to totipotency is complex and not fully understood. In 2011, research revealed that cells may differentiate not into a fully totipotent cell, but instead into a "complex cellular variation" of totipotency. Stem cells resembling totipotent blastomere
In biology, a blastomere is a type of cell produced by cell division (cleavage) of the zygote after fertilization; blastomeres are an essential part of blastula formation, and blastocyst formation in mammals.
Human blastomere characteristics
In ...
s from 2-cell stage embryos can arise spontaneously in mouse embryonic stem cell cultures and also can be induced to arise more frequently ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology an ...
'' through down-regulation of the chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in r ...
assembly activity of CAF-1.
The human development model can be used to describe how totipotent cells arise. Human development begins when a sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, whi ...
fertilizes an egg and the resulting fertilized egg creates a single totipotent cell, a zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicellula ...
. In the first hours after fertilization, this zygote divides into identical totipotent cells, which can later develop into any of the three germ layers of a human (endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
, mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical E ...
, or ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from t ...
), or into cells of the placenta
The placenta is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas and waste exchange between the physically separate mater ...
( cytotrophoblast or syncytiotrophoblast). After reaching a 16-cell stage, the totipotent cells of the morula
A morula (Latin, ''morus'': mulberry) is an early-stage embryo consisting of a solid ball of cells called blastomeres, contained in mammals, and other animals within the zona pellucida shell. The blastomeres are the daughter cells of the zygote ...
differentiate into cells that will eventually become either the blastocyst
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the ''embryoblast'' which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called the t ...
's Inner cell mass
The inner cell mass (ICM) or embryoblast (known as the pluriblast in marsupials) is a structure in the early development of an embryo. It is the mass of cells inside the blastocyst that will eventually give rise to the definitive structures of ...
or the outer trophoblast
The trophoblast (from Greek : to feed; and : germinator) is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the p ...
s. Approximately four days after fertilization and after several cycles of cell division, these totipotent cells begin to specialize. The inner cell mass, the source of embryonic stem cells
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre- implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they co ...
, becomes pluripotent.
Research on ''Caenorhabditis elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (ro ...
'' suggests that multiple mechanisms including RNA regulation may play a role in maintaining totipotency at different stages of development in some species. Work with zebrafish
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a freshwater fish belonging to the minnow family ( Cyprinidae) of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often ...
and mammals suggest a further interplay between miRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. miRN ...
and RNA-binding protein
RNA-binding proteins (often abbreviated as RBPs) are proteins that bind to the double or single stranded RNA in cells and participate in forming ribonucleoprotein complexes.
RBPs contain various structural motifs, such as RNA recognition motif ( ...
s (RBPs) in determining development differences.
Primordial germ cells
In mouse primordialgerm cells
Germ or germs may refer to:
Science
* Germ (microorganism), an informal word for a pathogen
* Germ cell, cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually
* Germ layer, a primary layer of cells that forms during embr ...
, genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
-wide reprogramming leading to totipotency involves erasure of epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "o ...
imprints. Reprogramming is facilitated by active DNA demethylation
For molecular biology in mammals, DNA demethylation causes replacement of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in a DNA sequence by cytosine (C) (see figure of 5mC and C). DNA demethylation can occur by an active process at the site of a 5mC in a DNA sequenc ...
involving the DNA base excision repair
Base excision repair (BER) is a cellular mechanism, studied in the fields of biochemistry and genetics, that repairs damaged DNA throughout the cell cycle. It is responsible primarily for removing small, non-helix-distorting base lesions from t ...
enzymatic pathway. This pathway entails erasure of CpG methylation (5mC) in primordial germ cells via the initial conversion of 5mC to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), a reaction driven by high levels of the ten-eleven dioxygenase enzymes
TET-1 and
TET-2.
Pluripotency
 In cell biology, ''
In cell biology, ''pluripotency Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
'' (Lat. ''pluripotentia'', "ability for many hings) refers to a stem cell that has the potential to differentiate into any of the three germ layers
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce two or three pr ...
: endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
(gut, lungs, yolk sac), mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical E ...
(muscle, skeleton, blood vascular, urogenital, dermis), or ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from t ...
(nervous, sensory, epidermis), but not into extra-embryonic tissues like the placenta. However, cell pluripotency is a continuum, ranging from the completely pluripotent cell that can form every cell of the embryo proper, e.g., embryonic stem cells and iPSCs, to the incompletely or partially pluripotent cell that can form cells of all three germ layers but that may not exhibit all the characteristics of completely pluripotent cells.
Induced pluripotency
Induced pluripotent stem cells, commonly abbreviated as iPS cells or iPSCs, are a type of pluripotentstem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type o ...
artificially derived from a non-pluripotent cell, typically an adult somatic cell
A somatic cell (from Ancient Greek σῶμα ''sôma'', meaning "body"), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Such cells compo ...
, by inducing a "forced" expression of certain gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
s and transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The fu ...
s. These transcription factors play a key role in determining the state of these cells and also highlights the fact that these somatic cells do preserve the same genetic information as early embryonic cells. The ability to induce cells into a pluripotent state was initially pioneered in 2006 using mouse fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound ...
s and four transcription factors, Oct4
Oct-4 (octamer-binding transcription factor 4), also known as POU5F1 (POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''POU5F1'' gene. Oct-4 is a homeodomain transcription factor of the POU family. I ...
, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' (MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' (MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes refe ...
; this technique, called reprogramming
In biology, reprogramming refers to erasure and remodeling of epigenetic marks, such as DNA methylation, during mammalian development or in cell culture. Such control is also often associated with alternative covalent modifications of histones.
...
, later earned Shinya Yamanaka
is a Japanese stem cell researcher and a Nobel Prize laureate. He serves as the director of Center for iPS Cell (induced Pluripotent Stem Cell) Research and Application and a professor at the Institute for Frontier Medical Sciences at Kyo ...
and John Gurdon
Sir John Bertrand Gurdon (born 2 October 1933) is a British developmental biologist. He is best known for his pioneering research in nuclear transplantation and cloning. He was awarded the Lasker Award in 2009. In 2012, he and Shinya Yamanaka ...
the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. This was then followed in 2007 by the successful induction of human iPSCs derived from human dermal fibroblasts using methods similar to those used for the induction of mouse cells. These induced cells exhibit similar traits to those of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) but do not require the use of embryos. Some of the similarities between ESCs and iPSCs include pluripotency, morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
, self-renewal ability, a trait that implies that they can divide and replicate indefinitely, and gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. The ...
.
Epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "o ...
factors are also thought to be involved in the actual reprogramming of somatic cells in order to induce pluripotency. It has been theorized that certain epigenetic factors might actually work to clear the original somatic epigenetic marks in order to acquire the new epigenetic marks that are part of achieving a pluripotent state. Chromatin is also reorganized in iPSCs and becomes like that found in ESCs in that it is less condensed and therefore more accessible. Euchromatin
Euchromatin (also called "open chromatin") is a lightly packed form of chromatin ( DNA, RNA, and protein) that is enriched in genes, and is often (but not always) under active transcription. Euchromatin stands in contrast to heterochromatin, whic ...
modifications are also common which is also consistent with the state of euchromatin
Euchromatin (also called "open chromatin") is a lightly packed form of chromatin ( DNA, RNA, and protein) that is enriched in genes, and is often (but not always) under active transcription. Euchromatin stands in contrast to heterochromatin, whic ...
found in ESCs.
Due to their great similarity to ESCs, the medical and research communities are interested iPSCs. iPSCs could potentially have the same therapeutic implications and applications as ESCs but without the controversial use of embryos in the process, a topic of great bioethical debate. The induced pluripotency of somatic cells into undifferentiated iPS cells
IPS, ips, or iPS may refer to:
Science and technology Biology and medicine
* ''Ips'' (genus), a genus of bark beetle
* Induced pluripotent stem cell or iPS cells
* Intermittent photic stimulation, a neuroimaging technique
* Intraparietal sulcu ...
was originally hailed as the end of the controversial use of embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre- implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consi ...
s. However, iPSCs were found to be potentially tumorigenic
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abno ...
, and, despite advances, were never approved for clinical stage research in the United States. Setbacks such as low replication rates and early senescence have also been encountered when making iPSCs, hindering their use as ESCs replacements.
Somatic expression of combined transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The fu ...
s can directly induce other defined somatic cell fates (transdifferentiation
Transdifferentiation, also known as lineage reprogramming, is the process in which one mature somatic cell is transformed into another mature somatic cell without undergoing an intermediate pluripotent state or progenitor cell type. It is a type ...
); researchers identified three neural-lineage-specific transcription factors that could directly convert mouse fibroblasts (connective tissue cells) into fully functional neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
s. This result challenges the terminal nature of cellular differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
and the integrity of lineage commitment; and implies that with the proper tools, ''all'' cells are totipotent and may form all kinds of tissue.
Some of the possible medical and therapeutic uses for iPSCs derived from patients include their use in cell and tissue transplants without the risk of rejection that is commonly encountered. iPSCs can potentially replace animal models unsuitable as well as ''in vitro'' models used for disease research.
Naive vs. primed pluripotency states
Findings with respect toepiblast
In amniote embryonic development, the epiblast (also known as the primitive ectoderm) is one of two distinct cell layers arising from the inner cell mass in the mammalian blastocyst, or from the blastula in reptiles and birds, the other layer is t ...
s before and after implantation have produced proposals for classifying pluripotency into two distinct phases: "naive" and "primed". The baseline stem cells commonly used in science that are referred as embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are derived from a pre-implantation epiblast; such epiblast is able to generate the entire fetus, and one epiblast cell is able to contribute to all cell lineages if injected into another blastocyst. On the other hand, several marked differences can be observed between the pre- and post-implantation epiblasts, such as their difference in morphology, in which the epiblast after implantation changes its morphology into a cup-like shape called the "egg cylinder" as well as chromosomal alteration in which one of the X-chromosomes under random inactivation in the early stage of the egg cylinder, known as X-inactivation
X-inactivation (also called Lyonization, after English geneticist Mary Lyon) is a process by which one of the copies of the X chromosome is inactivated in therian female mammals. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by being packaged into ...
. During this development, the egg cylinder epiblast cells are systematically targeted by Fibroblast growth factors
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by macrophages; they are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in their ...
, Wnt signaling, and other inductive factors via the surrounding yolk sac and the trophoblast tissue, such that they become instructively specific according to the spatial organization.
Another major difference is that post-implantation epiblast stem cells are unable to contribute to blastocyst chimera
Chimera, Chimaera, or Chimaira (Greek for " she-goat") originally referred to:
* Chimera (mythology), a fire-breathing monster of Ancient Lycia said to combine parts from multiple animals
* Mount Chimaera, a fire-spewing region of Lycia or Cilicia ...
s, which distinguishes them from other known pluripotent stem cells. Cell lines derived from such post-implantation epiblasts are referred to as epiblast-derived stem cells
After the blastocyst stage, once an embryo implanted in endometrium (in case of rodent), the inner cell mass (ICM) of a fertilized embryo segregates into two layers: hypoblast and epiblast. The epiblast cells are the functional progenitors of som ...
, which were first derived in laboratory in 2007. Both ESCs and EpiSCs are derived from epiblasts but at difference phases of development. Pluripotency is still intact in the post-implantation epiblast, as demonstrated by the conserved expression of Nanog, Fut4
Fucosyltransferase 4 (alpha (1,3) fucosyltransferase, myeloid-specific), also known as FUT4, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the ''FUT4'' gene.
Function
The product of this gene transfers fucose to N-acetyllactosamine polysaccharide ...
, and Oct-4
Oct-4 (octamer-binding transcription factor 4), also known as POU5F1 ( POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''POU5F1'' gene. Oct-4 is a homeodomain transcription factor of the POU family. ...
in EpiSCs, until somitogenesis
Somitogenesis is the process by which somites form. Somites are bilaterally paired blocks of paraxial mesoderm that form along the anterior-posterior axis of the developing embryo in segmented animals. In vertebrates, somites give rise to skelet ...
and can be reversed midway through induced expression of Oct-4
Oct-4 (octamer-binding transcription factor 4), also known as POU5F1 ( POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''POU5F1'' gene. Oct-4 is a homeodomain transcription factor of the POU family. ...
.
Native pluripotency in plants
Un-induced pluripotency has been observed inroot meristem
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often b ...
tissue culture, especially by Kareem et al 2015, Kim et al 2018, and Rosspopoff et al 2017. This pluripotency is regulated by various regulators, including PLETHORA 1 and PLETHORA 2 Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
; and PLETHORA 3 Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
, PLETHORA 5 Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
, and PLETHORA 7 Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
, whose expression were found by Kareem to be auxin
Auxins (plural of auxin ) are a class of plant hormones (or plant-growth regulators) with some morphogen-like characteristics. Auxins play a cardinal role in coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in plant life cycles and are essenti ...
-provoked. (These are also known as PLT1, PLT2, PLT3, PLT5, PLT7, and expressed by genes of the same names.) , this is expected to open up future research into pluripotency in root tissues.
Multipotency
progenitor cell
A progenitor cell is a Cell (biology), biological cell that can Cellular differentiation, differentiate into a specific cell type. Stem cells and progenitor cells have this ability in common. However, stem cells are less specified than progenitor ...
s have the gene activation potential to differentiate into discrete cell types. For example, a hematopoietic stem cell —and this cell type can differentiate itself into several types of blood cell like lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adap ...
, monocytes
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also infl ...
, neutrophils
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
, etc., but it is still ambiguous whether HSC possess the ability to differentiate into brain cells
Brain cells make up the functional tissue of the brain. The rest of the brain tissue is structural or connective called the stroma which includes blood vessels. The two main types of cells in the brain are neurons, also known as nerve cells, an ...
, bone cells
An osteocyte, an oblate shaped type of bone cell with dendritic processes, is the most commonly found cell in mature bone. It can live as long as the organism itself. The adult human body has about 42 billion of them. Osteocytes do not divide and ...
or other non-blood cell types.
Research related to multipotent cells suggests that multipotent cells may be capable of conversion into unrelated cell types. In another case, human umbilical cord blood stem cells were converted into human neurons. There is also research on converting multipotent cells into pluripotent cells.
Multipotent cells are found in many, but not all human cell types. Multipotent cells have been found in cord blood
Cord blood (umbilical cord blood) is blood that remains in the placenta and in the attached umbilical cord after childbirth. Cord blood is collected because it contains stem cells, which can be used to treat hematopoietic and genetic disorders su ...
, adipose tissue, cardiac cells, bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
, and mesenchymal stem cell
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) also known as mesenchymal stromal cells or medicinal signaling cells are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types, including osteoblasts (bone cells), chondrocytes (cartilage c ...
s (MSCs) which are found in the third molar
A third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is one of the three molars per quadrant of the human dentition. It is the most posterior of the three. The age at which wisdom teeth come through ( erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs betw ...
.
MSCs may prove to be a valuable source for stem cells from molars at 8–10 years of age, before adult dental calcification. MSCs can differentiate into osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and adipocytes.
Oligopotency
In biology, oligopotency is the ability of progenitor cells to differentiate into a fewcell types
A cell type is a classification used to identify cells that share morphological or phenotypical features. A multicellular organism may contain cells of a number of widely differing and specialized cell types, such as muscle cells and skin cells, ...
. It is a degree of potency
Potency may refer to:
* Potency (pharmacology), a measure of the activity of a drug in a biological system
* Virility
* Cell potency, a measure of the differentiation potential of stem cells
* In homeopathic dilutions, potency is a measure of how ...
. Examples of oligopotent stem cells are the lymphoid or myeloid stem cells.
A lymphoid cell specifically, can give rise to various blood cells such as B and T cells, however, not to a different blood cell type like a red blood cell. Examples of progenitor cells are vascular stem cells that have the capacity to become both endothelial
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
or smooth muscle cells.
Unipotency
Incell biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and ...
, a unipotent cell is the concept that one stem cell has the capacity to differentiate into only one cell type. It is currently unclear if true unipotent stem cells exist. Hepatoblasts, which differentiate into hepatocytes
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass.
These cells are involved in:
* Protein synthesis
* Protein storage
* Transformation of carbohydrates
* Synthesis of cholesterol, b ...
(which constitute most of the liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
) or cholangiocytes
Cholangiocytes are the epithelial cells of the bile duct. They are cuboidal epithelium in the small interlobular bile ducts, but become columnar and HCO3:-secreting in larger bile ducts approaching the porta hepatis and the extrahepatic ducts. T ...
(epithelial cells of the bile duct), are bipotent. A close synonym for ''unipotent cell'' is ''precursor cell
In cell biology, a precursor cell, also called a blast cell or simply blast, is a partially differentiated cell, usually referred to as a unipotent cell that has lost most of its stem cell properties. A precursor cell is also known as a pro ...
.''
See also
Antimalarial Drug Discovery Many substances with exceptional levels of whole-cell potency against CQR strains have been created by the production of compounds having two quinoline cores connected by an aliphatic chain or aromatic ring. Piperaquine, which has outstanding in vivo effectiveness and has been used extensively in clinical settings in China, is the counterpart that has been most thoroughly documented. Although the drug is still effective against CQR strains in Africa, broad resistance has recently appeared in places where piperaquine has been widely administered. Clinical studies have demonstrated the great effectiveness of a drug combination called Eurartesim, which contains piperaquine and dihydroartemisinin (DHA). Sigma-tau and the Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV) together developed Eurartesim, which has just recently received EMA approval after being routinely used in clinics for more than ten years 4 Other compounds, such the bisquinoline reported by Ridely, have also demonstrated great effectiveness against CQR strains; however, in this instance, toxicity implications (phototoxicity) were found, and its advancement as a clinical candidate was halted. Generation of Organs Based on Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Scaffolds: One of the biggest problems in modern medicine is the lack of donated organs for patients who have organ failure and require an organ transplant. This is particularly impressive for those who have had spinal cord injuries or renal or heart problems. Even though there are more of these patients every year, the availability of donated organs is quite constrained. To prevent transplant rejection, immunological incompatibility between donors and recipients, storage space restrictions, and even dthe onor's family approval of organ donation can all have an impact on this restriction. Hence, it appears important that alternate solutions be developed. Regenerative medicine is a cutting-edge treatment strategy that combines nuclear transfer, tissue engineering, and stem cell biology to repair damaged tissue. The word was first used by William Haseltine in 1999. He discovered that embryonic SCs can differentiate into every form of human body cell. William's explanation may appear straightforward at first, but if we dig a little further, we can see how regenerative medicine has great promise for the near future and might drastically alter how we treat patients whose organs have been severely damaged or failed. Different treatment procedures have been created today and regenerative medicine has given itself a specific position, while most of them are still in the early stages. Antimalarial Drug Discovery Many substances with exceptional levels of whole-cell potency against CQR strains have been created by the production of compounds having two quinoline cores connected by an aliphatic chain or aromatic ring. Piperaquine, which has outstanding in vivo effectiveness and has been used extensively in clinical settings in China, is the counterpart that has been most thoroughly documented. Although the drug is still effective against CQR strains in Africa, broad resistance has recently appeared in places where piperaquine has been widely administered. Clinical studies have demonstrated the great effectiveness of a drug combination called Eurartesim, which contains piperaquine and dihydroartemisinin (DHA). Sigma-tau and the Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV) together developed Eurartesim, which has just recently received EMA approval after being routinely used in clinics for more than ten years 4 Other compounds, such the bisquinoline reported by Ridely, have also demonstrated great effectiveness against CQR strains; however, in this instance, toxicity implications (phototoxicity) were found, and its advancement as a clinical candidate was halted. *Induced stem cells
Induced stem cells (iSC) are stem cells derived from somatic, reproductive, pluripotent or other cell types by deliberate epigenetic reprogramming. They are classified as either totipotent (iTC), pluripotent (iPSC) or progenitor (multipotent – ...
References
External Links
Blog on treatment therapy using pluripotent stem cells and pluripotent stem cell derived exosomes
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cell Potency Developmental biology Cell biology Stem cells