History
/ref> The first known Europeans to enter the region were the French explorers/traders Robert de La Salle and Martin Chartier from Quebec during their 1669 expedition down the Ohio River. European pioneers, primarily Dutch, followed in the early 18th century. Michael Bezallion was the first to describe the forks of the Ohio in a 1717 manuscript, and later that year European fur traders established area posts and settlements. In 1749, French soldiers from Quebec launched an expedition to the forks to unite Canada (New France), Canada with Louisiana (New France), French Louisiana via the rivers. During 1753–1754, the British hastily built Fort Prince George before a larger French force drove them off. The French built Fort Duquesne based on LaSalle's 1669 claims. The French and Indian War, the North American front of the Seven Years' War, began with the future Pittsburgh as its center. British General Edward Braddock was dispatched with Major George Washington as his aide to take Fort Duquesne. The British and colonial force were defeated at Braddock's Field. General John Forbes finally took the forks in 1758. He began construction on Fort Pitt (Pennsylvania), Fort Pitt, named after William Pitt the Elder while the settlement was named "Pittsborough". During Pontiac's War, a loose confederation of Native American tribes Siege of Fort Pitt, laid siege to Fort Pitt in 1763; the siege was eventually lifted after Colonel Henry Bouquet defeated a portion of the besieging force at the Battle of Bushy Run. Bouquet strengthened the defenses of Fort Pitt the next year. During this period, the powerful nations of the Iroquois Confederacy, based in New York, had maintained control of much of the Ohio Valley as hunting grounds by right of conquest after defeating other tribes. By the terms of the 1768 Treaty of Fort Stanwix, the William Penn, Penns were allowed to purchase the modern region from the Iroquois. A 1769 survey referenced the future city as the "Manor of Pittsburgh". Both the Colony of Virginia and the Province of Pennsylvania claimed the region under their colonial charters until 1780, when they agreed under a federal initiative to extend the Mason–Dixon line westward, placing Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania. On March 8, 1771, Bedford County, Pennsylvania was created to govern the frontier. On April 16, 1771, the city's first civilian local government was created as Pitt Township, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Pitt Township. William Teagarden was the first constable, and William Troop was the first clerk. Following the American Revolution, the village of Pittsburgh continued to grow. One of its earliest industries was boat building for settlers of the Ohio Country. In 1784, Thomas Viceroy completed a town plan which was approved by the Penn family attorney. Pittsburgh became a possession of Pennsylvania in 1785. The following year, the Pittsburgh Post-Gazette was started, and in 1787, the University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh Academy was chartered. Unrest during the Whiskey Rebellion of 1794 resulted in federal troops being sent to the area. By 1797, glass manufacture began, while the population grew to around 1,400. Settlers came via routes over the Appalachian Mountains or through the Great Lakes. Fort Pitt (Pennsylvania), Fort Pitt (now Pittsburgh) at the source of the Ohio River became the main base for settlers moving into the Northwest Territory.
1800 to 1900
 The federal government recognizes Pittsburgh as the starting point for the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Preparations began in Pittsburgh in 1803 when Meriwether Lewis purchased a keelboat that would later be used to ascend the Missouri River.
The War of 1812 cut off the supply of British goods, stimulating American industry. By 1815, Pittsburgh was producing significant quantities of iron, brass, tin, and glass. On March 18, 1816, the 46-year-old local government became a city. It was served by numerous river steamboats, that increased trading traffic on the rivers.
In the 1830s, many Welsh people from the Merthyr steelworks immigrated to the city following the aftermath of the Merthyr Rising. By the 1840s, Pittsburgh was one of the largest cities west of the Allegheny Mountains. The Great Fire of Pittsburgh destroyed over a thousand buildings in 1845. The city rebuilt with the aid of Irish immigrants who came to escape the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine. By 1857, Pittsburgh's 1,000 factories were consuming 22 million coal bushels yearly. Coal mining and iron manufacturing attracted waves of European immigrants to the area, the most came from Germany.
Because Pennsylvania had been established as a free state after the Revolution, enslaved African Americans sought freedom here through escape as refugees from the South, or occasionally fleeing from travelers they were serving who stayed in the city. There were active stations of the Underground Railroad in the city, and numerous refugees were documented as getting help from station agents and African-American workers in city hotels. The Drennen Slave Girl walked out of the Monongahela House in 1850, apparently to freedom.William J. Switala, ''Underground Railroad in Pennsylvania'', Stackpole Books, 2001, pp. 88-89 The Merchant's Hotel was also a place where African-American workers would advise slaves the state was free and aid them in getting to nearby stations of the Underground Railroad.Exhibit: ''Free at Last? Slavery in Pittsburgh in the 18th and 19th Centuries''
The federal government recognizes Pittsburgh as the starting point for the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Preparations began in Pittsburgh in 1803 when Meriwether Lewis purchased a keelboat that would later be used to ascend the Missouri River.
The War of 1812 cut off the supply of British goods, stimulating American industry. By 1815, Pittsburgh was producing significant quantities of iron, brass, tin, and glass. On March 18, 1816, the 46-year-old local government became a city. It was served by numerous river steamboats, that increased trading traffic on the rivers.
In the 1830s, many Welsh people from the Merthyr steelworks immigrated to the city following the aftermath of the Merthyr Rising. By the 1840s, Pittsburgh was one of the largest cities west of the Allegheny Mountains. The Great Fire of Pittsburgh destroyed over a thousand buildings in 1845. The city rebuilt with the aid of Irish immigrants who came to escape the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine. By 1857, Pittsburgh's 1,000 factories were consuming 22 million coal bushels yearly. Coal mining and iron manufacturing attracted waves of European immigrants to the area, the most came from Germany.
Because Pennsylvania had been established as a free state after the Revolution, enslaved African Americans sought freedom here through escape as refugees from the South, or occasionally fleeing from travelers they were serving who stayed in the city. There were active stations of the Underground Railroad in the city, and numerous refugees were documented as getting help from station agents and African-American workers in city hotels. The Drennen Slave Girl walked out of the Monongahela House in 1850, apparently to freedom.William J. Switala, ''Underground Railroad in Pennsylvania'', Stackpole Books, 2001, pp. 88-89 The Merchant's Hotel was also a place where African-American workers would advise slaves the state was free and aid them in getting to nearby stations of the Underground Railroad.Exhibit: ''Free at Last? Slavery in Pittsburgh in the 18th and 19th Centuries''2009, University of Pittsburgh Library Sometimes refugee slaves from the South stayed in Pittsburgh, but other times they continued North, including into Canada. Many slaves left the city and county for Canada after Congress passed the 1850 Fugitive Slave Act, as it required cooperation from law enforcement even in free states and increased penalties. From 1850 to 1860, the black population in Allegheny County dropped from 3,431 to 2,725 as people headed to more safety in Canada. The American Civil War boosted the city's economy with increased iron and armament demand by the Union. Andrew Carnegie began steel production in 1875 at the Edgar Thomson Steel Works in North Braddock, Pennsylvania, which evolved into the Carnegie Steel Company. He adopted the Bessemer process to increase production. Manufacturing was key to growth of Pittsburgh and the surrounding region. Railroad lines were built into the city along both rivers, increasing transportation access to important markets.
1900 to present
 In 1901, J. P. Morgan and attorney Elbert Henry Gary, Elbert H. Gary merged Carnegie Steel Company and several other companies into U.S. Steel. By 1910, Pittsburgh was the Largest cities in the United States by population by decade, nation's 8th-largest city, accounting for between one-third and one-half of national steel output.
The Pittsburgh Agreement was subscribed in May 1918 between the Czech and Slovak nationalities, as envisioned by T. G. Masaryk, concerning the future foundation of Czechoslovakia.
The city suffered severe flooding in March 1936.
The city's population swelled to more than a half million, attracting numerous European immigrants to its industrial jobs. By 1940, non-Hispanic whites were 90.6% of the city's population. Pittsburgh also became a main destination of the African-American Great Migration (African American), Great Migration from the rural South during the first half of the 20th century. Limited initially by discrimination, some 95% percent of the men became unskilled steel workers.
During World War II, demand for steel increased and area mills operated 24 hours a day to produce 95 million tons of steel for the war effort. This resulted in the highest levels of air pollution in the city's almost century of industry. The city's reputation as the "arsenal of democracy" was being overshadowed by James Parton's 1868 observation of Pittsburgh being "hell with the lid off."
Following the war, the city launched a clean air and civic revitalization project known as the "Renaissance," cleaning up the air and the rivers. The "Renaissance II" project followed in 1977, focused on cultural and neighborhood development. The industrial base continued to expand through the 1970s, but beginning in the early 1980s both the area's steel and electronics industries imploded during national industrial restructuring. There were massive layoffs from mill and plant closures.
In the later 20th century, the area shifted its economic base to education, tourism, and services, largely based on healthcare/medicine, finance, and high technology such as robotics. Although Pittsburgh successfully shifted its economy and remained viable, the city's population has never rebounded to its industrial-era highs. While 680,000 people lived in the city proper in 1950, a combination of suburbanization and economic turbulence resulted in a decrease in city population, even as the metropolitan area population increased again.
During the late 2000s recession, Pittsburgh was economically strong, adding jobs when most cities were losing them. It was one of the few cities in the United States to see housing property values rise. Between 2006 and 2011, the Pittsburgh metropolitan area, Pittsburgh metropolitan statistical area (MSA) experienced over 10% appreciation in housing prices—the highest appreciation of the largest 25 MSAs in the United States, as 22 of the top 25 MSAs saw a depreciation of housing values. Pittsburgh's story of economic regeneration was the inspiration of President Barack Obama to host the 2009 G-20 Pittsburgh summit.
In 1901, J. P. Morgan and attorney Elbert Henry Gary, Elbert H. Gary merged Carnegie Steel Company and several other companies into U.S. Steel. By 1910, Pittsburgh was the Largest cities in the United States by population by decade, nation's 8th-largest city, accounting for between one-third and one-half of national steel output.
The Pittsburgh Agreement was subscribed in May 1918 between the Czech and Slovak nationalities, as envisioned by T. G. Masaryk, concerning the future foundation of Czechoslovakia.
The city suffered severe flooding in March 1936.
The city's population swelled to more than a half million, attracting numerous European immigrants to its industrial jobs. By 1940, non-Hispanic whites were 90.6% of the city's population. Pittsburgh also became a main destination of the African-American Great Migration (African American), Great Migration from the rural South during the first half of the 20th century. Limited initially by discrimination, some 95% percent of the men became unskilled steel workers.
During World War II, demand for steel increased and area mills operated 24 hours a day to produce 95 million tons of steel for the war effort. This resulted in the highest levels of air pollution in the city's almost century of industry. The city's reputation as the "arsenal of democracy" was being overshadowed by James Parton's 1868 observation of Pittsburgh being "hell with the lid off."
Following the war, the city launched a clean air and civic revitalization project known as the "Renaissance," cleaning up the air and the rivers. The "Renaissance II" project followed in 1977, focused on cultural and neighborhood development. The industrial base continued to expand through the 1970s, but beginning in the early 1980s both the area's steel and electronics industries imploded during national industrial restructuring. There were massive layoffs from mill and plant closures.
In the later 20th century, the area shifted its economic base to education, tourism, and services, largely based on healthcare/medicine, finance, and high technology such as robotics. Although Pittsburgh successfully shifted its economy and remained viable, the city's population has never rebounded to its industrial-era highs. While 680,000 people lived in the city proper in 1950, a combination of suburbanization and economic turbulence resulted in a decrease in city population, even as the metropolitan area population increased again.
During the late 2000s recession, Pittsburgh was economically strong, adding jobs when most cities were losing them. It was one of the few cities in the United States to see housing property values rise. Between 2006 and 2011, the Pittsburgh metropolitan area, Pittsburgh metropolitan statistical area (MSA) experienced over 10% appreciation in housing prices—the highest appreciation of the largest 25 MSAs in the United States, as 22 of the top 25 MSAs saw a depreciation of housing values. Pittsburgh's story of economic regeneration was the inspiration of President Barack Obama to host the 2009 G-20 Pittsburgh summit.
Geography
 Pittsburgh has an area of , of which is land and , or 4.75%, is water. The 80th meridian west passes directly through the city's downtown.
The city is on the Allegheny Plateau, within the ecoregion of the Western Allegheny Plateau (ecoregion), Western Allegheny Plateau. The Downtown Pittsburgh, Downtown area (also known as the Golden Triangle) sits where the Allegheny River flows from the northeast and the Monongahela River from the southeast to form the Ohio River. The convergence is at Point State Park and is referred to as "the Point." The city extends east to include the Oakland (Pittsburgh), Oakland and Shadyside (Pittsburgh), Shadyside sections, which are home to the University of Pittsburgh, Carnegie Mellon University, Chatham University, Carnegie Museums of Pittsburgh, Carnegie Museum and Carnegie Library of Pittsburgh, Library, and many other educational, medical, and cultural institutions. The southern, western, and northern areas of the city are primarily residential.
Many list of Pittsburgh neighborhoods, Pittsburgh neighborhoods are steeply sloped with two-lane roads. More than a quarter of neighborhood names make reference to "hills," "heights," or similar features.
The steps of Pittsburgh consist of 800 sets of outdoor public stairways with 44,645 treads and 24,090 vertical feet. They include hundreds of streets composed entirely of stairs, and many other steep streets with stairs for sidewalks. Many provide vistas of the Pittsburgh area while attracting hikers and fitness walkers.
Bike and walking trails have been built to border many of the city's rivers and hollows. The Great Allegheny Passage and Chesapeake and Ohio Canal Towpath connect the city directly to downtown Washington, D.C. (some away) with a continuous bike/running trail.
Pittsburgh has an area of , of which is land and , or 4.75%, is water. The 80th meridian west passes directly through the city's downtown.
The city is on the Allegheny Plateau, within the ecoregion of the Western Allegheny Plateau (ecoregion), Western Allegheny Plateau. The Downtown Pittsburgh, Downtown area (also known as the Golden Triangle) sits where the Allegheny River flows from the northeast and the Monongahela River from the southeast to form the Ohio River. The convergence is at Point State Park and is referred to as "the Point." The city extends east to include the Oakland (Pittsburgh), Oakland and Shadyside (Pittsburgh), Shadyside sections, which are home to the University of Pittsburgh, Carnegie Mellon University, Chatham University, Carnegie Museums of Pittsburgh, Carnegie Museum and Carnegie Library of Pittsburgh, Library, and many other educational, medical, and cultural institutions. The southern, western, and northern areas of the city are primarily residential.
Many list of Pittsburgh neighborhoods, Pittsburgh neighborhoods are steeply sloped with two-lane roads. More than a quarter of neighborhood names make reference to "hills," "heights," or similar features.
The steps of Pittsburgh consist of 800 sets of outdoor public stairways with 44,645 treads and 24,090 vertical feet. They include hundreds of streets composed entirely of stairs, and many other steep streets with stairs for sidewalks. Many provide vistas of the Pittsburgh area while attracting hikers and fitness walkers.
Bike and walking trails have been built to border many of the city's rivers and hollows. The Great Allegheny Passage and Chesapeake and Ohio Canal Towpath connect the city directly to downtown Washington, D.C. (some away) with a continuous bike/running trail.
Cityscape
Areas
=Golden Triangle
=
 Downtown Pittsburgh has 30 skyscrapers, nine of which top . The U.S. Steel Tower is the tallest, at . The Cultural District, Pittsburgh, Cultural District consists of a 14-block area of downtown along the Allegheny River. This district contains many theaters and arts venues and is home to a growing residential segment. Most significantly, the Pittsburgh Cultural Trust is embarking on RiverParc, a four-block mixed-use "green" community, featuring 700 residential units and multiple towers of between 20 and 30 stories. The Firstside Historic District, Firstside portion of Downtown borders the Monongahela River, the historic Mon Wharf and hosts the distinctive PPG Place Gothic-style glass skyscraper complex. New condo towers have been constructed and historic office towers are converted to residential use, increasing 24-hour residents. Downtown is served by the Port Authority of Allegheny County, Port Authority's Pittsburgh light rail, light rail system and Bridges of Pittsburgh, multiple bridges leading north and south.
It is also home to Point Park University and Duquesne University which borders Bluff (Pittsburgh), Uptown.
Downtown Pittsburgh has 30 skyscrapers, nine of which top . The U.S. Steel Tower is the tallest, at . The Cultural District, Pittsburgh, Cultural District consists of a 14-block area of downtown along the Allegheny River. This district contains many theaters and arts venues and is home to a growing residential segment. Most significantly, the Pittsburgh Cultural Trust is embarking on RiverParc, a four-block mixed-use "green" community, featuring 700 residential units and multiple towers of between 20 and 30 stories. The Firstside Historic District, Firstside portion of Downtown borders the Monongahela River, the historic Mon Wharf and hosts the distinctive PPG Place Gothic-style glass skyscraper complex. New condo towers have been constructed and historic office towers are converted to residential use, increasing 24-hour residents. Downtown is served by the Port Authority of Allegheny County, Port Authority's Pittsburgh light rail, light rail system and Bridges of Pittsburgh, multiple bridges leading north and south.
It is also home to Point Park University and Duquesne University which borders Bluff (Pittsburgh), Uptown.
=North Side
==South Side
= The South Side was once the site of railyards and associated dense, inexpensive housing for mill and railroad workers. Since the late 20th century, the city undertook a Main Street program in cooperation with the National Trust for Historic Preservation, encouraging design and landscape improvements on East Carson Street, and supporting new retail. The area has become a local Pittsburgher destination, and the value of homes in the South Side had increased in value by about 10% annually for the 10 years up to 2014. East Carson Street has developed as one of the most vibrant areas of the city, packed with diverse shopping, ethnic eateries, vibrant nightlife, and live music venues.
In 1993 the Urban Redevelopment Authority of Pittsburgh purchased the South Side Works steel mill property. It collaborated with the community and various developers to create a master plan for a mixed-use development, to include a riverfront park, office space, housing, health-care facilities, and indoor practice fields for the Pittsburgh Steelers and Pitt Panthers. Construction began in 1998. The SouthSide Works has been open since 2005, featuring many stores, restaurants, offices, and the world headquarters for American Eagle Outfitters.
The South Side was once the site of railyards and associated dense, inexpensive housing for mill and railroad workers. Since the late 20th century, the city undertook a Main Street program in cooperation with the National Trust for Historic Preservation, encouraging design and landscape improvements on East Carson Street, and supporting new retail. The area has become a local Pittsburgher destination, and the value of homes in the South Side had increased in value by about 10% annually for the 10 years up to 2014. East Carson Street has developed as one of the most vibrant areas of the city, packed with diverse shopping, ethnic eateries, vibrant nightlife, and live music venues.
In 1993 the Urban Redevelopment Authority of Pittsburgh purchased the South Side Works steel mill property. It collaborated with the community and various developers to create a master plan for a mixed-use development, to include a riverfront park, office space, housing, health-care facilities, and indoor practice fields for the Pittsburgh Steelers and Pitt Panthers. Construction began in 1998. The SouthSide Works has been open since 2005, featuring many stores, restaurants, offices, and the world headquarters for American Eagle Outfitters.
=East End
= The East End of Pittsburgh is home to the University of Pittsburgh, Carnegie Mellon University, Carlow University, Chatham University, Carnegie Museums of Pittsburgh, The Carnegie Institute's Museums of Art and Natural History, Phipps Conservatory, and Soldiers and Sailors Memorial Hall. It is also home to many parks and public spaces including Mellon Park, Westinghouse Park, Schenley Park, Frick Park, The Frick Pittsburgh, Bakery Square, and the Pittsburgh Zoo and PPG Aquarium. The neighborhoods of Shadyside (Pittsburgh), Shadyside and Squirrel Hill (Pittsburgh), Squirrel Hill are large, wealthy neighborhoods with some apartments and condos, and pedestrian-oriented shopping/business districts. Squirrel Hill is also known as the hub of Jewish life in Pittsburgh, home to approximately 20 synagogues. Oakland (Pittsburgh), Oakland, heavily populated by undergraduate and graduate students, is home to most of the universities, and the Petersen Events Center. The Strip District, Pittsburgh, Strip District to the west along the Allegheny River is an open-air marketplace by day and a clubbing destination by night. Bloomfield (Pittsburgh), Bloomfield is Pittsburgh's Little Italy and is known for its Italian restaurants and grocers. Lawrenceville (Pittsburgh), Lawrenceville is a revitalizing rowhouse neighborhood popular with artists and designers. The Hill District (Pittsburgh), Hill District was home to photographer Charles Harris (photographer), Charles Harris as well as various African-American jazz clubs. Other East End neighborhoods include Point Breeze (Pittsburgh), Point Breeze, Regent Square (Pittsburgh), Regent Square, Highland Park (Pittsburgh neighborhood), Highland Park, Homewood (Pittsburgh), Homewood, Lincoln-Lemington-Belmar (Pittsburgh), Lincoln-Lemington-Belmar, Larimer (Pittsburgh), Larimer, East Hills (Pittsburgh), East Hills, East Liberty (Pittsburgh), East Liberty, Polish Hill (Pittsburgh), Polish Hill, Hazelwood (Pittsburgh), Hazelwood, Garfield, Morningside, and Stanton Heights.
The East End of Pittsburgh is home to the University of Pittsburgh, Carnegie Mellon University, Carlow University, Chatham University, Carnegie Museums of Pittsburgh, The Carnegie Institute's Museums of Art and Natural History, Phipps Conservatory, and Soldiers and Sailors Memorial Hall. It is also home to many parks and public spaces including Mellon Park, Westinghouse Park, Schenley Park, Frick Park, The Frick Pittsburgh, Bakery Square, and the Pittsburgh Zoo and PPG Aquarium. The neighborhoods of Shadyside (Pittsburgh), Shadyside and Squirrel Hill (Pittsburgh), Squirrel Hill are large, wealthy neighborhoods with some apartments and condos, and pedestrian-oriented shopping/business districts. Squirrel Hill is also known as the hub of Jewish life in Pittsburgh, home to approximately 20 synagogues. Oakland (Pittsburgh), Oakland, heavily populated by undergraduate and graduate students, is home to most of the universities, and the Petersen Events Center. The Strip District, Pittsburgh, Strip District to the west along the Allegheny River is an open-air marketplace by day and a clubbing destination by night. Bloomfield (Pittsburgh), Bloomfield is Pittsburgh's Little Italy and is known for its Italian restaurants and grocers. Lawrenceville (Pittsburgh), Lawrenceville is a revitalizing rowhouse neighborhood popular with artists and designers. The Hill District (Pittsburgh), Hill District was home to photographer Charles Harris (photographer), Charles Harris as well as various African-American jazz clubs. Other East End neighborhoods include Point Breeze (Pittsburgh), Point Breeze, Regent Square (Pittsburgh), Regent Square, Highland Park (Pittsburgh neighborhood), Highland Park, Homewood (Pittsburgh), Homewood, Lincoln-Lemington-Belmar (Pittsburgh), Lincoln-Lemington-Belmar, Larimer (Pittsburgh), Larimer, East Hills (Pittsburgh), East Hills, East Liberty (Pittsburgh), East Liberty, Polish Hill (Pittsburgh), Polish Hill, Hazelwood (Pittsburgh), Hazelwood, Garfield, Morningside, and Stanton Heights.
=West End
= The West End includes Mount Washington, Pittsburgh (neighborhood), Mt. Washington, with its famous view of the Downtown skyline and numerous other residential neighborhoods such as Sheraden (Pittsburgh), Sheraden and Elliott (Pittsburgh), Elliott.Ethnicities
Many of Pittsburgh's patchwork of neighborhoods still retain Ethnic group, ethnic characters reflecting the city's settlement history. These include: * ''German'': Troy Hill (Pittsburgh), Troy Hill, Mount Washington, Pittsburgh (neighborhood), Mt. Washington, and East Allegheny (Pittsburgh), East Allegheny (Deutschtown) * ''Italian'': Brookline (Pittsburgh), Brookline, Bloomfield (Pittsburgh), Bloomfield, Morningside (Pittsburgh), Morningside, Oakland (Pittsburgh), Oakland * ''Hispanic/Latino'': Beechview (Pittsburgh), Beechview/Brookline (Pittsburgh), Brookline * ''Polish, Austrian, Belgian, Czech, Slovakia, Slovak, German, Greek, Hungarian, Luxembourgish, Dutch, Romanian, Swiss, Slovenia and the northern marginal regions of Italy, Croatian, as well as northeastern France, Central European'': Southside (Pittsburgh), South Side, Lawrenceville (Pittsburgh), Lawrenceville, and Polish Hill (Pittsburgh), Polish Hill * ''Lithuanian'': Southside (Pittsburgh), South Side, Uptown (Pittsburgh), Uptown * ''African American/Multiracial African American'': Hill District (Pittsburgh), Hill District, Homewood (Pittsburgh), Homewood, Lincoln-Lemington-Belmar (Pittsburgh), Lincoln-Lemington-Belmar, Larimer (Pittsburgh), Larimer, East Hills (Pittsburgh), East Hills, and Hazelwood (Pittsburgh), Hazelwood * ''Jewish'' (Ashkenazi): Squirrel Hill (Pittsburgh), Squirrel Hill * ''Irish'': Mount Washington, Pittsburgh (neighborhood), Mt. Washington, Carrick (Pittsburgh), CarrickPopulation densities
Several neighborhoods on the edges of the city are less urban, featuring tree-lined streets, yards and garages, with a more suburban character. Oakland, the South Side, the North Side, and the Golden Triangle are characterized by more density of housing, walking neighborhoods, and a more diverse, urban feel.Images


Regional identity
Pittsburgh falls within the borders of the Northeastern United States as defined by multiple US Government agencies. Pittsburgh is the principal city of the Pittsburgh-New Castle-Weirton, PA-OH-WV Combined Statistical Area, Pittsburgh Combined Statistical Area, a Combined statistical area defined by the U.S. Census Bureau. Pittsburgh falls within the borders of Appalachia as defined by the Appalachian Regional Commission, and has long been characterized as the "northern urban industrial anchor of Appalachia." In its post-industrial state, Pittsburgh has been characterized as the "Paris of Appalachia", recognizing the city's cultural, educational, healthcare, and technological resources, as well as its status as Appalachia's largest city.Climate
Under the Köppen climate classification, Pittsburgh falls within either a hot-summer humid continental climate (''Dfa'') if the isotherm is used or a humid subtropical climate (''Cfa'') if the isotherm is used. Summers are hot and winters are moderately cold with wide variations in temperature. Despite this, it has one of the most pleasant summer climates between medium and large cities in the U.S. The city and river valleys lie in the USDA plant hardiness zone 6b while higher elevated areas and some suburbs lie in zone 6a. The area has four distinct seasons: winters are cold and snowy, springs and falls are mild with moderate levels of sunshine, and summers are warm. As measured by percent possible sunshine, summer is by far the sunniest season. The warmest month of the year in Pittsburgh is July, with a 24-hour average of . Conditions are often humid, and combined with highs reaching on an average 9.5 days a year, a considerable heat index arises. The coolest month is January, when the 24-hour average is , and lows of or below can be expected on an average 2.6 nights per year. Officially, record temperatures range from , on 1994 North American cold wave, January 19, 1994 to , which occurred three times, most recently on July 16, 1988; the record cold daily maximum is , which occurred three times, most recently the day of the all-time record low, while, conversely, the record warm daily minimum is on July 1, 1901. Due to elevation and location on the windward side of the Appalachian Mountains, + readings are very rare, and were last seen on July 15, 1995. Average annual precipitation is and precipitation is greatest in May while least in October; annual precipitation has historically ranged from in 1930 to in 2018. On average, December and January have the greatest number of precipitation days. Snowfall averages per season, but has historically ranged from in 1918–19 to in 1950–51. There is an average of 59 clear days and 103 partly cloudy days per year, while 203 days are cloudy. In terms of annual percent-average possible sunshine received, Pittsburgh (45%) is similar to Seattle (49%).Air quality
In 2019, the "State of the Air" report from the American Lung Association (ALA) found that air quality in the Pittsburgh-New Castle-Weirton, PA-OH-WV metro area worsened, not only for ozone (smog), but also for the second year in a row for both the daily and long-term measures of fine particle pollution. Outside of California, Allegheny County is the only county in the United States that recorded failing grades for all three. In a 2013 ranking of 277 metropolitan areas in the United States, the American Lung Association ranked only six U.S. metro areas as having higher amounts of short-term particle pollution, and only seven U.S. metro areas having higher amounts of year-round particle pollution than Pittsburgh. For ozone (smog) pollution, Pittsburgh was ranked 24th among U.S. metro areas. The area has improved its air quality with every annual survey. The ALA's rankings have been disputed by the Allegheny County Health Department (ACHD), since data from only the worst of the region's 20 air quality monitors is considered by the ALA, without any context or averaging. The lone monitor used is immediately downwind and adjacent to U.S. Steel's Clairton Coke Works, the nation's largest Coke (fuel), coke mill, and several municipalities outside the city's jurisdiction of pollution controls, leading to possible confusion that Pittsburgh is the source or center of the emissions cited in the survey. The region's readings also reflect pollution swept in from Ohio and West Virginia. Although the county was still below the "pass" threshold, the report showed substantial improvement over previous decades on every air quality measure. Fewer than 15 high ozone days were reported between 2007 and 2009, and just 10 between 2008 and 2010, compared to more than 40 between 1997 and 1999. ACHD spokesman Guillermo Cole stated "It's the best it's been in the lifetime for virtually every resident in this county ... We've seen a steady decrease in pollution levels over the past decade and certainly over the past 20, 30, 40, 50 years, or more." In the summer of 2017, a crowd sourced air quality monitoring application, Smell PGH, was launched. As air quality is still a concern of many in the area, the app allows for users to report odd smells and informs local authorities. The city contains 31,000 trees on 900 miles of streets, by the last count conducted in 2005. A 2011 analysis of Pittsburgh's tree cover, which involved sampling more than 200 small plots throughout the city, showed a value of between $10 and $13 million in annual benefits based on the urban forest contributions to aesthetics, energy use and air quality. Energy savings from shade, impact on city air and water quality, and the boost in property values were taken into account in the analysis. The city spends $850,000 annually on street tree planting and maintenance.Water quality
 The local rivers continue to have pollution levels exceeding EPA limits. This is caused by Allegheny County Sanitary Authority#Pittsburgh's sewer overflow problem, frequently overflowing untreated sewage into local waterways, due to flood conditions and antiquated infrastructure. Pittsburgh has a combined sewer system, where its sewage pipes contain both stormwater and wastewater. The pipes were constructed in the early 1900s, and the sewage treatment plant was built in 1959. Due to insufficient improvements over time, the city is faced with public health concerns regarding its water. As little as a tenth of an inch of rain causes runoffs from the sewage system to drain into local rivers. Nine billion gallons of untreated waste and stormwater flow into rivers, leading to health hazards and Clean Water Act violations. The local sewage authority, Allegheny County Sanitary Authority, or ALCOSAN, is operating under Consent Decree from the Environmental Protection Agency, EPA to come up with solutions. In 2017, ALCOSAN proposed a $2 billion upgrade to the system which is moving closer to EPA approval.
Pittsburgh Water and Sewer Authority (PWSA) is the city's agency required to replace pipes and charge water rates. They have come under fire from both city and state authorities due to alleged mismanagement. In 2017, Bill Peduto, Mayor William Peduto advocated for a restructuring of the PWSA and a partially privatized water authority. Governor Wolf subsequently assigned the PWSA to be under the oversight of the Public Utilities Commission (PUC).
The local rivers continue to have pollution levels exceeding EPA limits. This is caused by Allegheny County Sanitary Authority#Pittsburgh's sewer overflow problem, frequently overflowing untreated sewage into local waterways, due to flood conditions and antiquated infrastructure. Pittsburgh has a combined sewer system, where its sewage pipes contain both stormwater and wastewater. The pipes were constructed in the early 1900s, and the sewage treatment plant was built in 1959. Due to insufficient improvements over time, the city is faced with public health concerns regarding its water. As little as a tenth of an inch of rain causes runoffs from the sewage system to drain into local rivers. Nine billion gallons of untreated waste and stormwater flow into rivers, leading to health hazards and Clean Water Act violations. The local sewage authority, Allegheny County Sanitary Authority, or ALCOSAN, is operating under Consent Decree from the Environmental Protection Agency, EPA to come up with solutions. In 2017, ALCOSAN proposed a $2 billion upgrade to the system which is moving closer to EPA approval.
Pittsburgh Water and Sewer Authority (PWSA) is the city's agency required to replace pipes and charge water rates. They have come under fire from both city and state authorities due to alleged mismanagement. In 2017, Bill Peduto, Mayor William Peduto advocated for a restructuring of the PWSA and a partially privatized water authority. Governor Wolf subsequently assigned the PWSA to be under the oversight of the Public Utilities Commission (PUC).
Demographics
At the 2010 census, there were 305,704 people residing in Pittsburgh, a decrease of 8.6% since 2000; 66.0% of the population was White, 25.8% Black or African American, 0.2% American Indian and Alaska Native, 4.4% Asian, 0.3% Other, and 2.3% mixed; in 2020, 2.3% of Pittsburgh's population was of Hispanic or Latino American origin of any race. Non-Hispanic Whites, Non-Hispanic whites were 64.8% of the population in 2010, compared to 78.7% in 1970. By the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population slightly declined further to 302,971. Its racial and ethnic makeup in 2020 was 64.7% non-Hispanic white, 23.0% Black or African American, 5.8% Asian, and 3.2% Hispanic or Latino American of any race.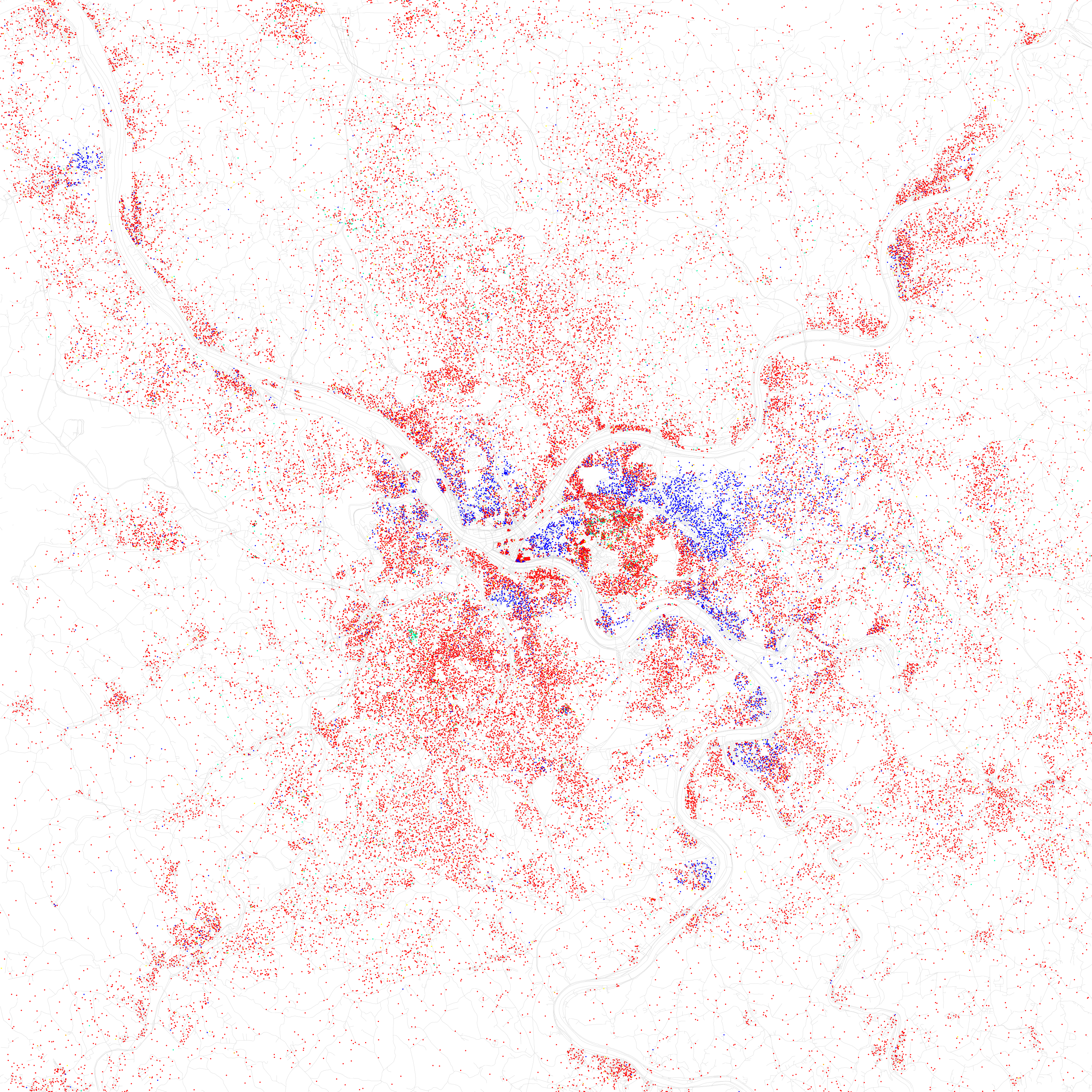 Since the beginning of the 21st century, the five largest European ethnic groups in the city were German (19.7%), Irish (15.8%), Italian (11.8%), Polish (8.4%), and English (4.6%), while the metropolitan area is approximately 22% German-American, 15.4% Italian American and 11.6% Irish American. Pittsburgh has one of the largest Italian-American communities in the nation, and the fifth-largest Ukrainians, Ukrainian community per the 1990 census. Pittsburgh has one of the most extensive Croats, Croatian communities in the United States. Overall, the Pittsburgh metro area has one of the largest populations of Slavic Americans in the country.
Pittsburgh has a sizable Black and African American population, concentrated in various neighborhoods especially in the East End. There is also a small Asian community consisting of Indian immigrants, and a small Hispanic community consisting of Mexicans and Puerto Ricans.The Association of Religion Data Archives , Maps & Reports
Since the beginning of the 21st century, the five largest European ethnic groups in the city were German (19.7%), Irish (15.8%), Italian (11.8%), Polish (8.4%), and English (4.6%), while the metropolitan area is approximately 22% German-American, 15.4% Italian American and 11.6% Irish American. Pittsburgh has one of the largest Italian-American communities in the nation, and the fifth-largest Ukrainians, Ukrainian community per the 1990 census. Pittsburgh has one of the most extensive Croats, Croatian communities in the United States. Overall, the Pittsburgh metro area has one of the largest populations of Slavic Americans in the country.
Pittsburgh has a sizable Black and African American population, concentrated in various neighborhoods especially in the East End. There is also a small Asian community consisting of Indian immigrants, and a small Hispanic community consisting of Mexicans and Puerto Ricans.The Association of Religion Data Archives , Maps & Reports. Thearda.com. Retrieved on August 17, 2013. According to a 2010 Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) study, residents include 773,341 "Catholics"; 326,125 "Mainline Protestants"; 174,119 "Evangelical Protestants;" 20,976 "Black Protestants;" and 16,405 "Orthodox Christians," with 996,826 listed as "unclaimed" and 16,405 as "other" in the metro area. A 2017 study by the Cohen Center for Modern Jewish Studies at Brandeis University estimated the History of the Jews in Pittsburgh, Jewish population of Greater Pittsburgh was 49,200. According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, 78% of the population of the city identified themselves as Christians, with 42% professing attendance at a variety of churches that could be considered Protestant, and 32% professing Catholic beliefs. while 18% claim no religious affiliation. The same study says that other religions (including Judaism, Buddhism, Islam, and Hinduism) collectively make up about 4% of the population. In 2010, there were 143,739 households, out of which 21.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 31.2% were married couples living together, 16.5% had a female householder with no husband present, and 48.4% were non-families. 39.4% of all households were made up of individuals, and 13.7% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.17 and the average family size was 2.95. In the city, the population was spread out, with 19.9% under the age of 18, 14.8% from 18 to 24, 28.6% from 25 to 44, 20.3% from 45 to 64, and 16.4% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 36 years. For every 100 females, there were 90.7 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 87.8 males. The median income for a household in the city was $28,588, and the median income for a family was $38,795. Males had a median income of $32,128 versus $25,500 for females. The per capita income for the city was $18,816. About 15.0% of families and 20.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 27.5% of those under the age of 18 and 13.5% ages 65 or older. By the 2019 American Community Survey, the median income for a household increased to $53,799. Families had a median income of $68,922; married-couple families had a median income of $93,500; and non-family households had a median income of $34,448. Pittsburgh's wealthiest suburbs within city limits are Squirrel Hill (Pittsburgh), Squirrel Hill and Point Breeze, Pittsburgh, Point Breeze, the only two areas of the city which have average household incomes over $100,000 a year. Outside of city limits, Sewickley Heights, Pennsylvania, Sewickley Heights is by a wide margin the wealthiest suburb of Pittsburgh within Allegheny County, with an average yearly household income of just over $218,000. Sewickely Heights is seen as one of Pittsburgh's wealthiest suburbs culturally as well, titles which the suburbs of Upper St. Clair Township, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Upper St. Clair, Fox Chapel, Pennsylvania, Fox Chapel, Wexford, Pennsylvania, Wexford, and Warrendale, Pennsylvania, Warrendale also have been bestowed. In a 2002 study, Pittsburgh ranked 22nd of 69 urban places in the U.S. in the number of residents 25 years or older who had completed a bachelor's degree, at 31%. Pittsburgh ranked 15th of the 69 places in the number of residents 25 years or older who completed a high school degree, at 84.7%. The Pittsburgh Metropolitan Area, metro area has shown greater residential racial integration during the last 30 years. The 2010 census ranked 18 other U.S. metros as having greater black-white Racial segregation in the United States, segregation, while 32 other U.S. metros rank higher for black-white isolation. As of 2018, much of Pittsburgh's population density was concentrated in the central, southern, and eastern areas. The city limits itself have a population density of 5,513 people per square mile; its most densely populated parts are Oakland (Pittsburgh), North Oakland (at 21,200 per square mile) and Uptown Pittsburgh (at 19,869 per square mile). Outside of the city limits, Dormont, Pennsylvania, Dormont and Mount Oliver (Pittsburgh), Mount Oliver are Pittsburgh's most densely-populated neighborhoods, with 11,167 and 9,902 people per square mile respectively.
Economy
Pittsburgh has adapted since the collapse of its century-long steel and electronics industries. The region has shifted to high technology, robotics, health care, nuclear engineering, tourism, biomedical technology, finance, education, and services. Annual payroll of the region's technology industries, when taken in aggregate, exceeded $10.8 billion in 2007, and in 2010 there were 1,600 technology companies. A National Bureau of Economic Research 2014 report named Pittsburgh the second-best U.S. city for intergenerational economic mobility or the American Dream. Reflecting the citywide shift from industry to technology, former factories have been renovated as modern office space. Google has research and technology offices in a refurbished 1918–1998 Nabisco factory, a complex known as Bakery Square. Some of the factory's original equipment, such as a large dough mixer, were left standing in homage to the site's industrial roots. Pittsburgh's transition from its industrial heritage has earned it praise as "the poster child for managing industrial transition". Other major cities in the northeast and mid-west have increasingly borrowed from Pittsburgh's Conceptual model, model in order to renew their industries and economic base. The largest employer in the city is the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, with 48,000 employees. All hospitals, outpatient clinics, and doctor's office positions combine for 116,000 jobs, approximately 10% of the jobs in the region. An analyst recently observed of the city's medical sector: "That's both more jobs and a higher share of the region's total employment than the steel industry represented in the 1970s." Education is a major economic driver in the region. The largest single employer in education is the University of Pittsburgh, with 10,700 employees. Ten Fortune 500 companies call the Pittsburgh area home. They are (in alphabetical order): Alcoa, Alcoa Corporation (NYSE: AA), Arconic, Arconic Corporation (NYSE: ARNC), Dick's Sporting Goods (NYSE: DKS), Kraft Heinz, The Kraft Heinz Company (NASDAQ: KHC), PNC Financial Services (NYSE: PNC), PPG Industries (NYSE: PPG), U.S. Steel, U.S. Steel Corporation (NYSE: X), Viatris (NASDAQ: VRTS), Wabtec, Wabtec Corporation (NYSE: WAB), and WESCO International (WYSE: WCC). The region is home to Aurora Innovation, Aurora, Allegheny Technologies, American Eagle Outfitters, EQT, EQT Corporation, CONSOL Energy, Howmet Aerospace, Kennametal and II-VI Incorporated, II-VI headquarters. Other major employers include BNY Mellon, GlaxoSmithKline, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and Lanxess. The Northeast U.S. regional headquarters for Chevron Corporation, Nova Chemicals, Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu, FedEx Ground, Ariba, and the RAND Corporation call the area home. 84 Lumber, Giant Eagle, Highmark, Rue 21, General Nutrition Center (GNC), CNX Gas (CXG), and Genco Supply Chain Solutions are major non-public companies headquartered in the region. The global impact of Pittsburgh technology and business was recently demonstrated in several key components of the Boeing 787 Dreamliner being manufactured and supplied by area companies. Area retail is anchored by over 35 Pittsburgh shopping malls, shopping malls and a healthy downtown retail sector, as well as boutique shops along Walnut Street (Pittsburgh), Walnut Street, in Squirrel Hill (Pittsburgh), Squirrel Hill, Lawrenceville (Pittsburgh), Lawrenceville and Station Square. The nonprofit arts and cultural industry in Allegheny County generates $341 million in economic activity that supports over 10,000 full-time equivalent jobs with nearly $34 million in local and state taxes raised. A leader in Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, environmental design, the city is home to 60 total and 10 of the world's first green buildings while billions have been invested in the area's Marcellus Formation#Economic impact, Marcellus natural gas fields. A renaissance of Pittsburgh's 116-year-old film industry—that boasts the world's first Nickelodeon (movie theater), movie theater—has grown from the long-running Three Rivers Film Festival to an influx of List of television shows shot in Pittsburgh, major television and List of films shot in Pittsburgh, movie productions. including Disney Research, Disney and Paramount Pictures, Paramount offices with the largest sound stage outside Los Angeles and New York City. Pittsburgh has hosted many conventions, including INPEX (invention show), INPEX, the world's largest invention trade show, since 1984; Tekko (convention), Tekko, a four-day anime convention, since 2003; Anthrocon, a furry convention, since 2006; and the Developing Unconventional Gas, DUG East energy trade show since 2009.Arts and culture
Entertainment
 Pittsburgh has a rich history in arts and culture dating from 19th century industrialists commissioning and donating public works, such as Heinz Hall for the Performing Arts and the Benedum Center, home to the Pittsburgh Symphony Orchestra and Pittsburgh Opera, respectively as well as such groups as the River City Brass Band and the Pittsburgh Youth Symphony Orchestra.
Pittsburgh has a number of small and mid-size arts organizations including the Pittsburgh Irish and Classical Theatre, Quantum Theatre, the Renaissance and Baroque Society of Pittsburgh, and the early music ensemble Chatham Baroque. Several choirs and singing groups are also present at the cities' universities; some of the most notable include the Pitt Men's Glee Club and the Heinz Chapel Choir.
Pittsburgh Dance Council and the Pittsburgh Ballet Theater host a variety of dance events. Polka, folk, square, and round dancing have a long history in the city and are celebrated by the Duquesne University Tamburitzans, a multicultural academy dedicated to the preservation and presentation of folk songs and dance.
Hundreds of major films have been shot partially or wholly in Pittsburgh. ''The Dark Knight Rises'' was largely filmed in Downtown, Oakland, and the North Shore. Pittsburgh has also teamed up with a Los Angeles-based production company, and has built the largest and most advanced movie studio in the eastern United States.
Pittsburgh's major art museums include the Andy Warhol Museum, the Carnegie Museum of Art, The Frick Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh Center for the Arts, the Mattress Factory, and the Carnegie Museum of Natural History, which has extensive dinosaur, mineral, animal, and Ancient Egypt, Egyptian collections. The Carnegie Science Center and associated Highmark SportsWorks, SportsWorks has interactive technology and science exhibits. The Heinz History Center, Senator John Heinz History Center and Western Pennsylvania Sports Museum is a Smithsonian affiliated regional history museum in the Strip District and its associated Fort Pitt Museum is in Point State Park. Soldiers and Sailors Memorial Hall and Museum in Oakland houses Western Pennsylvania military exhibits from the Civil War to present. The Children's Museum of Pittsburgh on the North Side features interactive exhibits for children. The eclectic Bayernhof Music Museum is six miles (9km) from downtown while The Clemente Museum is in the city's Lawrenceville section. The Cathedral of Learning's Nationality Rooms showcase pre-19th century learning environments from around the world. There are regular guided and self-guided architectural tours in numerous neighborhoods. Downtown's cultural district hosts quarterly Gallery Crawls and the annual Three Rivers Arts Festival. Pittsburgh is home to a number of art galleries and centers including the Miller Gallery at Carnegie Mellon University, Frick Fine Arts Building#University Arts Gallery, University Art Gallery of the University of Pittsburgh, the American Jewish Museum, and the Wood Street Galleries.
The Pittsburgh Zoo and PPG Aquarium, Phipps Conservatory and Botanical Gardens, and the National Aviary have served the city for over a century. Pittsburgh is home to the amusement park Kennywood. Pittsburgh is home to one of the several state licensed casinos. The Rivers Casino (Pittsburgh), Rivers Casino is on the North Shore (Pittsburgh), North Shore along the Ohio River, just west of Carnegie Science Center and Acrisure Stadium.
Pittsburgh is home to the world's second largest furry convention known as Anthrocon, which has been held annually at the David L. Lawrence Convention Center since 2006. In 2017, Anthrocon drew over 7,000 visitors and has had a cumulative economic impact of $53 million over the course of its 11 years of being hosted in Pittsburgh.
Lifetime (TV network), Lifetime's reality show, Dance Moms, is filmed at Pittsburgh's Abby Lee Dance Company.
Pittsburgh has a rich history in arts and culture dating from 19th century industrialists commissioning and donating public works, such as Heinz Hall for the Performing Arts and the Benedum Center, home to the Pittsburgh Symphony Orchestra and Pittsburgh Opera, respectively as well as such groups as the River City Brass Band and the Pittsburgh Youth Symphony Orchestra.
Pittsburgh has a number of small and mid-size arts organizations including the Pittsburgh Irish and Classical Theatre, Quantum Theatre, the Renaissance and Baroque Society of Pittsburgh, and the early music ensemble Chatham Baroque. Several choirs and singing groups are also present at the cities' universities; some of the most notable include the Pitt Men's Glee Club and the Heinz Chapel Choir.
Pittsburgh Dance Council and the Pittsburgh Ballet Theater host a variety of dance events. Polka, folk, square, and round dancing have a long history in the city and are celebrated by the Duquesne University Tamburitzans, a multicultural academy dedicated to the preservation and presentation of folk songs and dance.
Hundreds of major films have been shot partially or wholly in Pittsburgh. ''The Dark Knight Rises'' was largely filmed in Downtown, Oakland, and the North Shore. Pittsburgh has also teamed up with a Los Angeles-based production company, and has built the largest and most advanced movie studio in the eastern United States.
Pittsburgh's major art museums include the Andy Warhol Museum, the Carnegie Museum of Art, The Frick Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh Center for the Arts, the Mattress Factory, and the Carnegie Museum of Natural History, which has extensive dinosaur, mineral, animal, and Ancient Egypt, Egyptian collections. The Carnegie Science Center and associated Highmark SportsWorks, SportsWorks has interactive technology and science exhibits. The Heinz History Center, Senator John Heinz History Center and Western Pennsylvania Sports Museum is a Smithsonian affiliated regional history museum in the Strip District and its associated Fort Pitt Museum is in Point State Park. Soldiers and Sailors Memorial Hall and Museum in Oakland houses Western Pennsylvania military exhibits from the Civil War to present. The Children's Museum of Pittsburgh on the North Side features interactive exhibits for children. The eclectic Bayernhof Music Museum is six miles (9km) from downtown while The Clemente Museum is in the city's Lawrenceville section. The Cathedral of Learning's Nationality Rooms showcase pre-19th century learning environments from around the world. There are regular guided and self-guided architectural tours in numerous neighborhoods. Downtown's cultural district hosts quarterly Gallery Crawls and the annual Three Rivers Arts Festival. Pittsburgh is home to a number of art galleries and centers including the Miller Gallery at Carnegie Mellon University, Frick Fine Arts Building#University Arts Gallery, University Art Gallery of the University of Pittsburgh, the American Jewish Museum, and the Wood Street Galleries.
The Pittsburgh Zoo and PPG Aquarium, Phipps Conservatory and Botanical Gardens, and the National Aviary have served the city for over a century. Pittsburgh is home to the amusement park Kennywood. Pittsburgh is home to one of the several state licensed casinos. The Rivers Casino (Pittsburgh), Rivers Casino is on the North Shore (Pittsburgh), North Shore along the Ohio River, just west of Carnegie Science Center and Acrisure Stadium.
Pittsburgh is home to the world's second largest furry convention known as Anthrocon, which has been held annually at the David L. Lawrence Convention Center since 2006. In 2017, Anthrocon drew over 7,000 visitors and has had a cumulative economic impact of $53 million over the course of its 11 years of being hosted in Pittsburgh.
Lifetime (TV network), Lifetime's reality show, Dance Moms, is filmed at Pittsburgh's Abby Lee Dance Company.
Music
Pittsburgh has a long tradition of jazz, blues, and bluegrass music. The National Negro Opera Company was founded in the city as the first all African-American opera company in the United States. This led to the prominence of African-American singers like Leontyne Price in the world of opera. One of the greatest American musicians and composers of the 20th century, Billy Strayhorn, grew up and was educated in Pittsburgh. Pittsburgh's Wiz Khalifa is a recent artist to have a number one record. His anthem "Black and Yellow" (a tribute to Pittsburgh's official colors) reached number one on Billboard's "Hot 100" for the Week of February 19, 2011. Perry Como and Christina Aguilera are from Pittsburgh suburbs. The city is also where the band Rusted Root was formed. Liz Berlin of Rusted Root owns Mr. Smalls, a popular music venue for touring national acts in Pittsburgh. Hip hop artist Mac Miller was also a Pittsburgh native, with his debut album ''Blue Slide Park'' named after the local Frick Park. Many punk rock and Hardcore punk acts, such as Aus Rotten and Anti-Flag, originated in Pittsburgh. Pittsburgh has also seen many metal bands gain prominence in recent years, most notably Code Orange (band), Code Orange, who were nominated for a Grammy. Pittsburgh has emerged as a leading city in the United States' heavy metal music scene. Ranking as the third 'most metal city' in a study conducted by MetalSucks, Pittsburgh has earned a reputation for its heavy metal community. Pittsburgh is home to over six-hundred heavy metal bands, as well as heavy metal coffee shops and bars. The city is noted for its doom metal, metalcore, and death metal scenes. Throughout the 1990s there was an electronic music subculture in Pittsburgh which likely traced its origins to similar Internet chat room, chatroom-based movements in Detroit, Cleveland, Minneapolis, and across the United States. Pittsburgh promoter (entertainment), promoters and disk jockey, DJs organized raves in warehouses, ice rinks, barns, and fields which eventually attracted thousands of attendees, some of whom were high school students or even younger. As the events grew more popular, they drew internationally known DJs such as Adam Beyer and Richie Hawtin. Pittsburgh rave culture itself spawned at least one well-known artist, the drum and bass DJ Dieselboy, who attended the University of Pittsburgh between 1990 and 1995. Since 2012, Pittsburgh has been the home of Hot Mass, an afterhours electronic music dance party which critics have compared favorably to European nightclubs and parties. Electronic music artist and DJ Yaeji credits Hot Mass with her "indoctrination into nightlife"; she regularly attended the party while studying at Carnegie Mellon University.Theatre
 The city's first play was produced at the Market Square, Pittsburgh, old courthouse in 1803 and the first theater built in 1812. Collegiate companies include the University of Pittsburgh's University of Pittsburgh Repertory Theatre, Repertory Theatre and Kuntu Repertory Theatre, Point Park University's resident companies at its Pittsburgh Playhouse, and Carnegie Mellon University's School of Drama productions and Scotch'n'Soda organization. The Duquesne University Red Masquers, founded in 1912, are the oldest, continuously producing theater company in Pennsylvania. The city's longest-running theater show, Friday Nite Improvs, is an improv jam that has been performed in the Cathedral of Learning and other locations for 20 years. The Pittsburgh New Works Festival utilizes local theater companies to stage productions of original one-act plays by playwrights from all parts of the country. Similarly, Future Ten showcases new ten-minute plays. Saint Vincent Summer Theatre, Off the Wall Productions, Mountain Playhouse, The Theatre Factory, and Stage Right! in nearby Latrobe, Pennsylvania, Latrobe, Carnegie, Pennsylvania, Carnegie, Jennerstown, Pennsylvania, Jennerstown, Trafford, Pennsylvania, Trafford, and Greensburg, Pennsylvania, Greensburg, respectively, employ Pittsburgh actors and contribute to the culture of the region.
The city's first play was produced at the Market Square, Pittsburgh, old courthouse in 1803 and the first theater built in 1812. Collegiate companies include the University of Pittsburgh's University of Pittsburgh Repertory Theatre, Repertory Theatre and Kuntu Repertory Theatre, Point Park University's resident companies at its Pittsburgh Playhouse, and Carnegie Mellon University's School of Drama productions and Scotch'n'Soda organization. The Duquesne University Red Masquers, founded in 1912, are the oldest, continuously producing theater company in Pennsylvania. The city's longest-running theater show, Friday Nite Improvs, is an improv jam that has been performed in the Cathedral of Learning and other locations for 20 years. The Pittsburgh New Works Festival utilizes local theater companies to stage productions of original one-act plays by playwrights from all parts of the country. Similarly, Future Ten showcases new ten-minute plays. Saint Vincent Summer Theatre, Off the Wall Productions, Mountain Playhouse, The Theatre Factory, and Stage Right! in nearby Latrobe, Pennsylvania, Latrobe, Carnegie, Pennsylvania, Carnegie, Jennerstown, Pennsylvania, Jennerstown, Trafford, Pennsylvania, Trafford, and Greensburg, Pennsylvania, Greensburg, respectively, employ Pittsburgh actors and contribute to the culture of the region.
Literature
Pittsburgh is the birthplace of Gertrude Stein and Rachel Carson, a Chatham University graduate from the suburb of Springdale, Pennsylvania. Modern writers include Pulitzer Prize-winning playwright August Wilson and Michael Chabon with his Pittsburgh-focused commentary on student and college life. Two-time Pulitzer Prize winner and recipient of the Presidential Medal of Freedom, David McCullough was born and raised in Pittsburgh. Annie Dillard, a Pulitzer Prize–winning writer, was born and raised in Pittsburgh. Much of her memoir An American Childhood takes place in post-World War II Pittsburgh. Award-winning author John Edgar Wideman grew up in Pittsburgh and has based several of his books, including the memoir ''Brothers and Keepers'', in his hometown. Poet Terrance Hayes, winner of the 2010 National Book Award and a 2014 MacArthur Foundation Fellow, received his MFA from the University of Pittsburgh, where he is a faculty member. Poet Michael Simms (publisher), Michael Simms, founder of Autumn House Press, resides in the Mount Washington neighborhood of Pittsburgh. Poet Samuel John Hazo, the first poet Laureate of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, also resides in the city. New writers include Chris Kuzneski who attended the University of Pittsburgh and mentions Pittsburgh in his works and Pittsburgher Brian Celio, author of ''Catapult Soul'' who captured the Pittsburgh 'Yinzer' dialect in his writing. Pittsburgh's unique literary style extends to playwrights, as well as local graffiti and hip hop artists. Pittsburgh's position as the birthplace for community owned television and networked commercial television helped spawn the modern children's show genres exemplified by ''Mister Rogers' Neighborhood'', ''Where in the World Is Carmen Sandiego? (TV series), Where in the World is Carmen Sandiego?'', ''Happy's Party'', ''Cappelli & Company'', and ''The Children's Corner'', all nationally broadcast. The ''Pittsburgh Dad'' series has showcased the Pittsburghese genre to a global YouTube audience since 2011. The modern fantasy, macabre and science fiction genre was popularized by director George A. Romero, television's Bill Cardille and his ''Chiller Theatre (Pittsburgh), Chiller Theatre'', director and writer Rusty Cundieff and makeup effects guru Tom Savini. The genre continues today with the PARSEC science fiction organization, The It's Alive Show, the annual "Zombie Fest", and several writer's workshops including Write or Die, Pittsburgh SouthWrites, and Pittsburgh Worldwrights with Barton Paul Levenson, Kenneth Chiacchia and Elizabeth Humphreys Penrose.Food
Pittsburgh is known for several specialties including pierogies, kielbasa, chipped chopped ham sandwiches, and Klondike bars. In 2019, Pittsburgh was deemed "Food City of the Year" by the San Francisco-based restaurant and hospitality consulting firm af&co. Many restaurants were favorably mentioned, among them were Superior Motors in Braddock, Pennsylvania, Braddock, Driftwood Oven in Lawrenceville (Pittsburgh), Lawrenceville, Spork in Bloomfield (Pittsburgh), Bloomfield, Fish nor Fowl in Garfield (Pittsburgh), Garfield, Bitter Ends Garden & Luncheonette in Bloomfield (Pittsburgh), Bloomfield, and Rolling Pepperoni in Lawrenceville (Pittsburgh), Lawrenceville.Local dialect
The Pittsburgh English dialect, commonly called ''Pittsburgh English, Pittsburghese'', was influenced by Scots-Irish American, Scots-Irish, German, and Eastern European immigrants and African Americans. Locals who speak the dialect are sometimes referred to as "Yinzers" (from the local word "yinz" [var. ''yunz''], a blended form of "you ones," similar to "y'all" and "you all" in the South). Common Pittsburghese terms are: "slippy" (slippery), "redd up" (clean up), "jagger bush" (thorn bush), and "gum bands" (rubber bands). The dialect is also notable for dropping the verb "to be". In Pittsburghese one would say "the car needs washed" instead of "needs to be washed," "needs washing," or "needs a wash." The dialect has some tonal similarities to other nearby regional dialects of Erie and Baltimore, but is noted for its somewhat staccato rhythms. The staccato qualities of the dialect are thought to originate either from Welsh or other European languages. The many local peculiarities have prompted ''The New York Times'' to describe Pittsburgh as "the Galapagos Islands of American dialect". The lexicon itself contains notable loans from Polish language, Polish and other European languages; examples include ''headscarf, babushka'', ''pierogi'', and ''halušky''.Livability
 Pittsburgh has five city parks and several parks managed by the Nature Conservancy. The largest, Frick Park, provides of woodland park with extensive hiking and biking trails throughout steep valleys and wooded slopes. Birding enthusiasts visit the Clayton Hill area of Frick Park, where over 100 species of birds have been recorded.
Residents living in extremely low-lying areas near the rivers or one of the 1,400 creeks and streams may have occasional floods, such as those caused when the remnants of Hurricane Ivan hit rainfall records in 2004. River flooding is relatively rare due to federal flood control efforts extensively managing locks, dams, and reservoirs. Residents living near smaller tributary streams are less protected from occasional flooding. The cost of a comprehensive flood control program for the region has been estimated at a prohibitive $50 billion.
Pittsburgh has the greatest number of bars per capita in the nation.
Pittsburgh has five city parks and several parks managed by the Nature Conservancy. The largest, Frick Park, provides of woodland park with extensive hiking and biking trails throughout steep valleys and wooded slopes. Birding enthusiasts visit the Clayton Hill area of Frick Park, where over 100 species of birds have been recorded.
Residents living in extremely low-lying areas near the rivers or one of the 1,400 creeks and streams may have occasional floods, such as those caused when the remnants of Hurricane Ivan hit rainfall records in 2004. River flooding is relatively rare due to federal flood control efforts extensively managing locks, dams, and reservoirs. Residents living near smaller tributary streams are less protected from occasional flooding. The cost of a comprehensive flood control program for the region has been estimated at a prohibitive $50 billion.
Pittsburgh has the greatest number of bars per capita in the nation.
Sports
Pittsburgh hosted the History of American football, first professional football game and the 1903 World Series, first World Series. In 2009, Pittsburgh won the ''Sporting News'' title of "Best Sports City" in the United States and, in 2013, ''Sperling's Best Places'' "top 15 cities for baseball". College sports also have large followings with the University of Pittsburgh in football and sharing Division I basketball fans with Robert Morris and Duquesne. Pittsburgh has a long history with its major professional sports teams—the Pittsburgh Steelers, Steelers of the National Football League, the Pittsburgh Penguins, Penguins of the National Hockey League, and the Pittsburgh Pirates, Pirates of Major League Baseball—which all share the same team colors, the Flag of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, official city colors of black and gold. Pittsburgh is the only city in the United States where this practice of sharing team colors in solidarity takes place. The black-and-gold color scheme has since become widely associated with the city and personified in its famous Terrible Towel. "Rails to Trails", has converted miles of former rail tracks to recreational trails, including a Pittsburgh-Washington D.C. bike/walking trail. Several mountain biking trails are within the city and suburbs, Frick Park has biking trails and Hartwood Acres Park has many miles of Single track (mountain biking), single track trails.Professional
Major league Minor league/otherCollege
Power 5 OtherBaseball
 The Pittsburgh Pirates baseball team, often referred to as the Bucs or the Buccos (derived from buccaneer), is the city's oldest professional sports franchise, having been founded in 1881, and plays in the National League Central, Central Division of the National League. The Pirates are nine-time Pennant winners and five-time World Series Champions, were in the first 1903 World Series, World Series (1903) and claim two pre-World Series titles in 1901 and 1902. The Pirates play in PNC Park.
Pittsburgh also has a rich Negro league history, with the former Pittsburgh Crawfords and the Homestead Grays credited with as many as 14 league titles and 11 Hall of Famers between them in the 1930s and 1940s, while the Pittsburgh Keystones (baseball), Keystones fielded teams in the 1920s. In addition, in 1971 the Pirates were the first Major League team to field an all-minority lineup. One sportswriter claimed, "No city is more synonymous with black baseball than Pittsburgh."
Since the late 20th century, the Pirates had three consecutive National League Championship Series appearances (1990–92) (going 6, 7 and 7 games each), followed by setting the MLB record for most consecutive losing seasons, with 20 from 1993 until 2012. This era was followed by three consecutive postseason appearances: the 2013 National League Division Series and the 2014–2015 Wild Card games. Their 1997 Pittsburgh Pirates season, September pennant race in 1997 featured the franchises' last no-hitter and last award for The Sporting News Executive of the Year Award, Sporting News' Executive of the Year.
The Pittsburgh Pirates baseball team, often referred to as the Bucs or the Buccos (derived from buccaneer), is the city's oldest professional sports franchise, having been founded in 1881, and plays in the National League Central, Central Division of the National League. The Pirates are nine-time Pennant winners and five-time World Series Champions, were in the first 1903 World Series, World Series (1903) and claim two pre-World Series titles in 1901 and 1902. The Pirates play in PNC Park.
Pittsburgh also has a rich Negro league history, with the former Pittsburgh Crawfords and the Homestead Grays credited with as many as 14 league titles and 11 Hall of Famers between them in the 1930s and 1940s, while the Pittsburgh Keystones (baseball), Keystones fielded teams in the 1920s. In addition, in 1971 the Pirates were the first Major League team to field an all-minority lineup. One sportswriter claimed, "No city is more synonymous with black baseball than Pittsburgh."
Since the late 20th century, the Pirates had three consecutive National League Championship Series appearances (1990–92) (going 6, 7 and 7 games each), followed by setting the MLB record for most consecutive losing seasons, with 20 from 1993 until 2012. This era was followed by three consecutive postseason appearances: the 2013 National League Division Series and the 2014–2015 Wild Card games. Their 1997 Pittsburgh Pirates season, September pennant race in 1997 featured the franchises' last no-hitter and last award for The Sporting News Executive of the Year Award, Sporting News' Executive of the Year.
Football
 The city's professional team, National Football League, NFL's Pittsburgh Steelers, is named after the distribution company the Pittsburgh Steeling company established in 1927. News of the team has preempted news of elections and other events, and are important to the region and its diaspora. The Steelers have been owned by the Rooney family since the team's founding in 1933, show consistency in coaching (only three coaches since the 1960s all with the same basic philosophy) and are noted as one of sports' most respectable franchises. The Steelers have a long waiting list for season tickets, and have sold out every home game since 1972. The team won four Super Bowls in a six-year span in the 1970s, a Super Bowl XL, fifth Super Bowl in 2006, and a league record Super Bowl XLIII, sixth Super Bowl in 2009. Since the AFL-NFL merger in 1970 they have qualified for the most NFL playoff berths (28) and have played in (15) and hosted (11) the most NFL conference championship games.
High school football routinely attract 10,000 fans per game and extensive press coverage. The Tom Cruise film All the Right Moves (film), All the Right Moves and ESPN's Bound for Glory (ESPN), Bound for Glory with Dick Butkus both filmed in the area to capture the tradition and passion of local high school football.
College football in the city dates to 1889 with the Division I (NCAA), Division I (FBS) Pittsburgh Panthers football, Panthers of the University of Pittsburgh posting nine NCAA Division I FBS National Football Championship, national championships and qualifying 34 total bowl games and appearing in the 2018 ACC Championship Game. Local universities Duquesne and Robert Morris have loyal fan bases that follow their lower NCAA Division I Football Championship, (FCS) teams. Duquesne, Carnegie Mellon University, and Washington & Jefferson College all posted major bowl games and AP Poll rankings from the 1920s to the 1940s as that era's equivalent of Top 25 FBS programs.
Acrisure Stadium serves as home for the Steelers, Panthers, and both the suburban and city high school championships. Playoff franchises Pittsburgh Power and Pittsburgh Gladiators competed in the Arena Football League in the 1980s and 2010s respectively. The Gladiators hosted ArenaBowl I in the city, competing in two, but losing both before moving to Tampa, Florida and becoming the Tampa Bay Storm, Storm. The Pittsburgh Passion has been the city's professional women's football team since 2002 and plays its home games at Highmark Stadium (Pennsylvania), Highmark Stadium. The Edward J. DeBartolo, Sr., Ed Debartolo owned Pittsburgh Maulers (1984), Pittsburgh Maulers featured a Heisman Trophy winner in the mid-1980s, former superstar University of Nebraska running back Mike Rozier.
The city's professional team, National Football League, NFL's Pittsburgh Steelers, is named after the distribution company the Pittsburgh Steeling company established in 1927. News of the team has preempted news of elections and other events, and are important to the region and its diaspora. The Steelers have been owned by the Rooney family since the team's founding in 1933, show consistency in coaching (only three coaches since the 1960s all with the same basic philosophy) and are noted as one of sports' most respectable franchises. The Steelers have a long waiting list for season tickets, and have sold out every home game since 1972. The team won four Super Bowls in a six-year span in the 1970s, a Super Bowl XL, fifth Super Bowl in 2006, and a league record Super Bowl XLIII, sixth Super Bowl in 2009. Since the AFL-NFL merger in 1970 they have qualified for the most NFL playoff berths (28) and have played in (15) and hosted (11) the most NFL conference championship games.
High school football routinely attract 10,000 fans per game and extensive press coverage. The Tom Cruise film All the Right Moves (film), All the Right Moves and ESPN's Bound for Glory (ESPN), Bound for Glory with Dick Butkus both filmed in the area to capture the tradition and passion of local high school football.
College football in the city dates to 1889 with the Division I (NCAA), Division I (FBS) Pittsburgh Panthers football, Panthers of the University of Pittsburgh posting nine NCAA Division I FBS National Football Championship, national championships and qualifying 34 total bowl games and appearing in the 2018 ACC Championship Game. Local universities Duquesne and Robert Morris have loyal fan bases that follow their lower NCAA Division I Football Championship, (FCS) teams. Duquesne, Carnegie Mellon University, and Washington & Jefferson College all posted major bowl games and AP Poll rankings from the 1920s to the 1940s as that era's equivalent of Top 25 FBS programs.
Acrisure Stadium serves as home for the Steelers, Panthers, and both the suburban and city high school championships. Playoff franchises Pittsburgh Power and Pittsburgh Gladiators competed in the Arena Football League in the 1980s and 2010s respectively. The Gladiators hosted ArenaBowl I in the city, competing in two, but losing both before moving to Tampa, Florida and becoming the Tampa Bay Storm, Storm. The Pittsburgh Passion has been the city's professional women's football team since 2002 and plays its home games at Highmark Stadium (Pennsylvania), Highmark Stadium. The Edward J. DeBartolo, Sr., Ed Debartolo owned Pittsburgh Maulers (1984), Pittsburgh Maulers featured a Heisman Trophy winner in the mid-1980s, former superstar University of Nebraska running back Mike Rozier.
Hockey
The NHL's Pittsburgh Penguins have played in Pittsburgh since the team's founding in 1967. The team has won 6 Eastern Conference (NHL), Eastern Conference titles (1991, 1992, 2008, 2009, 2016 and 2017) and 5 Stanley Cup championships (1991, 1992, 2009, 2016 and 2017). Since 1999, Hall of Famer and back-to-back playoff MVP Mario Lemieux has served as Penguins owner. Until moving into the PPG Paints Arena in 2010 (when it was known as Consol Energy Center), the team played their home games at the world's first retractable domed stadium, the Civic Arena (Pittsburgh), Civic Arena, or in local parlance "The Igloo". Ice hockey has had a regional fan base since the 1890s semi-pro Pittsburgh Keystones (ice hockey), Keystones. The city's first ice rink dates back to 1889, when there was an ice rink at the Casino in Schenley Park. From 1896 to 1956, the Exposition Building on the Allegheny River near The Point and Duquesne Gardens in Oakland offered indoor skating. The NHL awarded one of its first franchises to the city in 1924 on the strength of the back-to-back USAHA championship winning Pittsburgh Yellow Jackets featuring future Hall of Famers and a Stanley Cup winning coach. The NHL's Pittsburgh Pirates (hockey), Pittsburgh Pirates made several Stanley Cup playoff runs with a future Hall of Famer before folding from Great Depression financial pressures. Hockey survived with the Pittsburgh Hornets farm team (1936–1967) and their seven finals appearances and three championships in 18 playoff seasons. Robert Morris Colonials men's ice hockey, Robert Morris University fields a Division I college hockey team at thIsland Sports Center
Pittsburgh has semi-pro and amateur teams such as the Pittsburgh Penguins Elite. Pro-grade ice rinks such as the Rostraver Ice Garden, Mt. Lebanon Recreation Center and Iceoplex at Southpointe have trained several native Pittsburgh players for NHL play. RMU hosted the city's first 2013 NCAA Division I Men's Ice Hockey Tournament, Frozen Four college championship in 2013 with the four PPG Paints Arena games televised by ESPN.
Basketball
Professional basketball in Pittsburgh dates to the 1910s with teams "Monticello" and "Loendi" winning Black Fives#Colored Basketball World's Champions, five national titles, the Pittsburgh Pirates (NBL), Pirates (1937–45 in the National Basketball League (United States), NBL), the Pittsburgh Ironmen (1947–48 NBA inaugural season), the Pittsburgh Rens (1961–63), the Pittsburgh Pipers (first American Basketball Association championship in 1968) led by Connie Hawkins (team then moved); the Pittsburgh Condors (ABA returned in 1970–72), the Pittsburgh Piranhas (CBA Finals in 1995), the Pittsburgh Xplosion (2004–08) and Pittsburgh Phantoms (ABA), Phantoms (2009–10) both of the American Basketball Association (2000–present), ABA. The city has hosted dozens of pre-season and 15 regular season "neutral site" NBA games, including Wilt Chamberlain's record setting performance in both consecutive field goals and field goal percentage on February 24, 1967, NBA records that still stand. The Duquesne University Duquesne Dukes men's basketball, Dukes and the University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh Panthers men's basketball, Panthers have played college basketball in the city since 1914 and 1905 respectively. Pitt and Duquesne have played the annual City Game since 1932. Duquesne was the city's first team to appear in a Final Four (1940), obtain a number one AP Poll ranking (1954), and to win a post-season national title, the 1955 National Invitation Tournament on its second straight trip to the NIT title game. Duquesne is the only college program to produce back-to-back NBA No. 1 overall draft picks with 1955's Dick Ricketts and 1956's Sihugo Green. Duquesne's Chuck Cooper (basketball), Chuck Cooper was the first African American drafted by an NBA team. The Panthers won two pre-tournament era Helms Athletic Foundation Mythical national championship, National Championships in 1928 and 1930, competed in a "national title game" against LSU Tigers basketball, LSU in 1935, and made a Final Four appearance in 1941. Pitt has won 13 conference titles, qualified for the NCAA tournament 26 times including a post season tournament every season between 1999 and 2000 and 2015-2016 during which time it regularly sold out the Petersen Events Center. The program has produced 27 NBA draft picks and 15 All Americans while ranking No. 1 in the nation as recently as 2009. The suburban Robert Morris Colonials men's basketball, Robert Morris University's Colonials have competed in NCAA Division I basketball since the 1970s, qualifying for the NCAA tournament in each of the last four decades (8). In the 2013 National Invitation Tournament the Colonials notched an upset win over the defending national champions Kentucky Wildcats. Pittsburgh Panthers women's basketball has qualified for 14 post season tournaments (including 4 NCAA tournaments) and boasts of 5 All-Americans selected 6 times with 3 WNBA players. Pitt women began play in 1914 before being reintroduced in 1970. Both Duquesne and Robert Morris also have competitive Division I women's basketball programs. Pittsburgh launched the nation's first high school all-star game in 1965. The Roundball Classic annually featured future NBA hall of famers at the Civic Arena with ESPN televising. The Civic Arena also hosted the Atlantic 10 men's basketball tournament, championship tournament for the Eastern Eight Conference from 1978 until 1982.Soccer
The Pittsburgh Riverhounds SC, Riverhounds, an American professional soccer team, were founded in 1998. Like the major league teams in the city, the Riverhounds wear black and gold kits. The club plays in the Eastern Conference (USL Championship), Eastern Conference of the USL Championship, the second tier of the American soccer pyramid. The Riverhounds play their home games at Highmark Stadium (Pennsylvania), Highmark Stadium, a soccer-specific stadium located in Station Square.Golf
Golf has deep roots in the area. The oldest U.S. course in continuous use, Foxburg Country Club dating from 1887 calls the region home. Suburban Oakmont Country Club holds the record for most times as host for the U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open (8). U.S. Women's Open (2), PGA Championships (3), and U.S. Amateurs (8) have also called Oakmont home. Golf legends Arnold Palmer, Jim Furyk, and Rocco Mediate learned the game and began their careers on Pittsburgh area courses. Suburban courses such as Laurel Valley Golf Club and the Fox Chapel Golf Club have hosted PGA Championships (1937, 1965), the Ryder Cup (1975), LPGA Championships (1957–58), Senior Players Championships (2012–14), and the Senior PGA Championship (2005). Local courses have sponsored annual major tournaments for 40 years: * Pennsylvania Open Championship 1920–1940 (even years) * Dapper Dan Open 1939–1949 * Pittsburgh Open (LPGA Tour) 1956 * Pittsburgh Senior Classic 1993–1998 * 84 Lumber Classic 2001–2006 * Mylan Classic 2010–2013Professional wrestling
Many notable Professional wrestling, professional wrestlers and promoters have hailed from the city or started their careers in Pittsburgh, including Bruno Sammartino, Kurt Angle, Shane Douglas, Corey Graves, Dominic DeNucci, Elias Samson, Elias, Britt Baker and many more. The Fineview (Pittsburgh), Fineview section of Pittsburgh served as the base of the televised show Studio Wrestling during the 1960s. The Keystone State Wrestling Alliance (KSWA) is a professional wrestling promotion which was founded in Pittsburgh in 2000. It is the only promotion based in Pittsburgh. It operates in the city's Lawrenceville (Pittsburgh), Lawrenceville neighborhood. The KSWA performs Monthly on Saturdays at its main venue on 51st Street.Annual sporting events
 Pittsburgh hosts several annual major sporting events initiated in the late 20th century, including the:
* Three Rivers Regatta (since 1977)
* Pittsburgh Vintage Grand Prix (since 1983)
* Dirty Dozen (bicycle competition), Dirty Dozen Cycle Race (since 1983)
* Pittsburgh Marathon (since 1985)
* Richard S. Caliguiri City of Pittsburgh Great Race, Great Race 10K (since 1985)
* Head of the Ohio Regatta (since 1987)
The city's vibrant rivers have attracted annual world-title fishing competitions of the FLW Outdoors, Forrest Wood Cup in 2009 and the Bassmaster Classic in 2005.
Annual events continue during the winter months at area ski resorts such as Boyce Park, Seven Springs Mountain Resort, Seven Springs, Hidden Valley Resort (Pennsylvania), Hidden Valley Resort, Laurel Mountain Ski Resort, Laurel Mountain, and Wisp Ski Resort, Wisp. Ice skating rinks are enjoyed at PPG Place#Sites, PPG Place and North Park (Pittsburgh), North Park.
Pittsburgh hosts several annual major sporting events initiated in the late 20th century, including the:
* Three Rivers Regatta (since 1977)
* Pittsburgh Vintage Grand Prix (since 1983)
* Dirty Dozen (bicycle competition), Dirty Dozen Cycle Race (since 1983)
* Pittsburgh Marathon (since 1985)
* Richard S. Caliguiri City of Pittsburgh Great Race, Great Race 10K (since 1985)
* Head of the Ohio Regatta (since 1987)
The city's vibrant rivers have attracted annual world-title fishing competitions of the FLW Outdoors, Forrest Wood Cup in 2009 and the Bassmaster Classic in 2005.
Annual events continue during the winter months at area ski resorts such as Boyce Park, Seven Springs Mountain Resort, Seven Springs, Hidden Valley Resort (Pennsylvania), Hidden Valley Resort, Laurel Mountain Ski Resort, Laurel Mountain, and Wisp Ski Resort, Wisp. Ice skating rinks are enjoyed at PPG Place#Sites, PPG Place and North Park (Pittsburgh), North Park.
Government and politics
Government
 The Government of Pittsburgh is composed of the Mayor of Pittsburgh, the Pittsburgh City Council, and various boards and commissions. The mayor and the nine-member council each serve four-year terms. Since the 1950s the Pittsburgh Mayoral Chief of Staff, Mayor's Chief of Staff has assumed a large role in advising, long term planning, and as a "gatekeeper" to the mayor. City council members are chosen by plurality voting system, plurality elections in each of nine districts. The government's official offices are in the Pittsburgh City-County Building.
The Pennsylvania Supreme Court holds sessions in Pittsburgh, as well as Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, Harrisburg and Philadelphia. Pittsburgh is represented in the Pennsylvania General Assembly by three Pennsylvania State Senate, Senate Districts and nine Pennsylvania House of Representatives, House Districts. Federally, Pittsburgh is part of Pennsylvania's 18th congressional district.
The Government of Pittsburgh is composed of the Mayor of Pittsburgh, the Pittsburgh City Council, and various boards and commissions. The mayor and the nine-member council each serve four-year terms. Since the 1950s the Pittsburgh Mayoral Chief of Staff, Mayor's Chief of Staff has assumed a large role in advising, long term planning, and as a "gatekeeper" to the mayor. City council members are chosen by plurality voting system, plurality elections in each of nine districts. The government's official offices are in the Pittsburgh City-County Building.
The Pennsylvania Supreme Court holds sessions in Pittsburgh, as well as Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, Harrisburg and Philadelphia. Pittsburgh is represented in the Pennsylvania General Assembly by three Pennsylvania State Senate, Senate Districts and nine Pennsylvania House of Representatives, House Districts. Federally, Pittsburgh is part of Pennsylvania's 18th congressional district.
Politics
Law enforcement
Crime
Pittsburgh annually ranks as one of America's safest big cities, in 2013 being named the 3rd "most secure" big city by Farmers Insurance. Among United States cities by crime rate, crime rates of the 60 largest U.S. cities, 43 had more instances of property crime while 16 had less when compared to Pittsburgh. More instances of violent crime were reported in 21 of the largest cities while 37 had less. The FBI recommends against using data for ranking. Per 100,000 persons stats (2012): At the end of 2019, the Pittsburgh Bureau of Police reported 37 murders in the city that year.Education

 Pittsburgh is home to many colleges, universities and research facilities, the most well-known of which are Carnegie Mellon University, the University of Pittsburgh, and Duquesne University. Also in the city are Carlow University, Chatham University, Point Park University, the Community College of Allegheny County, Pittsburgh Theological Seminary, Reformed Presbyterian Theological Seminary, and the Pittsburgh Institute of Mortuary Science.
The campuses of Carlow, Carnegie Mellon, and the University of Pittsburgh are near each other in the Oakland neighborhood that is the city's traditional cultural center. Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university founded by Andrew Carnegie and Andrew Mellon. CMU contains the Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon College of Engineering, College of Engineering, Tepper School of Business, School of Business, Heinz College, Carnegie Mellon College of Fine Arts, College of Fine Arts, writing, Social and Decision Sciences, information systems, statistics, and psychology programs.
The University of Pittsburgh, established in 1787 and popularly referred to as "Pitt", is a Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related school with one of the nation's largest research programs. Pitt is known for the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public and International Affairs, University of Pittsburgh School of Information Sciences, Swanson School of Engineering, University of Pittsburgh College of Business Administration, University of Pittsburgh School of Law, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh School of Social Work, and other biomedical and health-related sciences.
Carlow University is a small private Catholic university that while coeducational, has traditionally educated women. Chatham University, a liberal arts college that was founded as a woman's college but became fully coeducational in 2015, is in the Shadyside neighborhood, but also maintains a Eden Hall Farm campus in the North Hills, Pennsylvania, North Hills. Duquesne University, a private Catholic university in the Bluff (Pittsburgh), Bluff neighborhood and is noted for its song and dance troupe, the Duquesne University Tamburitzans, as well as programs in law, business, and pharmacy. Point Park University was founded in 1961 and is well known for its Conservatory of Performing Arts and its Pittsburgh Playhouse.
Pittsburgh Public Schools teachers are paid well relative to their peers, ranking 17th in 2000 among the 100 largest cities by population for the highest minimum salary. In 2018 the starting teacher salary offered to teachers with a BA was $46,920. The maximum annual salary for a teacher with a master's degree was $95,254.
Local public schools include many charter and magnet schools, including City Charter High School (computer and technology focused), Pittsburgh Montessori School (formerly Homewood Montessori), Pittsburgh Gifted Center, Barack Obama Academy of International Studies 6-12, Pittsburgh Creative and Performing Arts School, Pittsburgh Creative and Performing Arts 6–12, Pittsburgh Science and Technology Academy, the Western Pennsylvania School for Blind Children, and the Western Pennsylvania School for the Deaf.
Private schools in Pittsburgh include Bishop Canevin High School, Central Catholic High School (Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania), Central Catholic High School, Oakland Catholic High School, Winchester Thurston School, St. Edmund's Academy, Hillel Academy of Pittsburgh, Yeshiva Schools and The Ellis School. Shady Side Academy maintains a PK–5 primary school campus in the Point Breeze, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Point Breeze neighborhood, in addition to its 6–12 middle and upper school campuses in nearby suburban Fox Chapel, Pennsylvania, Fox Chapel. Other private institutions outside of Pittsburgh's limits include North Catholic High School and Seton-La Salle Catholic High School.
The city also has an extensive library system, both public and university. Most notable are the Carnegie Library of Pittsburgh and the University of Pittsburgh's University Library System, which rank 9th-largest (public) and 18th-largest (academic) in the nation, respectively.
Pittsburgh is home to many colleges, universities and research facilities, the most well-known of which are Carnegie Mellon University, the University of Pittsburgh, and Duquesne University. Also in the city are Carlow University, Chatham University, Point Park University, the Community College of Allegheny County, Pittsburgh Theological Seminary, Reformed Presbyterian Theological Seminary, and the Pittsburgh Institute of Mortuary Science.
The campuses of Carlow, Carnegie Mellon, and the University of Pittsburgh are near each other in the Oakland neighborhood that is the city's traditional cultural center. Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university founded by Andrew Carnegie and Andrew Mellon. CMU contains the Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon College of Engineering, College of Engineering, Tepper School of Business, School of Business, Heinz College, Carnegie Mellon College of Fine Arts, College of Fine Arts, writing, Social and Decision Sciences, information systems, statistics, and psychology programs.
The University of Pittsburgh, established in 1787 and popularly referred to as "Pitt", is a Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related school with one of the nation's largest research programs. Pitt is known for the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public and International Affairs, University of Pittsburgh School of Information Sciences, Swanson School of Engineering, University of Pittsburgh College of Business Administration, University of Pittsburgh School of Law, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh School of Social Work, and other biomedical and health-related sciences.
Carlow University is a small private Catholic university that while coeducational, has traditionally educated women. Chatham University, a liberal arts college that was founded as a woman's college but became fully coeducational in 2015, is in the Shadyside neighborhood, but also maintains a Eden Hall Farm campus in the North Hills, Pennsylvania, North Hills. Duquesne University, a private Catholic university in the Bluff (Pittsburgh), Bluff neighborhood and is noted for its song and dance troupe, the Duquesne University Tamburitzans, as well as programs in law, business, and pharmacy. Point Park University was founded in 1961 and is well known for its Conservatory of Performing Arts and its Pittsburgh Playhouse.
Pittsburgh Public Schools teachers are paid well relative to their peers, ranking 17th in 2000 among the 100 largest cities by population for the highest minimum salary. In 2018 the starting teacher salary offered to teachers with a BA was $46,920. The maximum annual salary for a teacher with a master's degree was $95,254.
Local public schools include many charter and magnet schools, including City Charter High School (computer and technology focused), Pittsburgh Montessori School (formerly Homewood Montessori), Pittsburgh Gifted Center, Barack Obama Academy of International Studies 6-12, Pittsburgh Creative and Performing Arts School, Pittsburgh Creative and Performing Arts 6–12, Pittsburgh Science and Technology Academy, the Western Pennsylvania School for Blind Children, and the Western Pennsylvania School for the Deaf.
Private schools in Pittsburgh include Bishop Canevin High School, Central Catholic High School (Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania), Central Catholic High School, Oakland Catholic High School, Winchester Thurston School, St. Edmund's Academy, Hillel Academy of Pittsburgh, Yeshiva Schools and The Ellis School. Shady Side Academy maintains a PK–5 primary school campus in the Point Breeze, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Point Breeze neighborhood, in addition to its 6–12 middle and upper school campuses in nearby suburban Fox Chapel, Pennsylvania, Fox Chapel. Other private institutions outside of Pittsburgh's limits include North Catholic High School and Seton-La Salle Catholic High School.
The city also has an extensive library system, both public and university. Most notable are the Carnegie Library of Pittsburgh and the University of Pittsburgh's University Library System, which rank 9th-largest (public) and 18th-largest (academic) in the nation, respectively.
Media
Newspapers
 There are two major daily newspapers in Pittsburgh: the ''Pittsburgh Post-Gazette'' and the ''Pittsburgh Tribune-Review'' online only (no longer in print for Pittsburgh Area). Weekly papers in the region include the ''Pittsburgh Business Times'', ''Pittsburgh City Paper'', ''Pittsburgh Catholic'', ''Pittsburgh Jewish Chronicle'', ''The New People'', and the ''New Pittsburgh Courier''. Independent student-written university-based newspapers include ''The Pitt News'' of the University of Pittsburgh, ''The Tartan (Carnegie Mellon University), The Tartan'' of Carnegie Mellon University, ''The Duquesne Duke'' of Duquesne University, and ''The Globe student newspaper, The Globe'' of Point Park University. The University of Pittsburgh School of Law is also home to JURIST, the world's only university-based legal news service.
There are two major daily newspapers in Pittsburgh: the ''Pittsburgh Post-Gazette'' and the ''Pittsburgh Tribune-Review'' online only (no longer in print for Pittsburgh Area). Weekly papers in the region include the ''Pittsburgh Business Times'', ''Pittsburgh City Paper'', ''Pittsburgh Catholic'', ''Pittsburgh Jewish Chronicle'', ''The New People'', and the ''New Pittsburgh Courier''. Independent student-written university-based newspapers include ''The Pitt News'' of the University of Pittsburgh, ''The Tartan (Carnegie Mellon University), The Tartan'' of Carnegie Mellon University, ''The Duquesne Duke'' of Duquesne University, and ''The Globe student newspaper, The Globe'' of Point Park University. The University of Pittsburgh School of Law is also home to JURIST, the world's only university-based legal news service.
Television
The Pittsburgh metro area is served by many local television and radio stations. The Pittsburgh designated market area (DMA) is the 22nd-largest in the U.S. with 1,163,150 homes (1.045% of the total U.S.).Holmes, GaryNielsen Reports 1.1% increase in U.S. Television Households for the 2006–2007 Season
. ''Nielsen Media Research.'' August 23, 2006. Retrieved on January 26, 2008. The major network television affiliates are KDKA-TV 2 (CBS), WTAE-TV, WTAE 4 (American Broadcasting Company, ABC), WPXI 11 (NBC), WPGH-TV 53 (Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox), KNNP-TV, WPCW 19 (The CW), WINP-TV 16 (Ion), WPNT 22 (MyNetworkTV), and WPCB 40 (Cornerstone Television, Cornerstone). KDKA-TV, WINP-TV, and WPCB are network owned-and-operated stations. WQED (TV), WQED 13 is the local PBS station in Pittsburgh. It was established on April 1, 1954, and was the first community-sponsored television station and the fifth public station in the United States. The station has produced much original content for PBS, including ''Mr. Rogers' Neighborhood'', several National Geographic Society, National Geographic specials, and ''Where in the World Is Carmen Sandiego? (game show), Where in the World is Carmen Sandiego?''
Radio
There is a wide variety of Radio broadcasting, radio stations serving the Pittsburgh market. The first was KDKA (AM), KDKA 1020 AM, also the world's first commercially licensed radio station, airing on November 2, 1920. Other stations include KQV 1410 AM (News radio, news), WBGG (AM), WBGG 970 AM (Sports radio, sports), KDKA-FM 93.7 FM (sports), WKST-FM 96.1 FM (Mainstream Top 40, Top 40), WAMO-AM 660 AM and 107.3 FM (Urban contemporary music, urban contemporary) WBZZ 100.7 FM (Adult contemporary music, adult contemporary), WDVE 102.5 FM (Album Rock, album rock), WPGB 104.7 FM (Country), and WXDX 105.9 FM (modern rock). There are also three public broadcasting, public radio stations in the area; including WESA (FM), WESA 90.5 FM (National Public Radio affiliate), WQED-FM, WQED 89.3 FM (classical), and WYEP 91.3 FM (Adult Alternative, adult alternative). Three non-commercial stations are run by Carnegie Mellon University (WRCT 88.3 FM), the University of Pittsburgh (WPTS 92.1 FM), and Point Park University (WPPJ 670 AM).Film
Pittsburgh's 116-year-old film industry accelerated after the 2006 passage of the Pennsylvania Film Production Tax Credit. According to the Pittsburgh Film Office, over 124 major motion pictures have been filmed, in whole or in part, in Pittsburgh, including ''The Mothman Prophecies'', ''Wonder Boys (film), Wonder Boys'', ''Dogma (film), Dogma'', ''Hoffa (film), Hoffa'', ''The Silence of the Lambs (film), The Silence of the Lambs'', ''Sudden Death (1995 film), Sudden Death'', ''Flashdance'', Southpaw (film), ''Southpaw'', ''Striking Distance'', ''Mrs. Soffel'', Jack Reacher (film), ''Jack Reacher'', ''Inspector Gadget (film), Inspector Gadget'', ''The Next Three Days'', ''The Perks of Being a Wallflower'', ''Zack and Miri Make a Porno'', and ''Fences (film), Fences''. Pittsburgh became "Gotham City" in 2011 during filming of ''The Dark Knight Rises''. George A. Romero shot nearly all his films in the area, including his ''Romero's Dead series, Living Dead'' series.Utilities
The city is served by Duquesne Light, one of the original 1912 power companies founded by George Westinghouse. Water service is provided by the Pittsburgh Water and Sewer Authority and Pennsylvania American Water. Natural gas is provided by Equitable Gas, Columbia Gas, Dominion Resources, Direct Energy, and Novec.Health care

 The two largest area health care providers are the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) (since 1893) and Allegheny Health Network (since 1882). Both hospitals annually rank as among the best overall in the United States, with UPMC being among ''U.S. News & World Report'' "Honor Roll" every year since 2000.
The first military hospital in U.S. history and the first west of the Atlantic Plain—General Edward Hand Hospital—served the area from 1777 to 1845. Since 1847, Pittsburgh has hosted the world's first "Mercy Hospital". This was followed by West Penn hospital in 1848, Passavant Hospital in 1849, the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine in 1883, Children's Hospital in 1887, and Magee-Womens Hospital of UPMC, Magee Womens Hospital in 1911. In 1954, Allegheny General (AGH) was among the first to administer Cobalt therapy.
In 1980, UPMC announced a $250 million ($ today) expansion and also hired transplant pioneer Thomas Starzl, Dr. Thomas Starzl. In 1984, Allegheny General surgeons pioneered modern brain surgery. Dr. Starzl arranged the 1985 liver transplant of 5-year-old Amie Garrison as a UPMC surgery team flew to Baylor University, starting its transplant program. Also in 1985, UPMC surgeons Drs. Griffith, Hardesty, and Trento revealed a new device after a heart-lung transplant. In 1986, UPMC announced a $230 million ($ today) modernization. In 1996, UPMC's planned Sicily ISMETT branch was approved by the Italian government as transplant surgeons to supervise and deliver the world's third (both earlier ones done at UPMC)--and first public—cross species marrow transplant at University of California, San Francisco. UPMC's Thomas Detre founded the International Society for Bipolar Disorders at a world medical conference in Pittsburgh in 1999.
The $80 million ($ today) UPMC Sports Performance Complex for the Pittsburgh Panthers & Pittsburgh Steelers opened in 2000. In 2002, AGH opened its $30 million ($ today), 5-floor, 100,000 sq. ft., cancer center. The $130 million ($ today) 350,000 sq. ft. Hillman Cancer Center opened in 2003 as UPMC entered into an 8-year, $420 million ($ today) agreement with IBM to upgrade medical technologies & health information systems.
In 2009, the $600 million ($ today) UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh opened. The campus was featured in world news in 2012 for several unique approaches to patient care. UPMC officially adopted in Erie, Pennsylvania's UPMC Hamot, Hamot Medical Center in 2010. The Pittsburgh Penguins announced a state of the art training facility with UPMC in 2012. UPMC announced in 2013 it had partnered with Nazarbayev University to help found its medical school.
The two largest area health care providers are the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) (since 1893) and Allegheny Health Network (since 1882). Both hospitals annually rank as among the best overall in the United States, with UPMC being among ''U.S. News & World Report'' "Honor Roll" every year since 2000.
The first military hospital in U.S. history and the first west of the Atlantic Plain—General Edward Hand Hospital—served the area from 1777 to 1845. Since 1847, Pittsburgh has hosted the world's first "Mercy Hospital". This was followed by West Penn hospital in 1848, Passavant Hospital in 1849, the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine in 1883, Children's Hospital in 1887, and Magee-Womens Hospital of UPMC, Magee Womens Hospital in 1911. In 1954, Allegheny General (AGH) was among the first to administer Cobalt therapy.
In 1980, UPMC announced a $250 million ($ today) expansion and also hired transplant pioneer Thomas Starzl, Dr. Thomas Starzl. In 1984, Allegheny General surgeons pioneered modern brain surgery. Dr. Starzl arranged the 1985 liver transplant of 5-year-old Amie Garrison as a UPMC surgery team flew to Baylor University, starting its transplant program. Also in 1985, UPMC surgeons Drs. Griffith, Hardesty, and Trento revealed a new device after a heart-lung transplant. In 1986, UPMC announced a $230 million ($ today) modernization. In 1996, UPMC's planned Sicily ISMETT branch was approved by the Italian government as transplant surgeons to supervise and deliver the world's third (both earlier ones done at UPMC)--and first public—cross species marrow transplant at University of California, San Francisco. UPMC's Thomas Detre founded the International Society for Bipolar Disorders at a world medical conference in Pittsburgh in 1999.
The $80 million ($ today) UPMC Sports Performance Complex for the Pittsburgh Panthers & Pittsburgh Steelers opened in 2000. In 2002, AGH opened its $30 million ($ today), 5-floor, 100,000 sq. ft., cancer center. The $130 million ($ today) 350,000 sq. ft. Hillman Cancer Center opened in 2003 as UPMC entered into an 8-year, $420 million ($ today) agreement with IBM to upgrade medical technologies & health information systems.
In 2009, the $600 million ($ today) UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh opened. The campus was featured in world news in 2012 for several unique approaches to patient care. UPMC officially adopted in Erie, Pennsylvania's UPMC Hamot, Hamot Medical Center in 2010. The Pittsburgh Penguins announced a state of the art training facility with UPMC in 2012. UPMC announced in 2013 it had partnered with Nazarbayev University to help found its medical school.
Health discoveries
While he was a professor at the University of Pittsburgh, American virologist Jonas Salk developed one of the first successful polio vaccines, which came into use in 1955. UPMC has pioneered several world firsts including the first known cystic fibrosis heart-lung transplant (1983), the world's first simultaneous liver and heart transplant operation on a child (6-year-old Stormie Jones in 1984), the youngest heart-lung transplant (9 years old in 1985), the world's first heart-liver-kidney transplant (1989), the world's first heart-liver transplant on an infant (1997), the first pediatric heart-double lung-liver transplant (1998), the nation's first double hand transplant (2009), and the first total forearm and hand transplant (2010), as well as the state's first heart transplant (1968). The Lancet published a 2012 UPMC study of two 9-year quadriplegics being able to move a robotic arm by thought, to pick up objects, shake hands, and even eat. Wiring the brain around spine damage to restore arm and leg muscle function was successful using robotic arms controlled via an embedded computer to translate signals near a small group of neurons with 200 needles.Transportation
 Pittsburgh is a Bridges of Pittsburgh, city of bridges. With 446, it has three bridges more than Venice, Italy, which has historically held the title "City of Bridges." Around 40 bridges cross the three rivers near the city. The Smithfield Street Bridge was the world's first lenticular truss bridge. The city's Three Sisters Bridges offer a picturesque view of the city from the North. The south-western "entrance" to Downtown for travelers coming in from Interstate 79 and the Pittsburgh International Airport is through the Fort Pitt Tunnel and over the Fort Pitt Bridge. The Fort Duquesne Bridge carrying Interstate 279 is the main gateway from Downtown to both PNC Park, Acrisure Stadium and the Rivers Casino (Pittsburgh), Rivers Casino. The Panhandle Bridge carries the Port Authority's Blue/Red/Silver subway lines across the Monongahela River. The renovated Jones and Laughlin Steel Company, J&L Steel Company bridge has been a key traffic/running-biking trail conduit connecting the Southside Works and Pittsburgh Technology Center. Over 2,000 bridges span the landscape of Allegheny County.
Pittsburgh is a Bridges of Pittsburgh, city of bridges. With 446, it has three bridges more than Venice, Italy, which has historically held the title "City of Bridges." Around 40 bridges cross the three rivers near the city. The Smithfield Street Bridge was the world's first lenticular truss bridge. The city's Three Sisters Bridges offer a picturesque view of the city from the North. The south-western "entrance" to Downtown for travelers coming in from Interstate 79 and the Pittsburgh International Airport is through the Fort Pitt Tunnel and over the Fort Pitt Bridge. The Fort Duquesne Bridge carrying Interstate 279 is the main gateway from Downtown to both PNC Park, Acrisure Stadium and the Rivers Casino (Pittsburgh), Rivers Casino. The Panhandle Bridge carries the Port Authority's Blue/Red/Silver subway lines across the Monongahela River. The renovated Jones and Laughlin Steel Company, J&L Steel Company bridge has been a key traffic/running-biking trail conduit connecting the Southside Works and Pittsburgh Technology Center. Over 2,000 bridges span the landscape of Allegheny County.
Public transportation statistics
The average amount of time people spend commuting with public transit in Pittsburgh, for example to and from work, on a weekday is 73 min. 23% of public transit riders ride for more than 2 hours every day. The average amount of time people wait at a stop or station for public transit is 17 minutes, while 33% of riders wait for over 20 minutes on average every day. The average distance people usually ride in a single trip with public transit is , while 11% travel for over in a single direction.Expressways and highways
Airports
Pittsburgh International Airport provides commercial passenger service from over 15 airlines to the Pittsburgh metropolitan area. Arnold Palmer Regional Airport also provides limited commercial passenger service and is east of Pittsburgh. Other airports with scheduled commercial service include Morgantown Municipal Airport ( south of Pittsburgh), Youngstown–Warren Regional Airport ( northwest of Pittsburgh), Akron–Canton Airport ( northwest of Pittsburgh), and Erie International Airport ( north of Pittsburgh).Intercity passenger rail and bus
Amtrak provides intercity rail service to Union Station (Pittsburgh), Pittsburgh Union Station, via the ''Capitol Limited (Amtrak train), Capitol Limited'' between Chicago and Washington, D.C., and the ''Pennsylvanian (Amtrak), Pennsylvanian'' to New York City. Megabus (North America), Megabus, Greyhound Lines, and Fullington Trailways connect Pittsburgh with distant cities by bus; Greyhound and Fullington Trailways buses stop at the Grant Street Transportation Center intercity bus terminal. Popular destinations include Philadelphia, New York City, and Washington, D.C. Until declines in passenger travel in the 1950s and 1960s, several stations served Pittsburgh: Baltimore and Ohio Station (Pittsburgh), Baltimore & Ohio Station, Pittsburgh & Lake Erie Railroad Station, Wabash Pittsburgh Terminal and Pittsburgh Union Station.Regional mass transit
Freight rail
 Pittsburgh's rail industry dates to 1851 when the Pennsylvania Railroad first opened service between the city and Philadelphia, the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad entered the city in 1871. In 1865 Andrew Carnegie opened the Pittsburgh Locomotive and Car Works which manufactured for the industry until 1919. Carnegie also founded the Union Railroad (Pittsburgh), Union Railroad in 1894 for heavy freight services and it still serves the area's steel industry, while George Westinghouse's Wabtec has been a leader in rail engines and switching since 1869.
Pittsburgh is home to one of Norfolk Southern Railway's busiest freight corridors, the Pittsburgh Line, and operates up to 70 trains per day through the city. The suburban Conway Yard, Conway Rail Yard—originally built in 1889—was the largest freight rail center in the world from 1956 until 1980 and is today the nation's second-largest. CSX, the other major freight railroad in the eastern U.S. also has Pittsburgh Subdivision, major operations around Pittsburgh.
Pittsburgh's rail industry dates to 1851 when the Pennsylvania Railroad first opened service between the city and Philadelphia, the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad entered the city in 1871. In 1865 Andrew Carnegie opened the Pittsburgh Locomotive and Car Works which manufactured for the industry until 1919. Carnegie also founded the Union Railroad (Pittsburgh), Union Railroad in 1894 for heavy freight services and it still serves the area's steel industry, while George Westinghouse's Wabtec has been a leader in rail engines and switching since 1869.
Pittsburgh is home to one of Norfolk Southern Railway's busiest freight corridors, the Pittsburgh Line, and operates up to 70 trains per day through the city. The suburban Conway Yard, Conway Rail Yard—originally built in 1889—was the largest freight rail center in the world from 1956 until 1980 and is today the nation's second-largest. CSX, the other major freight railroad in the eastern U.S. also has Pittsburgh Subdivision, major operations around Pittsburgh.
Port
The Port of Pittsburgh Commission, Port of Pittsburgh ranks as the List of ports in the United States, 20th-largest port in the United States with almost 34 million short tons of river cargo for 2011, the port ranked 9th-largest in the U.S. when measured in domestic trade.Notable people
Sister cities
Pittsburgh's Sister city, sister cities are: * Bilbao, Spain * Da Nang, Vietnam * Fernando de la Mora, Paraguay, Fernando de la Mora, Paraguay * Gaziantep, Turkey * Glasgow, Scotland * Karmiel, Israel * Matanzas, Cuba * Misgav Regional Council, Misgav, Israel * Naucalpan, Mexico * Ostrava, Czech Republic * Prešov, Slovakia * Saarbrücken, Germany * Saitama (city), Saitama, Japan * San Isidro, Matagalpa, San Isidro, Nicaragua * Sheffield, England * Skopje, North Macedonia * Sofia, Bulgaria * Wuhan, China * Zagreb, CroatiaSee also
* Greater Pittsburgh Region * List of fiction set in Pittsburgh * List of municipalities in Pennsylvania * List of people from PittsburghExplanatory notes
References
Further reading
* Allen Dieterich-Ward, ''Beyond Rust: Metropolitan Pittsburgh and the Fate of Industrial America'' (U of Pennsylvania Press, 2016). viii, 347 pp. * Kenneth J. Kobus, ''City of Steel: How Pittsburgh Became the World's Steelmaking Capital During the Carnegie Era.'' Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2015. * Charles McCollester, ''The Point of Pittsburgh: Production and Struggle at the Forks of the Ohio.'' Pittsburgh, PA: Battle of Homestead Foundation, 2008.External links
*Pittsburgh Convention and Visitors Bureau – Tourism
Historic Pittsburgh Maps Collection
''Pittsburgh Daily Gazette''
Google Newspaper archive. PDFs of 5,794 issues, dating primarily 1834–1841 and 1850–1863. * {{authority control Pittsburgh, Cities in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania Cities in Pennsylvania County seats in Pennsylvania Inland port cities and towns of Pennsylvania Pennsylvania populated places on the Monongahela River Pennsylvania populated places on the Ohio River Pittsburgh metropolitan area Populated places established in 1758