Pippin The Younger on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pepin the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was
 As mayor of the palace, Pepin was formally subject to the decisions of Childeric III, who had only the title of king, with no power. Since Pepin had control over the magnates and actually had the power of a king, he now addressed to
As mayor of the palace, Pepin was formally subject to the decisions of Childeric III, who had only the title of king, with no power. Since Pepin had control over the magnates and actually had the power of a king, he now addressed to

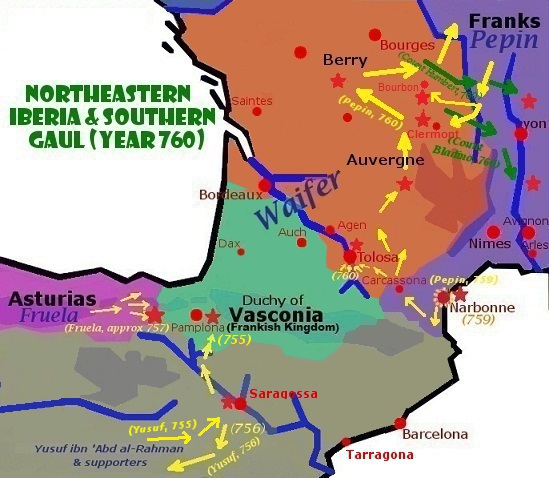 Pepin's first major act as king was to go to war against the Lombard king
Pepin's first major act as king was to go to war against the Lombard king
King of the Franks
The Franks, Germanic-speaking peoples that invaded the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, were first led by individuals called dukes and reguli. The earliest group of Franks that rose to prominence was the Salian Merovingians, who con ...
from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippin ...
to become king.
The younger was the son of the Frankish prince Charles Martel and his wife Rotrude, Pepin's upbringing was distinguished by the ecclesiastical education he had received from the monks of St. Denis. Succeeding his father as the Mayor of the Palace in 741, Pepin reigned over Francia jointly with his elder brother Carloman. Pepin ruled in Neustria, Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
, and Provence, while his older brother Carloman established himself in Austrasia
Austrasia was a territory which formed the north-eastern section of the Merovingian Kingdom of the Franks during the 6th to 8th centuries. It was centred on the Meuse, Middle Rhine and the Moselle rivers, and was the original territory of the F ...
, Alemannia, and Thuringia. The brothers were active in suppressing revolts led by the Bavarians
Bavarians ( Bavarian: ''Boarn'', Standard German: ''Baiern'') are an ethnographic group of Germans of the Bavaria region, a state within Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as the Bavarian language, native to Altbayern ("Old Bava ...
, Aquitanians
The Aquitani were a tribe that lived in the region between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic ocean, and the Garonne, in present-day southwestern France in the 1st century BCE. The Romans dubbed this region ''Gallia Aquitania''. Classical authors such a ...
, Saxons, and the Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
in the early years of their reign. In 743, they ended the Frankish interregnum by choosing Childeric III, who was to be the last Merovingian monarch, as figurehead king of the Franks.
Being well disposed towards the church and papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
on account of their ecclesiastical upbringing, Pepin and Carloman continued their father's work in supporting Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB ( la, Bonifatius; 675 – 5 June 754) was an English Benedictines, Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of the Frankish Empire during the eighth century. He organised significant ...
in reforming the Frankish church, and evangelizing the Saxons. After Carloman, who was an intensely pious man, retired to religious life in 747, Pepin became the sole ruler of the Franks. He suppressed a revolt led by his half-brother Grifo, and succeeded in becoming the undisputed master of all Francia. Giving up pretense, Pepin then forced Childeric into a monastery and had himself proclaimed king of the Franks with support of Pope Zachary
Pope Zachary ( la, Zacharias; 679 – March 752) was the bishop of Rome from 28 November 741 to his death. He was the last pope of the Byzantine Papacy. Zachary built the original church of Santa Maria sopra Minerva, forbade the traffic of slav ...
in 751. The decision was not supported by all members of the Carolingian family and Pepin had to put down a revolt led by Carloman's son, Drogo, and again by Grifo.
As king, Pepin embarked on an ambitious program to expand his power. He reformed the legislation of the Franks and continued the ecclesiastical reforms of Boniface. Pepin also intervened in favour of the papacy of Stephen II against the Lombards in Italy. In the midsummer of 754, Stephen II anointed Pepin afresh, together with his two sons, Charles and Carloman. The ceremony took place in the Abbey Church of St. Denis, near Paris, and the Pope formally forbade the Franks ever to elect as king anyone who was not of the sacred race of Pepin. He also bestowed upon Pepin and his sons the title of 'Patrician of Rome'. Pepin was able to secure several cities, which he then gave to the Pope as part of the Donation of Pepin. This formed the legal basis for the Papal States in the Middle Ages. The Byzantines, keen to make good relations with the growing power of the Frankish empire, gave Pepin the title of Patricius. In wars of expansion, Pepin conquered Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septima ...
from the Islamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the mai ...
Umayyads, and subjugated the southern realms by repeatedly defeating Waiofar and his Gascon troops, after which the Gascon and Aquitanian lords saw no option but to pledge loyalty to the Franks. Pepin was, however, troubled by the relentless revolts of the Saxons and the Bavarians. He campaigned tirelessly in Germany, but the final subjugation of these tribes was left to his successors.
Pepin died in 768 and was succeeded by his sons Charlemagne and Carloman. Although unquestionably one of the most powerful and successful rulers of his time, Pepin's reign is largely overshadowed by that of his more famous son, Charlemagne.
Assumption of power
Pepin's father Charles Martel died in 741. He divided the rule of the Frankish kingdom between Pepin and his elder brother, Carloman, his surviving sons by his first wife: Carloman became Mayor of the Palace of Austrasia, Pepin became Mayor of the Palace of Neustria. Grifo, Charles's son by his second wife, Swanahild (also known as Swanhilde), demanded a share in the inheritance, but he was besieged in Laon, forced to surrender and imprisoned in a monastery by his two half-brothers. In the Frankish realm the unity of the kingdom was essentially connected with the person of the king. So Carloman, to secure this unity, raised the Merovingian Childeric to the throne (743). Then in 747 Carloman resolved to entering a monastery after years of consideration. This left Francia in the hands of Pepin as sole mayor of the palace and ''dux et princeps Francorum''. At the time of Carloman's retirement, Grifo escaped his imprisonment and fled to Duke Odilo of Bavaria, who was married to Hiltrude, Pepin's sister. Pepin put down the renewed revolt led by his half-brother and succeeded in completely restoring the boundaries of the kingdom. Under the reorganization of Francia by Charles Martel, the ''dux et princeps Francorum'' was the commander of the armies of the kingdom, in addition to his administrative duties as mayor of the palace.First Carolingian king
 As mayor of the palace, Pepin was formally subject to the decisions of Childeric III, who had only the title of king, with no power. Since Pepin had control over the magnates and actually had the power of a king, he now addressed to
As mayor of the palace, Pepin was formally subject to the decisions of Childeric III, who had only the title of king, with no power. Since Pepin had control over the magnates and actually had the power of a king, he now addressed to Pope Zachary
Pope Zachary ( la, Zacharias; 679 – March 752) was the bishop of Rome from 28 November 741 to his death. He was the last pope of the Byzantine Papacy. Zachary built the original church of Santa Maria sopra Minerva, forbade the traffic of slav ...
a suggestive question:
:''In regard to the kings of the Franks who no longer possess the royal power: is this state of things proper?''
Hard pressed by the Lombards, Pope Zachary welcomed this move by the Franks to end an intolerable condition and lay the constitutional foundations for the exercise of the royal power. The Pope replied that such a state of things is not proper. Under these circumstances, the wielder of actual power should be called King. After this decision, Childeric III was deposed and confined to a monastery. He was the last of the Merovingians.
Pepin was then elected King of the Franks by an assembly of Frankish nobles, with a large portion of his army on hand. The earliest account of his election and anointing is the '' Clausula de Pippino'', written around 767. Meanwhile, Grifo continued his rebellion, but was eventually killed in the battle of Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne in 753.
Pepin was assisted by his friend Vergilius of Salzburg
Virgil (– 27 November 784), also spelled Vergil, Vergilius, Virgilius, Feirgil or Fearghal, was an Irish churchman and early astronomer. He left Ireland around 745, intending to visit the Holy Land; but, like many of his countrymen, he settled ...
, an Irish monk who probably used a copy of the "Collectio canonum Hibernensis
The ''Collectio canonum Hibernensis'' ( en, Irish Collection of Canon law) (or ''Hib'') is a systematic Latin collection of Continental canon law, scriptural and patristic excerpts, and Irish synodal and penitential decrees. ''Hib'' is thought t ...
" (an Irish collection of canon law) to advise him to receive royal unction to assist his recognition as king. Anointed a first time in 751 in Soissons
Soissons () is a commune in the northern French department of Aisne, in the region of Hauts-de-France. Located on the river Aisne, about northeast of Paris, it is one of the most ancient towns of France, and is probably the ancient capital ...
, Pepin added to his power after Pope Stephen II
Pope Stephen II ( la, Stephanus II; 714 – 26 April 757) was born a Roman aristocrat and member of the Orsini family. Stephen was the bishop of Rome from 26 March 752 to his death. Stephen II marks the historical delineation between the Byzant ...
traveled all the way to Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
to anoint him a second time in a lavish ceremony at the Basilica of St Denis in 754, bestowing upon him the additional title of Patricius Romanorum (Patrician of the Romans). This was the first recorded crowning of a civil ruler by a Pope. As life expectancies were short in those days, and Pepin wanted family continuity, the Pope also anointed Pepin's sons, Charles (eventually known as Charlemagne), who was 12, and Carloman, who was 3.
The significance of the ceremony of anointment is visible in that it was newly adopted by the Pope and was unheard of in Rome. This, together with granting the title of Patrician of the Romans, which was connected to the role of Defensor Civitatis (protector of oppressed citizens), meant that Pippin was now designated as the defender of the Church.
Expansion of the Frankish realm

 Pepin's first major act as king was to go to war against the Lombard king
Pepin's first major act as king was to go to war against the Lombard king Aistulf
Aistulf (also Ahistulf, Aistulfus, Haistulfus, Astolf etc.; it, Astolfo; died December 756) was the Duke of Friuli from 744, King of the Lombards from 749, and Duke of Spoleto from 751. His reign was characterized by ruthless and ambitious ef ...
, who had expanded into the '' ducatus Romanus''. After a meeting with Pope Stephen II at Ponthion, Pepin forced the Lombard king to return property seized from the Church. He confirmed the papacy in possession of Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the ca ...
and the Pentapolis
A pentapolis (from Ancient Greek, Greek ''penta-'', 'five' and ''polis'', 'city') is a geographic and/or institutional grouping of five cities. Cities in the ancient world probably formed such groups for political, commercial and military reaso ...
, the so-called Donation of Pepin, whereby the Papal States were established and the temporal reign of the papacy officially began. At about 752, he turned his attention to Septimania. The new king headed south in a military expedition down the Rhone valley and received the submission of eastern Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septima ...
(i.e. Nîmes, Maguelone, Beziers and Agde
Agde (; ) is a commune in the Hérault department in Southern France. It is the Mediterranean port of the Canal du Midi.
Location
Agde is located on the Hérault river, from the Mediterranean Sea, and from Paris. The Canal du Midi ...
) after securing count Ansemund's allegiance. The Frankish king went on to invest Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in Southern France in the Occitanie region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the M ...
, the main Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
stronghold in Septimania, but could not capture it from the Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a la ...
n Muslims until seven years later in 759, when they were driven out to Hispania.
Aquitaine still remained under Waiofar's Gascon-Aquitanian rule, however, and beyond Frankish reach. Duke Waiofar appears to have confiscated Church lands, maybe distributing them among his troops. In 760, after conquering the Roussillon
Roussillon ( , , ; ca, Rosselló ; oc, Rosselhon ) is a historical province of France that largely corresponded to the County of Roussillon and part of the County of Cerdagne of the former Principality of Catalonia. It is part of th ...
from the Muslims and denouncing Waiofar's actions, Pepin moved his troops over to Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. The city is on t ...
and Albi
Albi (; oc, Albi ) is a commune in France, commune in southern France. It is the prefecture of the Tarn (department), Tarn Departments of France, department, on the river Tarn (river), Tarn, 85 km northeast of Toulouse. Its inhabitants ar ...
, ravaged with fire and sword most of Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 Januar ...
, and, in retaliation, counts loyal to Waiofar ravaged Burgundy. Pepin, in turn, besieged the Aquitanian-held towns and strongholds of Bourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by ...
, Clermont, Chantelle, Bourges
Bourges () is a commune in central France on the river Yèvre. It is the capital of the department of Cher, and also was the capital city of the former province of Berry.
History
The name of the commune derives either from the Bituriges, ...
and Thouars
Thouars () is a commune in the Deux-Sèvres department in western France. On 1 January 2019, the former communes Mauzé-Thouarsais, Missé and Sainte-Radegonde were merged into Thouars.
It is on the River Thouet. Its inhabitants are known ...
, defended by Waiofar's Gascon troops, who were overcome, captured and deported into northern France with their children and wives.
In 763, Pepin advanced further into the heart of Waiofar's domains and captured major strongholds (Poitiers, Limoges, Angoulême, etc.), after which Waiofar counterattacked and war became bitter. Pepin opted to spread terror, burning villas, destroying vineyards and depopulating monasteries. By 765, the brutal tactics seemed to pay off for the Franks, who destroyed resistance in central Aquitaine and devastated the whole region. The city of Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger Regions of France, region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania. The city is on t ...
was conquered
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, t ...
by Pepin in 767 as was Waiofar's capital of Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefecture ...
.
As a result, Aquitanian nobles and Gascons from beyond the Garonne too saw no option but to accept a pro-Frankish peace treaty (Fronsac, c. 768). Waiofar escaped but was assassinated by his own frustrated followers in 768.
Legacy
Pepin died during a campaign, in 768 at the age of 54. He was interred in the Basilica of Saint Denis in modern-day Metropolitan Paris. His wife Bertrada was also interred there in 783. Charlemagne rebuilt the Basilica in honor of his parents and placed markers at the entrance. The Frankish realm was divided according to the Salic law between his two sons: Charlemagne andCarloman I
Carloman I (28 June 751 – 4 December 771), also Karlmann, was king of the Franks from 768 until his death in 771. He was the second surviving son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon and was a younger brother of Charlemagne. His death al ...
.
Historical opinion often seems to regard him as the lesser son and lesser father of two greater men, though a great man in his own right. He continued to build up the heavy cavalry
Heavy cavalry was a class of cavalry intended to deliver a battlefield charge and also to act as a tactical reserve; they are also often termed '' shock cavalry''. Although their equipment differed greatly depending on the region and histori ...
which his father had begun. He maintained the standing army that his father had found necessary to protect the realm and form the core of its full army in wartime. He not only contained the Spanish Muslims as his father had, but drove them out of what is now France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
and, as important, he managed to subdue the Aquitanians and the Gascons after three generations of on-off clashes, so opening the gate to central and southern Gaul and Muslim Spain. He continued his father's expansion of the Frankish church (missionary work in Germany and Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Swe ...
) and the institutional infrastructure (feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structu ...
) that would prove the backbone of medieval Europe.
His rule was historically important and of great benefit to the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
as a people. Pepin's assumption of the crown, and the title of Patrician of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, were harbingers of his son's imperial coronation. He made the Carolingians the ruling dynasty of the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, ...
and the foremost power of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
. Known as a great conqueror, he was undefeated during his lifetime.
Family
Pepin married Leutberga from theDanube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
region. They had five children. She was repudiated some time after the birth of Charlemagne and her children were sent to convents.
In 741, Pepin married Bertrada, daughter of Caribert of Laon. They are known to have had eight children, at least three of whom survived to adulthood:
* Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was ...
(Charlemagne) (2 April 742 – 28 January 814)
* Carloman (751 – 4 December 771)
* Pepin (756–762)
* Gisela (757–810)
* Berthe, died young
* Adelais (Adelaide), died young, buried in Metz
* Chrothais (Rothaide), died young, buried in Metz.
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * Document by Pepin for Fulda Abbey, 760, . , - {{Authority control 714 births 768 deaths Frankish warriors Mayors of the Palace Monarchs killed in action Burials at the Basilica of Saint-Denis Carolingian dynasty People from Liège 8th-century Frankish kings